Abstract
Introduction
Congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (CHH) is a rare, genetic, reproductive endocrine disorder characterized by absent puberty and infertility. Limited information is available on the psychosocial impact of CHH and psychosexual development in these patients.
Aim
The aim of this study was to determine the impact of CHH on psychosexual development in men on long-term treatment.
Methods
A sequential mixed methods explanatory design was used. First, an online survey (quantitative) was used to quantify the frequency of psychosexual problems among CHH men. Second, patient focus groups (qualitative) were conducted to explore survey findings in detail and develop a working model to guide potential nursing and interdisciplinary interventions.
Main Outcome Measures
Patient characteristics, frequency of body shame, difficulty with intimate relationships, and never having been sexually active were assessed. Additionally, we collected subjective patient-reported outcomes regarding the impact of CHH on psychological/emotional well-being, intimate relationships, and sexual activity.
Results
A total of 101 CHH men on long-term treatment (>1 year) were included for the analysis of the online survey (mean age 37 ± 11 years, range 19–66, median 36). Half (52/101, 51%) of the men had been seen at a specialized academic center and 37/101 (37%) reported having had fertility-inducing treatment. A high percentage of CHH men experience psychosexual problems including difficulty with intimate relationships (70%) and body image concerns/body shame (94/101, 93%), and the percentage of men never having been sexually active is five times the rate in a reference group (26% vs. 5.4%, P < 0.001). Focus groups revealed persisting body shame and low self-esteem despite long-term treatment that has lasting impact on psychosexual functioning.
Conclusions
CHH men frequently experience psychosexual problems that pose barriers to intimate relationships and initiating sexual activity. These lingering effects cause significant distress and are not ameliorated by long-term treatment. Psychosexual assessment in CHH men with appropriate psychological support and treatment should be warranted in these patients. Dwyer AA, Quinton R, Pitteloud N, and Morin D. Psychosexual development in men with congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism on long-term treatment: A mixed methods study. Sex Med 2015;3:32–41.
Keywords: Kallmann Syndrome, Psychosocial Factors, Body Image, Self-Esteem, Psychosexual Outcome, Nursing, Mixed Methods, Congenital Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism
Introduction
Congenital deficiency of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (CHH) is an endocrine disorder resulting from gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) deficiency. This genetic condition is clinically characterized by absent puberty and infertility and may be accompanied by a variety of associated phenotypes including cryptorchidism, micropenis, and anosmia (termed Kallmann syndrome [KS]) [1]. CHH is rare with incidence estimated at 1 in 4,000–10,000 [2] and has a striking gender discordance (approximately 2–5 males for each female case) [3],[4]. This gender difference remains genetically unexplained and may well represent an ascertainment bias as amenorrheic women presenting for gynecologic evaluation may likely receive empiric treatment, as opposed to being referred for an endocrine evaluation [5]. Importantly, CHH patients cannot initiate puberty spontaneously and require hormonal treatment to develop secondary sexual characteristics [6]. It is a treatable form of infertility with approximately 80% of men able to develop sperm with either pulsatile GnRH or exogenous gonadotropin therapy 7–9.
CHH patients typically present to medical attention with failure to undergo spontaneous puberty [10]. The challenge being to differentiate this rare condition from more frequent variants in the timing and onset of puberty such as constitutional delay of puberty [11],[12]. CHH adolescent males presenting with absent puberty after 14 years of age may be inaccurately defined as “late bloomers” and their treatment unnecessarily delayed; the “watchful waiting” approach finally ends with the patients re-presenting as pubertal young adults with frank hypogonadotropic hypogonadism [10]. As captured in a recent patient report, such delays in diagnosis can have lasting psychological and emotional effects on patients [13].
Puberty is a developmental process characterized by numerous physiologic, psychosocial, and emotional changes culminating in reproductive capacity. While timing of onset of pubertal development is variable, late sexual development can carry a psychological burden. Delayed puberty can result in body image concerns, low self-esteem and social isolation, and later sexual activity 14–16. Further, many late maturers experience victimization or bullying, which are important and common risk factors for developing depression [17] as well as other significant psychological problems [18]. For CHH men, who represent the most extreme form of delayed puberty, data on psychological aspects are limited to a handful of descriptive case series with few patients 19–21. Prior to starting treatment, adolescents with CHH exhibit impaired quality of life and increased anxiety and depression compared with peers [22],[23]. However, the existing literature has solely focused on the time of diagnosis or during the initial pubertal induction and therefore, data regarding the psychosocial impact of CHH in men on long-term treatment are lacking. Accordingly, we do not know whether long-term sex steroid treatment and/or fertility-inducing treatments mitigate the impact on psychosexual development of CHH men.
