Abstract
The nervous system plays an important role in the regulation of epithelial homeostasis and has also been postulated to play a role in tumorigenesis. We provide evidence that proper innervation is critical at all stages of gastric tumorigenesis. In three separate mouse models of gastric cancer, surgical or pharmacological denervation of the stomach (bilateral or unilateral truncal vagotomy, or local injection of botulinum toxin type A) markedly reduced tumor incidence and progression, but only in the denervated portion of the stomach. Vagotomy or botulinum toxin type A treatment also enhanced the therapeutic effects of systemic chemotherapy and prolonged survival. Denervation-induced suppression of tumorigenesis was associated with inhibition of Wnt signaling and suppression of stem cell expansion. In gastric organoid cultures, neurons stimulated growth in a Wnt-mediated fashion through cholinergic signaling. Furthermore, pharmacological inhibition or genetic knockout of the muscarinic acetylcholine M3 receptor suppressed gastric tumorigenesis. In gastric cancer patients, tumor stage correlated with neural density and activated Wnt signaling, whereas vagotomy reduced the risk of gastric cancer. Together, our findings suggest that vagal innervation contributes to gastric tumorigenesis via M3 receptor–mediated Wnt signaling in the stem cells, and that denervation might represent a feasible strategy for the control of gastric cancer.
INTRODUCTION
The nervous system regulates epithelial homeostasis in different ways, and this regulation by the nervous system partly involves modulation of stem and progenitor cells (1, 2). There is also crosstalk between tumor cells and nerves, such that tumors induce active neurogenesis, resulting in increased neuronal density in preneoplastic and neoplastic tissues (3–6). In addition, activation of muscarinic receptors has been shown to promote cell transformation and cancer progression (3–6). A recent study demonstrated that prostate tumors are infiltrated by autonomic nerves contributing to cancer development and dissemination (7). Given the potential ability of nerves to influence gut stem and progenitor cells, and the prevailing notion that persistently elevated gut epithelial proliferation predisposes to cancer formation, it is believed that axonal reflexes could also modulate the conversion of stem or progenitor cells into cancer cells (8, 9).
Gastric cancer is the fifth most common cancer and the third leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide, with a 5-year survival rate of less than 25% (10, 11). It has been demonstrated that vagotomy decreases gastric mucosal thickness and cellular proliferation (12, 13). An epidemiological study showed that the risk of gastric cancer [standardized incidence ratio (SIR)] after vagotomy was not reduced during the first 10-year period, but was reduced by 50% (SIR 0.5) during the second 10-year follow-up (14, 15). Here, we provide evidence that proper innervation is critical for gastric tumorigenesis, and suggest that nerves may represent a therapeutic target for the treatment of gastric cancer.
RESULTS
Gastric lesser curvature has high vagal innervation and high incidence of tumors
In humans, there is a higher incidence of gastric cancer in the lesser (~80% of tumors) than the greater curvature (16, 17). We also observed this distribution in the INS-GAS mouse model, a genetic mouse model of spontaneous gastric cancer (18, 19), in which there was a similar prevalence (77%) of tumors in the lesser curvature (Fig. 1A). INS-GAS mice do not display obvious preneoplastic lesions until 6 months of age, but afterward, they develop gastric cancer through stages of atrophy, meta-plasia, and finally, dysplasia at 12 months of age (18, 19). Topographic analysis of vagus nerve fibers and terminals in the murine stomach revealed a higher density of neurons and larger ganglia in the lesser curvature compared to the greater curvature (Fig. 1B), correlating with the observed pattern of tumor formation. This possible association between the distribution of vagal nerve fibers and the appearance of gastric tumors in INS-GAS mice prompted us to study the role of nerves in gastric tumorigenesis (fig. S1 and table S1).
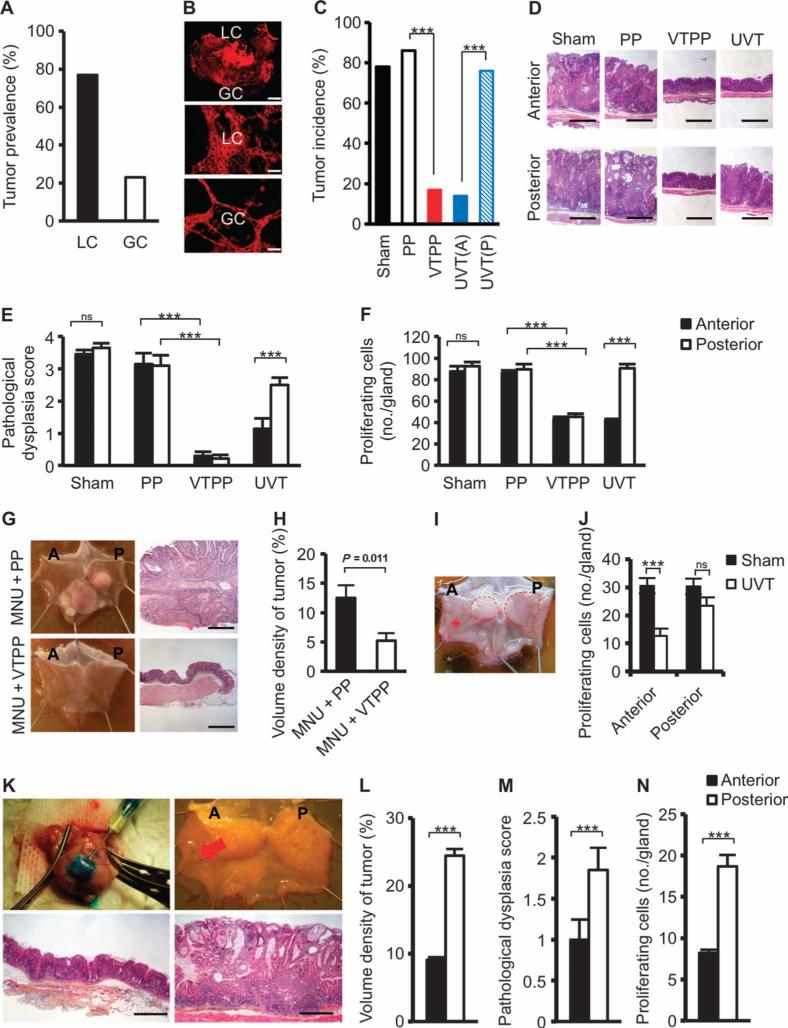
Fig. 1. Denervation attenuates tumorigenesis at the preneoplastic stage in mouse models of gastric cancer.
(A) Tumor prevalence at the lesser curvature (LC) and greater curvature (GC) of the stomach of INS-GAS mice. (B) Images of carbocyanine dye (DiI)–labeled vagal terminals in an adult mouse stomach. A montage of a low-power image showing the lesser curvature and greater curvature of the gastric wall (top scale bar, 2.0 μm), and higher-power images of lesser curvature (middle) and greater curvature (bottom) show a higher density of vagal innervation in lesser curvature than in greater curvature (89 and 54% of the visual field, estimated by point counting method) (middle and bottom scale bars, 72 μm). (C) Tumor incidence at 12 months of age in INSGAS mice that underwent sham operation (Sham), pyloroplasty alone (PP), bilateral vagotomy with pyloroplasty (VTPP), or anterior unilateral vagotomy (UVT) (A, anterior; P, posterior side of the stomachs) at 6 months of age. ***P = 4.9 × 10−7 (VTPP versus PP), P = 1.32 × 10−6 [UVT(A) versus UVT(P)] (Fisher's exact test). (D) Representative microphotographs of histopathological appearance of the anterior and posterior sides of the stomach from INS-GAS mice (at 12 months of age) that underwent sham, PP, VTPP, and UVT at 6 months of age. Scale bars, 100 μm. (E) Pathological score for dysplasia. Means ± SEM. Comparisons between anterior and posterior sides were performed by paired t test within sham (n = 27) and UVT (n = 30), or by Tukey test between PP (n = 25) and VTPP (n = 25). ***P = 5.31 × 10−5 (UVT), P = 0.0001 or 0.00006 (PP and VTPP, anterior or posterior side, respectively). ns, not significant (P = 0.987). (F) Number of proliferating cells. Means ± SEM. Comparisons between anterior and posterior sides were performed by paired t test within sham (n = 27) and UVT (n = 30), or by Tukey test between PP (n = 25) and VTPP (n = 25). ***P = 5.77 × 10−3 (UVT), P = 1.90 × 10−4 (anterior), and P = 1.49 × 10−3 (posterior) between PP and VTPP. ns, not significant (P = 0.229). (G) Representative photographs showing gross appearance of stomachs opened along the greater curvature and corresponding microphotographs of histopathological appearance of the stomachs (antrum) from mice treated with MNU + PP or MNU + VTPP. Scale bars, 100 μm. (H) Volume density of tumor (measured by point counting method). Means ± SEM. Student's t test was used to compare between MNU + PP (n = 11) and MNU + VTPP (n = 9). (I) Representative photograph showing gross appearance of gastric tumors (indicated by dashed line) in a stomach opened along the greater curvature from an Hp-infected H+/K+– ATPase–IL-1β mouse, which underwent UVT in the anterior side (indicated by asterisk).(J)Number of proliferating cells in Hp-infectedH+/K+–ATPase–IL-1β mouse stomachs subjected to UVT in the anterior side. Means ± SEM. ***P = 0.00006 (Student's t test). ns, not significant (P = 0.120) between sham (n = 12) and UVT (n = 12) in the anterior and the posterior sides. (K) Photographs showing the Botox injection procedure (upper left), gross appearance of Botox-injected stomach after 6 months (A, anterior where Botox was injected; P, posterior) (upper right), and representative microphotographs of histopathological appearance of anterior (lower left) and posterior (lower right) stomach (corpus). Red arrow, injection site. Scale bars, 100 μm. (L to N) Volume density of tumor, pathological score for dysplasia, and number of proliferating cells after anterior Botox injection. Means ± SEM (n = 16). ***P = 2.75 × 10−11 (L), P = 0.01 (M), or P = 0.001 (N) between the anterior and posterior sides of the stomach (paired t test).
