Abstract
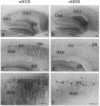
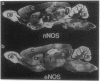
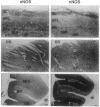
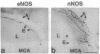
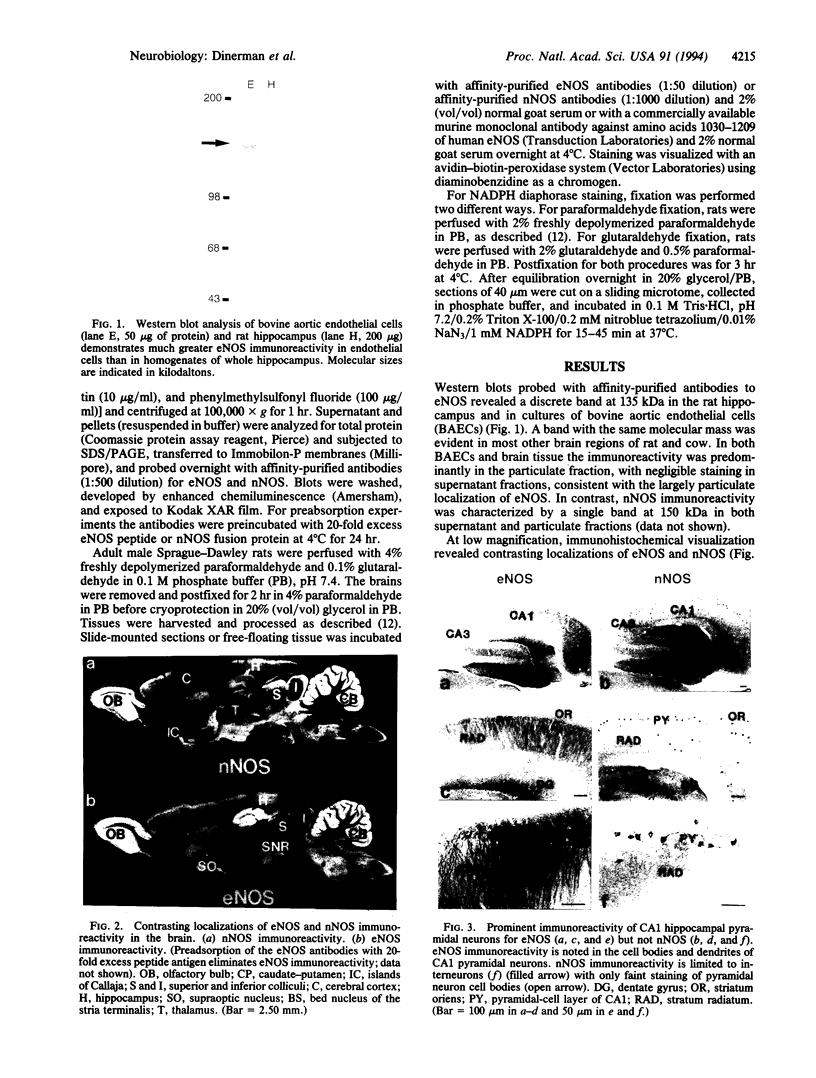
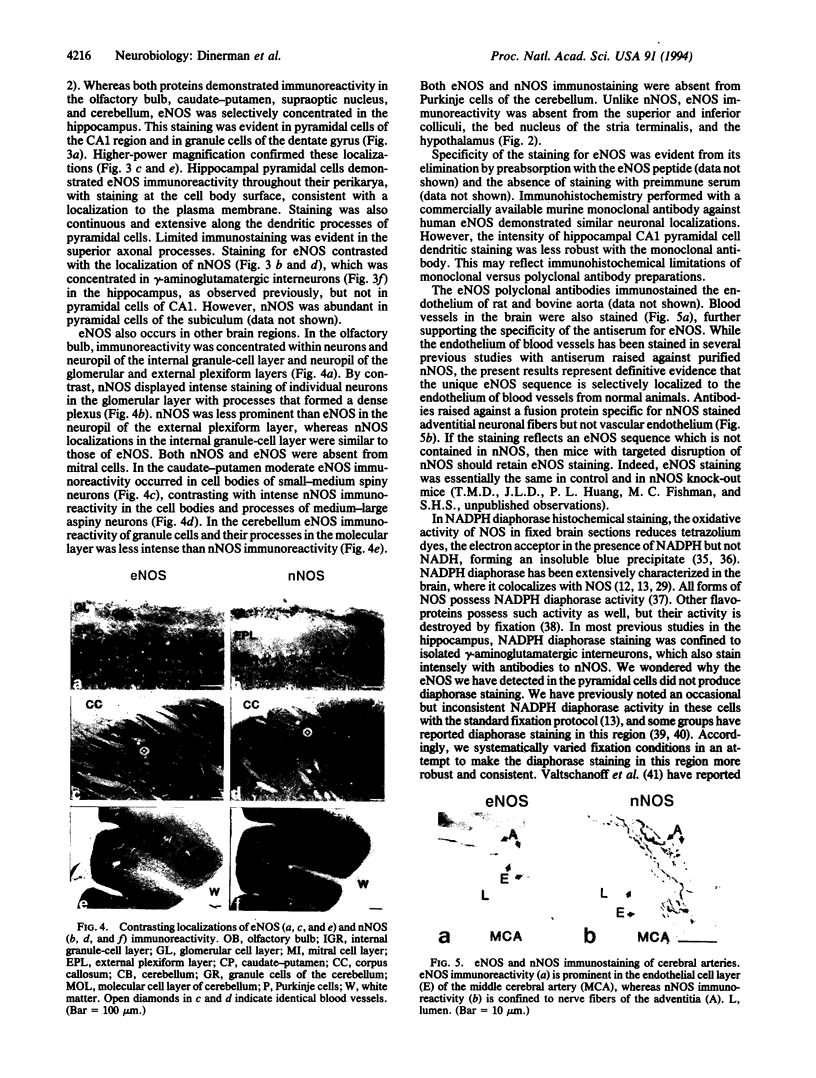
Using antibodies that react selectively with peptide sequences unique to endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), we demonstrate localizations to neuronal populations in the brain. In some brain regions, such as the cerebellum and olfactory bulb, eNOS and neuronal NOS (nNOS) occur in the same cell populations, though in differing proportions. In the hippocampus, localizations of the two enzymes are strikingly different, with eNOS more concentrated in hippocampal pyramidal cells than in any other brain area, whereas nNOS is restricted to occasional interneurons. In many brain regions NADPH diaphorase staining reflects NOS catalytic activity. Hippocampal pyramidal cells do not stain for diaphorase with conventional paraformaldehyde fixation but stain robustly with glutaraldehyde fixatives, presumably reflecting eNOS catalytic activity. eNOS in hippocampal pyramidal cells may generate the NO that has been postulated as a retrograde messenger of long-term potentiation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bliss T. V., Collingridge G. L. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993 Jan 7;361(6407):31–39. doi: 10.1038/361031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Glatt C. E., Hwang P. M., Fotuhi M., Dawson T. M., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide synthase protein and mRNA are discretely localized in neuronal populations of the mammalian CNS together with NADPH diaphorase. Neuron. 1991 Oct;7(4):615–624. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90374-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Glatt C. E., Lowenstein C., Reed R. R., Snyder S. H. Cloned and expressed nitric oxide synthase structurally resembles cytochrome P-450 reductase. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):714–718. doi: 10.1038/351714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Snyder S. H. Localization of nitric oxide synthase indicating a neural role for nitric oxide. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):768–770. doi: 10.1038/347768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busconi L., Michel T. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase. N-terminal myristoylation determines subcellular localization. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8410–8413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhme G. A., Bon C., Stutzmann J. M., Doble A., Blanchard J. C. Possible involvement of nitric oxide in long-term potentiation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 9;199(3):379–381. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90505-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles I. G., Palmer R. M., Hickery M. S., Bayliss M. T., Chubb A. P., Hall V. S., Moss D. W., Moncada S. Cloning, characterization, and expression of a cDNA encoding an inducible nitric oxide synthase from the human chondrocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11419–11423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson T. M., Bredt D. S., Fotuhi M., Hwang P. M., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide synthase and neuronal NADPH diaphorase are identical in brain and peripheral tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7797–7801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson T. M., Dawson V. L., Snyder S. H. A novel neuronal messenger molecule in brain: the free radical, nitric oxide. Ann Neurol. 1992 Sep;32(3):297–311. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fotuhi M., Sharp A. H., Glatt C. E., Hwang P. M., von Krosigk M., Snyder S. H., Dawson T. M. Differential localization of phosphoinositide-linked metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR1) and the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1993 May;13(5):2001–2012. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-05-02001.