Aim
This study aimed to test the hypothesis that men with CHH experience psychosexual problems that are not fully ameliorated by long-term treatment.
Methods
A community-based participatory research framework [24] was utilized for developing and conducting this sequential, explanatory mixed method study [25]. In the context of a European network focused on CHH/KS (COST Action BM1105), partnerships with patient community leaders (i.e., moderators of online patient support sites) were developed to include patient perspectives into the process. Additionally, developing links with patient support groups was essential for reaching a sufficient number of patients with this rare condition. Patient community leaders participated in developing and improving the language and clarity of the survey, facilitated recruitment efforts, and provided feedback on study findings at each stage of analysis. This sequential mixed methods approach employed quantitative methods to identify the scope and prevalence of issues facing these dispersed patients followed by qualitative methods (focus groups) to explore the findings in greater detail and to identify possible mechanistic explanations of the survey results. The quantitative online survey was used to collect patient characteristics and information on diagnosis/treatment as well as body image, relationship status, and sexual activity. Subsequently, qualitative patient focus groups were conducted to explore the impact of CHH on patients' lives and psychosexual development. Focus groups were held in concert with CHH patient support meetings jointly planned by patient community leaders and study investigators. The psychosexual assessment of men with CHH was part of a larger research project examining health-promoting behavior [26] and factors affecting quality of life among CHH men. The ultimate goal of this study is to design innovative nursing and interdisciplinary interventions to address unmet health needs in these dispersed rare disease patients. The study was approved by the Health Research Ethics Committee (Canton Vaud) and all participants provided informed consent prior to the initiation of study-related activities. For the online survey, an opt-in electronic consent was used while focus group participants provided written informed consent.
Subjects
As male patients outnumber female patients in this rare disorder [3], we focused our attention on male subjects. Adult CHH men (18–70 years) on treatment for at least 1 year were recruited for the study. A random sampling (40%) of online survey respondents was contacted and interviewed to confirm diagnosis. Those men with other causes of hypogonadism (i.e., Klinefelter syndrome, adult-onset hypogonadism) were excluded and surveys with multiple incomplete or conflicting responses were excluded. The study was publicized online via a closed/private CHH/KS social media group (Facebook), CHH/KS forum (chat room), a clinical trials registry, and the COST Action website. Data from the American National Survey of Sexual Health and Behavior were used as a comparison reference group [27].
Statistics
Survey results were analyzed using descriptive statistics (mean ± standard deviation, range, median), Student's t-test (Wilcoxon rank-sum test for data not normally distributed) to evaluate differences between groups, and Z score to assess differences in proportions between the CHH and the reference group. SigmaStat (Systat Software Inc., San Jose, CA, USA) was used for statistical analyses and a P < 0.05 was considered significant.
Qualitative Analysis
Thematic analysis (coding) of focus group transcripts was performed by two separate investigators (A.A. Dwyer and D. Morin) using NVivo10 (QSR International PSY Ltd., Melbourne, Australia). Categories of responses and themes were first classified on the basis of the Health Promotion Model [26]. Iterative coding occurred until no further themes were identified, suggesting a saturation point had been reached. Additionally, connections between coded terms were mapped to examine connections both within and between categories (i.e., whether or not certain themes appear together repeatedly), and those themes arising frequently and expansively were given particular emphasis [28].
Main Outcome Measures
For the online survey, patient characteristics, age of diagnosis, age of initiating treatment, frequency of body shame, difficulty with intimate relationships, and never having been sexually active were the main outcome measures. For patient focus group discussions, subjective patient-reported outcomes regarding the impact of CHH on psychological/emotional well-being, intimate relationships, and sexual activity were recorded.
