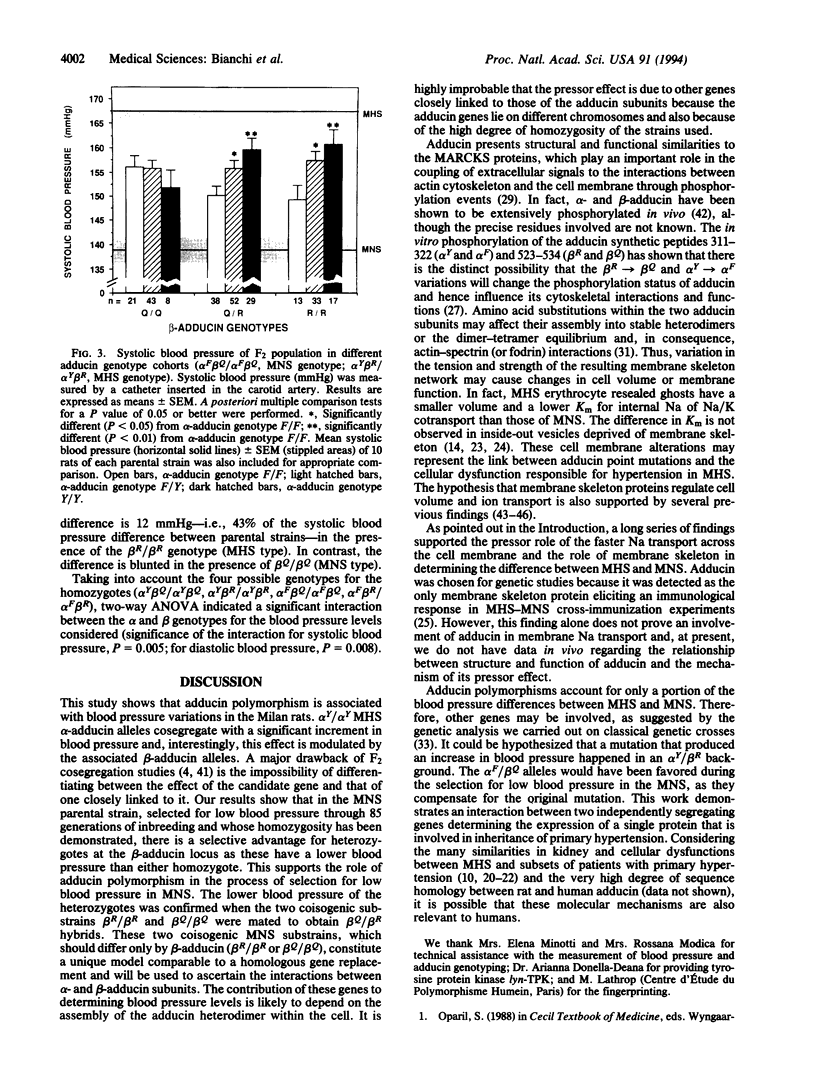
Abstract
The Milan hypertensive strain of rats (MHS) develops a genetic form of renal hypertension that, when compared to its normotensive control (MNS), shows renal dysfunction similar to that of a subset of human patients with primary hypertension. MHS and MNS were shown to be homozygous by multilocus minisatellite analysis and monolocus microsatellite markers. We show here that one point mutation in each of two genes coding for the membrane skeleton protein adducin is associated with blood pressure in the Milan strain of rats. Adducin is a heterodimer formed by alpha and beta subunits that promotes the assembly of actin with spectrin. MHS and MNS differ, respectively, by the amino acids Y and F at position 316 of the alpha subunit. In the beta-adducin locus, MHS is always homozygous for R at position 529 while in MNS either R or Q occurs in that position. The R/Q heterozygotes showed lower blood pressure than any of the homozygotes. In vitro phosphorylation studies suggest that both of these amino acid substitutions occur within protein kinase recognition sites. Analysis of an F2 generation demonstrated that Y alleles segregated with a significant increment in blood pressure. This effect is modulated by the presence of the R allele of the beta subunit. Taken together, these findings strongly support a role for adducin polymorphisms in causing variation of blood pressure in the Milan strain of rats.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderem A. The MARCKS brothers: a family of protein kinase C substrates. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):713–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90546-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper S. L., Palfrey H. C., DeRiemer S. A., Greengard P. Hormonal control of protein phosphorylation in turkey erythrocytes. Phosphorylation by cAMP-dependent and Ca2+-dependent protein kinases of distinct sites in goblin, a high molecular weight protein of the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):11029–11039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi G., Baer P. G., Fox U., Duzzi L., Pagetti D., Giovannetti A. M. Changes in renin, water balance, and sodium balance during development of high blood pressure in genetically hypertensive rats. Circ Res. 1975 Jun;36(6 Suppl 1):153–161. doi: 10.1161/01.res.36.6.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi G., Cusi D., Barlassina C., Lupi G. P., Ferrari P., Picotti G. B., Gatti M., Polli E. Renal dysfunction as a possible cause of essential hypertension in predisposed subjects. Kidney Int. 1983 Jun;23(6):870–875. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi G., Ferrari P., Trizio D., Ferrandi M., Torielli L., Barber B. R., Polli E. Red blood cell abnormalities and spontaneous hypertension in the rat. A genetically determined link. Hypertension. 1985 May-Jun;7(3 Pt 1):319–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi G., Fox U., Di Francesco G. F., Giovanetti A. M., Pagetti D. Blood pressure changes produced by kidney cross-transplantation between spontaneously hypertensive rats and normotensive rats. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Nov;47(5):435–448. doi: 10.1042/cs0470435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunati A. M., Donella-Deana A., Ralph S., Marchiori F., Borin G., Fischer S., Pinna L. A. Stimulation by NaCl, polylysine and heparin of two forms of spleen tyrosine protein kinase immunologically related with the protein expressed by lyn oncogene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 10;1091(1):123–126. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90232-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantiello H. F., Prat A. G., Bonventre J. V., Cunningham C. C., Hartwig J. H., Ausiello D. A. Actin-binding protein contributes to cell volume regulatory ion channel activation in melanoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):4596–4599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicila G. T., Rapp J. P., Wang J. M., St Lezin E., Ng S. C., Kurtz T. W. Linkage of 11 beta-hydroxylase mutations with altered steroid biosynthesis and blood pressure in the Dahl rat. Nat Genet. 