Abstract
The Heimlich valve is a small one-way valve used for chest drainage that empties into a flexible collection device and prevents return of gases or fluids into the pleural space. The Heimlich valve is less than 13 cm (5 inches) long and facilitates patient ambulation. Currently there are several systems in the market. It can be used in many patients instead of a traditional water seal drainage system. The Heimlich chest drainage valve was developed so that the process of draining the pleural cavity could be accomplished in a safe, relatively simple, and efficient manner. This valve system has replaced the cumbersome underwater drainage bottle system. Moreover; the Heimlich valve system connects to chest tubing and allows fluid and air to pass in one direction only. This system functions in any position, and it does not ever need to be clamped, a regulated suction can be attached to it if necessary. The valve drains into a plastic bag that can be held at any level, allowing the patient undergoing chest drainage to be ambulatory simply by carrying the bag. In the current mini review we will present the Heimlich valve system and method of insertion.
Keywords: Pneumothorax, Heimlich valve, VATS
First introduced in 1965, the Heimlich flutter valve is a one-way portable device that was designed for use as a drainage procedure in order to avoid the need for intrapleural suction after thoracotomy (1). The inventor of the valve was Henry Heimlich, an American thoracic surgeon who also first described the Heimlich maneuver. Soon, it became very popular in the outpatient management of patients with prolonged air-leakage from various causes (2), and has also been used in emergency treatment of pneumothorax in battle fronts (3).
As already mentioned, it is a one-way valve, thus it prevents the evacuated air from travelling back to the thoracic cavity along the attached chest tube. The valve is made of a plastic case with a rubber sleeve inside. It has two nozzles, the inlet nozzle which allows the air to pass in the valve through the chest drainage tube attached to it, and the outlet nozzle which allows the air to pass to the environment or a collecting device during expiration. The rubber sleeve is attached to the inlet nozzle in such a manner that, during inhalation, it closes off, thus preventing air to be sucked in, through the valve, to the pleural cavity (Figure 1). The free end of the rubber sleeve is compressed, so that the two sides remain in contact with each other, in order to achieve this function. When the air passes through the inlet nozzle in the rubber sleeve, the latter one opens allowing the air to escape during expiration. But during inhalation the free end remains closed, due its compression, preventing the air to be sucked back in the thoracic cavity. This way pneumothorax is safely evacuated. By the same mechanism, the Heimlich flutter valve may also facilitate the evacuation of fluid. The inlet nozzle is securely attached to one end of a chest drainage tube, while the other one lies within the patient’s pleural cavity. The attachment may be secured with pieces of adhesive tape. The valve is also attached to the patient’s chest wall, but care must be taken that the distal end, the outlet nozzle, remains unimpeded (1).
Figure 1.
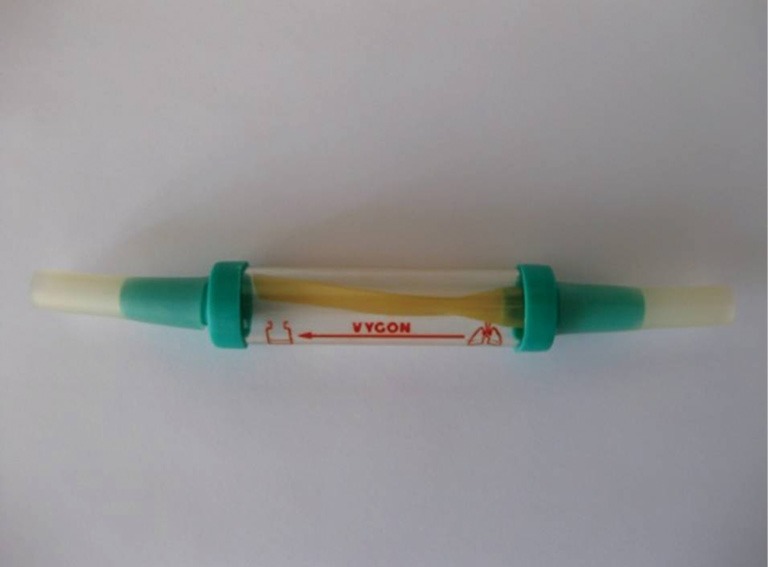

A Heimlich flutter valve.
When air passes through the valve, a distinct “flutter” sound can be heard, ensuring that the device is working properly. Absence of the sound accompanied with no movement of the rubber sleeve during placement means that no air passes through the valve, which indicates either the resolution of pneumothorax or possible clogging of the chest tube. Auscultation of the chest or a chest X-ray might be helpful.