Results
The survey was online for 7 months and received a total of 230 hits of which 101 surveys (44%) were retained for analysis. The men (mean age 37 ± 11 years, range 19–66, median 36) had all been on long-term treatment (>1 year) and half (52/101, 51%) had been seen at a specialized or academic medical center. Participant characteristics and treatment information are presented in Table1. Overall, these men were well educated and employed and worked across a variety of fields and responsibilities (Supporting Information Table S1). In this cohort, CHH was diagnosed neonatally in four men and as late as 32 years (mean 18 ± 6, median 18 years) (Figure 1). Notably, men with a familial pattern of inheritance (14/101, 14%) were not diagnosed earlier than sporadic counterparts (P = 0.1) The age of initiating treatment to develop secondary sexual characteristics ranged from 11 to 32 years (mean 19 ± 4, median 18 years) and nearly all men (98/101) had been on some form of testosterone replacement (injection, implanted pellets, patches, or gel). Over a third of men (37/101, 37%) reported having had fertility-inducing treatment (exogenous gonadotropins or pulsatile GnRH therapy) with variable outcomes (Table1). Nearly a quarter of the men receiving fertility-inducing treatment (8/37, 22%) were single or had never been in a relationship, suggesting a motivation for pursuing these time and resource-intensive programs extended beyond an immediate desire to achieve fertility. Those CHH men with children were older than those without children (median age 43.5 vs. 32.0 years, P < 0.001).
Table 1.
Sociodemographic and treatment information of CHH men (n = 101)
| Age | n |
| 19–29 years | 30 |
| 30–39 years | 38 |
| 40–49 years | 19 |
| 50–59 years | 11 |
| 60+ yrs | 3 |
| Education | |
| High school/vocational | 35 |
| University | 35 |
| Postgraduate | 31 |
| Employment | |
| Working full-time | 67 |
| Working part-time | 9 |
| Unemployed | 10 |
| Retired | 5 |
| Student | 9 |
| No response given | 1 |
| Relationship status | |
| Married | 36 |
| In a relationship | 16 |
| Single | 24 |
| Never been in a relationship | 23 |
| Divorced | 1 |
| No response given | 1 |
| Children | |
| None | 75 |
| Biologic children | 8 |
| Adopted children | 18 |
| Treatment | n (%) |
| Testosterone (ever) | 98/101 |
| Fertility treatment* | 37/101 |
| Single/never in a relationship | 8/37 (22%) |
| No children | 14/29 (48%) |
| Adopted children | 7/29 (24%) |
| Biological children | 8/29 (28%) |
Gonadotropin therapy or pulsatile GnRH therapy.
CHH = congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism; GnRH = gonadotropin-releasing hormone.
Figure 1.
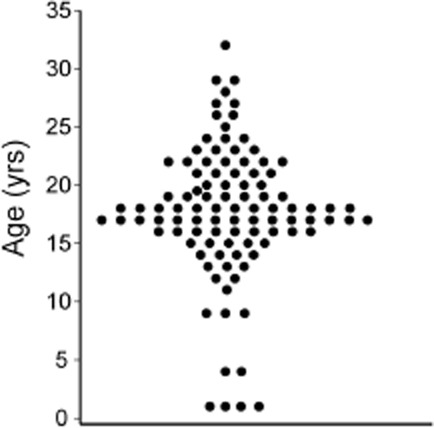
Age at diagnosis in the cohort of congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (CHH) men (n = 101).
Despite Long-Term Treatment, a High Proportion of CHH Men Have Psychosexual Problems
As no data are available on the sex lives of men on long-term treatment, we asked participants if they had ever been sexually active. Notably, 26/101 (26%) of men reported they had never been sexually active. This is nearly five times the rate (26% vs. 5.4%, P < 0.001) observed in adult men (18+ years) in a large (n > 2,000) probability survey examining sexual activity [27]. During survey development, discussions with patient community leaders suggested that traumatic experiences, body image concerns, and difficulty with intimate relationships were frequently raised in private, online discussions. When we inquired about these points, 72% (73/101) stated that they had been teased or ridiculed because of CHH and 93% (94/101) reported that they had felt embarrassed or ashamed of their body and avoided undressing in public such as at the gym or beach. Further, 70% (69/99) of men agreed that intimate relationships were difficult because of CHH. Neither age of diagnosis nor age of treatment initiation was significantly related to any of these results. We hypothesized that concerns about testicular size could be a factor in these findings, yet no differences were observed between those men who had received fertility-inducing treatment (inducing testicular growth) and those men on testosterone only (no testicular development). These data point to a significant impact of CHH on the psychosexual development. To explore this in greater detail, we conducted three patient focus groups. These discussions provided further insight into the survey findings and helped explain the lasting psychosexual impact of CHH that pose barriers to dating, developing intimate relationships, and initiating sexual activity.