Surgical denervation at preneoplastic stage attenuates tumorigenesis in mouse models of gastric cancer
In the first set of experiments, vagotomy was performed in INS-GAS mice at 6 months of age. Subsequently, the effects of vagotomy were examined 6 months after surgery. One hundred seven INS-GAS mice were subjected to either subdiaphragmatic VTPP, UVT (fig. S2), sham operation, or PP. The unilateral vagotomy approach takes advantage of the fact that each (anterior or posterior) vagal trunk innervates only one-half of the stomach. Consequently, denervation of one side of the stomach does not impair the overall functional capacity of the stomach, leaving gastric acid output, circulating gastrin levels, and gastric motility unchanged (13, 20).
Six months after surgery, body weight was unchanged in either male or female mice (fig. S3). Tumor incidence was 17% after VTPP versus 86% after PP alone, 14% in the anterior side versus 76% in the posterior side after anterior UVT, and 78% in the sham-operated mice (Fig. 1C). Histological examination revealed the reduction of mucosal thickness after VTPP (compared to PP) or UVT (compared to the corresponding posterior side) (Fig. 1D and fig. S4), indicating successful denervation (12, 13). Pathological evaluation (21) revealed that vagotomy attenuated the score for dysplasia and reduced the number of proliferating cells (Fig. 1, E and F) and the scores for inflammation, epithelial defects, oxyntic atrophy, epithelial hyperplasia, pseudopyloric metaplasia, and gastric histological activity index (GHAI) (fig. S5, A to F).
To confirm these findings, we tested the surgical approach in two other mouse models of gastric cancer, namely, the carcinogen-induced [N-nitroso-N-methylurea (MNU)] (22) and the Helicobacter pylori (Hp)–infected H+/K+–ATPase (adenosine triphosphatase)– IL-1β (interleukin-1β) mouse models (23). In the MNU model, VTPP performed 1 week after completion of MNU treatment inhibited tumor development at 13 months of age (Fig. 1, G and H). Infection of H+/K+–ATPase–IL-1β mice with Hp accelerated gastric tumorigenesis, resembling Hp-related atrophy-metaplasia-dysplasia sequence in humans. UVT performed 8.5 months after Hp infection (at 12 months of age) reduced tumor size and number of proliferating cells in the denervated side of the stomach at 18 months of age (Fig. 1, I and J). Thus, the findings from these three independent models demonstrate the importance of functional innervation in gastric tumorigenesis.
Pharmacological denervation at an early preneoplastic stage attenuates gastric tumorigenesis
To prove that the effects of surgical denervation were primarily local (acting at vagus nerve terminals within the gastric mucosa), unilateral injection of botulinum toxin A (Botox) into the gastric wall was performed in INS-GAS mice at 6 months of age. Botox enters into the axon terminal through vesicle internalization and cleaves synaptosomal-associated protein 25, leading to impaired exocytosis of neurotransmitters, including acetylcholine (24). Botox was injected subserosally along the greater curvature in the anterior side of the stomach (Fig. 1K). Six months later, tumor size, score for dysplasia, and number of proliferating cells were markedly reduced in the anterior wall compared with the posterior side of the stomach (Fig. 1, L to N). Moreover, these changes were associated with attenuated scores for inflammation, epithelial defects, atrophy, hyperplasia, pseudopyloric metaplasia, and GHAI (fig. S6, A and B). Hence, these findings confirm an important role of local signaling from vagus nerve endings in early gastric tumorigenesis.
Surgical or pharmacological denervation attenuates gastric tumor progression
Because vagotomy or Botox treatment had a protective effect at preneoplastic stages, we next examined whether gastric denervation could also inhibit tumor progression at later stages. INS-GAS mice at 8, 10, or 12 months of age were subjected to anterior UVT and euthanized at 18 months of age. In these mice, the tumors were smaller with less severe dysplasia in the anterior side compared to the posterior side of the stomach, suggesting that denervation inhibits tumor progression in mice with established neoplastic changes (Fig. 2, A to C).
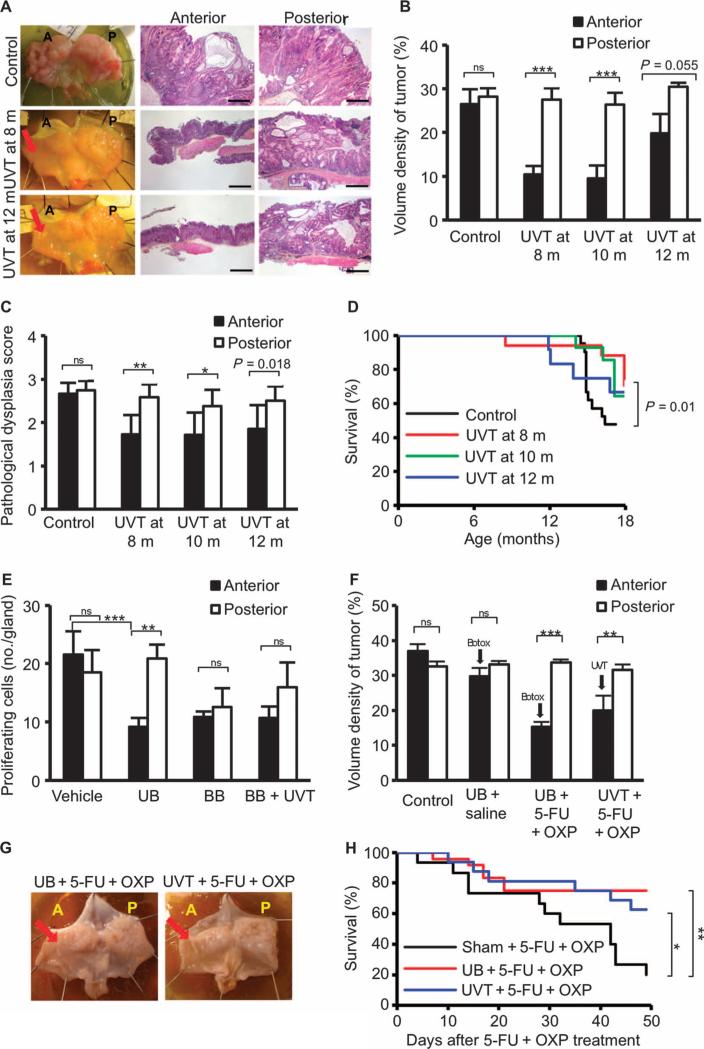
Fig. 2. Denervation attenuates gastric tumor progression in mice.