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Jothianandan D. Endothelium-dependent and -independent vasodilation involving cyclic GMP: relaxation induced by nitric oxide, carbon monoxide and light. Blood Vessels. 1991;28(1-3):52–61. doi: 10.1159/000158843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J. Glutamate, nitric oxide and cell-cell signalling in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Feb;14(2):60–67. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90022-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller D. A., Lowenstein C. J., Shapiro R. A., Nussler A. K., Di Silvio M., Wang S. C., Nakayama D. K., Simmons R. L., Snyder S. H., Billiar T. R. Molecular cloning and expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase from human hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3491–3495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribkoff V. K., Lum-Ragan J. T. Evidence for nitric oxide synthase inhibitor-sensitive and insensitive hippocampal synaptic potentiation. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Aug;68(2):639–642. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.2.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakes D. J., Dixon J. E. New vectors for high level expression of recombinant proteins in bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1992 May 1;202(2):293–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90108-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley J. E., Wilcox G. L., Chapman P. F. The role of nitric oxide in hippocampal long-term potentiation. Neuron. 1992 Feb;8(2):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90288-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiki K., Hattori R., Kawai C., Yui Y. Purification of insoluble nitric oxide synthase from rat cerebellum. J Biochem. 1992 May;111(5):556–558. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope B. T., Michael G. J., Knigge K. M., Vincent S. R. Neuronal NADPH diaphorase is a nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2811–2814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang P. L., Dawson T. M., Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H., Fishman M. C. Targeted disruption of the neuronal nitric oxide synthase gene. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1273–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90615-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J. Endothelium-derived nitric oxide: actions and properties. FASEB J. 1989 Jan;3(1):31–36. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.1.2642868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobzik L., Bredt D. S., Lowenstein C. J., Drazen J., Gaston B., Sugarbaker D., Stamler J. S. Nitric oxide synthase in human and rat lung: immunocytochemical and histochemical localization. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993 Oct;9(4):371–377. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/9.4.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamas S., Marsden P. A., Li G. K., Tempst P., Michel T. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase: molecular cloning and characterization of a distinct constitutive enzyme isoform. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6348–6352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein C. J., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide, a novel biologic messenger. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):705–707. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90301-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lum-Ragan J. T., Gribkoff V. K. The sensitivity of hippocampal long-term potentiation to nitric oxide synthase inhibitors is dependent upon the pattern of conditioning stimulation. Neuroscience. 1993 Dec;57(4):973–983. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90042-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A. Nitric oxide synthase structure and mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12231–12234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A. Nitric oxide: biosynthesis and biological significance. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Dec;14(12):488–492. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto T., Nakane M., Pollock J. S., Kuk J. E., Förstermann U. A correlation between soluble brain nitric oxide synthase and NADPH-diaphorase activity is only seen after exposure of the tissue to fixative. Neurosci Lett. 1993 May 28;155(1):61–64. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90673-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel T., Li G. K., Busconi L. Phosphorylation and subcellular translocation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6252–6256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Higgs A. The L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway. N Engl J Med. 1993 Dec 30;329(27):2002–2012. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312303292706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mammalian cells. FASEB J. 1992 Sep;6(12):3051–3064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dell T. J., Hawkins R. D., Kandel E. R., Arancio O. Tests of the roles of two diffusible substances in long-term potentiation: evidence for nitric oxide as a possible early retrograde messenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11285–11289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi Y., Katayama M., Hirata K., Suematsu M., Kawashima S., Yokoyama M. Activation of nitric oxide synthase from cultured aortic endothelial cells by phospholipids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Sep 30;195(3):1314–1320. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock J. S., Förstermann U., Mitchell J. A., Warner T. D., Schmidt H. H., Nakane M., Murad F. Purification and characterization of particulate endothelium-derived relaxing factor synthase from cultured and native bovine aortic endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10480–10484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakar N. R., Kumar G. K., Chang C. H., Agani F. H., Haxhiu M. A. Nitric oxide in the sensory function of the carotid body. Brain Res. 1993 Oct 15;625(1):16–22. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90132-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane F., Takahashi K., Takayama H., Koyama J. Stabilizing effect of glutaraldehyde on the respiratory burst NADPH oxidase of guinea pig polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biochem. 1987 Aug;102(2):247–253. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H. H., Gagne G. D., Nakane M., Pollock J. S., Miller M. F., Murad F. Mapping of neural nitric oxide synthase in the rat suggests frequent co-localization with NADPH diaphorase but not with soluble guanylyl cyclase, and novel paraneural functions for nitrinergic signal transduction. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Oct;40(10):1439–1456. doi: 10.1177/40.10.1382087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H. H., Gagne G. D., Nakane M., Pollock J. S., Miller M. F., Murad F. Mapping of neural nitric oxide synthase in the rat suggests frequent co-localization with NADPH diaphorase but not with soluble guanylyl cyclase, and novel paraneural functions for nitrinergic signal transduction. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Oct;40(10):1439–1456. doi: 10.1177/40.10.1382087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuman E. M., Madison D. V. A requirement for the intercellular messenger nitric oxide in long-term potentiation. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1503–1506. doi: 10.1126/science.1720572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide: first in a new class of neurotransmitters. Science. 1992 Jul 24;257(5069):494–496. doi: 10.1126/science.1353273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springall D. R., Riveros-Moreno V., Buttery L., Suburo A., Bishop A. E., Merrett M., Moncada S., Polak J. M. Immunological detection of nitric oxide synthase(s) in human tissues using heterologous antibodies suggesting different isoforms. Histochemistry. 1992 Nov;98(4):259–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00271040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. F., Wang Y. Reversal of long-term potentiation by inhibitors of haem oxygenase. Nature. 