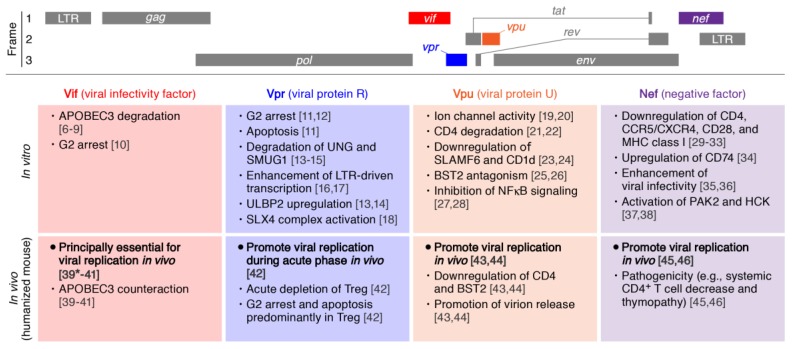
Figure 1.
Roles of Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) accessory proteins in vitro and in vivo. (Top) The scheme of HIV-1 genome. Three reading frames are respectively indicated. (Middle) Major roles of HIV-1 accessory proteins reported from the experiments using cell cultures. (Bottom) The roles of HIV-1 accessory proteins elucidated from the experiments using humanized mouse models. The numbers in parentheses indicate the references. *, as an exception; Vif is dispensable if a vif-deficient CXCR4-tropic HIV-1 (strain LAI) is intravenously inoculated into BLT humanized mice [39]. APOBEC3, apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like 3; UNG, Uracil-DNA glycosylase; SMUG1, single-strand-selective monofunctional uracil-DNA glycosylase 1; LTR, long terminal repeat; ULBP2, UL16 binding protein 2; SLX4, SLX4 structure-specific endonuclease subunit; BST2, bone marrow stromal cell antigen 2; SLAMF6, signaling lymphocyte activation molecule family member 6; PAK2, p21 protein (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 2; HCK, hematopoietic cell kinase.