Abstract
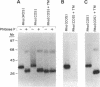
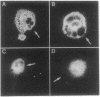
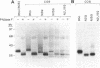
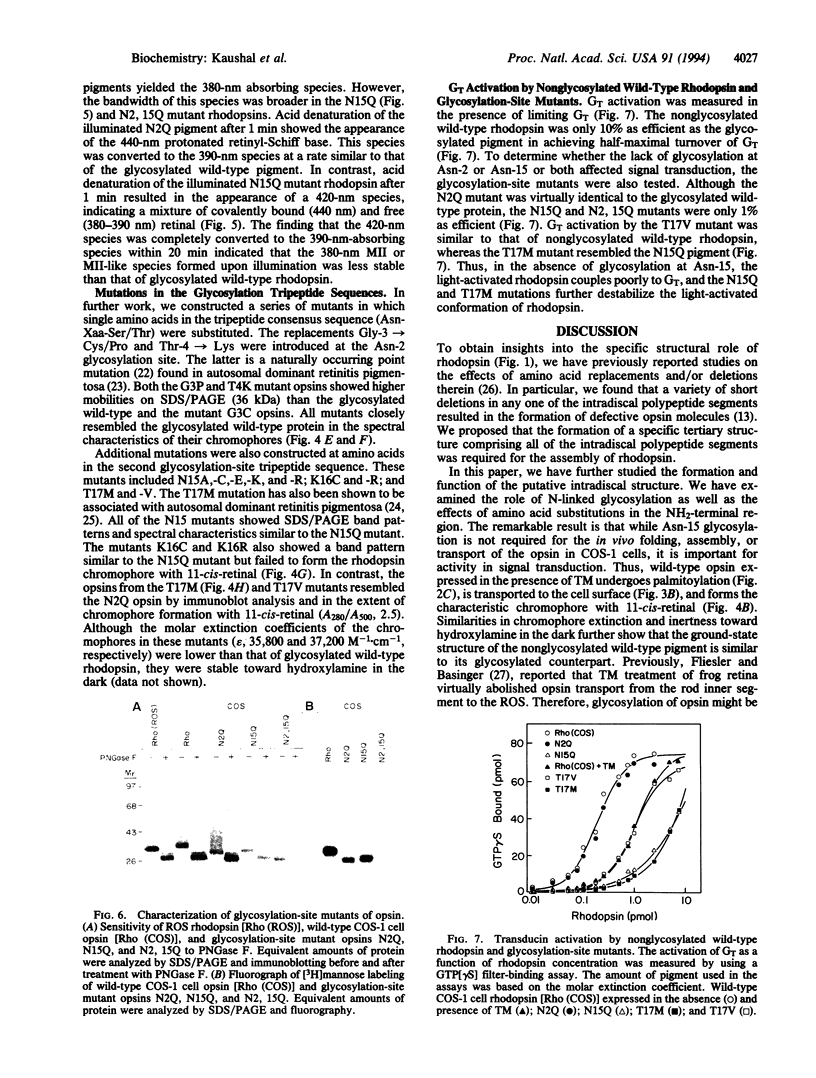
Rhodopsin, the dim light photoreceptor of the rod cell, is an integral membrane protein that is glycosylated at Asn-2 and Asn-15. Here we report experiments on the role of the glycosylation in rhodopsin folding and function. Nonglycosylated opsin was prepared by expression of a wild-type bovine opsin gene in COS-1 cells in the presence of tunicamycin, an inhibitor of asparagine-linked glycosylation. The non-glycosylated opsin folded correctly as shown by its normal palmitoylation, transport to the cell surface, and the formation of the characteristic rhodopsin chromophore (lambda max, 500 nm) with 11-cis-retinal. However, the nonglycosylated rhodopsin showed strikingly low light-dependent activation of GT at concentration levels comparable with those of glycosylated rhodopsin. Amino acid replacements at positions 2 and 15 and the cognate tripeptide consensus sequence [Asn-2-->Gln, Gly-3-->Cys(Pro), Thr-4-->Lys, Asn-15-->Ala(Cys, Glu, Lys, Gln, Arg), Lys-16-->Cys(Arg), Thr-17-->Met(Val)] showed that the substitutions at Asn-2, Gly-3, and Thr-4 had no significant effect on the folding, cellular transport, and/or function of rhodopsin, whereas those at Asn-15 and Lys-16 caused poor folding and were defective in transport to the cell surface. Further, mutant pigments with amino acid replacements at Asn-15 and Thr-17 activated GT very poorly. We conclude that Asn-15 glycosylation is important in signal transduction.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. A., Hutton W. C., Stott J. R. The resistance to flexion of the lumbar intervertebral joint. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1980 May-Jun;5(3):245–253. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198005000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya S., Ridge K. D., Knox B. E., Khorana H. G. Light-stable rhodopsin. I. A rhodopsin analog reconstituted with a nonisomerizable 11-cis retinal derivative. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6763–6769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boege F., Ward M., Jürss R., Hekman M., Helmreich E. J. Role of glycosylation for beta 2-adrenoceptor function in A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):9040–9049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunge S., Wedemann H., David D., Terwilliger D. J., van den Born L. I., Aulehla-Scholz C., Samanns C., Horn M., Ott J., Schwinger E. Molecular analysis and genetic mapping of the rhodopsin gene in families with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Genomics. 1993 Jul;17(1):230–233. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson F. F., Loewen P. C., Khorana H. G. Structure and function in rhodopsin: replacement by alanine of cysteine residues 110 and 187, components of a conserved disulfide bond in rhodopsin, affects the light-activated metarhodopsin II state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):4029–4033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.4029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi T., Molday R. S., Khorana H. G. Role of the intradiscal domain in rhodopsin assembly and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4991–4995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti L., Karnik S. S., Khorana H. G., Nassal M., Oprian D. D. Total synthesis of a gene for bovine rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):599–603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliesler S. J., Basinger S. F. Tunicamycin blocks the incorporation of opsin into retinal rod outer segment membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1116–1120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke R. R., Sakmar T. P., Graham R. M., Khorana H. G. Structure and function in rhodopsin. Studies of the interaction between the rhodopsin cytoplasmic domain and transducin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14767–14774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke R. R., Sakmar T. P., Oprian D. D., Khorana H. G. A single amino acid substitution in rhodopsin (lysine 248----leucine) prevents activation of transducin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2119–2122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda M. N., Papermaster D. S., Hargrave P. A. Rhodopsin carbohydrate. Structure of small oligosaccharides attached at two sites near the NH2 terminus. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8201–8207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K., Hurley J. B., Stryer L. Flow of information in the light-triggered cyclic nucleotide cascade of vision. