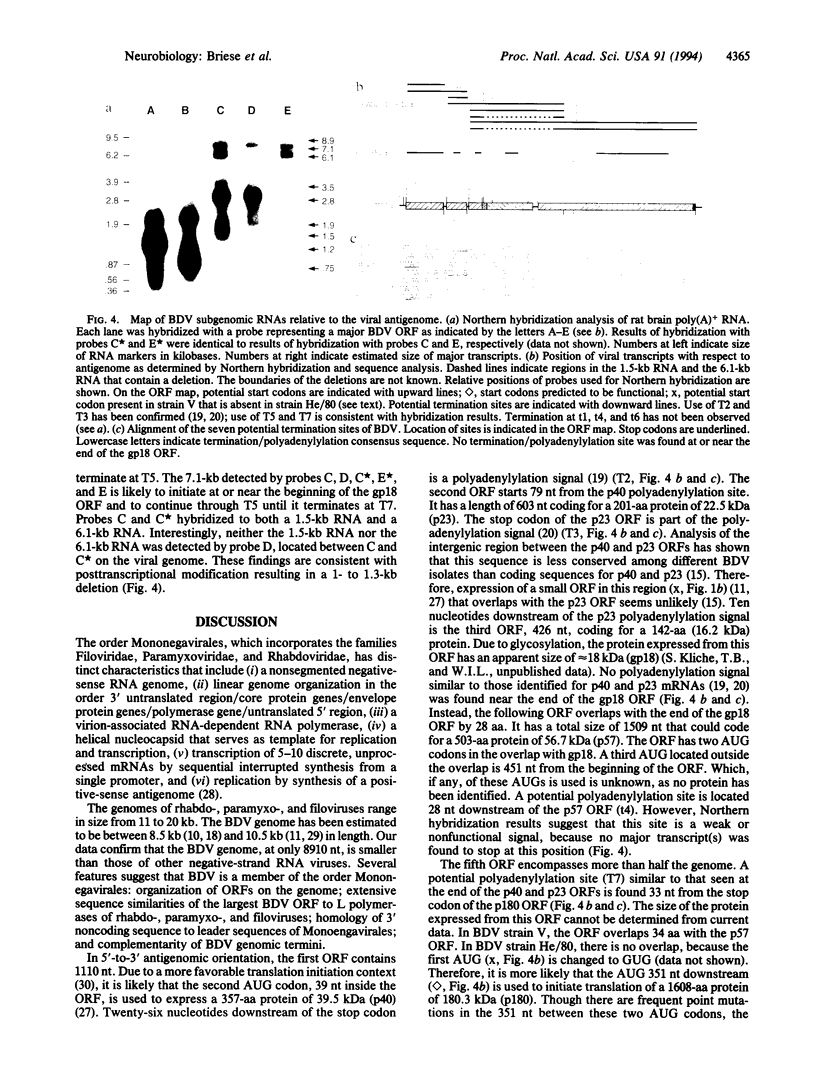
Abstract
Borna disease virus is a neurotropic negative-strand RNA virus that infects a wide range of vertebrate hosts, causing disturbances in movement and behavior. We have cloned and sequenced the 8910-nucleotide viral genome by using RNA from Borna disease virus particles. The viral genome has complementary 3' and 5' termini and contains antisense information for five open reading frames. Homology to Filoviridae, Paramyxoviridae, and Rhabdoviridae is found in both cistronic and extracistronic regions. Northern analysis indicates that the virus transcribes mono- and polycistronic RNAs and uses termination/polyadenylylation signals reminiscent of those observed in other negative-strand RNA viruses. Borna disease virus is likely to represent a previously unrecognized genus, bornaviruses, or family, Bornaviridae, within the order Mononegavirales.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee A. K., Barik S., De B. P. Gene expression of nonsegmented negative strand RNA viruses. Pharmacol Ther. 1991;51(1):47–70. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(91)90041-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barik S., Rud E. W., Luk D., Banerjee A. K., Kang C. Y. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the L gene of vesicular stomatitis virus (New Jersey serotype): identification of conserved domains in L proteins of nonsegmented negative-strand RNA viruses. Virology. 1990 Mar;175(1):332–337. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90218-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode L., Ferszt R., Czech G. Borna disease virus infection and affective disorders in man. Arch Virol Suppl. 1993;7:159–167. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-9300-6_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briese T., de la Torre J. C., Lewis A., Ludwig H., Lipkin W. I. Borna disease virus, a negative-strand RNA virus, transcribes in the nucleus of infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11486–11489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Z. F., Amsterdam J. D., Kao M., Shankar V., Koprowski H., Dietzschold B. Detection of Borna disease virus-reactive antibodies from patients with affective disorders by western immunoblot technique. J Affect Disord. 1993 Jan;27(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0165-0327(93)90098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene J. D., Schubert M., Lazzarini R. A. Terminal sequences of vesicular stomatitis virus RNA are both complementary and conserved. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):167–174. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.167-174.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin W. I., Travis G. H., Carbone K. M., Wilson M. C. Isolation and characterization of Borna disease agent cDNA clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4184–4188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig H., Bode L., Gosztonyi G. Borna disease: a persistent virus infection of the central nervous system. Prog Med Virol. 1988;35:107–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren A. L., Czech G., Bode L., Ludwig H. Natural Borna disease in domestic animals others than horses and sheep. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1993 Jun;40(4):298–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1993.tb00142.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkinson M., Weisman Y., Ashash E., Bode L., Ludwig H. Borna disease in ostriches. Vet Rec. 1993 Sep 18;133(12):304–304. doi: 10.1136/vr.133.12.304-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandl C. W., Heinz F. X., Puchhammer-Stöckl E., Kunz C. Sequencing the termini of capped viral RNA by 5'-3' ligation and PCR. Biotechniques. 1991 Apr;10(4):484–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure M. A., Thibault K. J., Hatalski C. G., Lipkin W. I. Sequence similarity between Borna disease virus p40 and a duplicated domain within the paramyxovirus and rhabdovirus polymerase proteins. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6572–6577. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6572-6577.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poch O., Blumberg B. M., Bougueleret L., Tordo N. Sequence comparison of five polymerases (L proteins) of unsegmented negative-strand RNA viruses: theoretical assignment of functional domains. J Gen Virol. 1990 May;71(Pt 5):1153–1162. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-5-1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poch O., Sauvaget I., Delarue M., Tordo N. Identification of four conserved motifs among the RNA-dependent polymerase encoding elements. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3867–3874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08565.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyper J. M., Richt J. A., Brown L., Rott R., Narayan O., Clements J. E. Genomic organization of the structural proteins of borna disease virus revealed by a cDNA clone encoding the 38-kDa protein. Virology. 1993 Jul;195(1):229–238. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richt J. A., Vande Woude S., Zink M. C., Narayan O., Clements J. E. Analysis of Borna disease virus-specific RNAs in infected cells and tissues. J Gen Virol. 1991 Sep;72(Pt 9):2251–2255. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-9-2251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rott R., Herzog S., Fleischer B., Winokur A., Amsterdam J., Dyson W., Koprowski H. Detection of serum antibodies to Borna disease virus in patients with psychiatric disorders. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):755–756. doi: 10.1126/science.3922055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider P. A., Briese T., Zimmermann W., Ludwig H., Lipkin W. I. Sequence conservation in field and experimental isolates of Borna disease virus. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):63–68. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.63-68.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schädler R., Diringer H., Ludwig H. Isolation and characterization of a 14500 molecular weight protein from brains and tissue cultures persistently infected with borna disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1985 Nov;66(Pt 11):2479–2484. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-11-2479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprankel H., Richarz K., Ludwig H., Rott R. Behavior alterations in tree shrews (Tupaia glis, Diard 1820) induced by Borna disease virus. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1978 May 26;165(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF02121228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitz L., Krey H., Ludwig H. Borna disease in rhesus monkeys as a models for uveo-cerebral symptoms. J Med Virol. 1981;6(4):333–340. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890060408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiedemann N., Presek P., Rott R., Stitz L. Antigenic relationship and further characterization of two major Borna disease virus-specific proteins. J Gen Virol. 1992 May;73(Pt 5):1057–1064. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-5-1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierer J., Riehle H., Grebenstein O., Binz T., Herzog S., Thiedemann N., Stitz L., Rott R., Lottspeich F., Niemann H. The 24K protein of Borna disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1992 Feb;73(Pt 2):413–416. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-2-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tordo N., Poch O., Ermine A., Keith G., Rougeon F. Completion of the rabies virus genome sequence determination: highly conserved domains among the L (polymerase) proteins of unsegmented negative-strand RNA viruses. Virology. 1988 Aug;165(2):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90600-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang S. S., Yin X., Guzzo-Arkuran C., Jones V. S., Davison A. J. Loss of resolution in gel electrophoresis of RNA: a problem associated with the presence of formaldehyde gradients. Biotechniques. 1993 Mar;14(3):380–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VandeWoude S., Richt J. A., Zink M. C., Rott R., Narayan O., Clements J. E. A borna virus cDNA encoding a protein recognized by antibodies in humans with behavioral diseases. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1278–1281. doi: 10.1126/science.2244211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waelchli R. O., Ehrensperger F., Metzler A., Winder C. Borna disease in a sheep. Vet Rec. 1985 Nov 9;117(19):499–500. doi: 10.1136/vr.117.19.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Torre J. C., Carbone K. M., Lipkin W. I. Molecular characterization of the Borna disease agent. Virology. 1990 Dec;179(2):853–856. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90154-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]