(A) Gross appearance of mouse stomachs at 18 months of age and representative micro-photographs of the histopatho-logical appearance of the corpus region of the anterior and posterior sides of the stomach from age-matchedINS-GAS mice (Control) and mice that underwent anterior UVT at 8 or 12 months of age. Scale bars, 100 μm. Red arrows, vagotomy side. (B) Volume density of tumor. Means ± SEM. Paired t test between the anterior and the posterior sides of the stomach: P = 0.589 (n = 21, Control), P = 2.56 × 10−5 (n = 17, UVT at 8months ofage),P=2.17×10−4 (n = 14, UVT at 10 months), P = 0.055 (n = 12, UVT at 12 months). (C)Pathological score for dysplasia. Means ± SEM. Paired t test between the anterior and the posterior sides of the stomach: P = 0.38 (n = 21, Control), P = 0.002 (n = 17, UVT at 8 months of age), P=0.047(n=14,UVT at 10 months), P=0.018(n=12,UVT at 12 months). (D) Kaplan-Meier curves showing survival of INS-GAS mice that underwentUVTat8(red),10(green), or 12 months of age (blue), or of age-matched INS-GAS mice (Control) (black). P = 0.01 between control and UVT groups at 8 months. (E) Proliferating cells in the anterior and posterior mucosa of the stomach of INS-GAS mice at 2 months after vagotomy and/or Botox injection. Means ± SEM. Paired t test was used to compare the anterior and posterior sides of the stomach. P = 0.291 (n = 6, Vehicle), P = 0.007 [n = 6, unilateral anterior Botox (UB)], P = 0.595 [n = 7, bilateral Botox (BB)], P = 0.326 [n = 7, bilateral Botox plus anterior UVT (BB + UVT)], P = 0.0007 (Vehicle anterior versus UB anterior, Dunnett's test). (F) Volume density of tumor in INS-GAS mice subjected to saline (intraperitoneally) (Control), UB + saline (intraperitoneally), UB + 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) + oxaliplatin (OXP) (intra peritoneally), or UVT + 5-FU + OXP (intraperitoneally). Means ± SEM. Paired t test was used to compare the anterior and posterior sides of the stomach. P = 0.172 (n = 10, Control), P = 0.200 (n = 10, UB + saline), P = 0.0004 (n = 24, UB + 5-FU + OXP), P = 0.006 (n = 16, UVT + 5-FU + OXP). (G) Gross appearance of representative stomachs from INS-GAS mice subjected to 5-FU + OXP with UB or UVT (reduced tumor burden indicated by arrows). (H) Kaplan-Meier curves showing survival of INS-GAS mice that underwent sham operation and 5-FU + OXP treatment (black), UB and 5-FU + OXP (red), or anterior UVT and 5-FU + OXP (blue). *P = 0.041, **P = 0.0069.
Whereas the average life span of wild-type FVB/N mice is well over 24 months, the survival of INS-GAS mice at 18 months of age was 53% (16 of 30 mice). Attenuation of tumor burden by UVT improved the 18-month survival when compared to age-matched INS-GAS mice: 71% when UVT was performed at 8 months, 64% when performed at 10 months, and 67% when performed at 12 months, respectively (Fig. 2D). Next, INS-GAS mice at 12 months of age were subjected to vehicle or Botox treatment unilaterally or bilaterally, with or without UVT. The tumor cell proliferation was reduced in the anterior side of the stomach where Botox was injected, when compared to the posterior side or vehicle-treated anterior side (Fig. 2E). The combination of UVT and Botox did not further reduce cellular proliferation, indicating that vagotomy and Botox likely act through the same mechanism. These results further suggest that surgical or pharmacological denervation inhibits gastric cancer progression even when applied at later stages of gastric tumorigenesis.
Denervation enhances the effect of chemotherapy in the treatment of gastric cancer
Next, we examined whether denervation could enhance the effects of systemic chemotherapy in gastric cancer. INS-GAS mice at 12 to 14 months of age received systemic administration of 5-FU + oxaliplatin or saline along with unilateral Botox treatment or UVT. The experiment was designed such that the nondenervated half of the stomach in each animal served as an internal control, either a chemotherapy-only control (the posterior side of the stomach in two of the groups received chemotherapy alone) or an untreated control. An additional group of INS-GAS mice was included as untreated controls. As early as 2 months after starting treatment, tumor size was reduced in mice treated with chemotherapy, specifically in the denervated areas of the stomach (the anterior side) after unilateral vagotomy or Botox injection (Fig. 2, F and G). The combination of either Botox or UVT with chemotherapy increased survival compared to chemo-therapy alone (Fig. 2H). Together, these findings suggest that the combination of denervation and chemotherapy has an enhanced effect on tumor growth and survival.
Denervation inhibits gastric Wnt signaling and suppresses stem cell expansion through the M3 receptor
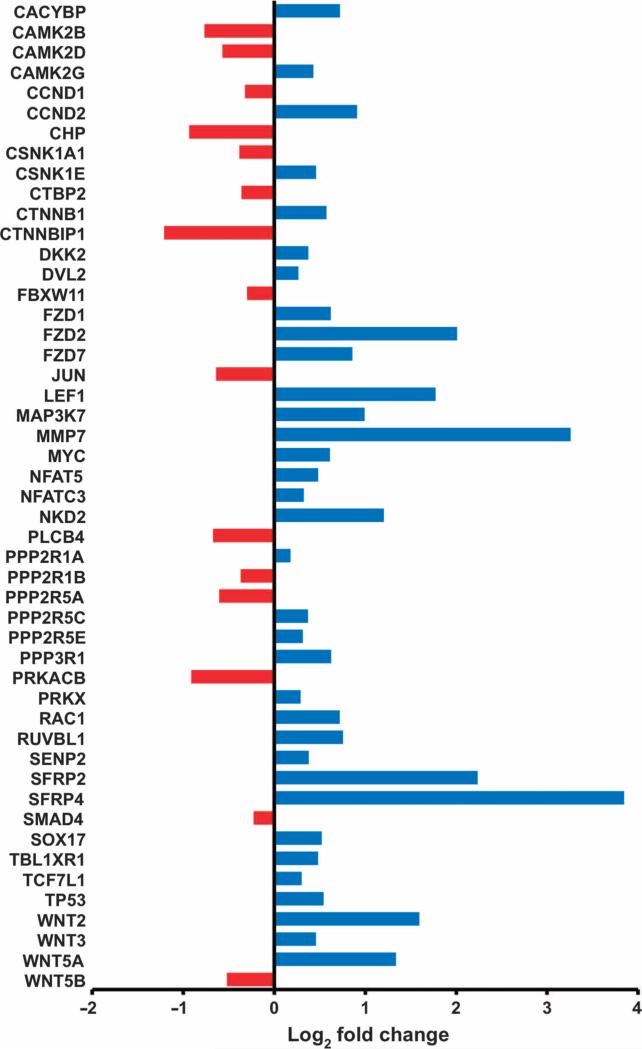
We performed gene expression profiling in INS-GAS mice versus wild-type mice, and in unilaterally vagotomized INS-GAS mice (UVT performed at 6 months of age). Comparison between INS-GAS mice and wild-type mice showed up-regulation of the Wnt signaling pathway in INS-GAS mice (fig. S7). Comparison between the vagotomized anterior and the untreated posterior side of the same stomach revealed many differentially expressed KEGG pathways, including those involved in gastric acid secretion, mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling, cell cycle, apoptosis, autophagy, vascular endothelial growth factor signaling, and actin cytoskeleton (fig. S8). The Wnt and Notch signaling pathways were markedly inhibited in the vagotomized side [validated by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) arrays] (Fig. 3 and fig. S9). The inhibition of Wnt signaling was persistent at 2, 6, 8, and 10 months after vagotomy. Inflammation-related pathways, including T cell receptor signaling, natural killer cell–mediated cytotoxicity, leukocyte transendothelial migration, and chemokine signaling, were activated at 2 months, but then inhibited at 4 and 6 months after vagotomy, whereas Toll-like receptor signaling was inhibited at all the time points (Fig. 4A).
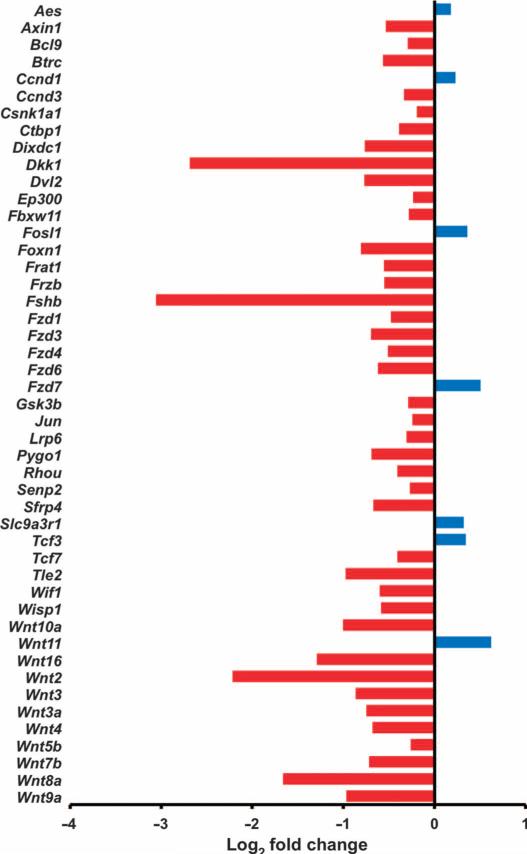
Fig. 3. Denervation leads to inhibition of Wnt signaling in the mouse model of gastric cancer.