CHH-Related Body Shame Has Lasting Impact on Psychosexual Functioning
Patient focus group discussions grew from two questions: “What has been the most difficult part of living with CHH?” and “How has CHH affected your sex life and intimate relationships?” Twenty-six men participated in the focus groups (mean age 37 ± 13 years, range 18–66, median 36 years) revealing consistent, overarching themes of shame and isolation related to CHH. Patients frequently cited their frustration at what they perceived as a late diagnosis and thus did not have puberty induced until much later than their peers. More specifically, patients reported their sense of isolation resulted from their absent sexual development and feeling “left behind” as peers developed physically, became sexual active, and assumed adult roles (Figure 2, Table2). This marginalization fed fears of being exposed and many (20/26) attempted to hide their lack of puberty by avoiding situations possibly involving nudity and in some cases, avoiding social events. Problems with body image dominated focus group discussions both in terms of the number of comments and the proportion of participants (23/26) reporting body shame (Figure 2, Table2).
Figure 2.
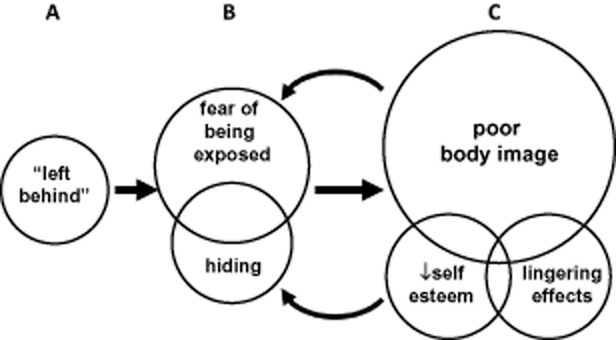
Focus group themes related to the impact of disrupted sexual maturation on psychosexual development and intimate relationships. (A) Focus group participants reported feeling isolated and “left behind” as peers underwent sexual development, started dating, and began taking on more adult roles. (B) Patients often developed fear and anxiety about being exposed and tried to hide their lack of sexual development as a coping response. (C) Body shame and body image concerns were the most frequently cited issues which co-occurred with low self-esteem. These issues interacted with existing fears/anxiety creating a cyclic pattern with effects lasting far after treatment initiation. Circles depict themes from focus group discussions, circles are sized proportionally with the number of references, overlapping circles depict co-occurring themes, and interactions are noted by arrows.
Table 2.
Themes and representative quotes arising from focus group discussions
| Theme | Representative quotes |
|---|---|
| Feeling left behind (isolation) |
|
| Fear of being exposed |
|
| Hiding |
|
| Body shame/poor body image |
|
| Body shame/poor body image |
|
| Low self-esteem |
|
| Lingering effects |
|
| Mediating factors |
|
CHH = congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism.
Similar to the literature on late maturing adolescent boys 14–17 and the online survey results, men in the focus groups reported traumatic experiences including teasing, victimization, and bullying related to their youthful appearance, underdeveloped genitalia and in some cases, gynecomastia resulting from CHH. Notably, despite virilization on long-term hormone treatment, these men struggled to overcome a self image of the undeveloped, youthful adolescent of their past. These negative thoughts persisted well into adulthood—even though many realized that these thoughts were not rational. Discussions revealed a cycle of isolation and shame wherein hiding and removing oneself from social situations only worsened the body image and self-esteem issues (Figure 2, Table2).
Importantly, patients reported ameliorating factors that helped them cope with their disrupted psychosexual development including meeting other patients with CHH (Table2). In total, 15/26 men provided unsolicited comments stating that this was a life-changing event enabling them to overcome some of their feelings of shame and isolation. Half of the men (13/26) shared that coping with the psychosexual aspects of CHH became easier with age and that this was often related to finding someone who accepted them as they are (i.e., an understanding healthcare provider, therapist, partner, or spouse). These highlight potential interventions such as connecting patients for peer-to-peer support.
