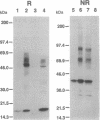
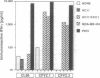
Abstract
Experimental approaches which exploit the targeted cytolytic activity of lymphocytes are being developed for cancer therapy. We generated cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) with specificity for ERBB2 receptor-expressing tumor cells. A binding function was conferred directly on the zeta chain of the T-cell receptor (TCR) complex to circumvent major histocompatibility complex-restricted antigen recognition through the alpha and beta chains of the TCR. A chimeric gene was constructed which encoded a single-chain Fv antibody (scFv, consisting of the joined heavy- and light-chain variable domains of a monoclonal antibody against the extracellular domain of the ERBB2 receptor), a hinge region as a spacer, and the zeta chain of the TCR. This gene was introduced into CTLs by retroviral gene transfer. The signaling potential of the scFv/hinge/zeta receptors was demonstrated by secretion of interferon gamma upon coincubation with ERBB2-expressing cells. Target cells expressing the ERBB2 gene were lysed in vitro with high specificity by the scFv/hinge/zeta-expressing T cells. The growth of ERBB2-transformed cells in athymic nude mice was retarded by adoptively transferred scFv/hinge/zeta-expressing CTLs. Transduced CTLs labeled with a fluorescent dye were specifically detected in tumor sections. Our results suggest that tumor cell lysis by CTLs grafted in vitro with a major histocompatibility complex-independent recognition could become a gene-therapy approach to cancer treatment.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham R. T., Karnitz L. M., Secrist J. P., Leibson P. J. Signal transduction through the T-cell antigen receptor. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):434–438. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aebersold P., Hyatt C., Johnson S., Hines K., Korcak L., Sanders M., Lotze M., Topalian S., Yang J., Rosenberg S. A. Lysis of autologous melanoma cells by tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes: association with clinical response. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1991 Jul 3;83(13):932–937. doi: 10.1093/jnci/83.13.932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth R. J., Jr, Bock S. N., Mulé J. J., Rosenberg S. A. Unique murine tumor-associated antigens identified by tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1531–1537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basse P., Herberman R. B., Nannmark U., Johansson B. R., Hokland M., Wasserman K., Goldfarb R. H. Accumulation of adoptively transferred adherent, lymphokine-activated killer cells in murine metastases. J Exp Med. 1991 Aug 1;174(2):479–488. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.2.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Molecular themes in oncogenesis. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):235–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90636-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boon T. Toward a genetic analysis of tumor rejection antigens. Adv Cancer Res. 1992;58:177–210. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60295-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. E., Shu S. Immunotherapy with sensitized lymphocytes. Cancer Invest. 1992;10(5):357–369. doi: 10.3109/07357909209024795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lohmann-Matthes M. L. A quick and simple method for the quantitation of lactate dehydrogenase release in measurements of cellular cytotoxicity and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) activity. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Nov 25;115(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90310-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann K., Ehrfeld A., Falk I., Goebel H., Kupsch J., Reimann A., Zgaga-Griesz A., Saizawa K. M., Yachelini P., Tomonari K. Affinity enhancement and transmembrane signaling are associated with distinct epitopes on the CD8 alpha beta heterodimer. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;147(7):2075–2081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshhar Z., Waks T., Gross G., Schindler D. G. Specific activation and targeting of cytotoxic lymphocytes through chimeric single chains consisting of antibody-binding domains and the gamma or zeta subunits of the immunoglobulin and T-cell receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):720–724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox B. A., Rosenberg S. A. Heterogeneous lymphokine-activated killer cell precursor populations. Development of a monoclonal antibody that separates two populations of precursors with distinct culture requirements and separate target-recognition repertoires. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1989;29(3):155–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00199990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank S. J., Niklinska B. B., Orloff D. G., Merćep M., Ashwell J. D., Klausner R. D. Structural mutations of the T cell receptor zeta chain and its role in T cell activation. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):174–177. doi: 10.1126/science.2371564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg P. D. Adoptive T cell therapy of tumors: mechanisms operative in the recognition and elimination of tumor cells. Adv Immunol. 1991;49:281–355. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60778-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross G., Eshhar Z. Endowing T cells with antibody specificity using chimeric T cell receptors. FASEB J. 1992 Dec;6(15):3370–3378. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.15.1464371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwerth I. M., Wels W., Marte B. M., Hynes N. E. Monoclonal antibodies against the extracellular domain of the erbB-2 receptor function as partial ligand agonists. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):15160–15167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwu P., Shafer G. E., Treisman J., Schindler D. G., Gross G., Cowherd R., Rosenberg S. A., Eshhar Z. Lysis of ovarian cancer cells by human lymphocytes redirected with a chimeric gene composed of an antibody variable region and the Fc receptor gamma chain. J Exp Med. 1993 Jul 1;178(1):361–366. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.1.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwu P., Yannelli J., Kriegler M., Anderson W. F., Perez C., Chiang Y., Schwarz S., Cowherd R., Delgado C., Mulé J. Functional and molecular characterization of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes transduced with tumor necrosis factor-alpha cDNA for the gene therapy of cancer in humans. J Immunol. 1993 May 1;150(9):4104–4115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N. E. Amplification and overexpression of the erbB-2 gene in human tumors: its involvement in tumor development, significance as a prognostic factor, and potential as a target for cancer therapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 1993 Feb;4(1):19–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N. E., Taverna D., Harwerth I. M., Ciardiello F., Salomon D. S., Yamamoto T., Groner B. Epidermal growth factor receptor, but not c-erbB-2, activation prevents lactogenic hormone induction of the beta-casein gene in mouse mammary epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4027–4034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving B. A., Weiss A. The cytoplasmic domain of the T cell receptor zeta chain is sufficient to couple to receptor-associated signal transduction pathways. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):891–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90314-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasuyama H., Melchers F. Establishment of mouse cell lines which constitutively secrete large quantities of interleukin 2, 3, 4 or 5, using modified cDNA expression vectors. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jan;18(1):97–104. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kast W. M., Offringa R., Peters P. J., Voordouw A. C., Meloen R. H., van der Eb A. J., Melief C. J. Eradication of adenovirus E1-induced tumors by E1A-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):603–614. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Samelson L. E. T cell antigen receptor activation pathways: the tyrosine kinase connection. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):875–878. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90310-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneur F., Klausner R. D. T-cell and basophil activation through the cytoplasmic tail of T-cell-receptor zeta family proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8905–8909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melief C. J. Tumor eradication by adoptive transfer of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Adv Cancer Res. 1992;58:143–175. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60294-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Rosman G. J. Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. Biotechniques. 1989 Oct;7(9):980-2, 984-6, 989-90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern J. P., Land H. Advanced mammalian gene transfer: high titre retroviral vectors with multiple drug selection markers and a complementary helper-free packaging cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3587–3596. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo C., Seed B. Cellular immunity to HIV activated by CD4 fused to T cell or Fc receptor polypeptides. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):1037–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90327-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Aebersold P., Cornetta K., Kasid A., Morgan R. A., Moen R., Karson E. M., Lotze M. T., Yang J. C., Topalian S. L. Gene transfer into humans--immunotherapy of patients with advanced melanoma, using tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes modified by retroviral gene transduction. N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 30;323(9):570–578. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008303230904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A. Immunotherapy and gene therapy of cancer. Cancer Res. 1991 Sep 15;51(18 Suppl):5074s–5079s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlichtholz B., Legros Y., Gillet D., Gaillard C., Marty M., Lane D., Calvo F., Soussi T. The immune response to p53 in breast cancer patients is directed against immunodominant epitopes unrelated to the mutational hot spot. Cancer Res. 1992 Nov 15;52(22):6380–6384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toes R. E., den Haan J. M., Feltkamp M. C., Blom R. J., Melief C. J., Claassen E., Kast W. M. In vivo detection of fluorescent tumor-specific cytotoxic T cell clones. J Immunol Methods. 1993 Jul 6;163(1):23–32. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(93)90235-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINN H. J. Immune mechanisms in homotransplantation. II. Quantitative assay of the immunologic activity of lymphoid cells stimulated by tumor homografts. J Immunol. 1961 Feb;86:228–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. T cell antigen receptor signal transduction: a tale of tails and cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):209–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90221-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman A. M., Baniyash M., Hou D., Samelson L. E., Burgess W. H., Klausner R. D. Molecular cloning of the zeta chain of the T cell antigen receptor. Science. 1988 Feb 26;239(4843):1018–1021. doi: 10.1126/science.3278377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wels W., Harwerth I. M., Mueller M., Groner B., Hynes N. E. Selective inhibition of tumor cell growth by a recombinant single-chain antibody-toxin specific for the erbB-2 receptor. Cancer Res. 1992 Nov 15;52(22):6310–6317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wels W., Harwerth I. M., Zwickl M., Hardman N., Groner B., Hynes N. E. Construction, bacterial expression and characterization of a bifunctional single-chain antibody-phosphatase fusion protein targeted to the human erbB-2 receptor. Biotechnology (N Y) 1992 Oct;10(10):1128–1132. doi: 10.1038/nbt1092-1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamoyska R., Vollmer A. C., Sizer K. C., Liaw C. W., Parnes J. R. Two Lyt-2 polypeptides arise from a single gene by alternative splicing patterns of mRNA. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]