Gene expression of Wnt signaling pathway (determined by qRT-PCR array analysis) in vagotomized anterior stomach of INS-GAS mice at 12 months of age (6 months UVT). Log2 fold changes of expressed genes in comparison with the posterior side of the same stomach are shown. Red, down-regulation; blue, up-regulation.
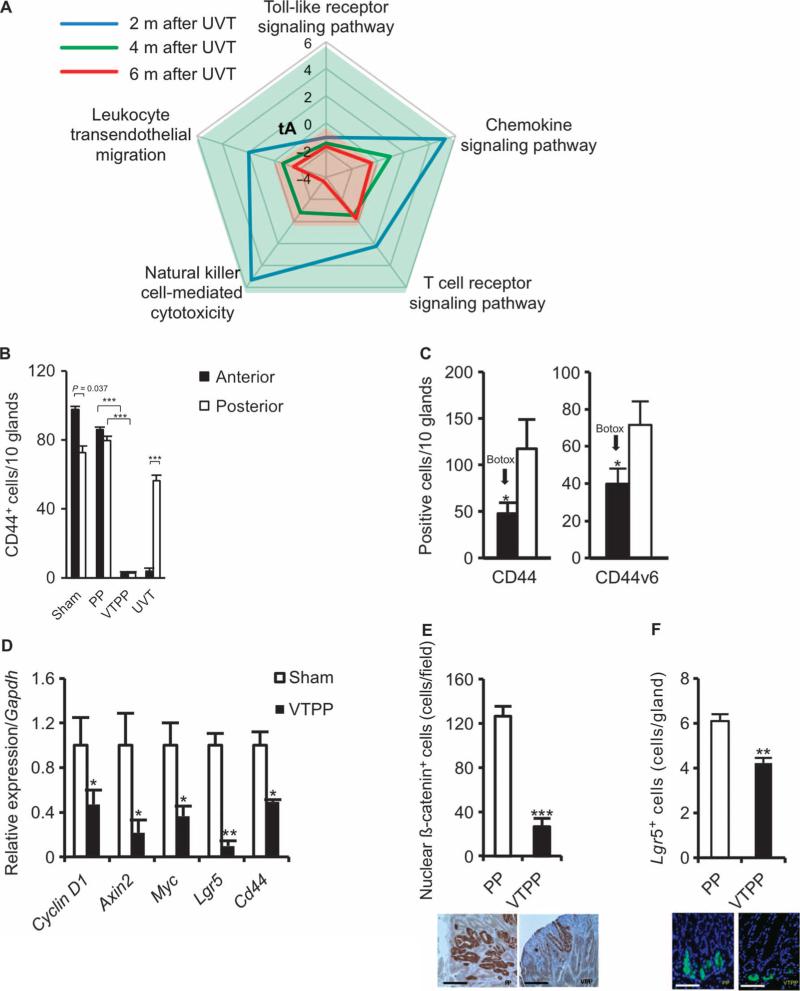
Fig. 4. Denervation alters inflammation-related signaling and suppresses stem cell expansion in mouse models of gastric cancer.
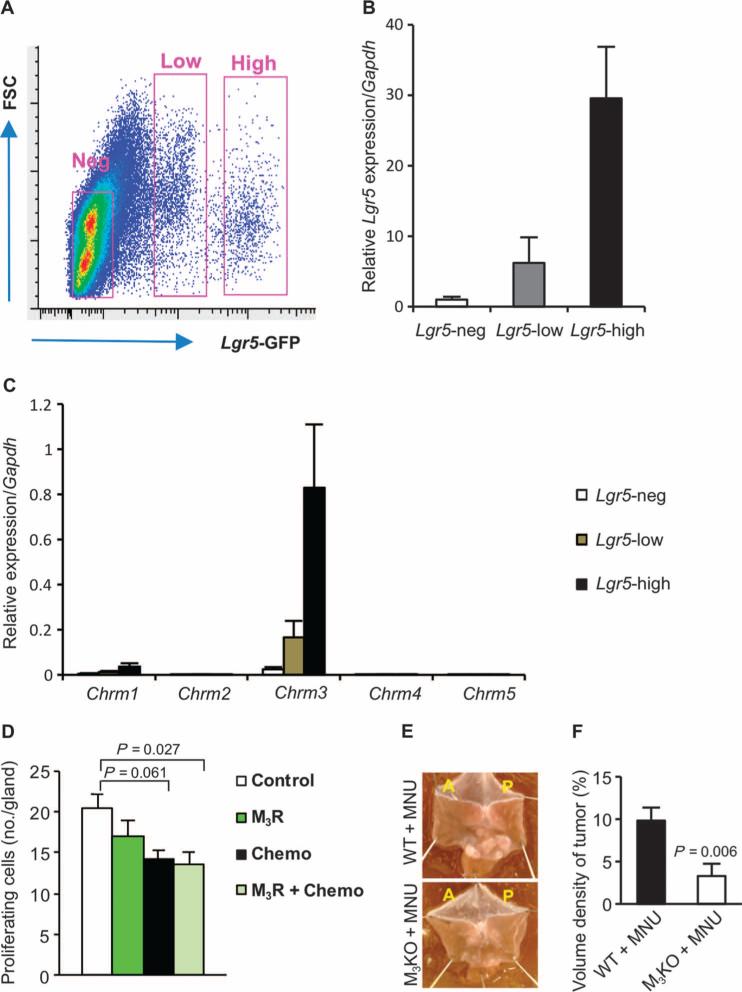
(A) Time course of five signaling pathways determined by microarray analysis in the anterior side of the stomach at 2 (blue), 4 (green), and 6 (red) months after anterior UVT compared with the posterior side of the stomach in INSGAS mice. Total net accumulated perturbation (expressed as tA score): −4 to 6. tA score > 0: activation; tA score < 0: inhibition. (B) Numbers of CD44+ cells in the anterior and the posterior sides of the stomach of INS-GAS mice at 6 months after surgery. Means ± SEM. P = 0.037 (n = 27, paired t test) between the anterior and the posterior sides in sham operation (Sham), P = 1.00 × 10−6 or P = 6.00 × 10−6 (n = 25, Dunnett's test) between PP and VTPP (anterior and posterior sides, respectively), and P = 1.74 × 10−3 (n = 30, paired t test) between the anterior and the posterior sides within anterior UVT. (C) Numbers of CD44-immunoreactive cells (CD44) and CD44v6-immunoreactive cells (CD44v6) in the anterior and the posterior sides of the stomach of INSGAS mice at 6 months after Botox injection. Means ± SEM. P = 0.034 and P = 0.021, respectively (n = 16, paired t test) between the anterior and the posterior sides of the stomach. (D) Relative gene expression of Cyclin D1, Axin2, Myc, Lgr5, and Cd44 in the gastric tumors of sham-operated or VTPP-treated mice 36 weeks after MNU treatment (n = 4 per group). Means ± SEM. P = 0.04 (Cyclin D1), 0.04 (Axin2), 0.03 (Myc), 0.001 (Lgr5), and 0.01 (Cd44) (Student's t test). (E) Number of cells showing nuclear β-catenin accumulation in the gastric tumors of PP- or VTPP-treated mice 36 weeks after MNU treatment (n = 4 per group). Means ± SEM. P = 7.00 × 10−6 (Student's t test). Representative immunohistochemical microphotographs are shown below. Scale bars, 40 μm. (F) Number of Lgr5+ cells in the stomachs of PP- or VTPP-treated mice 6 weeks after MNU treatment (n = 5 per group). Means ± SEM. P = 4.00 × 10−6 (Student's t test). Representative Lgr5-GFP+ microphotographs are shown below. Scale bars, 20 μm.
The Wnt signaling pathway is a major regulator of gastrointestinal stem cells and tumorigenesis (25, 26). CD44 is a known target of the Wnt signaling pathway (27) and has been shown to label a cancer-initiating cell population (28). Lgr5 is a marker of gastric stem cells in normal as well as cancer tissues, and also a target of the Wnt signaling pathway (29). Either vagotomy (VTPP and UVT) or Botox treatment induced down-regulation of CD44 (and CD44v6) in the gastric mucosa of INS-GAS mice, although the combination of vagotomy and Botox did not lead to a further decrease in CD44 expression (Fig. 4, B and C, and figs. S10 and S11). Vagotomy also reduced the expression of Wnt target genes, such as Cyclin D1, Axin2, Myc, Lgr5, and Cd44, in MNU-treated mice (Fig. 4D). The number of cells with nuclear translocation of β-catenin and the number of Lgr5+ cells in MNU-treated mice were reduced after vagotomy (Fig. 4, E and F). These results suggest that disruption of neuronal signaling inhibits Wnt signaling and thereby stem cell expansion, resulting in the suppression of tumor development in both INS-GAS and MNU mouse models.
