Abstract
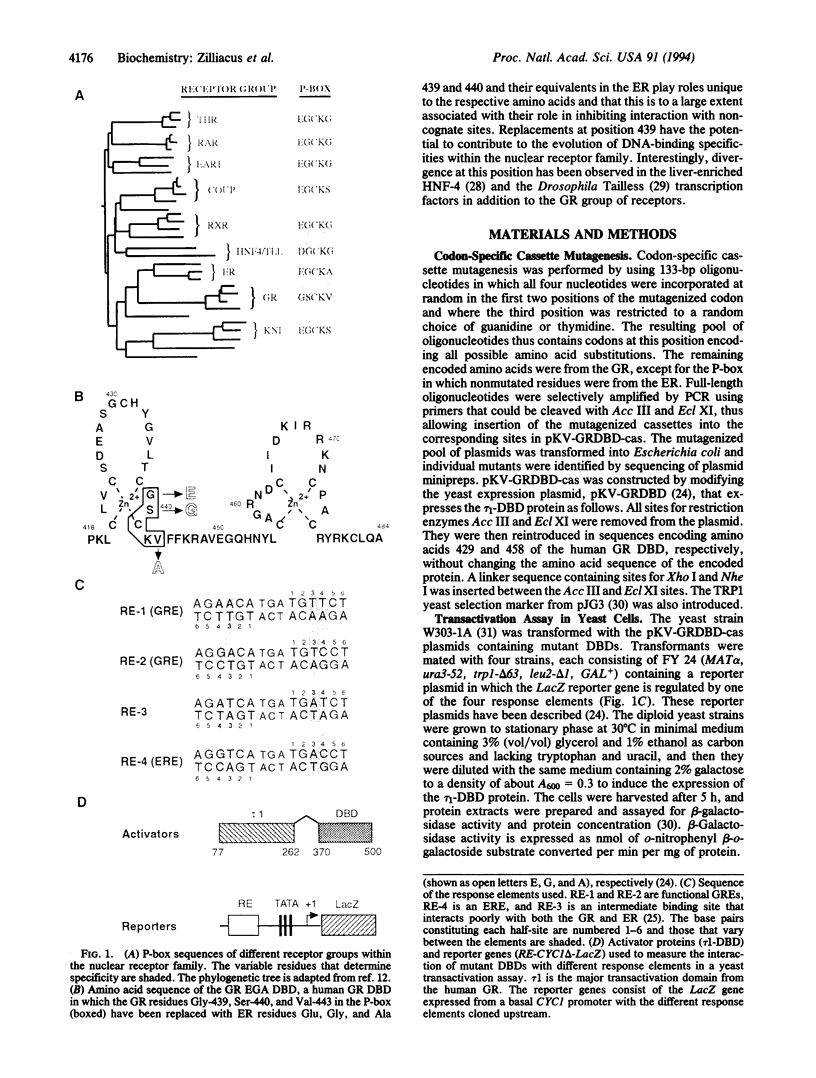
Nuclear receptors are ligand-activated transcription factors that interact with response elements within regulated genes. Most receptors, typified by the estrogen receptor, have three amino acids within the DNA-binding domain that specify recognition of the sequence TGACCT within the response element. However, in the glucocorticoid group of receptors, these residues have evolved to recognize the sequence TGTTCT. Saturation mutagenesis was used to investigate the role played by two of these residues (Gly-439 and Ser-440 of the human glucocorticoid receptor) in receptor specificity. We conclude that these residues, and their equivalents in the estrogen receptor, play roles unique to the respective amino acids. In the glucocorticoid receptor the side chain hydroxyl group is the important component of Ser-440 that contributes to specificity by inhibiting interaction with estrogen response elements. Several substitution mutants at position 439 interact well with estrogen response elements; therefore, the unique specificity feature of Glu-439, which mimics the estrogen receptor, is its inhibition of interaction with noncognate sites. In contrast to position 440, where most substitutions prevent interaction with DNA, replacements of residue 439 have the potential to contribute to the evolution of DNA-binding specificities within the nuclear receptor family. The liver-enriched HNF-4 and Drosophila Tailless transcription factors are known examples of receptors that have diverged at this position.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alroy I., Freedman L. P. DNA binding analysis of glucocorticoid receptor specificity mutants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 11;20(5):1045–1052. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.5.1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugge T. H., Pohl J., Lonnoy O., Stunnenberg H. G. RXR alpha, a promiscuous partner of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1409–1418. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsen M., Hinck L., Ringold G. M. Two amino acids within the knuckle of the first zinc finger specify DNA response element activation by the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1131–1138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. B., Wright A. P., Cheung W. Y., Lancashire W. E., Hartley B. S. The structure and regulation of phosphoglucose isomerase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Dec;215(1):100–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00331310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo W., Chen M., Yen T. S., Ou J. H. Hepatocyte-specific expression of the hepatitis B virus core promoter depends on both positive and negative regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):443–448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Härd T., Kellenbach E., Boelens R., Maler B. A., Dahlman K., Freedman L. P., Carlstedt-Duke J., Yamamoto K. R., Gustafsson J. A., Kaptein R. Solution structure of the glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):157–160. doi: 10.1126/science.2115209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor interacts with nuclear receptors in retinoic acid, thyroid hormone and vitamin D3 signalling. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):446–449. doi: 10.1038/355446a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klock G., Strähle U., Schütz G. Oestrogen and glucocorticoid responsive elements are closely related but distinct. Nature. 1987 Oct 22;329(6141):734–736. doi: 10.1038/329734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knegtel R. M., Katahira M., Schilthuis J. G., Bonvin A. M., Boelens R., Eib D., van der Saag P. T., Kaptein R. The solution structure of the human retinoic acid receptor-beta DNA-binding domain. J Biomol NMR. 1993 Jan;3(1):1–17. doi: 10.1007/BF00242472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Chambon P. The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladias J. A., Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., Kardassis D., Cardot P., Cheng J., Zannis V., Cladaras C. Transcriptional regulation of human apolipoprotein genes ApoB, ApoCIII, and ApoAII by members of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily HNF-4, ARP-1, EAR-2, and EAR-3. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15849–15860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudet V., Hänni C., Coll J., Catzeflis F., Stéhelin D. Evolution of the nuclear receptor gene superfamily. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1003–1013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05139.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Kliewer S. A., Provencal J., Wright P. E., Evans R. M. Structure of the retinoid X receptor alpha DNA binding domain: a helix required for homodimeric DNA binding. Science. 1993 May 21;260(5111):1117–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.8388124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luisi B. F., Xu W. X., Otwinowski Z., Freedman L. P., Yamamoto K. R., Sigler P. B. Crystallographic analysis of the interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor with DNA. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):497–505. doi: 10.1038/352497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mader S., Kumar V., de Verneuil H., Chambon P. Three amino acids of the oestrogen receptor are essential to its ability to distinguish an oestrogen from a glucocorticoid-responsive element. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):271–274. doi: 10.1038/338271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mader S., Leroy P., Chen J. Y., Chambon P. Multiple parameters control the selectivity of nuclear receptors for their response elements. Selectivity and promiscuity in response element recognition by retinoic acid receptors and retinoid X receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):591–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. S., Hallenbeck P. L., Nagata T., Segars J. H., Appella E., Nikodem V. M., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP (RXR beta) heterodimerization provides a mechanism for combinatorial diversity in the regulation of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone responsive genes. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1419–1435. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05187.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietus-Snyder M., Sladek F. M., Ginsburg G. S., Kuo C. F., Ladias J. A., Darnell J. E., Jr, Karathanasis S. K. Antagonism between apolipoprotein AI regulatory protein 1, Ear3/COUP-TF, and hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 modulates apolipoprotein CIII gene expression in liver and intestinal cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1708–1718. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- När A. M., Boutin J. M., Lipkin S. M., Yu V. C., Holloway J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. The orientation and spacing of core DNA-binding motifs dictate selective transcriptional responses to three nuclear receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1267–1279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90021-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Transcription factors: structural families and principles of DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1053–1095. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignoni F., Baldarelli R. M., Steingrímsson E., Diaz R. J., Patapoutian A., Merriam J. R., Lengyel J. A. The Drosophila gene tailless is expressed at the embryonic termini and is a member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90249-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reijnen M. J., Sladek F. M., Bertina R. M., Reitsma P. H. Disruption of a binding site for hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 results in hemophilia B Leyden. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6300–6303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe J. W., Neuhaus D., Rhodes D. Solution structure of the DNA-binding domain of the oestrogen receptor. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):458–461. doi: 10.1038/348458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladek F. M., Zhong W. M., Lai E., Darnell J. E., Jr Liver-enriched transcription factor HNF-4 is a novel member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2353–2365. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Carlstedt-Duke J., Weigel N. L., Dahlman K., Gustafsson J. A., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Molecular interactions of steroid hormone receptor with its enhancer element: evidence for receptor dimer formation. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Evans R. M. Determinants of target gene specificity for steroid/thyroid hormone receptors. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1139–1146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. P., Carlstedt-Duke J., Gustafsson J. A. Ligand-specific transactivation of gene expression by a derivative of the human glucocorticoid receptor expressed in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14763–14769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Delsert C., Andersen B., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., När A. M., Kim S. Y., Boutin J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1251–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Hoffmann B., Tran P. B., Graupner G., Pfahl M. Retinoid X receptor is an auxiliary protein for thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):441–446. doi: 10.1038/355441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilliacus J., Dahlman-Wright K., Wright A., Gustafsson J. A., Carlstedt-Duke J. DNA binding specificity of mutant glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domains. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3101–3106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilliacus J., Wright A. P., Norinder U., Gustafsson J. A., Carlstedt-Duke J. Determinants for DNA-binding site recognition by the glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):24941–24947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]