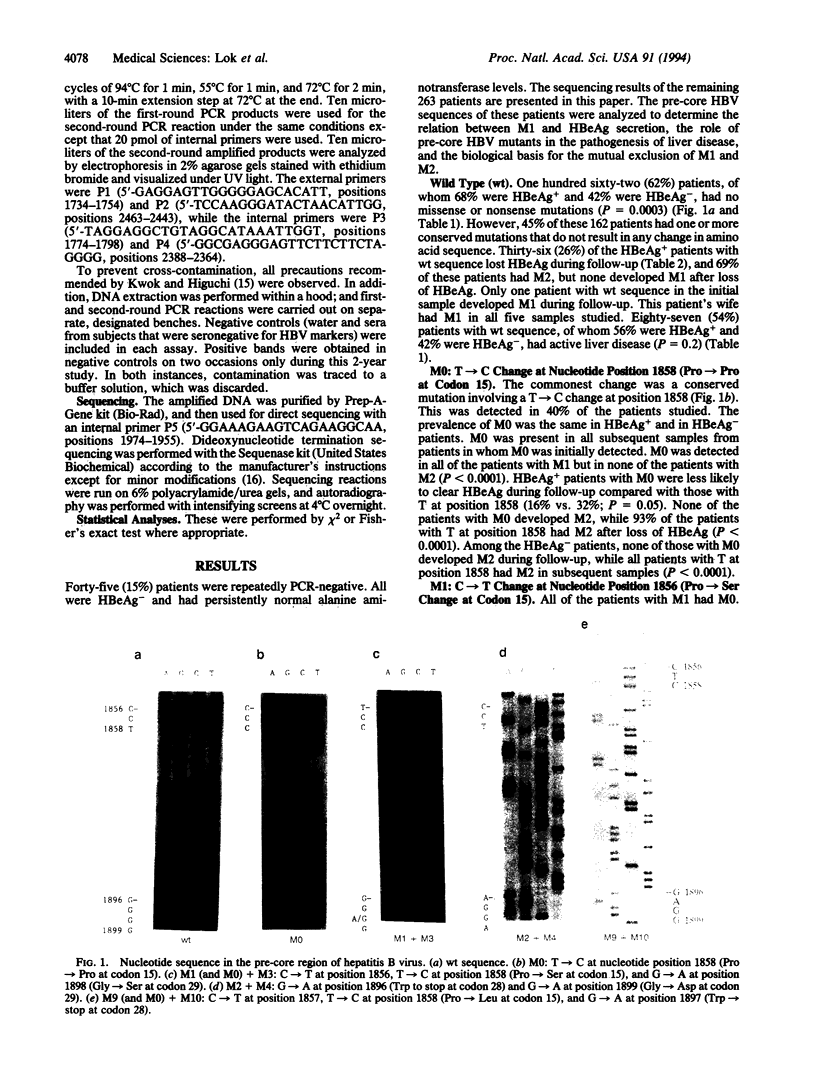
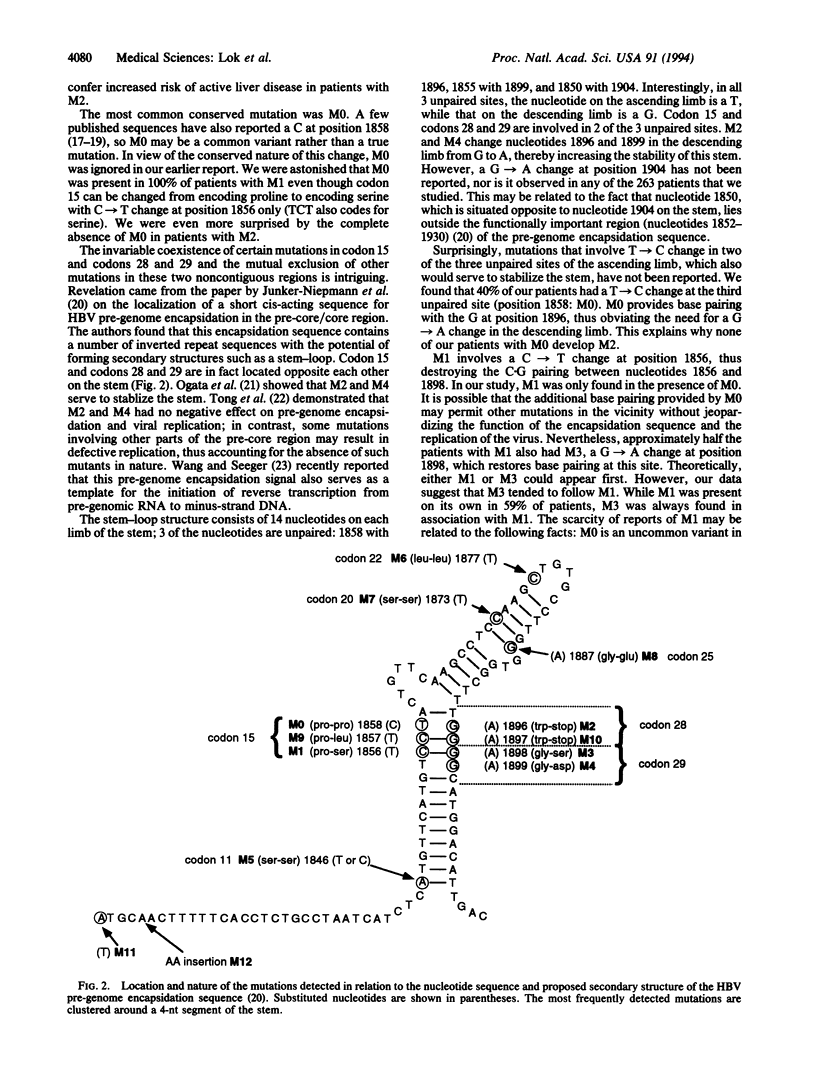
Abstract
We conducted a large-scale survey to determine the frequency and clinical significance of mutations in the pre-core region of hepatitis B virus (HBV). Sera from 263 patients with chronic HBV infection were analyzed by direct sequencing of PCR-amplified HBV DNA. Four major missense/nonsense mutations (M) were found: (M1) C-->T at nucleotide position 1856, Pro-->Ser at codon 15; (M2) G-->A at position 1896, Trp-->stop at codon 28; (M3) G-->A at position 1898, Gly-->Ser at codon 29; and (M4) G-->A at position 1899, Gly-->Asp at codon 29. The commonest conserved mutation was M0: T-->C at position 1858, Pro-->Pro at codon 15. We found that M1 and M2 were mutually exclusive, M3 was only found in association with M1, and M4 was predominantly found in association with M2. All patients with M1 but none of those with M2 had M0. The invariable coexistence of certain mutations in codon 15 and codons 28 and 29 and the mutual exclusion of other mutations in these two noncontiguous regions is related to the stem-loop structure of the pre-genome encapsidation sequence located in the precore/core region. M2 and M4 enhance the stability of the stem by providing two additional paired sites. M1 destroys an existing base pair. However, M1 only occurred in the presence of M0, which provides an extra paired site, and 50% of patients with M1 had M3, a compensatory mutation that restores base pairing at this site. Our data support the proposed secondary structure of the pre-genome encapsidation sequence. The primary function of the mutations in the pre-core region is to enhance stability of this secondary structure to ensure perpetuation of viral replication.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackrill A. M., Naoumov N. V., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Comparison of pre-core/core hepatitis B virus region in liver tissue and serum from patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. J Hepatol. 1992 Sep;16(1-2):224–227. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(05)80120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akahane Y., Yamanaka T., Suzuki H., Sugai Y., Tsuda F., Yotsumoto S., Omi S., Okamoto H., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Chronic active hepatitis with hepatitis B virus DNA and antibody against e antigen in the serum. Disturbed synthesis and secretion of e antigen from hepatocytes due to a point mutation in the precore region. Gastroenterology. 1990 Oct;99(4):1113–1119. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90632-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat R. A., Ulrich P. P., Vyas G. N. Molecular characterization of a new variant of hepatitis B virus in a persistently infected homosexual man. Hepatology. 1990 Feb;11(2):271–276. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840110218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carman W. F., Ferrao M., Lok A. S., Ma O. C., Lai C. L., Thomas H. C. Precore sequence variation in Chinese isolates of hepatitis B virus. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;165(1):127–133. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.1.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carman W. F., Jacyna M. R., Hadziyannis S., Karayiannis P., McGarvey M. J., Makris A., Thomas H. C. Mutation preventing formation of hepatitis B e antigen in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. Lancet. 1989 Sep 9;2(8663):588–591. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90713-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova J. L., Pannetier C., Jaulin C., Kourilsky P. Optimal conditions for directly sequencing double-stranded PCR products with sequenase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):4028–4028. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiordalisi G., Cariani E., Mantero G., Zanetti A., Tanzi E., Chiaramonte M., Primi D. High genomic variability in the pre-C region of hepatitis B virus in anti-HBe, HBV DNA-positive chronic hepatitis. J Med Virol. 