Wnt signaling is also known to be involved in tumor regeneration (30). We have established a mouse model of tumor regeneration through topical application of acetic acid in INS-GAS mice (31). In this model, vagotomy delayed tumor regeneration in the denervated side of the stomach (fig. S12).
We next examined whether vagotomy down-regulated Lgr5 expression via the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Gastric epithelial cells from Lgr5-GFP mice were sorted on the basis of green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression. Afterward, gene expression of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors was tested in Lgr5-negative, Lgr5-low, and Lgr5-high cell populations (Fig. 5A). We found that there was coexpression of Lgr5 and Chrm3, the gene encoding muscarinic acetylcho-line receptor 3 (M3R), in the sorted cells from Lgr5-GFP mouse stomach, but other subtypes of muscarinic receptor were little expressed in those cells (Fig. 5, B and C), suggesting that Lgr5+ stem cell function may be modulated by M3R signaling. To investigate the involvement of M3 receptors in gastric tumorigenesis, we treated INS-GAS mice by continuous infusion of the specific M3 receptor antagonist, darifenacin (32), in combination with chemotherapy. Using an experimental design similar to that of the Botox and vagotomy experiment, we found that the combination of darifenacin and chemotherapy reduced cellular proliferation of the tumors (Fig. 5D). Furthermore, we analyzed the Wnt signaling pathway in M3KO versus wild-type mice and found that several key genes, including one encoding β-catenin, were down-regulated (fig. S13). We then exposed M3KO and wild-type mice to MNU treatment. At 7.5 months after MNU treatment (11 months of age), M3KO mice had less tumor induction (57.1% versus 100%) and smaller tumor size when compared to wild-type controls (Fig. 5, E and F). Thus, the vagus nerve regulates gastric tumorigenesis at least in part through M3 receptor–mediated Wnt signaling, which is operative in Lgr5+ stem cells.
Fig. 5. M3 receptor signaling in gastric stem cells regulates tumorigenesis in mouse models of gastric cancer.
(A) Representative fluorescence-activated cell sorting gating showing forward scatter (FSC) and Lgr5-GFP expression. (B and C) Relative gene expression of Lgr5 and muscarinic receptors (Chrm1 to Chrm5) in sorted Lgr5-negative, Lgr5-low, and Lgr5-high populations. Means ± SEM (n = 4). (D) Number of proliferating cells in the tumors of INS-GAS mice treated with saline (Control, n = 19), M3 receptor antagonist darifenacin (M3R, n = 15), 5-FU + oxaliplatin (Chemo, n = 12), or combination of 5-FU + oxaliplatin + darifenacin (M3R + Chemo, n = 8), respectively. Means ± SEM. P values were calculated by Dunnett's test. (E) Representative photographs showing gross appearance of stomachs opened along the greater curvature from wild-type (WT) or M3 receptor knockout mice (M3KO) treated with MNU. (F) Volume density of tumor in the stomachs of MNU-treated WT (n = 13) versus MNU-treated M3KO mice (n = 7). Means ± SEM (Student's t test).
Neurons activate Wnt signaling in gastric stem cells through M3 receptor
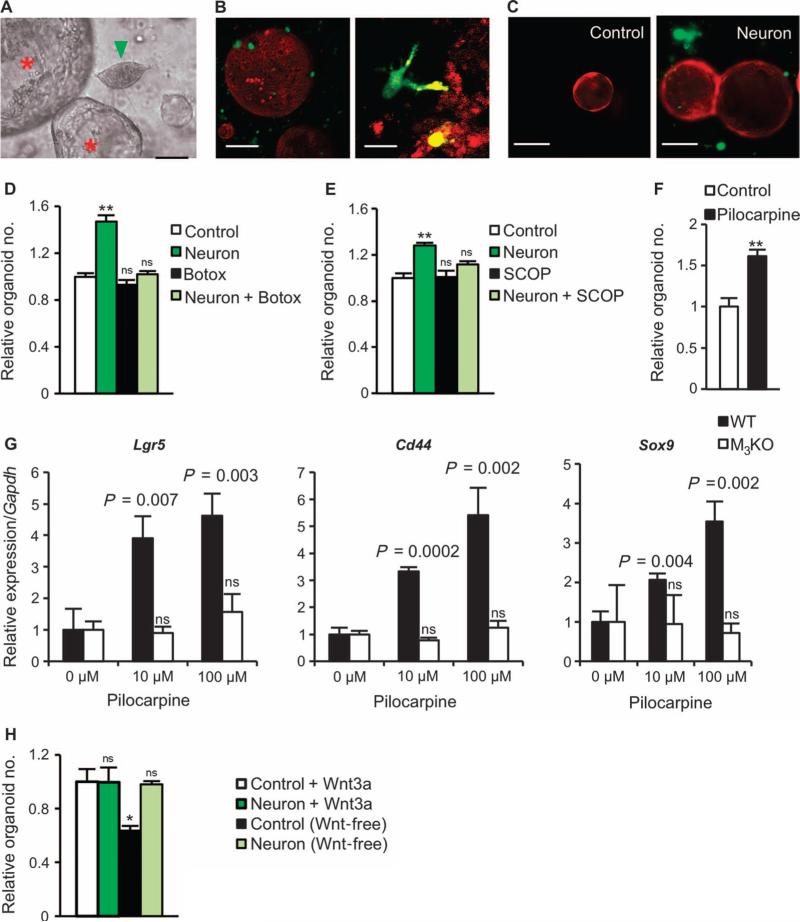
To demonstrate the potential regulatory role of nerves in the maintenance of gastric epithelium, we used an established in vitro culture system for gastric organoids (9). Primary neurons were isolated from murine spinal cord or the enteric nervous system of guinea pigs, and cocultured with gastric glands (9, 33, 34). In culture, neurons showed outgrowth of neurites and evidence of direct contact with the gastric organoids (Fig. 6, A to C). Furthermore, coculture with neurons markedly promoted gastric organoid growth (Fig. 6, D and E). The addition of either Botox or scopolamine (an unspecific muscarinic receptor antagonist) inhibited this stimulatory effect (Fig. 6, D and E), whereas pilocarpine (an unspecific muscarinic receptor agonist) stimulated organoid growth (Fig. 6F). Pilocarpine caused up-regulation of the gastric stem cell markers and Wnt target genes Lgr5, Cd44, and Sox9 (9) in a dose-dependent manner. However, in gastric organoids of M3KO mice, pilocarpine showed no effects on the expression of these genes (Fig. 6G), highlighting the importance of the M3 receptor for stem cell expansion. Furthermore, coculture with neurons could substitute for Wnt3a in gastric organoid cultures that are otherwise strictly dependent on addition of Wnt ligands (35) (Fig. 6H), confirming the ability of cholinergic signaling to induce ligand-independent Wnt signaling in this in vitro system.
Fig. 6. Neurons activate Wnt signaling in gastric stem cells through the M3 receptor.
(A to C) Representative microphotographs showing gastric organoids along with neurite outgrowth. (A) Guinea pig enteric neuron (green arrowhead) with gastric organoids (red asterisks). Scale bar, 5 μm. (B) Three-dimensional images (low and high magnifications) obtained by two-photon microscopy of gastric organoids (red) derived from an ACTB-tdTomato mouse and neurons (green) derived from a UBC-GFP mouse. Scale bars, 20 μm (left) and 5 μm (right). In (C), fluorescent images show gastric organoids (red) alone (left, Control) or cocultured with neurons (green) (right, Neuron) at day 4. Scale bars, 10 μm. (D) Relative number of organoids after 72 hours in control, neuron coculture, control plus Botox, or neuron coculture plus Botox. Means ± SEM. n = 4 per group. **P = 0.002 (Student's t test). ns, not significant compared to control. (E) Relative number of organoids after 72 hours in control or neuron coculture with or without scopolamine (SCOP) (1 μg/ml). Means ± SEM. n = 4 per group. **P = 0.003 (Student's t test). ns, not significant compared to control. (F) Relative number of organoids at day 10 with or without 100 μM pilocarpine. Means ± SEM. n = 4 per group. **P = 0.006 (Student's t test) between control and pilocarpine. (G) Relative mRNA expression for Lgr5, Cd44, and Sox9 in relation to Gapdh on day 7 with or without 10 or 100 μM pilocarpine in gastric organoids isolated from WT or M3KO mice. Means ± SEM. Student's t test between 0 μM and 10 or 100 μM pilocarpine. n = 4 per group. (H) Relative number of organoids at day 10 with or without neurons and/or Wnt3a. Means ± SEM. n = 4 per group. ns, not significant. *P = 0.030 compared to Control + Wnt3a (Student's t test).