Limitations
This type of study has inherent limitations including limited sample size. First, studying rare disease populations pose challenges for recruiting adequate number of patients [29],[30]. We attempted to overcome this by using web-based data collection via an online survey. This approach introduces potential bias as not everyone has internet access, so this convenience sample may be enriched with well-educated men and may reflect a response bias of more proactive and/or more severely affected patients. Second, participants were recruited via expert clinicians as well as among patient support groups. Because medical chart review of this dispersed disease population was beyond the scope this study, we recontacted 40% of respondents to confirm diagnosis. Thus, we cannot be sure that every respondent met all hormonal and clinical criteria of a CHH diagnosis. Importantly, the findings of the survey were mirrored in the focus group discussion (where all participants had confirmed CHH diagnosis), thus contributing to the validity of the study. Last, as no validated questionnaire is available for CHH men to assess health-related quality of life or sexual function [31], we developed our own questionnaire. Face validity was sought with input from patient advocates, but a full validation process was not performed. While validity and reliability in self-report responses are important, there is a growing acceptability of using patient-reported outcomes for managing chronic conditions [32]. Further, using focus groups with expert patients to explore these is an added value to the validity of the results.
Discussion
We report evidence of persisting psychosexual impact of CHH that is not ameliorated by long-term hormone replacement therapy. CHH is a rare disorder that has been previously used as a unique human disease model providing important insights into the hormonal control of the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis [33],[34]. Further, genetic studies on this extreme form of delayed puberty have informed our understanding of the molecular control of human puberty and reproduction [1],[35]. However, there are scant data on how the severe disruption of puberty impacts psychosexual development in CHH men.
Previous reports on the psychosocial aspects of CHH include several descriptive case series of small cohorts of CHH men during initial treatment. The 1964 report of eight cases of so-called “sexual infantilism” (including three CHH men 20–47 years of age) commented on embarrassment because of youthful appearance and feelings of sexual inadequacy [19]. A subsequent 1971 report documenting 13 cases from the Johns Hopkins University Hospital added observations on insecurity, decreased confidence, and low interest in dating among 13 CHH men (19–44 years old) after starting treatment [20]. Another study published in 1996 followed eight CHH men initiating pulsatile GnRH therapy for pubertal induction noting diminished social interactions and poorer views of their physique compared with controls [21]. In the present study, we examined these issues in a relatively large cohort of CHH men (n = 101), providing data on the prevalence of these issues. We then conducted focus groups to develop an explanatory model for these observations, thus enhancing our understanding of the unmet psychological and psychosexual needs of CHH men in order to better direct therapy and interventions.
In contrast to prior studies, we focused exclusively on men receiving long-term treatment to see if psychosocial and psychosexual issues are corrected by a longer period with a normalized sex steroid milieu. Testosterone replacement therapy has long been shown to be effective for inducing secondary sexual characteristics and normalizing sexual function [6] and has well-documented beneficial effects on muscle and fat-free (lean) body mass [36] as well as mood [37]. The CHH men on long-term treatment in this study struggled with psychosocial aspects of their condition. Thus, it seems that hypogonadal patients should first receive testosterone replacement then be offered psychosexual help to address these needs. Importantly, focus group discussions revealed CHH men are challenged to perceive themselves as a normal-appearing virilized men. This may relate to a form of body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) wherein individuals develop an altered view of personal appearance [38]. BDD has been linked with early traumatic life events [39] and can have significant impact on quality of life [40]. As BDD appears to be responsive to cognitive behavioral interventions, similar approaches may be warranted for CHH men to address their significant body image concerns.
A surprising finding was that fertility was never raised as a major concern within focus group discussions. Rather, attention centered on body shame and lack of genital development. Testosterone replacement induces secondary sexual characteristics and normalizes sexual function yet has no effect on testicular development and testis volume remains small (infantile in some cases). We found that 22% of men who had received fertility-inducing treatment had never been in a relationship. While the survey was not designed to specifically determine the motivation for choosing specific treatments, this observation suggests that these treatments were pursued to augment testicular volume and thus normalize genital appearance. Indeed, it would be interesting to utilize the recently developed genital self-image scale [41] to better understand how these factors may contribute to these men's sexual experiences and why they are five times more likely to never have been sexually active. Some have speculated that the atrophic testes and/or severely diminished phallus size sometimes associated with CHH can have serious negative effects on self-confidence and the sexual life of CHH men [6],[10],[42]. Herein, we provide direct evidence supporting these assertions.
