Abstract
Marrow blasts from children with B cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) were studied for differences in quantitative expression of the common ALL antigen (CALLA). Of 42 untreated patients, 35 had detectable amounts of CALLA by flow cytometric (FCM) analysis of J-5 monoclonal antibody binding. Using an FCM technique that provides correlated measurements of a given cell surface antigen, cell size, and DNA content, we detected increased CALLA expression as lymphoblasts moved from G0/G1 phase through S phase of the cell cycle. The density of the antigen (per unit of blast surface area) remained relatively constant over the same interval, indicating that the change was not due to S phase-specific enhancement of CALLA expression. Eight cases had hyperdiploid cellular DNA content and in seven of these, only cells with clonal abnormalities of DNA content expressed the CALLA marker. Mean amounts of CALLA for each patient ranged widely within the study group, from very high to marginally detectable. This variation had no discernible relation to cell size, stem-line DNA content, percentage of cells in S phase, or the presence or absence of cytoplasmic immunoglobulin. Results of a univariate proportional hazards analysis showed that both quantitative level of CALLA for S phase cells (P = 0.048) and white blood cell count (P = 0.012) had made significant contributions to treatment outcome. Patients with relative amounts of CALLA less than the median value for the entire CALLA+ group had a higher rate of failure, which was virtually identical to that for the seven HLA-DR+ patients whose blasts lacked detectable CALLA. The observed interpatient variation in quantitative expression of CALLA is consistent with recognized steps in B cell precursor differentiation and may be useful in distinguishing patients with a less favorable prognosis.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowman W. P., Melvin S. L., Aur R. J., Mauer A. M. A clinical perspective on cell markers in acute lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 2):4794–4801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
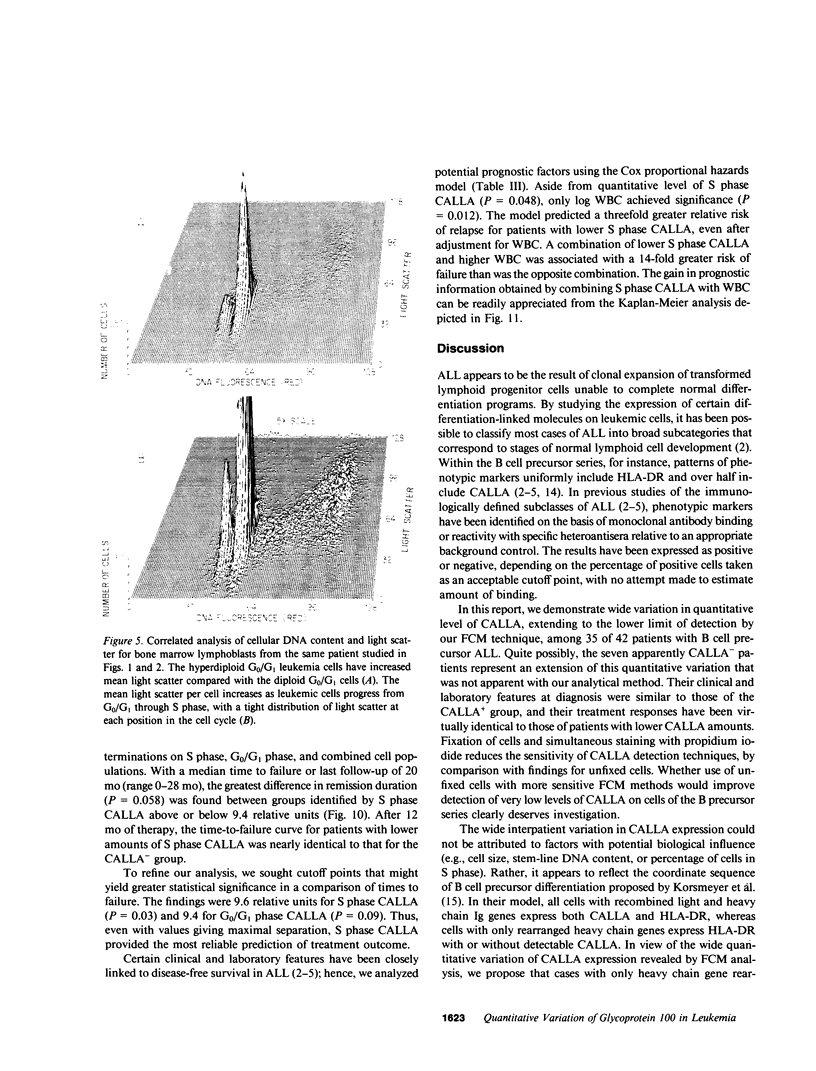
- Braylan R. C., Benson N. A., Nourse V., Kruth H. S. Correlated analysis of cellular DNA, membrane antigens and light scatter of human lymphoid cells. Cytometry. 1982 Mar;2(5):337–343. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990020511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchiel S. W., Martin J. C., Imai K., Ferrone S., Warner N. L. Heterogeneity of HLA-A,B, Ia-like, and melanoma-associated antigen expression by human melanoma cell lines analyzed with monoclonal antibodies and flow cytometry. Cancer Res. 1982 Oct;42(10):4110–4115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crissman H. A., Steinkamp J. A. Rapid, simultaneous measurement of DNA, protein, and cell volume in single cells from large mammalian cell populations. J Cell Biol. 1973 Dec;59(3):766–771. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.3.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandour D. M., Walker W. S. Macrophage cell cycling: influence on Fc receptors and antibody-dependent phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1108–1112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Brown G., Rapson N. T., Lister T. A. Antisera to acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 May;4(1):67–84. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Hariri G., Newman R. A., Sutherland D. R., Ritter M. A., Ritz J. Selective expression of the common acute lymphoblastic leukemia (gp 100) antigen on immature lymphoid cells and their malignant counterparts. Blood. 1983 Apr;61(4):628–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Janossy G., Peto J., Kay H. Immunologically defined subclasses of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in children: their relationship to presentation features and prognosis. Br J Haematol. 1981 Jun;48(2):179–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M., Delia D., Janossy G., Rapson N., Chessells J., Woods M., Prentice G. Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia associated antigen. IV. Expression on non-leukaemic 'lymphoid' cells. Leuk Res. 1980;4(1):15–32. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(80)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. R., Hayakawa K., Haaijman J., Herzenberg L. A. B-cell subpopulations identified by two-colour fluorescence analysis. Nature. 1982 Jun 17;297(5867):589–591. doi: 10.1038/297589a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Bollum F. J., Bradstock K. F., Ashley J. Cellular phenotypes of normal and leukemic hemopoietic cells determined by analysis with selected antibody combinations. Blood. 1980 Sep;56(3):430–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Bollum F. J., Bradstock K. F., McMichael A., Rapson N., Greaves M. F. Terminal transferase-positive human bone marrow cells exhibit the antigenic phenotype of common acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1525–1529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kersey J., Goldman A., Abramson C., Nesbit M., Perry G., Gajl-Peczalska K., LeBien T. Clinical usefulness of monoclonal-antibody phenotyping in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Lancet. 