The Heimlich flutter valve has some significant advantages compared to under water seal drainage, the most important being its small size and its portability, allowing this way the immediate ambulation of the patient, a very important factor in the successful treatment of pneumothorax (1). It can function in any position and doesn’t need clamping (4). It has a small production cost, thus allowing it to be a disposable device, with no need of re-sterilization. Its function is easily understood both by the medical staff and the patient, due to the distinct sound and movement of the rubber sleeve. If there is need for fluid evacuation, the distal end may be attached to a collecting device, e.g., a bag or Bulau device. Also negative pressure or under water suction may be applied to the outlet nozzle if needed (1). The size of the drainage chest tubes that it can be attached to, may vary (small or large calibre tubes) (5). It may be used over a long-term period in cases that air-leakage is persistent and surgical treatment is excluded, allowing the outpatient management of these patients. Full expansion of the lung is indicated by absence of the “flutter” sound and the immobilization of the rubber tube of the valve during breathing and coughing. After full expansion is diagnosed and confirmed, the system (chest tube drainage and valve) may be removed from the patient. Small recurrences of pneumothorax have been described in the literature but they are usually insignificant (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
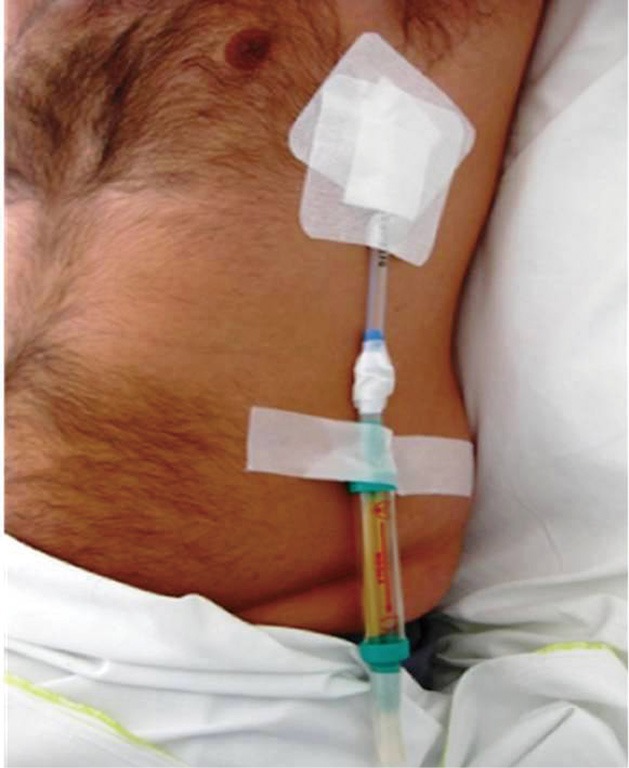
A Heimlich flutter valve connected to the chest drainage tube at the left chest wall.
Probably the most important thing about the Heimlich flutter valve is that it only functions properly under a specific orientation. This means that if it’s connected wrongly at the chest tube drainage it will not function at all. Furthermore, the patient undergoes great risk of developing tension pneumothorax, a very serious complication that may be fatal. If the outlet nozzle is attached to the tube, the rubber sleeve can’t open (due to its compression), the air can’t be evacuated and is accumulated in the pleural space, sometimes leading in tension pneumothorax. Case reports have been published describing this complication (6-8). For this reason, all the valves have distinct markings on the casing indicating clearly the inlet and outlet nozzles and the proper orientation of the valve during placement, so that reversal of the valve may be avoided.
Care must also be taken during attachment of bags or other collecting devices in the outlet nozzle, in order to not block the nozzle and prevent the evacuation of air (9). During outpatient management period, frequent inspection of the valve from the medical staff is mandatory.
Another major complication of the Heimlich flutter valve is the increased risk of developing chest empyema (10,11). This occurs through infection of the pleural space, mainly because of the prolonged remaining time of the chest tube drainage and the valve. The placement of the valve needs to be performed under sterile conditions (the valve itself is pre-sterilized) and all the attachments need to be secured and air-tight, in order to avoid further infection. Accidental dislodgements of the valve have been reported in the literature (2). In such case, re-attachment of the valve may be associated with increased risk of infection.
