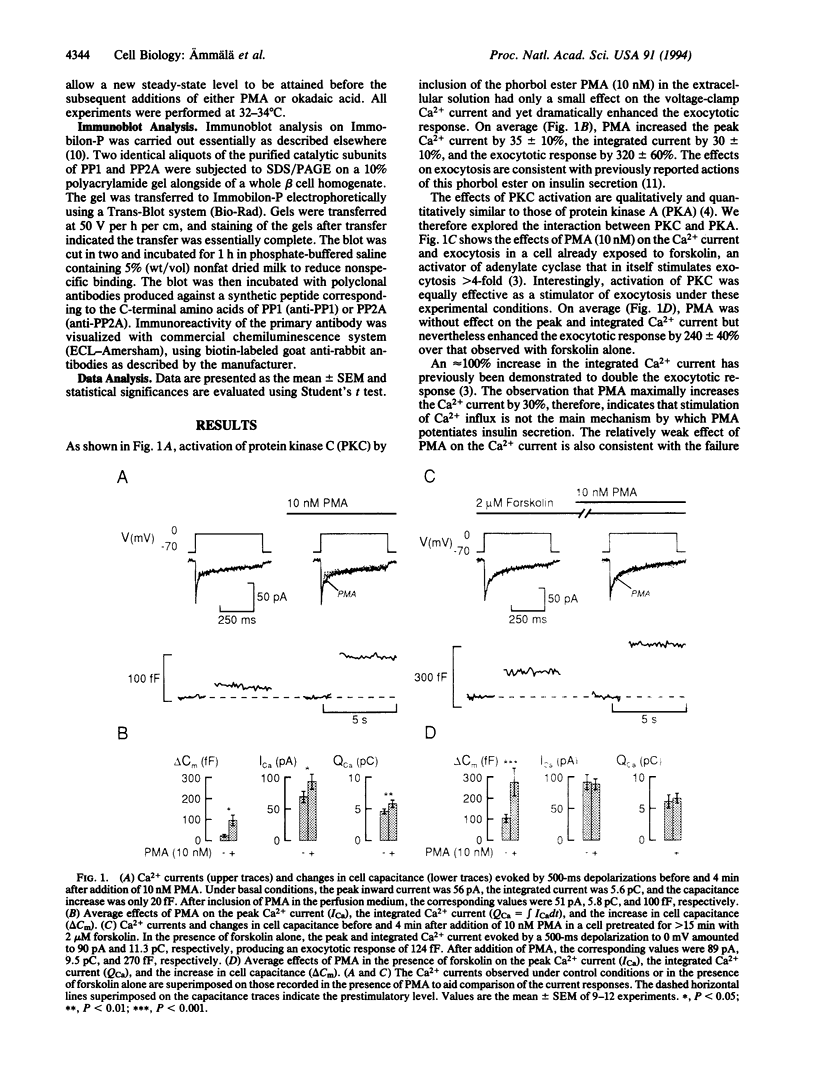
Abstract
The mechanisms that regulate insulin secretion were investigated using capacitance measurements of exocytosis in single beta cells maintained in tissue culture. Exocytosis was stimulated by voltage-clamp depolarizations to activate the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels that mediate Ca2+ influx into the beta cell. Under basal conditions, the exocytotic responses were small despite large Ca2+ currents. The exocytotic responses were dramatically increased (10- to 20-fold) by conditions that promote protein phosphorylation, such as activation of protein kinases A and C or inhibition of protein phosphatases. The stimulation of secretion was not due to an enhancement of Ca2+ influx and both peak and integrated Ca2+ currents were largely unaffected. Our data indicate that exocytosis in the insulin-secreting pancreatic beta cell is determined by a balance between protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. They further suggest that although Ca2+ is required for the initiation of exocytosis, modulation of exocytosis by protein kinases and phosphatases, at a step distal to the elevation of Ca2+, is of much greater quantitative importance. Thus an elevation of Ca2+ may represent a permissive rather than a decisive factor in the regulation of the insulin secretory process.