Gastric cancer patients display dysregulation of Wnt signaling and innervation in the tumors
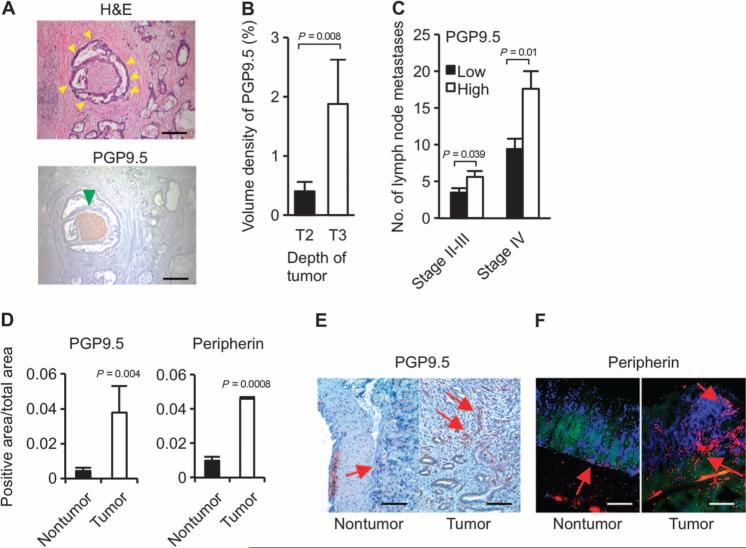
To further investigate the involvement of Wnt signaling, innervation, and gastric cancer progression in humans, we evaluated three separate cohort studies of gastric cancer patients (table S2). In tumors from 17 primary gastric cancer patients, Wnt signaling, neurotrophin signaling, and axonal guidance pathways (along with other pathways) were activated in cancerous tissue when compared to adjacent noncancerous tissue (Fig. 7 and fig. S14). In another group of 120 primary gastric cancers, neuronal density was correlated with more advanced tumor stages (Fig. 8, A to C). A similar increase in neuronal density was confirmed in tumors of mice treated with MNU (Fig. 8, D to F). In the third cohort of 37 patients, who developed gastric stump cancer after distal gastrectomy with or without vagotomy, 35% (13 of 37) of patients had undergone vagotomy. Of those 13 patients, only 1 had a tumor in the posterior wall and none had tumors in the anterior wall. In the 24 patients without vagotomy, tumors were observed in both anterior and posterior walls (fig. S15).
Fig. 7. Gastric cancer patients exhibit a dysregulation of Wnt signaling.
Gene expression of Wnt signaling pathway (microarray analysis) in human gastric cancer tissue. The graph shows log2 fold changes of expressed genes in comparison with the adjacent noncancerous tissue of the same stomach. Red, down-regulation; blue, up-regulation.
Fig. 8. PGP9.5 and peripherin may represent neural markers for gastric cancer progression.
(A) Representative microphotographs showing human gastric cancer [indicated by yellow arrowheads, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining] and PGP9.5-labeled nerve (green arrowhead). Scale bars, 50 μm. (B) Volume density of PGP9.5-labeled nerves in different levels of depth of tumor invasion [T2 (tumor invading muscularis propria) versus T3 (tumor penetrating subserosal connective tissue without invasion of visceral peritoneum or adjacent structures)] in the stage II and III gastric cancer patients. Means ± SEM (n = 120). P = 0.008 (Student's t test). (C) Number of lymph node metastases in patients with stage II and III or stage IV gastric cancer that has low or high expression of PGP9.5. Means ± SEM (n = 120). P values were calculated by Student's t test. (D) PGP9.5- and peripherin-immunoreactive nerve densities in gastric mucosa of control mice (nontumor) and MNU-treated mice (tumor). PGP9.5 is a ubiquitin-protein hydrolase that is expressed in the neuronal cell bodies and axons in the central and peripheral nervous system. Peripherin is a type III intermediate filament protein that is expressed in peripheral and some central nervous system neurons. Both can be used as neuronal markers in the gut. Means ± SEM (n = 6 per group). P values were calculated by Student's t test. (E and F) Representative immunohistochemical microphotographs showing PGP9.5 and peripherin (indicated by red arrows) in the nontumor and tumor areas of the mouse stomachs. Scale bars, 20 μm (E) and 40 μm (F).
DISCUSSION
The results of the present study, using three independent mouse models of gastric cancer, demonstrate that either surgical or pharmacological denervation suppresses gastric tumorigenesis. The effect takes place primarily on terminal and intramucosal vagal branches, as shown by the response to unilateral vagotomy and localized Botox injection. Denervation therapy was effective in both early preneoplasia and late neoplasia/dysplasia, and it enhanced the effect of chemotherapy and prolonged survival in mice with advanced tumors. Gene expression and immunohistochemical analysis of stem cell markers, along with the in vitro gastric organoid test, revealed that cholinergic nerves directly modulate epithelial stem cells through activation of Wnt signaling via the M3 receptor. Analysis of human patients with gastric cancer also showed correlations between neural pathways and Wnt signaling and increased innervation in more advanced tumors, with decreased tumor risk in vagotomized stomach.
In contrast to our current results, previous vagotomy studies in rat models of chemically induced gastric cancer did not reveal an inhibitory effect (12, 36, 37). This is likely due to the earlier approach of bilateral vagotomy without pyloroplasty, which delayed gastric emptying and therefore increased the exposure time of orally administered chemical carcinogens on the gastric mucosa. To ensure that dose and time of MNU exposure were equalized in all the groups and to prevent retention of gastric contents, we performed bilateral vagotomy with pyloroplasty or PP (as control) after completion of the MNU dosing protocol, allowing analysis of the specific effects of the vagus nerve on the gastric mucosa. Thus, we found that vagotomy inhibited gastric tumorigenesis in the MNU model. The data from two different genetically engineered mouse models of gastric cancer further established the inhibitory effect of denervation against gastric tumorigenesis. Given the limited availability of metastatic models of gastric cancer, the effect of denervation in metastatic lymph nodes or other organs remains unclear and needs to be further investigated in suitable models.
Previous studies suggested that nerves contribute to the normal stem cell niche (1, 2, 38), and a recent report has linked sympathetic nerves to prostate cancer progression (7). However, the stomach differs from other solid organs in that its autonomic innervation is largely parasym-pathetic in nature, and cholinergic nerves have been shown to regulate gastrointestinal proliferation (39). The present study demonstrated that Lgr5+ gastric stem cells express the M3 receptor, and that Wnt signaling in those cells is directly activated by cholinergic vagus stimulation, resulting in epithelial proliferation and stem cell expansion. Gastrointestinal stem cells are supported by a number of niche cells including Paneth cells, mesenchymal stem cells, myofibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, lymph and vascular endothelial cells, and bone marrow–derived stromal cells (40–42). Here, we identified nerves regulating gastric stem cell expansion during the tumorigenesis.
The vagus nerve has been shown to stimulate cell proliferation in the brain, liver, and stomach through the M3 receptor (43–45). Furthermore, activation of muscarinic receptors in cancer cells leads to enhanced Wnt signaling independent of Wnt ligands (46), and M3 receptor signaling has been implicated in the pathogenesis of intestinal neoplasia (6, 47, 48). Consistent with those findings, the present study demonstrates that genetic knockout or pharmacological inhibition of M3 receptor suppresses gastric tumor progression, pointing to the M3 receptor as a potential target for gastric cancer therapy. The M3 receptor antagonist darifenacin is already in clinical use for overactive urinary bladder (49) and has been shown to inhibit growth of small cell lung cancer xenografts (50). Given that chemotherapeutic agents and darifenacin appear to show cooperative effects, M3 receptor–targeting therapy combined with chemo-therapy in unresectable gastric cancer patients could be considered in future trials, although further studies are needed to evaluate the safety and long-term effects of those regimens.