Micropenis (with or without cryptorchidism) can be associated with CHH. We did not assess how many men were born with micropenis as this can be difficult to ascertain in the absence of medical documentation. However, outcome studies of patients with micropenis indicate diminished penis size persisting into adult life can have negative consequences on sexual quality of life [43]. Related to this, concern about penis size was pervasive and a frequently occurring topic in focus group discussions. Indeed, in every focus group patients made spontaneous inquiries regarding normative ranges for penis size among CHH men. While population-based normative data are available on penis size [44], corresponding data on a large cohort of CHH are lacking. CHH men experience significant preoccupation and shame regarding penis size. Accordingly, it could be useful to evaluate this using a validated instrument [45] before and after providing reference ranges for this patient population along with targeted cognitive behavioral interventions to address these body shame issues. Such an approach could be a possible avenue for alleviating this distressing problem for CHH men. The ultimate goal of this study was assess impact of CHH on psychosexual development in order to identify patient needs and design innovative nursing and interdisciplinary interventions for these dispersed patients. Importantly, one result of this study was that conducting patient focus groups brought together isolated patients and provided them with an opportunity to discuss these problems, share experiences, and seek support—which in and of itself was an important and empowering intervention for these patients.
Conclusions
This mixed methods study presents data demonstrating the pervasive psychosexual difficulties experienced by CHH men on long-term treatment. The CHH-related absent sexual development has lasting effects that pose barriers to intimate relationships and initiating sexual activity. Further, the psychosocial distress experienced by CHH men is not ameliorated by long-term treatment. These findings underscore the importance of psychosexual assessment of CHH men and the need for psychological support and interdisciplinary care for this patient population.
Acknowledgments
We thank the patients for their generous participation as well as Mr. Neil Smith and the other patient advocates for their important contributions to this work. We also wish to express our gratitude to Dr. Gerasimos Sykiotis for his constructive feedback during manuscript preparation. This study received funding support from the Endocrine Nurses Society and COST Action BM1105 (STSM # 15982). The study was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01914172).
Conflict of Interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Statement of Authorship
Category 1
-
Conception and Design
Andrew A. Dwyer; Nelly Pitteloud; Diane Morin
-
Acquisition of Data
Andrew A. Dwyer
-
Analysis and Interpretation of Data
Andrew A. Dwyer; Richard Quinton; Nelly Pitteloud; Diane Morin
Category 2
-
Drafting the Article
Andrew A. Dwyer
-
Revising It for Intellectual Content
Andrew A. Dwyer; Richard Quinton; Nelly Pitteloud; Diane Morin
Category 3
-
Final Approval of the Completed Article
Andrew A. Dwyer; Richard Quinton; Nelly Pitteloud; Diane Morin
Supporting Information
Table S1 Survey respondents' self-reported type. Open-ended responses were grouped into categories (noted by underlined text).
References
- Bianco SD, Kaiser UB. The genetic and molecular basis of idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2009;5:569–576. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2009.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromantin M, Gineste J, Didier A, Rouvier J. [Impuberism and hypogonadism at induction into military service. Statistical study] Probl Actuels Endocrinol Nutr. 1973;16:179–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seminara SB, Hayes FJ, Crowley WF., Jr Gonadotropin-releasing hormone deficiency in the human (idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and Kallmann's syndrome): Pathophysiological and genetic considerations. Endocr Rev. 1998;19:521–539. doi: 10.1210/edrv.19.5.0344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinton R, Duke VM, Robertson A, Kirk JM, Matfin G, de Zoysa PA, Azcona C, MacColl GS, Jacobs HS, Conway GS, Besser M, Stanhope RG, Bouloux PM. Idiopathic gonadotrophin deficiency: Genetic questions addressed through phenotypic characterization. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2001;55:163–174. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2265.2001.01277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell AL, Dwyer A, Pitteloud N, Quinton R. Genetic basis and variable phenotypic expression of Kallmann syndrome: Towards a unifying theory. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2011;22:249–258. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2011.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han TS, Bouloux PM. What is the optimal therapy for young males with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism? Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2010;72:731–737. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2009.03746.