1990 Aug;31(4):297–300. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890310410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junker-Niepmann M., Bartenschlager R., Schaller H. A short cis-acting sequence is required for hepatitis B virus pregenome encapsidation and sufficient for packaging of foreign RNA. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3389–3396. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07540.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko S., Feinstone S. M., Miller R. H. Rapid and sensitive method for the detection of serum hepatitis B virus DNA using the polymerase chain reaction technique. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):1930–1933. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.1930-1933.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka Y., Takase K., Kojima M., Shimizu M., Inoue K., Yoshiba M., Tanaka S., Akahane Y., Okamoto H., Tsuda F. Fulminant hepatitis B: induction by hepatitis B virus mutants defective in the precore region and incapable of encoding e antigen. Gastroenterology. 1991 Apr;100(4):1087–1094. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90286-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S., Higuchi R. Avoiding false positives with PCR. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):237–238. doi: 10.1038/339237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang T. J., Hasegawa K., Rimon N., Wands J. R., Ben-Porath E. A hepatitis B virus mutant associated with an epidemic of fulminant hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jun 13;324(24):1705–1709. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199106133242405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loncarevic I. F., Zentgraf H., Schröder C. H. Sequence of a replication competent hepatitis B virus genome with a preX open reading frame. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4940–4940. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miska S., Günther S., Vassilev M., Meisel H., Pape G., Will H. Heterogeneity of hepatitis B virus C-gene sequences: implications for amplification and sequencing. J Hepatol. 1993 Apr;18(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(05)80009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naoumov N. V., Schneider R., Grötzinger T., Jung M. C., Miska S., Pape G. R., Will H. Precore mutant hepatitis B virus infection and liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1992 Feb;102(2):538–543. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata N., Miller R. H., Ishak K. G., Purcell R. H. The complete nucleotide sequence of a pre-core mutant of hepatitis B virus implicated in fulminant hepatitis and its biological characterization in chimpanzees. Virology. 1993 May;194(1):263–276. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Yotsumoto S., Akahane Y., Yamanaka T., Miyazaki Y., Sugai Y., Tsuda F., Tanaka T., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Hepatitis B viruses with precore region defects prevail in persistently infected hosts along with seroconversion to the antibody against e antigen. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1298–1303. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1298-1303.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omata M., Ehata T., Yokosuka O., Hosoda K., Ohto M. Mutations in the precore region of hepatitis B virus DNA in patients with fulminant and severe hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jun 13;324(24):1699–1704. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199106133242404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Onda H., Sasada R., Igarashi K., Sugino Y., Nishioka K. The complete nucleotide sequences of the cloned hepatitis B virus DNA; subtype adr and adw. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1747–1757. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasek M., Goto T., Gilbert W., Zink B., Schaller H., MacKay P., Leadbetter G., Murray K. Hepatitis B virus genes and their expression in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):575–579. doi: 10.1038/282575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignatelli M., Waters J., Lever A., Iwarson S., Gerety R., Thomas H. C. Cytotoxic T-cell responses to the nucleocapsid proteins of HBV in chronic hepatitis. Evidence that antibody modulation may cause protracted infection. J Hepatol. 1987 Feb;4(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(87)80004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Schaller H. The secretory core protein of human hepatitis B virus is expressed on the cell surface. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5399–5404. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5399-5404.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K., Akahane Y., Suzuki H., Okamoto H., Tsuda F., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Defects in the precore region of the HBV genome in patients with chronic hepatitis B after sustained seroconversion from HBeAg to anti-HBe induced spontaneously or with interferon therapy. Hepatology. 1990 Dec;12(6):1284–1289. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong S. P., Li J. S., Vitvitski L., Trépo C. Active hepatitis B virus replication in the presence of anti-HBe is associated with viral variants containing an inactive pre-C region. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):596–603. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90030-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong S. P., Li J. S., Vitvitski L., Trépo C. Replication capacities of natural and artificial precore stop codon mutants of hepatitis B virus: relevance of pregenome encapsidation signal. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):237–245. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90185-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran A., Kremsdorf D., Capel F., Housset C., Dauguet C., Petit M. A., Brechot C. Emergence of and takeover by hepatitis B virus (HBV) with rearrangements in the pre-S/S and pre-C/C genes during chronic HBV infection. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3566–3574. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3566-3574.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tur-Kaspa R., Klein A., Aharonson S. Hepatitis B virus precore mutants are identical in carriers from various ethnic origins and are associated with a range of liver disease severity. Hepatology. 1992 Dec;16(6):1338–1342. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaudin M., Wolstenholme A. J., Tsiquaye K. N., Zuckerman A. J., Harrison T. J. The complete nucleotide sequence of the genome of a hepatitis B virus isolated from a naturally infected chimpanzee. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jun;69(Pt 6):1383–1389. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-6-1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakita T., Kakumu S., Shibata M., Yoshioka K., Ito Y., Shinagawa T., Ishikawa T., Takayanagi M., Morishima T. Detection of pre-C and core region mutants of hepatitis B virus in chronic hepatitis B virus carriers. J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;88(6):1793–1801. doi: 10.1172/JCI115500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. H., Seeger C. Novel mechanism for reverse transcription in hepatitis B viruses. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6507–6512. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6507-6512.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshiba M., Sekiyama K., Sugata F., Okamoto H., Yamamoto K., Yotsumoto S. Reactivation of precore mutant hepatitis B virus leading to fulminant hepatic failure following cytotoxic treatment. Dig Dis Sci. 1992 Aug;37(8):1253–1259. doi: 10.1007/BF01296569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]