Abstract
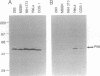
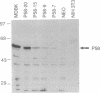
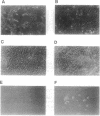
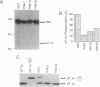
The interferon-induced RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) is considered to play an important role in the cellular defense against viral infection and, in addition, has been suggested to be a tumor suppressor gene because of its growth-suppressive properties. Activation of PKR by double-stranded RNAs leads to the phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF-2 alpha) and a resultant block to protein synthesis initiation. To avoid the consequences of kinase activation, many viruses have developed strategies to down-regulate PKR. Recently, we reported on the purification and characterization of a cellular inhibitor of PKR (referred to as p58), which is activated during influenza virus infection. Subsequent cloning and sequencing has revealed that p58 is a member of the tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) family of proteins. To further examine the physiological role of this PKR inhibitor, we stably transfected NIH 3T3 cells with a eukaryotic expression plasmid containing p58 cDNA under control of the cytomegalovirus early promoter. By taking advantage of a recently characterized p58 species-specific monoclonal antibody, we isolated cell lines that overexpressed p58. These cells exhibited a transformed phenotype, growing at faster rates and higher saturation densities and exhibiting anchorage-independent growth. Most importantly, inoculation of nude mice with p58-overexpressing cells gave rise to the production of tumors. Finally, murine PKR activity and endogenous levels of eIF-2 alpha phosphorylation were reduced in the p58-expressing cell lines compared with control cells. These data, taken together, suggest that p58 functions as an oncogene and that one mechanism by which the protein induces malignant transformation is through the down-regulation of PKR and subsequent deregulation of protein synthesis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barber G. N., Tomita J., Garfinkel M. S., Meurs E., Hovanessian A., Katze M. G. Detection of protein kinase homologues and viral RNA-binding domains utilizing polyclonal antiserum prepared against a baculovirus-expressed ds RNA-activated 68,000-Da protein kinase. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):670–679. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90242-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber G. N., Wambach M., Wong M. L., Dever T. E., Hinnebusch A. G., Katze M. G. Translational regulation by the interferon-induced double-stranded-RNA-activated 68-kDa protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4621–4625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazin R., Lemieux R. Increased proportion of B cell hybridomas secreting monoclonal antibodies of desired specificity in cultures containing macrophage-derived hybridoma growth factor (IL-6). J Immunol Methods. 1989 Jan 17;116(2):245–249. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90210-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll K., Elroy-Stein O., Moss B., Jagus R. Recombinant vaccinia virus K3L gene product prevents activation of double-stranded RNA-dependent, initiation factor 2 alpha-specific protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12837–12842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong K. L., Feng L., Schappert K., Meurs E., Donahue T. F., Friesen J. D., Hovanessian A. G., Williams B. R. Human p68 kinase exhibits growth suppression in yeast and homology to the translational regulator GCN2. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1553–1562. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05200.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dever T. E., Chen J. J., Barber G. N., Cigan A. M., Feng L., Donahue T. F., London I. M., Katze M. G., Hinnebusch A. G. Mammalian eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha kinases functionally substitute for GCN2 protein kinase in the GCN4 translational control mechanism of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4616–4620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederickson R. M., Sonenberg N. Signal transduction and regulation of translation initiation. Semin Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;3(2):107–115. doi: 10.1016/s1043-4682(10)80020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebl M., Yanagida M. The TPR snap helix: a novel protein repeat motif from mitosis to transcription. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 May;16(5):173–177. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90070-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré B., Leffers H., Madsen P., Rasmussen H. H., Vandekerckhove J., Celis J. E. Molecular cloning and expression of a transformation-sensitive human protein containing the TPR motif and sharing identity to the stress-inducible yeast protein STI1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8485–8491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovanessian A. G., Galabru J., Rivière Y., Montagnier L. Efficiency of poly(A).poly(U) as an adjuvant. Immunol Today. 1988 Jun;9(6):161–162. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91288-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovanessian A. G. Interferon-induced and double-stranded RNA-activated enzymes: a specific protein kinase and 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetases. J Interferon Res. 1991 Aug;11(4):199–205. doi: 10.1089/jir.1991.11.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judware R., Petryshyn R. Mechanism of action of a cellular inhibitor of the dsRNA-dependent protein kinase from 3T3-F442A cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21685–21690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., Tomita J., Black T., Krug R. M., Safer B., Hovanessian A. Influenza virus regulates protein synthesis during infection by repressing autophosphorylation and activity of the cellular 68,000-Mr protein kinase. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3710–3717. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3710-3717.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., Wambach M., Wong M. L., Garfinkel M., Meurs E., Chong K., Williams B. R., Hovanessian A. G., Barber G. N. Functional expression and RNA binding analysis of the interferon-induced, double-stranded RNA-activated, 68,000-Mr protein kinase in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5497–5505. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny A., Safer B. Purification of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2-eukaryotic initiation factor 2B complex and characterization of its guanine nucleotide exchange activity during protein synthesis initiation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3402–3408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koromilas A. E., Roy S., Barber G. N., Katze M. G., Sonenberg N. Malignant transformation by a mutant of the IFN-inducible dsRNA-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1685–1689. doi: 10.1126/science.1382315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of vertebrate mRNA sequences: intimations of translational control. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):887–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. G., Tomita J., Hovanessian A. G., Katze M. G. Characterization and regulation of the 58,000-dalton cellular inhibitor of the interferon-induced, dsRNA-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14238–14243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. G., Tomita J., Hovanessian A. G., Katze M. G. Purification and partial characterization of a cellular inhibitor of the interferon-induced protein kinase of Mr 68,000 from influenza virus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6208–6212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Tumor-suppressor genes: news about the interferon connection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5893–5895. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurs E. F., Galabru J., Barber G. N., Katze M. G., Hovanessian A. G. Tumor suppressor function of the interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):232–236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mundschau L. J., Faller D. V. Oncogenic ras induces an inhibitor of double-stranded RNA-dependent eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha-kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23092–23098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petryshyn R., Chen J. J., London I. M. Detection of activated double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase in 3T3-F442A cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1427–1431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E. Protein synthesis, cell growth and oncogenesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;3(6):1019–1024. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90123-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito S., Kawakita M. Inhibitor of interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase and its relevance to alteration of cellular protein kinase activity level in response to external stimuli. Microbiol Immunol. 1991;35(12):1105–1114. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1991.tb01632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. Antiviral actions of interferon. Interferon-regulated cellular proteins and their surprisingly selective antiviral activities. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90112-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Boguski M. S., Goebl M., Hieter P. A repeating amino acid motif in CDC23 defines a family of proteins and a new relationship among genes required for mitosis and RNA synthesis. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):307–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90745-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Michaud W. A., Wootton J. C., Boguski M. S., Connelly C., Hieter P. TPR proteins as essential components of the yeast cell cycle. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:663–673. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. A., Way J. C. Eukaryotic DnaJ homologs and the specificity of Hsp70 activity. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90287-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatsuka M., Mitsui H., Wada M., Nagata A., Nojima H., Okayama H. Elongation factor-1 alpha gene determines susceptibility to transformation. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):333–336. doi: 10.1038/359333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomis D. C., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action: autoregulation of RNA-dependent P1/eIF-2 alpha protein kinase (PKR) expression in transfected mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10837–10841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari R. K., Kusari J., Kumar R., Sen G. C. Gene induction by interferons and double-stranded RNA: selective inhibition by 2-aminopurine. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4289–4294. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., Keller A., Whittemore L. A., Maniatis T. 2-Aminopurine selectively inhibits the induction of beta-interferon, c-fos, and c-myc gene expression. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):210–213. doi: 10.1126/science.3281258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zullo J. N., Faller D. V. P21 v-ras inhibits induction of c-myc and c-fos expression by platelet-derived growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5080–5085. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]