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitteloud N, Hayes FJ, Dwyer A, Boepple PA, Lee H, Crowley WF., Jr Predictors of outcome of long-term GnRH therapy in men with idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:4128–4136. doi: 10.1210/jc.2002-020518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu PY, Baker HW, Jayadev V, Zacharin M, Conway AJ, Handelsman DJ. Induction of spermatogenesis and fertility during gonadotropin treatment of gonadotropin-deficient infertile men: Predictors of fertility outcome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:801–808. doi: 10.1210/jc.2008-1648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warne DW, Decosterd G, Okada H, Yano Y, Koide N, Howles CM. A combined analysis of data to identify predictive factors for spermatogenesis in men with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism treated with recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone and human chorionic gonadotropin. Fertil Steril. 2009;92:594–604. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.07.1720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. Approach to the male patient with congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:707–718. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-1664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmert MR, Dunkel L. Clinical practice. Delayed puberty. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:443–453. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1109290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington J, Palmert MR. Clinical review: Distinguishing constitutional delay of growth and puberty from isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: Critical appraisal of available diagnostic tests. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:3056–3067. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-1598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith N, Quinton R. Kallmann syndrome. BMJ. 2012;345:e6971. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e6971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waylen A, Wolke D. Sex “n” drugs “n” rock “n” roll: The meaning and social consequences of pubertal timing. Eur J Endocrinol. 2004;151(suppl 3):U151–159. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.151u151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaud PA, Suris JC, Deppen A. Gender-related psychological and behavioural correlates of pubertal timing in a national sample of Swiss adolescents. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2006;254–255:172–178. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2006.04.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golub MS, Collman GW, Foster PM, Kimmel CA, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Reiter EO, Sharpe RM, Skakkebaek NE, Toppari J. Public health implications of altered puberty timing. Pediatrics. 2008;121(suppl 3):S218–230. doi: 10.1542/peds.2007-1813G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thapar A, Collishaw S, Pine DS, Thapar AK. Depression in adolescence. Lancet. 2012;379:1056–1067. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60871-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellini G, Lelli L, Lo Sauro C, Vignozzi L, Maggi M, Faravelli C, Ricca V. Childhood abuse, sexual function and cortisol levels in eating disorders. Psychother Psychosom. 2012;81:380–382. doi: 10.1159/000337176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huffer V, Scott WH, Connor TB, Lovice H. Psychological studies of adult male patients with sexual infantilism before and after androgen therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1964;61:255–268. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-61-2-255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobrow NA, Money J, Lewis VG. Delayed puberty, eroticism, and sense of smell: A psychological study of hypogonadotropinism, osmatic and anosmatic (Kallmann's syndrome) Arch Sex Behav. 1971;1:329–344. doi: 10.1007/BF01638061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman J, Bosch JD, Delemarre vd Waal HA. Personality development of adolescents with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Psychol Rep. 1996;79(3 Pt 2):1123–1126. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1996.79.3f.1123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aydogan U, Aydogdu A, Akbulut H, Sonmez A, Yuksel S, Basaran Y, Uzun O, Bolu E, Saglam K. Increased frequency of anxiety, depression, quality of life and sexual life in young hypogonadotropic hypogonadal males and impacts of testosterone replacement therapy on these conditions. Endocr J. 2012;59:1099–1105. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.ej12-0134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasaite L, Ceponis J, Preiksa RT, Zilaitiene B. Impaired emotional state, quality of life and cognitive functions in young hypogonadal men. Andrologia. 2013 doi: 10.1111/and.12199. doi: 10.1111/and.12199[Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallerstein NB, Duran B. Using community-based participatory research to address health disparities. Health Promot Pract. 2006;7:312–323. doi: 10.1177/1524839906289376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creswell JW. Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. 3rd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, Inc; 2008. 296 p. [Google Scholar]
