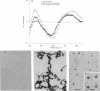
Abstract
Receptor-mediated gene transfer has been used to introduce genes into tissues of animals in vivo. The genes introduced by this approach have been transiently expressed at low levels in animal tissues. High levels of expression, for longer periods, have been attained by the induction of cell division (i.e., partial hepatectomy) or disruption of lysosomal degradation of the DNA. We have studied the correlation of specific structural features on the DNA/ligand complexes with their ability to efficiently introduce DNA into the livers of intact animals. A chimeric gene containing the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene promoter (nucleotides -460 to +73) linked to the structural gene for human factor IX (PEPCK-hFIX gene) was condensed with galactosylated poly(L-lysine) by titration with NaCl, resulting in complexes of defined size (10-12 nm in diameter) and shape. The PEPCK-hFIX gene complex was injected into the caudal vena cava of adult rats and the conjugated DNA was specifically targeted to the livers of the animals; no detectable DNA was noted in other tissues. The plasmid containing the PEPCK-hFIX gene was found as an episome in the livers of the rats 32 days after injection of the DNA complex. Human factor IX DNA, mRNA, and functional protein were detected up to 140 days after administration of the DNA complex (the duration of the experiment). Transcription from the PEPCK promoter could be induced over the entire course of the experiment by feeding the rats a high-protein, carbohydrate-free diet. We conclude that the structure of the DNA/ligand complexes is of key importance for the successful introduction of genes into the tissues of animals by receptor-mediated endocytosis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bijsterbosch M. K., Van Berkel T. J. Lactosylated high density lipoprotein: a potential carrier for the site-specific delivery of drugs to parenchymal liver cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;41(2):404–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijsterbosch M. K., Ziere G. J., Van Berkel T. J. Lactosylated low density lipoprotein: a potential carrier for the site-specific delivery of drugs to Kupffer cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;36(3):484–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll D. Optical properties of deoxyribonucleic acid--polylysine complexes. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 1;11(3):421–426. doi: 10.1021/bi00753a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennever J. F., Love S. M., Harpst J. A. Ionic effects on the structure of nucleoprotein cores from adenovirus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Oct 3;826(1):67–79. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4781(85)80008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eppler K., Wyckoff E., Goates J., Parr R., Casjens S. Nucleotide sequence of the bacteriophage P22 genes required for DNA packaging. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):519–538. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90981-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferkol T., Lindberg G. L., Chen J., Perales J. C., Crawford D. R., Ratnoff O. D., Hanson R. W. Regulation of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase/human factor IX gene introduced into the livers of adult rats by receptor-mediated gene transfer. FASEB J. 1993 Aug;7(11):1081–1091. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.11.8370479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J. E., Yun J. S., Patel Y. M., McGrane M. M., Hanson R. W. Glucocorticoids regulate the induction of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene transcription during diabetes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12952–12957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao L., Wagner E., Cotten M., Agarwal S., Harris C., Rømer M., Miller L., Hu P. C., Curiel D. Direct in vivo gene transfer to airway epithelium employing adenovirus-polylysine-DNA complexes. Hum Gene Ther. 1993 Feb;4(1):17–24. doi: 10.1089/hum.1993.4.1-17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes M., Garrett R. A., Gratzer W. B. Structure of nucleic acid-poly base complexes. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4410–4416. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrane M. M., de Vente J., Yun J., Bloom J., Park E., Wynshaw-Boris A., Wagner T., Rottman F. M., Hanson R. W. Tissue-specific expression and dietary regulation of a chimeric phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase/bovine growth hormone gene in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11443–11451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monsigny M., Roche A. C., Midoux P. Uptake of neoglycoproteins via membrane lectin(s) of L1210 cells evidenced by quantitative flow cytofluorometry and drug targeting. Biol Cell. 1984;51(2):187–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1984.tb00298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins D. E., Olins A. L., Von Hippel P. H. Model nucleoprotein complexes: studies on the interaction of cationic homopolypeptides with DNA. J Mol Biol. 1967 Mar 14;24(2):157–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90324-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., DAVIE E. W. The purification of activated Hageman factor (activated factor XII). Biochemistry. 1962 Nov;1:967–975. doi: 10.1021/bi00912a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich Z., Ghirlando R., Minsky A. Nucleic acids packaging processes: effects of adenine tracts and sequence-dependent curvature. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1992 Jun;9(6):1097–1109. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1992.10507981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlepper-Schäfer J., Hülsmann D., Djovkar A., Meyer H. E., Herbertz L., Kolb H., Kolb-Bachofen V. Endocytosis via galactose receptors in vivo. Ligand size directs uptake by hepatocytes and/or liver macrophages. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Aug;165(2):494–506. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90602-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. T., Leng M., Felsenfeld G. Deoxyribonucleic acid-polylysine complexes. Structure and nucleotide specificity. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3219–3232. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timsit Y., Moras D. Groove-backbone interaction in B-DNA. Implication for DNA condensation and recombination. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 5;221(3):919–940. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80184-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E., Cotten M., Foisner R., Birnstiel M. L. Transferrin-polycation-DNA complexes: the effect of polycations on the structure of the complex and DNA delivery to cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4255–4259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. M., Grossman M., Cabrera J. A., Wu C. H., Wu G. Y. A novel mechanism for achieving transgene persistence in vivo after somatic gene transfer into hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11483–11489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. M., Grossman M., Wu C. H., Chowdhury N. R., Wu G. Y., Chowdhury J. R. Hepatocyte-directed gene transfer in vivo leads to transient improvement of hypercholesterolemia in low density lipoprotein receptor-deficient rabbits. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):963–967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. H., Wilson J. M., Wu G. Y. Targeting genes: delivery and persistent expression of a foreign gene driven by mammalian regulatory elements in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):16985–16987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu G. Y., Wilson J. M., Shalaby F., Grossman M., Shafritz D. A., Wu C. H. Receptor-mediated gene delivery in vivo. Partial correction of genetic analbuminemia in Nagase rats. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14338–14342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]