Original citation: J. Clin. Invest. 113:1318–1327 (2004). doi:10.1172/JCI200419930.
Citation for this Erratum: J. Clin. Invest. 114:141 (2004). doi:10.1172/JCI200419930E1.
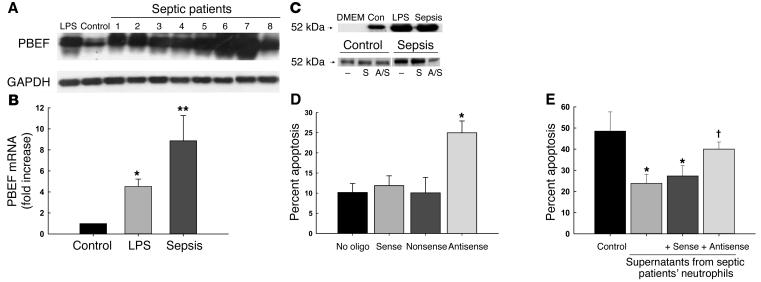
During the preparation of this manuscript for publication, errors were introduced into the panel labels of Figure 6. The correct figure appears below. We regret this error.
Figure 6.
PBEF is expressed and is biologically active in neutrophils harvested from critically ill septic patients. (A) PBEF mRNA in neutrophils from eight critically ill septic patients was expressed at higher levels than in control (Con) or LPS-stimulated neutrophils. Blots were reprobed with GAPDH to confirm comparability of loading. (B) Expression of PBEF mRNA transcripts in septic and LPS-treated neutrophils was evaluated by real-time PCR, normalizing expression to that for GAPDH. Expression was induced by LPS (*P < 0.05 versus unstimulated cells) and even more in septic neutrophils (**P < 0.05 versus both LPS-stimulated cells and unstimulated cells). (C) Immunoreactive PBEF was detectable by Western blot in supernatants from LPS-treated and septic neutrophils following 21 hours of in vitro culture in serum-free medium; antisense pretreatment blocked the secretion of PBEF. DMEM denotes medium only; studies were repeated three times, and a representative blot is shown. S, sense; A/S, antisense. (D) Neutrophils from 16 septic critically ill patients were incubated for 5 hours with PBEF antisense or the sense or nonsense controls, and apoptosis was evaluated 21 hours later. Antisense treated cells, but not controls, showed increased rates of apoptosis (*P = 0.002 versus no oligonucleotide [no oligo]; ANOVA). (E) Supernatants from control PMN had minimal effects on the apoptosis of resting PMN (black bar). In contrast, supernatants from septic PMN or septic PMN incubated with PBEF sense oligonucleotides significantly inhibited the apoptosis of control PMN (*P < 0.05), whereas supernatants from antisense-treated septic PMNs induced significantly less inhibition (†P < 0.05 versus sense or no oligonucleotide; P = NS versus controls, n = 5).