There isn’t any reported death in the literature, even in cases of accidental reversal of the valve and the development of tension pneumothorax. This proves that, if used correctly, and if the patient and the medical staff are properly instructed, the Heimlich flutter valve is a safe and efficient procedure for treating pneumothorax.
There is not any specific contraindication for the use of a Heimlich flutter valve in the literature. Relevant contraindications may be large hydro-pneumothorax with large volumes of fluid in the pleural space or thick secretions and blood which may cause occlusion of the rubber tube due to adhesions or clots, preventing the outflow of air (1,8). If such a case occurs, replacement of the valve or under water seal drainage is mandatory.
Studies have proved the safe use, with good results, of the valve in cases of primary pneumothorax treatment (1,12-30) and in many different cases of secondary pneumothorax in patients with Pneumonocystis carinii, AIDS, cystic fibrosis, lung metastases etc. (2,10,31-45).
The technological advances nowadays have allowed the construction of small, portable under water seal drainage devices, which also facilitate the immediate ambulation of the patient after placement and have lesser complications than the Heimlich flutter valve in cases where pneumothorax is accompanied by large volumes of fluid or blood (42,46-58). This has led to limited use of the valve over the recent years, but still holds a place in the outpatient management of patients with prolonged air-leakage, for whom further surgical treatment is not an option.
Acknowledgements
Disclosure: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Bernstein A, Waqaruddin M, Shah M.Management of spontaneous pneumothorax using a Heimlich flutter valve. Thorax 1973;28:386-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Edenborough FP, Hussain I, Stableforth DE. Use of a Heimlich flutter valve for pneumothorax in cystic fibrosis. Thorax 1994;49:1178-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fox B.Use of the Heimlich flutter valve for chest drainage in battle casualties. Aust N Z J Surg 1967;37:145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Heimlich HJ. Heimlich valve for chest drainage. Med Instrum 1983;17:29-31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chan KY, Fikri-Abdullah M, Sajjad M, et al. Outpatient treatment of spontaneous pneumothorax using an improved pocket sized Heimlich valve. Med J Malaysia 2003;58:597-9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mainini SE, Johnson FE. Tension pneumothorax complicating small-caliber chest tube insertion. Chest 1990;97:759-60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Spouge AR, Thomas HA. Tension pneumothorax after reversal of a Heimlich valve. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1992;158:763-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Crocker HL, Ruffin RE. Patient-induced complications of a Heimlich flutter valve. Chest 1998;113:838-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mariani PJ, Sharma S. Iatrogenic tension pneumothorax complicating outpatient Heimlich valve chest drainage. J Emerg Med 1994;12:477-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Van Hengel P, Van de Bergh JH. Heimlich valve treatment and outpatient management of bilateral metastatic pneumothorax. Chest 1994;105:1586-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Reinhold C, Illescas FF, Atri M, et al. Treatment of pleural effusions and pneumothorax with catheters placed percutaneously under imaging guidance. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1989;152:1189-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sargent EN, Turner AF. Emergency treatment of pneumothorax. A simple catheter technique for use in the radiology department. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 1970;109:531-5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kioumis IP, Zarogoulidis K, Huang H, et al. Pneumothorax in cystic fibrosis. J Thorac Dis 2014;6:S480-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kuhajda I, Zarogoulidis K, Kougioumtzi I, et al. Tube thoracostomy; chest tube implantation and follow up. J Thorac Dis 2014;6:S470-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Manika K, Kioumis I, Zarogoulidis K, et al. Pneumothorax in sarcoidosis. J Thorac Dis 2014;6:S466-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kuhajda I, Zarogoulidis K, Kougioumtzi I, et al. Penetrating trauma. J Thorac Dis 2014;6:S461-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Visouli AN, Zarogoulidis K, Kougioumtzi I, et al. Catamenial pneumothorax. J Thorac Dis 2014;6:S448-60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Huang Y, Huang H, Li Q, et al. Transbronchial lung biopsy and pneumothorax. J Thorac Dis 2014;6:S443-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Terzi E, Zarogoulidis K, Kougioumtzi I, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome and pneumothorax. J Thorac Dis 2014;6:S435-42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Boskovic T, Stojanovic M, Stanic J, et al. Pneumothorax after transbronchial needle biopsy. J Thorac Dis 