1993 Jul 8;364(6433):147–149. doi: 10.1038/364147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS E., PEARSE A. G. THE SOLITARY ACTIVE CELLS. HISTOCHEMICAL DEMONSTRATION OF DAMAGE-RESISTANT NERVE CELLS WITH A TPN-DIAPHORASE REACTION. Acta Neuropathol. 1964 Jan 2;3:238–249. doi: 10.1007/BF00684399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS E., PEARSE A. G. The fine localization of dehydrogenases in the nervous system. Z Zellforch Microsk Anat Histochem. 1961;2:266–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00736504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey W. R., Nakane M., Pollock J. S., Förstermann U. Nitric oxide synthases in neuronal cells, macrophages and endothelium are NADPH diaphorases, but represent only a fraction of total cellular NADPH diaphorase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Sep 15;195(2):1035–1040. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtschanoff J. G., Weinberg R. J., Rustioni A. NADPH diaphorase in the spinal cord of rats. J Comp Neurol. 1992 Jul 8;321(2):209–222. doi: 10.1002/cne.903210204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verge V. M., Xu Z., Xu X. J., Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Hökfelt T. Marked increase in nitric oxide synthase mRNA in rat dorsal root ganglia after peripheral axotomy: in situ hybridization and functional studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11617–11621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma A., Hirsch D. J., Glatt C. E., Ronnett G. V., Snyder S. H. Carbon monoxide: a putative neural messenger. Science. 1993 Jan 15;259(5093):381–384. doi: 10.1126/science.7678352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent S. R., Kimura H. Histochemical mapping of nitric oxide synthase in the rat brain. Neuroscience. 1992;46(4):755–784. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90184-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. N., Fredens K. Activated astrocytes of the mouse hippocampus contain high levels of NADPH-diaphorase. Neuroreport. 1992 Nov;3(11):953–956. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199211000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. Z., Bredt D. S., Fidone S. J., Stensaas L. J. Neurons synthesizing nitric oxide innervate the mammalian carotid body. J Comp Neurol. 1993 Oct 15;336(3):419–432. doi: 10.1002/cne.903360308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. H., Li Y. G., Nayak A., Errington M. L., Murphy K. P., Bliss T. V. The suppression of long-term potentiation in rat hippocampus by inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase is temperature and age dependent. Neuron. 1993 Nov;11(5):877–884. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90117-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W. Expression of nitric-oxide synthase (NOS) in injured CNS neurons as shown by NADPH diaphorase histochemistry. Exp Neurol. 1993 Apr;120(2):153–159. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1993.1050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga T., Sassa S., Kappas A. Purification and properties of bovine spleen heme oxygenase. Amino acid composition and sites of action of inhibitors of heme oxidation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7778–7785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z. G., Chopp M., Zaloga C., Pollock J. S., Förstermann U. Cerebral endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke. 1993 Dec;24(12):2016–2022. doi: 10.1161/01.str.24.12.2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo M., Small S. A., Kandel E. R., Hawkins R. D. Nitric oxide and carbon monoxide produce activity-dependent long-term synaptic enhancement in hippocampus. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1946–1950. doi: 10.1126/science.8100368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorumski C. F., Izumi Y. Nitric oxide and hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Sep 1;46(5):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90484-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]