Full text
PDF
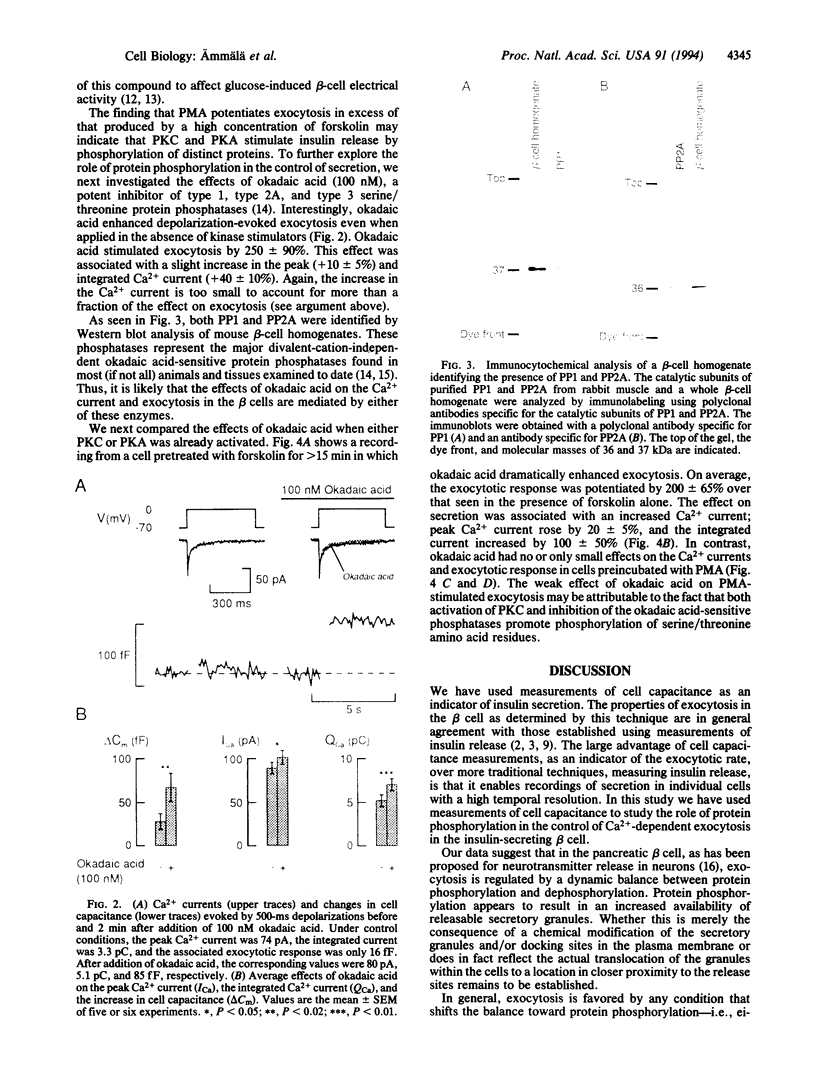
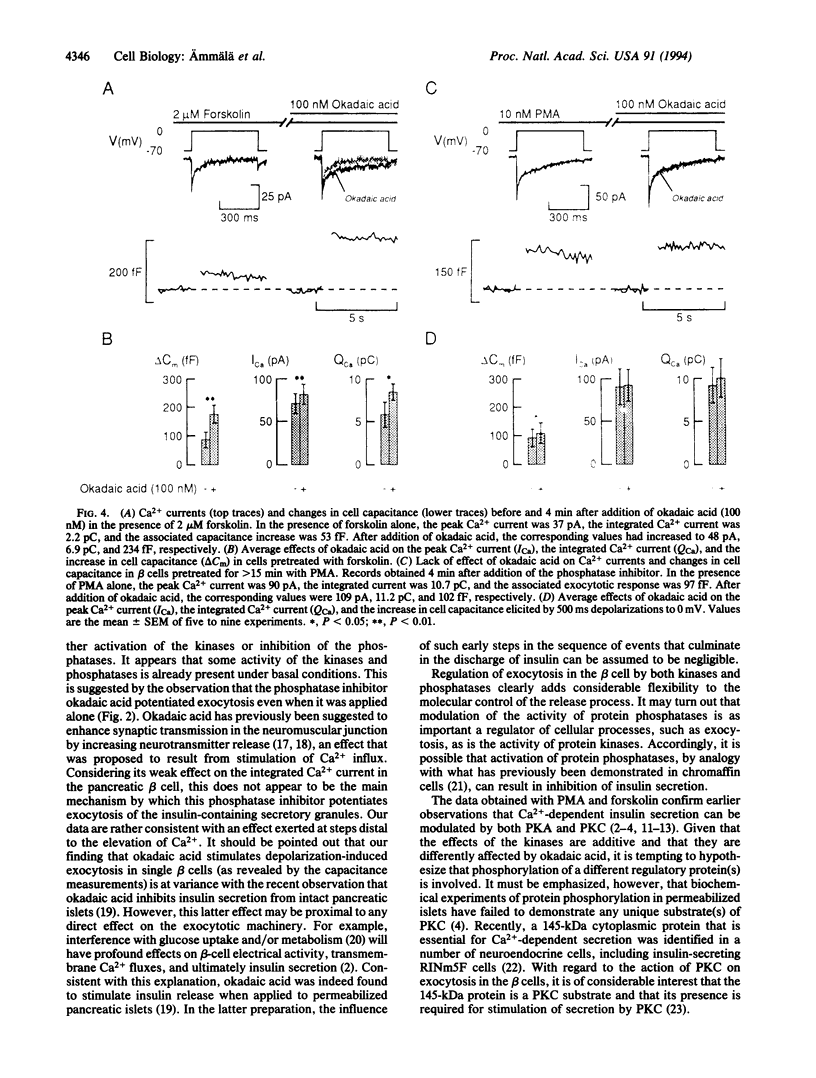

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdul-Ghani M., Kravitz E. A., Meiri H., Rahamimoff R. Protein phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid enhances transmitter release at neuromuscular junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1803–1807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammälä C., Ashcroft F. M., Rorsman P. Calcium-independent potentiation of insulin release by cyclic AMP in single beta-cells. Nature. 1993 May 27;363(6427):356–358. doi: 10.1038/363356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammälä C., Eliasson L., Bokvist K., Larsson O., Ashcroft F. M., Rorsman P. Exocytosis elicited by action potentials and voltage-clamp calcium currents in individual mouse pancreatic B-cells. J Physiol. 1993 Dec;472:665–688. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arkhammar P., Nilsson T., Welsh M., Welsh N., Berggren P. O. Effects of protein kinase C activation on the regulation of the stimulus-secretion coupling in pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem J. 1989 Nov 15;264(1):207–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2640207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozem M., Nenquin M., Henquin J. C. The ionic, electrical, and secretory effects of protein kinase C activation in mouse pancreatic B-cells: studies with a phorbol ester. Endocrinology. 1987 Sep;121(3):1025–1033. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-3-1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Holmes C. F., Tsukitani Y. Okadaic acid: a new probe for the study of cellular regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90192-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:453–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galindo E., Zwiller J., Bader M. F., Aunis D. Chromostatin inhibits catecholamine secretion in adrenal chromaffin cells by activating a protein phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7398–7402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P., Valtorta F., Czernik A. J., Benfenati F. Synaptic vesicle phosphoproteins and regulation of synaptic function. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):780–785. doi: 10.1126/science.8430330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honkanen R. E., Zwiller J., Daily S. L., Khatra B. S., Dukelow M., Boynton A. L. Identification, purification, and characterization of a novel serine/threonine protein phosphatase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6614–6619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Marty A. Muscarinic activation of ionic currents measured by a new whole-cell recording method. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Aug;92(2):145–159. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. M., Salmon D. M., Howell S. L. Protein phosphorylation in electrically permeabilized islets of Langerhans. Effects of Ca2+, cyclic AMP, a phorbol ester and noradrenaline. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 1;254(2):397–403. doi: 10.1042/bj2540397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Marty A. Discrete changes of cell membrane capacitance observed under conditions of enhanced secretion in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6712–6716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizaki T., Walent J. H., Kowalchyk J. A., Martin T. F. A key role for a 145-kDa cytosolic protein in the stimulation of Ca(2+)-dependent secretion by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23972–23981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace C. S., Goldsmith K. T. Action of a phorbol ester on B-cells: potentiation of stimulant-induced electrical activity. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):C527–C534. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.5.C527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D., in't Veld P. I., Maes E., Van De Winkel M. Glucose-induced insulin release depends on functional cooperation between islet cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7322–7325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Matschinsky F. M. Ca2+, cAMP, and phospholipid-derived messengers in coupling mechanisms of insulin secretion. Physiol Rev. 1987 Oct;67(4):1185–1248. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.4.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Zawalich K. C., Ganesan S., Calle R., Zawalich W. S. Physiology and pathophysiology of insulin secretion. Diabetes Care. 1990 Jun;13(6):655–666. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.6.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliff H., Jones P. M. Effects of okadaic acid on insulin secretion from rat islets of Langerhans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jan 17;1175(2):188–191. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(93)90022-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Trube G. Calcium and delayed potassium currents in mouse pancreatic beta-cells under voltage-clamp conditions. J Physiol. 1986 May;374:531–550. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain J. E., Robitaille R., Dass G. R., Charlton M. P. Phosphatases modulate transmission and serotonin facilitation at synapses: studies with the inhibitor okadaic acid. J Neurobiol. 1991 Nov;22(8):855–864. doi: 10.1002/neu.480220806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanti J. F., Grémeaux T., Van Obberghen E., Le Marchand-Brustel Y. Effects of okadaic acid, an inhibitor of protein phosphatases-1 and -2A, on glucose transport and metabolism in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2099–2103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walent J. H., Porter B. W., Martin T. F. A novel 145 kd brain cytosolic protein reconstitutes Ca(2+)-regulated secretion in permeable neuroendocrine cells. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):765–775. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90310-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]