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):152–156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. C., Ivatt R. J. Synthesis and processing of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:555–583. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J. J., Mulder W. R., De Caluwé G. L., Vlak J. M., De Grip W. J. In vitro expression of bovine opsin using recombinant baculovirus: the role of glutamic acid (134) in opsin biosynthesis and glycosylation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 2;1089(1):68–76. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnik S. S., Ridge K. D., Bhattacharya S., Khorana H. G. Palmitoylation of bovine opsin and its cysteine mutants in COS cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):40–44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khorana H. G., Knox B. E., Nasi E., Swanson R., Thompson D. A. Expression of a bovine rhodopsin gene in Xenopus oocytes: demonstration of light-dependent ionic currents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7917–7921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khorana H. G. Rhodopsin, photoreceptor of the rod cell. An emerging pattern for structure and function. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kito Y., Suzuki T., Azuma M., Sekoguti Y. Absorption spectrum of rhodopsin denatured with acid. Nature. 1968 Jun 8;218(5145):955–957. doi: 10.1038/218955a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S., Inglehearn C. F., Curtis A., Bhattacharya S. Molecular genetics of inherited retinal degenerations. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Jun;2(3):459–466. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X., Davis D., Segaloff D. L. Disruption of potential sites for N-linked glycosylation does not impair hormone binding to the lutropin/choriogonadotropin receptor if Asn-173 is left intact. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1513–1516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama T. A., Khorana H. G. Mapping of the amino acids in membrane-embedded helices that interact with the retinal chromophore in bovine rhodopsin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4269–4275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oprian D. D., Molday R. S., Kaufman R. J., Khorana H. G. Expression of a synthetic bovine rhodopsin gene in monkey kidney cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8874–8878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rands E., Candelore M. R., Cheung A. H., Hill W. S., Strader C. D., Dixon R. A. Mutational analysis of beta-adrenergic receptor glycosylation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10759–10764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resek J. F., Farahbakhsh Z. T., Hubbell W. L., Khorana H. G. Formation of the meta II photointermediate is accompanied by conformational changes in the cytoplasmic surface of rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 16;32(45):12025–12032. doi: 10.1021/bi00096a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmar T. P., Franke R. R., Khorana H. G. Glutamic acid-113 serves as the retinylidene Schiff base counterion in bovine rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8309–8313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield V. C., Fishman G. A., Beck J. S., Kimura A. E., Stone E. M. Identification of novel rhodopsin mutations associated with retinitis pigmentosa by GC-clamped denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Oct;49(4):699–706. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung C. H., Davenport C. M., Hennessey J. C., Maumenee I. H., Jacobson S. G., Heckenlively J. R., Nowakowski R., Fishman G., Gouras P., Nathans J. Rhodopsin mutations in autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6481–6485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung C. H., Schneider B. G., Agarwal N., Papermaster D. S., Nathans J. Functional heterogeneity of mutant rhodopsins responsible for autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8840–8844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varki A. Biological roles of oligosaccharides: all of the theories are correct. Glycobiology. 1993 Apr;3(2):97–130. doi: 10.1093/glycob/3.2.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessling-Resnick M., Johnson G. L. Allosteric behavior in transducin activation mediated by rhodopsin. Initial rate analysis of guanine nucleotide exchange. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3697–3705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zozulya S. A., Gurevich V. V., Zvyaga T. A., Shirokova E. P., Dumler I. L., Garnovskaya M. N., Natochin MYu, Shmukler B. E., Badalov P. R. Functional expression in vitro of bovine visual rhodopsin. Protein Eng. 1990 Apr;3(5):453–458. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.5.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]