- Pender NJ, Murdaugh CL, Parsons MA. Health promotion in nursing practice. 6th edition. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Leigh BC, Temple MT, Trocki KF. The sexual behavior of US adults: Results from a national survey. Am J Public Health. 1993;83:1400–1408. doi: 10.2105/ajph.83.10.1400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saldana J. Coding manual for qualitative researchers. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage; 2009. 223 p. [Google Scholar]
- Kruer MC, Steiner RD. The role of evidence-based medicine and clinical trials in rare genetic disorders. Clin Genet. 2008;74:197–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2008.01041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson MS, Epstein C, Howell RR, Jones MC, Korf BR, McCabe ER, Simpson JL. Developing a national collaborative study system for rare genetic diseases. Genet Med. 2008;10:325–329. doi: 10.1097/GIM.0b013e31817b80fd. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langham S, Maggi M, Schulman C, Quinton R, Uhl-Hochgraeber K. Health-related quality of life instruments in studies of adult men with testosterone deficiency syndrome: A critical assessment. J Sex Med. 2008;5:2842–2852. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2008.01015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss EA, Ellis JL, Shoup JA, Zeng C, McQuillan DB, Steiner JF. Association of patient-centered outcomes with patient-reported and ICD-9-based morbidity measures. Ann Fam Med. 2012;10:126–133. doi: 10.1370/afm.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitteloud N, Dwyer AA, DeCruz S, Lee H, Boepple PA, Crowley WF, Jr, Hayes FJ. Inhibition of luteinizing hormone secretion by testosterone in men requires aromatization for its pituitary but not its hypothalamic effects: Evidence from the tandem study of normal and gonadotropin-releasing hormone-deficient men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:784–791. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-2156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitteloud N, Dwyer AA, DeCruz S, Lee H, Boepple PA, Crowley WF, Jr, Hayes FJ. The relative role of gonadal sex steroids and gonadotropin-releasing hormone pulse frequency in the regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:2686–2692. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-2548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramanian R, Dwyer A, Seminara SB, Pitteloud N, Kaiser UB, Crowley WF., Jr Human GnRH deficiency: A unique disease model to unravel the ontogeny of GnRH neurons. Neuroendocrinology. 2010;92:81–99. doi: 10.1159/000314193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhasin S, Storer TW, Berman N, Yarasheski KE, Clevenger B, Phillips J, Lee WP, Bunnell TJ, Casaburi R. Testosterone replacement increases fat-free mass and muscle size in hypogonadal men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82:407–413. doi: 10.1210/jcem.82.2.3733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C, Alexander G, Berman N, Salehian B, Davidson T, McDonald V, Steiner B, Hull L, Callegari C, Swerdloff RS. Testosterone replacement therapy improves mood in hypogonadal men—A clinical research center study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81:3578–3583. doi: 10.1210/jcem.81.10.8855804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan RA, Rossell SL, Enticott PG, Castle DJ. Own-body perception in body dysmorphic disorder. Cognit Neuropsychiatry. 2013;18:594–614. doi: 10.1080/13546805.2012.758878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhlmann U, Marques LM, Wilhelm S. Traumatic experiences in individuals with body dysmorphic disorder. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2012;200:95–98. doi: 10.1097/NMD.0b013e31823f6775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IsHak WW, Bolton MA, Bensoussan JC, Dous GV, Nguyen TT, Powell-Hicks AL, Gardner JE, Ponton KM. Quality of life in body dysmorphic disorder. CNS Spectr. 2012;17:167–175. doi: 10.1017/S1092852912000624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbenick D, Schick V, Reece M, Sanders SA, Fortenberry JD. The development and validation of the Male Genital Self-Image Scale: Results from a nationally representative probability sample of men in the United States. J Sex Med. 2013;10:1516–1525. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvattier C, Maione L, Bouligand J, Dode C, Guiochon-Mantel A, Young J. Neonatal gonadotropin therapy in male congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012;8:172–182. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2011.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callens N, De Cuypere G, Van Hoecke E, T'Sjoen G, Monstrey S, Cools M, Hoebeke P. Sexual quality of life after hormonal and surgical treatment, including phalloplasty, in men with micropenis: A review. J Sex Med. 2013;10:2890–2903. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbenick D, Reece M, Schick V, Sanders SA. Erect penile length and circumference dimensions of 1,661 sexually active men in the United States. J Sex Med. 2014;11:93–101. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veale D, Eshkevari E, Read J, Miles S, Troglia A, Phillips R, Echeverria LM, Fiorito C, Wylie K, Muir G. Beliefs about penis size: Validation of a scale for men ashamed about their penis size. J Sex Med. 2014;11:84–92. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1 Survey respondents' self-reported type. Open-ended responses were grouped into categories (noted by underlined text).