1993 Apr;3(4):346–353. doi: 10.1038/ng0493-346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusi D., Fossali E., Piazza A., Tripodi G., Barlassina C., Pozzoli E., Vezzoli G., Stella P., Soldati L., Bianchi G. Heritability estimate of erythrocyte Na-K-Cl cotransport in normotensive and hypertensive families. Am J Hypertens. 1991 Sep;4(9):725–734. doi: 10.1093/ajh/4.9.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubay C., Vincent M., Samani N. J., Hilbert P., Kaiser M. A., Beressi J. P., Kotelevtsev Y., Beckmann J. S., Soubrier F., Sassard J. Genetic determinants of diastolic and pulse pressure map to different loci in Lyon hypertensive rats. Nat Genet. 1993 Apr;3(4):354–357. doi: 10.1038/ng0493-354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrandi M., Salardi S., Parenti P., Ferrari P., Bianchi G., Braw R., Karlish S. J. Na+/K+/Cl(-)-cotransporter mediated Rb+ fluxes in membrane vesicles from kidneys of normotensive and hypertensive rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jan 15;1021(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90377-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari P., Ferrandi M., Torielli L., Canessa M., Bianchi G. Relationship between erythrocyte volume and sodium transport in the Milan hypertensive rat and age-dependent changes. J Hypertens. 1987 Apr;5(2):199–206. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198704000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari P., Torielli L., Cirillo M., Salardi S., Bianchi G. Sodium transport kinetics in erythrocytes and inside-out vesicles from Milan rats. J Hypertens. 1991 Aug;9(8):703–711. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199108000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari P., Torielli L., Salardi S., Rizzo A., Bianchi G. Na+/K+/Cl- cotransport in resealed ghosts from erythrocytes of the Milan hypertensive rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Oct 19;1111(1):111–119. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90280-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkow B. Physiological aspects of primary hypertension. Physiol Rev. 1982 Apr;62(2):347–504. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.2.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner K., Bennett V. A new erythrocyte membrane-associated protein with calmodulin binding activity. Identification and purification. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1339–1348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidi E., Bianchi G., Rivolta E., Ponticelli C., Quarto di Palo F., Minetti L., Polli E. Hypertension in man with a kidney transplant: role of familial versus other factors. Nephron. 1985;41(1):14–21. doi: 10.1159/000183539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilbert P., Lindpaintner K., Beckmann J. S., Serikawa T., Soubrier F., Dubay C., Cartwright P., De Gouyon B., Julier C., Takahasi S. Chromosomal mapping of two genetic loci associated with blood-pressure regulation in hereditary hypertensive rats. Nature. 1991 Oct 10;353(6344):521–529. doi: 10.1038/353521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- House C., Wettenhall R. E., Kemp B. E. The influence of basic residues on the substrate specificity of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):772–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob H. J., Lindpaintner K., Lincoln S. E., Kusumi K., Bunker R. K., Mao Y. P., Ganten D., Dzau V. J., Lander E. S. Genetic mapping of a gene causing hypertension in the stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90584-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Hypervariable 'minisatellite' regions in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):67–73. doi: 10.1038/314067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi R., Gilligan D. M., Otto E., McLaughlin T., Bennett V. Primary structure and domain organization of human alpha and beta adducin. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):665–675. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser H. W., O'Keefe E., Bennett V. Adducin: Ca++-dependent association with sites of cell-cell contact. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):557–569. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy B. P., Davies P. L. Sites of phosphorylation on the high molecular weight basic nuclear proteins of the winter flounder. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4338–4344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz T. W., Simonet L., Kabra P. M., Wolfe S., Chan L., Hjelle B. L. Cosegregation of the renin allele of the spontaneously hypertensive rat with an increase in blood pressure. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1328–1332. doi: 10.1172/JCI114572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird P. W., Zijderveld A., Linders K., Rudnicki M. A., Jaenisch R., Berns A. Simplified mammalian DNA isolation procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4293–4293. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mische S. M., Mooseker M. S., Morrow J. S. Erythrocyte adducin: a calmodulin-regulated actin-bundling protein that stimulates spectrin-actin binding. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2837–2845. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J. Regulation of cell surface polarity from bacteria to mammals. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):948–955. doi: 10.1126/science.1439806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parenti P., Hanozet G. M., Bianchi G. Sodium and glucose transport across renal brush border membranes of Milan hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1986 Oct;8(10):932–939. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.8.10.932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongor S., Skerl V., Cserzö M., Hátsági Z., Simon G., Bevilacqua V. The SBASE protein domain library, release 2.0: a collection of annotated protein sequence segments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3111–3115. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp J. P., Wang S. M., Dene H. Effect of genetic background on cosegregation of renin alleles and blood pressure in Dahl rats. Am J Hypertens. 1990 May;3(5 Pt 1):391–396. doi: 10.1093/ajh/3.5.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salardi S., Saccardo B., Borsani G., Modica R., Ferrandi M., Tripodi M. G., Soria M., Ferrari P., Baralle F. E., Sidoli A. Erythrocyte adducin differential properties in the normotensive and hypertensive rats of the Milan strain. Characterization of spleen adducin m-RNA. Am J Hypertens. 1989 Apr;2(4):229–237. doi: 10.1093/ajh/2.4.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvati P., Ferrario R. G., Parenti P., Bianchi G. Renal function of isolated perfused kidneys from hypertensive (MHS) and normotensive (MNS) rats of the Milan strain: role of calcium. J Hypertens. 1987 Feb;5(1):31–38. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198702000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkadi B., Parker J. C. Activation of ion transport pathways by changes in cell volume. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 12;1071(4):407–427. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90005-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlager G., Barber B. R., Bianchi G. Genetic analysis of blood pressure in the Milan hypertensive strain of rat (Rattus norvegicus). Can J Genet Cytol. 1986 Dec;28(6):967–970. doi: 10.1139/g86-134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. A., Snell R. G., Buckler A., Ambrose C., Duyao M., Church D., Lin C. S., Altherr M., Bates G. P., Groot N. Cloning of the alpha-adducin gene from the Huntington's disease candidate region of chromosome 4 by exon amplification. Nat Genet. 1992 Nov;2(3):223–227. doi: 10.1038/ng1192-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripodi G., Piscone A., Borsani G., Tisminetzky S., Salardi S., Sidoli A., James P., Pongor S., Bianchi G., Baralle F. E. Molecular cloning of an adducin-like protein: evidence of a polymorphism in the normotensive and hypertensive rats of the Milan strain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jun 28;177(3):939–947. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90629-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waseem A., Palfrey H. C. Erythrocyte adducin. Comparison of the alpha- and beta-subunits and multiple-site phosphorylation by protein kinase C and cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Dec 15;178(2):563–573. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