1982 Dec 25;2(8313):1419–1423. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91326-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer S. J., Arnold A., Bakhshi A., Ravetch J. V., Siebenlist U., Hieter P. A., Sharrow S. O., LeBien T. W., Kersey J. H., Poplack D. G. Immunoglobulin gene rearrangement and cell surface antigen expression in acute lymphocytic leukemias of T cell and B cell precursor origins. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):301–313. doi: 10.1172/JCI110770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishan A. Rapid flow cytofluorometric analysis of mammalian cell cycle by propidium iodide staining. J Cell Biol. 1975 Jul;66(1):188–193. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Warner N. L. Cell cycle related heterogeneity of Ia antigen expression on a murine B lymphoma cell line:analysis by flow cytometry. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):626–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebien T. W., Boué D. R., Bradley J. G., Kersey J. H. Antibody affinity may influence antigenic modulation of the common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen in vitro. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2287–2292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loken M. R., Parks D. R., Herzenberg L. A. Two-color immunofluorescence using a fluorescence-activated cell sorter. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Jul;25(7):899–907. doi: 10.1177/25.7.330738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Look A. T., Melvin S. L., Williams D. L., Brodeur G. M., Dahl G. V., Kalwinsky D. K., Murphy S. B., Mauer A. M. Aneuploidy and percentage of S-phase cells determined by flow cytometry correlate with cell phenotype in childhood acute leukemia. Blood. 1982 Oct;60(4):959–967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minowada J., Tsubota T., Greaves M. F., Walters T. R. A non-T, non-B human leukemia cell line (NALM-1): establishment of the cell line and presence of leukemia-associated antigens. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Jul;59(1):83–87. doi: 10.1093/jnci/59.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler L. M., Stashenko P., Hardy R., Pesando J. M., Yunis E. J., Schlossman S. F. Monoclonal antibodies defining serologically distinct HLA-D/DR related Ia-like antigens in man. Hum Immunol. 1981 Feb;2(1):77–90. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(81)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman R. A., Sutherland R., Greaves M. F. The biochemical characterization of a cell surface antigen associated with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and lymphocyte precursors. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):2024–2030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritz J., Pesando J. M., Notis-McConarty J., Lazarus H., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody to human acute lymphoblastic leukaemia antigen. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):583–585. doi: 10.1038/283583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sallan S. E., Ritz J., Pesando J., Gelber R., O'Brien C., Hitchcock S., Coral F., Schlossman S. F. Cell surface antigens: prognostic implications in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 1980 Mar;55(3):395–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar S., Glassy M. C., Ferrone S., Jones O. W. Cell cycle and the differential expression of HLA-A,B and HLA-DR antigens on human B lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7297–7301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro H. M. Multistation multiparameter flow cytometry: a critical review and rationale. Cytometry. 1983 Jan;3(4):227–243. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990030402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slease R. B., Wistar R., Jr, Scher I. Surface immunoglobulin density on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Blood. 1979 Jul;54(1):72–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veit B. C., Melvin S. L., Bowman W. P. Identification of a leukemia-associated antigen of human acute lymphocytic leukemia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Jun;64(6):1321–1328. doi: 10.1093/jnci/64.6.1321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogler L. B., Crist W. M., Sarrif A. M., Pullen D. J., Bartolucci A. A., Falletta J. M., Dowell B., Humphrey G. B., Blackstock R., van Eys J. An analysis of clinical and laboratory features of acute lymphocytic leukemias with emphasis on 35 children with pre-B leukemia. Blood. 1981 Jul;58(1):135–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner N. L., Daley M. J., Richey J., Spellman C. Flow cytometry analysis of murine B cell lymphoma differentiation. Immunol Rev. 1979;48:197–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]