Canonical Wnt signaling controls epithelial homeostasis in the intestine and the stomach, and is thought to play a role in a subset of gastric cancers (9, 51). Here, we have shown that Wnt signaling is up-regulated in the tumorigenic stomach and is down-regulated after vagotomy, suggesting that vagus nerve is a critical regulator of Wnt signaling in gastric tumorigenesis. Furthermore, gastric Wnt signaling was down-regulated in M3KO mice, which were resistant to MNU-induced tumorigenesis. In addition, inhibition of Notch signaling was also observed after vagotomy, which is in line with both Wnt and Notch signaling promoting the initiation of intestinal tumors (52, 53). Therefore, therapeutic modulation of Wnt signaling blockade using tankyrase inhibitors could also be considered, although the dose-limiting toxicity of available agents has restricted their clinical use to this point (54). Finally, we cannot exclude a role for additional pathways (for example, prostaglandin E2 pathway) that may be modulated by nerves in gastric tumorigenesis.
Our finding that nerves play an important role in cancer initiation and progression highlights a component of the tumor microenvironment contributing to the cancer stem cell niche. The data strongly support the notion that denervation and cholinergic antagonism, in combination with other therapies, could represent a viable approach for the treatment of gastric cancer and possibly other solid malignancies.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We used 581 mice divided into 14 experimental groups. In each experiment, mice were randomly divided into different subgroups (fig. S1 and table S1). INS-GAS mice with spontaneous gastric cancer were used as previously described (18, 19). Denervation was achieved by subdiaphragmatic bilateral truncal vagotomy, unilateral vagotomy, or Botox local injection. The tumor prevalence/incidence, tumor size, tumor regeneration, pathological changes, gene expression profiles, and immunohisto-chemical biomarkers were examined after denervation. In vitro gastric organoid culture was performed as described previously (9). We also performed three cohort studies of human primary gastric cancer and gastric stump cancer, as well as gene expression profiling and KEGG pathway analysis. All studies and procedures involving animals and hu man subjects were approved by the Norwegian National Animal Research Authority, the Columbia University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, Gifu University, and the National Cancer Center Hospital East, Japan. Statistical comparisons were performed between experimental groups, between the anterior and posterior sides of the stomachs, and between groups of patients. See the Supplementary Materials for the complete Materials and Methods.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank A. Øverby, O. D. Røe, and J. E. Gronbech at Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) for valuable assistance and discussions; A. A. Diacou at Columbia University for extraction of enteric nervous system; and K. Takeuchi at Kyoto Pharmaceutical University for providing M3KO mice. The microarray and part of the bioinformatics work were provided by Norwegian Microarray Consortium–NTNU, a national technology platform supported by Functional Genomics Programme (FUGE) of Research Council of Norway (RCN) and NTNU. Funding: Supported by the RCN (D.C.), Joint Programme of the Medical Faculty of NTNU and St. Olavs University Hospital, Liaison Committee between the Central Norway Regional Health Authority and NTNU (C.-M.Z.), U.S. NIH (grants 1U54CA126513, RO1CA093405, and RO1CA120979) (T.C.W.), Clyde Wu Family Foundation (T.C.W.), Mitsukoshi Health and Welfare Foundation (Y.H.), Japan Society for the Promotion of Science Postdoctoral Fellowships for Research Abroad (Y.H.), and Uehara Memorial Foundation (Y.H.). Y.K., H.J., and G.T.A. are supported by Ph.D. fellowships from the FUGE of RCN, the European Union Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013, no. 266408), and the St. Olavs Hospital, respectively. C.B.W. and M.Q. are supported by the Max Eder Program of the Deutsche Krebshilfe. C.B.W. is supported by the German Research Foundation.
Footnotes
Author contributions: C.-M.Z. and Y.H. contributed equally to the design of the experiments, performance of the animal experiments and histology, the in vitro experiments, flow cytometry, and qRT-PCRs and contributed collection and analysis of the data. Y.K. performed the animal experiments (except for nos. 3 and 9 to 14 in table S1) and qRT-PCR arrays and contributed to collection and analysis of the data. A.F. and R.A.F. performed the bioinformatics analysis. S.M. and J.G.F. performed the pathological evaluation of mice. A.K.S. and V.B. performed the microarray experiments of mice and humans. G.T.A., H.J., and B.W.R. performed part of animal experiments. H.T. and A.H. performed the pathological evaluation of humans. C.B.W., M.Q., and H.T. performed some of the immunohistochemical analyses of mice and humans. Z.L. and M.D.G. performed the vagus nerve mapping. K.K. performed the analysis of human gastric stump cancer. T.C.W. and D.C. were joint senior authors; contributed to the study supervision, coordination, and performance of experiments; and wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to the discussion of results and the preparation of the final manuscript.
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Data and materials availability: Mouse microarray data are available through Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, accession no. GSE30295, and human data are in ArrayExpress, accession no. E-MTAB-1338.
Citation: C.-M. Zhao, Y. Hayakawa, Y. Kodama, S. Muthupalani, C. B. Westphalen, G. T. Andersen, A. Flatberg, H. Johannessen, R. A. Friedman, B. W. Renz, A. K. Sandvik, V. Beisvag, H. Tomita, A. Hara, M. Quante, Z. Li, M. D. Gershon, K. Kaneko, J. G. Fox, T. C. Wang, D. Chen, Denervation suppresses gastric tumorigenesis. Sci. Transl. Med. 6, 250ra115 (2014).
REFERENCES AND NOTES
- 1.Katayama Y, Battista M, Kao WM, Hidalgo A, Peired AJ, Thomas SA, Frenette PS. Signals from the sympathetic nervous system regulate hematopoietic stem cell egress from bone marrow. Cell. 2006;124:407–421. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.10.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lundgren O, Jodal M, Jansson M, Ryberg AT, Svensson L. Intestinal epithelial stem/ progenitor cells are controlled by mucosal afferent nerves. PLOS One. 2011;6:e16295. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mattingly RR, Sorisky A, Brann MR, Macara IG. Muscarinic receptors transform NIH 3T3 cells through a Ras-dependent signalling pathway inhibited by the Ras-GTPase-activating protein SH3 domain. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994;14:7943–7952. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.12.7943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ayala GE, Dai H, Powell M, Li R, Ding Y, Wheeler TM, Shine D, Kadmon D, Thompson T, Miles BJ, Ittmann MM, Rowley D. Cancer-related axonogenesis and neurogenesis in prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008;14:7593–7603. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Shah N, Khurana S, Cheng K, Raufman JP. Muscarinic receptors and ligands in cancer. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2009;296:C221–C232. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00514.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Raufman JP, Shant J, Xie G, Cheng K, Gao XM, Shiu B, Shah N, Drachenberg CB, Heath J, Wess J, Khurana S. Muscarinic receptor subtype-3 gene ablation and scopolamine butyl-bromide treatment attenuate small intestinal neoplasia in Apcmin/+ mice. Carcinogenesis. 2011;32:1396–1402. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgr118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Magnon C, Hall SJ, Lin J, Xue X, Gerber L, Freedland SJ, Frenette PS. Autonomic nerve development contributes to prostate cancer progression. Science. 2013;341:1236361. doi: 10.1126/science.1236361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pardal R, Clarke MF, Morrison SJ. Applying the principles of stem-cell biology to cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2003;3:895–902. doi: 10.1038/nrc1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Barker N, Huch M, Kujala P, van de Wetering M, Snippert HJ, van Es JH, Sato T, Stange DE, Begthel H, van den Born M, Danenberg E, van den Brink S, Korving J, Abo A, Peters PJ, Wright N, Poulsom R, Clevers H. Lgr5+ve stem cells drive self-renewal in the stomach and build long-lived gastric units in vitro. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;6:25–36. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2009.11.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int. J. Cancer. 2010;127:2893–2917. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jemal A, Center MM, DeSantis C, Ward EM. Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2010;19:1893–1907. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-10-0437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Håkanson R, Vallgren S, Ekelund M, Rehfeld JF, Sundler F. The vagus exerts trophic control of the stomach in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1984;86:28–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Axelson J, Ekelund M, Håkanson R, Sundler F. Gastrin and the vagus interact in the trophic control of the rat oxyntic mucosa. Regul. Pept. 1988;22:237–243. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(88)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lundegårdh G, Ekbom A, McLaughlin JK, Nyrén O. Gastric cancer risk after vagotomy. Gut. 1994;35:946–949. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.7.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bahmanyar S, Ye W, Dickman PW, Nyrén O. Long-term risk of gastric cancer by subsite in operated and unoperated patients hospitalized for peptic ulcer. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007;102:1185–1191. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Correa P, Cuello C, Duque E. Carcinoma and intestinal metaplasia of the stomach in Colombian migrants. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1970;44:297–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Cassaro M, Rugge M, Gutierrez O, Leandro G, Graham DY, Genta RM. Topographic patterns of intestinal metaplasia and gastric cancer. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000;95:1431–1438. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.02074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wang TC, Dangler CA, Chen D, Goldenring JR, Koh T, Raychowdhury R, Coffey RJ, Ito S, Varro A, Dockray GJ, Fox JG. Synergistic interaction between hypergastrinemia and Helicobacter infection in a mouse model of gastric cancer. Gastroenterology. 2000;118:36–47. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(00)70412-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fox JG, Wang TC. Inflammation, atrophy, and gastric cancer. J. Clin. Invest. 2007;117:60–69. doi: 10.1172/JCI30111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ericsson P, Håkanson R, Rehfeld JF, Norlén P. Gastrin release: Antrum microdialysis reveals a complex neural control. Regul. Pept. 2010;161:22–32. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2010.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rogers AB, Taylor NS, Whary MT, Stefanich ED, Wang TC, Fox JG. Helicobacter pylori but not high salt induces gastric intraepithelial neoplasia in B6129 mice. Cancer Res. 2005;65:10709–10715. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Tomita H, Takaishi S, Menheniott TR, Yang X, Shibata W, Jin G, Betz KS, Kawakami K, Minamoto T, Tomasetto C, Rio MC, Lerkowit N, Varro A, Giraud AS, Wang TC. Inhibition of gastric carcinogenesis by the hormone gastrin is mediated by suppression of TFF1 epigenetic silencing. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:879–891. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.11.037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Tu S, Bhagat G, Cui G, Takaishi S, Kurt-Jones EA, Rickman B, Betz KS, Penz-Oesterreicher M, Bjorkdahl O, Fox JG, Wang TC. Overexpression of interleukin-1β induces gastric inflammation and cancer and mobilizes myeloid-derived suppressor cells in mice. Cancer Cell. 2008;14:408–419. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.10.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dressler D, Adib Saberi F. Botulinum toxin: Mechanisms of action. Eur. Neurol. 2005;53:3–9. doi: 10.1159/000083259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Polakis P. Drugging Wnt signalling in cancer. EMBO J. 2012;31:2737–2746. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Takahashi-Yanaga F, Kahn M. Targeting Wnt signaling: Can we safely eradicate cancer stem cells? Clin. Cancer Res. 2010;16:3153–3162. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zöller M. CD44: Can a cancer-initiating cell profit from an abundantly expressed molecule? Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2011;11:254–267. doi: 10.1038/nrc3023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Takaishi S, Okumura T, Tu S, Wang SS, Shibata W, Vigneshwaran R, Gordon SA, Shimada Y, Wang TC. Identification of gastric cancer stem cells using the cell surface marker CD44. Stem Cells. 2009;27:1006–1020. doi: 10.1002/stem.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Schuijers J, Clevers H. Adult mammalian stem cells: The role of Wnt, Lgr5 and R-spondins. EMBO J. 2012;31:2685–2696. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Chen J, Li Y, Yu TS, McKay RM, Burns DK, Kernie SG, Parada LF. A restricted cell population propagates glioblastoma growth after chemotherapy. Nature. 2012;488:522–526. doi: 10.1038/nature11287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Okabe S, Kodama Y, Cao H, Johannessen H, Zhao CM, Wang TC, Takahashi R, Chen D. Topical application of acetic acid in cytoreduction of gastric cancer. A technical report using mouse model. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012;27(Suppl. 3):40–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2012.07070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Song P, Sekhon HS, Fu XW, Maier M, Jia Y, Duan J, Proskosil BJ, Gravett C, Lindstrom J, Mark GP, Saha S, Spindel ER. Activated cholinergic signaling provides a target in squamous cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2008;68:4693–4700. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Westphalen CB, Asfaha S, Hayakawa Y, Takemoto Y, Lukin DJ, Nuber AH, Brandtner A, Setlik W, Remotti H, Muley A, Chen X, May R, Houchen CW, Fox JG, Gershon MD, Quante M, Wang TC. Long-lived intestinal tuft cells serve as colon cancer–initiating cells. J. Clin. Invest. 2014;124:1283–1295. doi: 10.1172/JCI73434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gershon AA, Chen J, Gershon MD. A model of lytic, latent, and reactivating varicella-zoster virus infections in isolated enteric neurons. J. Infect. Dis. 2008;197(Suppl. 2):S61–S65. doi: 10.1086/522149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Barker N, Clevers H. Leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptors as markers of adult stem cells. Gastroenterology. 2010;138:1681–1696. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tatsuta M, Yamamura H, Iishi H, Ichii M, Noguchi S, Baba M, Taniguchi H. Promotion by vagotomy of gastric carcinogenesis induced by N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine in Wistar rats. Cancer Res. 1985;45:194–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tatsuta M, Iishi H, Yamamura H, Baba M, Taniguchi H. Effects of bilateral and unilateral vagotomy on gastric carcinogenesis induced by N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine in Wistar rats. Int. J. Cancer. 1988;42:414–418. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Frenette PS, Pinho S, Lucas D, Scheiermann C. Mesenchymal stem cell: Keystone of the hematopoietic stem cell niche and a stepping-stone for regenerative medicine. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013;31:285–316. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032712-095919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gross ER, Gershon MD, Margolis KG, Gertsberg ZV, Cowles RA. Neuronal serotonin regulates growth of the intestinal mucosa in mice. Gastroenterology. 2012;143:408–417. e2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.05.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sato T, van Es JH, Snippert HJ, Stange DE, Vries RG, van den Born M, Barker N, Shroyer NF, van de Wetering M, Clevers H. Paneth cells constitute the niche for Lgr5 stem cells in intestinal crypts. Nature. 2011;469:415–418. doi: 10.1038/nature09637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Powell DW, Pinchuk IV, Saada JI, Chen X, Mifflin RC. Mesenchymal cells of the intestinal lamina propria. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2011;73:213–237. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.70.113006.100646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Farin HF, Van Es JH, Clevers H. Redundant sources of Wnt regulate intestinal stem cells and promote formation of Paneth cells. Gastroenterology. 2012;143:1518–1529. e7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.08.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Revesz D, Tjernstrom M, Ben-Menachem E, Thorlin T. Effects of vagus nerve stimulation on rat hippocampal progenitor proliferation. Exp. Neurol. 2008;214:259–265. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Cassiman D, Libbrecht L, Sinelli N, Desmet V, Denef C, Roskams T. The vagal nerve stimulates activation of the hepatic progenitor cell compartment via muscarinic acetylcholine receptor type 3. Am. J. Pathol. 2002;161:521–530. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64208-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Aihara T, Fujishita T, Kanatani K, Furutani K, Nakamura E, Taketo MM, Matsui M, Chen D, Okabe S. Impaired gastric secretion and lack of trophic responses to hypergastrinemia in M3 muscarinic receptor knockout mice. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:1774–1784. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2003.09.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Salmanian S, Najafi SM, Rafipour M, Arjomand MR, Shahheydari H, Ansari S, Kashkooli L, Rasouli SJ, Jazi MS, Minaei T. Regulation of GSK-3b and b-catenin by Gaq in HEK293T cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010;395:577–582. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.04.087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Spindel ER. Muscarinic receptor agonists and antagonists: Effects on cancer. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2012:451–468. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-23274-9_19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Raufman JP, Samimi R, Shah N, Khurana S, Shant J, Drachenberg C, Xie G, Wess J, Cheng K. Genetic ablation of M3 muscarinic receptors attenuates murine colon epithelial cell proliferation and neoplasia. Cancer Res. 2008;68:3573–3578. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Veenboer PW, Bosch JL. Long-term adherence to antimuscarinic therapy in everyday practice: A systematic review. J. Urol. 2014;191:1003–1008. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.10.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Song P, Sekhon HS, Lu A, Arredondo J, Sauer D, Gravett C, Mark GP, Grando SA, Spindel ER. M3 muscarinic receptor antagonists inhibit small cell lung carcinoma growth and mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation induced by acetylcholine secretion. Cancer Res. 2007;67:3936–3944. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Oshima H, Oshima M. Mouse models of gastric tumors: Wnt activation and PGE2 induction. Pathol. Int. 2010;60:599–607. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2010.02567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.van Es JH, Jay P, Gregorieff A, van Gijn ME, Jonkheer S, Hatzis P, Thiele A, van den Born M, Begthel H, Brabletz T, Taketo MM, Clevers H. Wnt signalling induces maturation of Paneth cells in intestinal crypts. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005;7:381–386. doi: 10.1038/ncb1240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Fre S, Pallavi SK, Huyghe M, Laé M, Janssen KP, Robine S, Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Louvard D. Notch and Wnt signals cooperatively control cell proliferation and tumorigenesis in the intestine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2009;106:6309–6314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900427106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Lehtiö L, Chi NW, Krauss S. Tankyrases as drug targets. FEBS J. 2013;280:3576–3593. doi: 10.1111/febs.12320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.