2014;6:S427-34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Li Z, Huang H, Li Q, et al. Pneumothorax: observation. J Thorac Dis 2014;6:S421-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Huang Y, Huang H, Li Q, et al. Approach of the treatment for pneumothorax. J Thorac Dis 2014;6:S416-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Browning RF, Parrish S, Sarkar S, et al. Bronchoscopic interventions for severe COPD. J Thorac Dis 2014;6:S407-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Machairiotis N, Kougioumtzi I, Dryllis G, et al. Laparoscopy induced pneumothorax. J Thorac Dis 2014;6:S404-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ouellette DR, Parrish S, Browning RF, et al. Unusual causes of pneumothorax. J Thorac Dis 2014;6:S392-403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Parrish S, Browning RF, Turner JF, Jr, et al. The role for medical thoracoscopy in pneumothorax. J Thorac Dis 2014;6:S383-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Terzi E, Zarogoulidis K, Kougioumtzi I, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus infection and pneumothorax. J Thorac Dis 2014;6:S377-82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zarogoulidis P, Kioumis I, Pitsiou G, et al. Pneumothorax: from definition to diagnosis and treatment. J Thorac Dis 2014;6:S372-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Tsakiridis K, Mpakas A, Kesisis G, et al. Lung inflammatory response syndrome after cardiac-operations and treatment of lornoxicam. J Thorac Dis 2014;6Suppl 1:S78-98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tsakiridis K, Zarogoulidis P, Vretzkakis G, et al. Effect of lornoxicam in lung inflammatory response syndrome after operations for cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. J Thorac Dis 2014;6Suppl 1:S7-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Vricella LA, Trachiotis GD. Heimlich valve in the management of pneumothorax in patients with advanced AIDS. Chest 2001;120:15-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Driver AG, Peden JG, Adams HG, et al. Heimlich valve treatment of Pneumocystis carinii-associated pneumothorax. Chest 1991;100:281-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Argiriou M, Kolokotron SM, Sakellaridis T, et al. Right heart failure post left ventricular assist device implantation. J Thorac Dis 2014;6Suppl 1:S52-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Madesis A, Tsakiridis K, Zarogoulidis P, et al. Review of mitral valve insufficiency: repair or replacement. J Thorac Dis 2014;6Suppl 1:S39-51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Siminelakis S, Kakourou A, Batistatou A, et al. Thirteen years follow-up of heart myxoma operated patients: what is the appropriate surgical technique? J Thorac Dis 2014;6Suppl 1:S32-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Foroulis CN, Kleontas A, Karatzopoulos A, et al. Early reoperation performed for the management of complications in patients undergoing general thoracic surgical procedures. J Thorac Dis 2014;6Suppl 1:S21-31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nikolaos P, Vasilios L, Efstratios K, et al. Therapeutic modalities for Pancoast tumors. J Thorac Dis 2014;6Suppl 1:S180-93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Koutentakis M, Siminelakis S, Korantzopoulos P, et al. Surgical management of cardiac implantable electronic device infections. J Thorac Dis 2014;6Suppl 1:S173-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Spyratos D, Zarogoulidis P, Porpodis K, et al. Preoperative evaluation for lung cancer resection. J Thorac Dis 2014;6Suppl 1:S162-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Porpodis K, Zarogoulidis P, Spyratos D, et al. Pneumothorax and asthma. J Thorac Dis 2014;6Suppl 1:S152-61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Panagopoulos N, Leivaditis V, Koletsis E, et al. Pancoast tumors: characteristics and preoperative assessment. J Thorac Dis 2014;6Suppl 1:S108-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Visouli AN, Darwiche K, Mpakas A, et al. Catamenial pneumothorax: a rare entity? Report of 5 cases and review of the literature. J Thorac Dis 2012;4Suppl 1:17-31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zarogoulidis P, Chatzaki E, Hohenforst-Schmidt W, et al. Management of malignant pleural effusion by suicide gene therapy in advanced stage lung cancer: a case series and literature review. Cancer Gene Ther 2012;19:593-600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Papaioannou M, Pitsiou G, Manika K, et al. COPD assessment test: a simple tool to evaluate disease severity and response to treatment. COPD 2014;11:489-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Boskovic T, Stanic J, Pena-Karan S, et al. Pneumothorax after transthoracic needle biopsy of lung lesions under CT guidance. J Thorac Dis 2014;6Suppl 1:S99-107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Papaiwannou A, Zarogoulidis P, Porpodis K, et al. Asthma-chronic obstructive pulmonary disease overlap syndrome (ACOS): current literature review. J Thorac Dis 2014;6Suppl 1:S146-51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zarogoulidis P, Porpodis K, Kioumis I, et al. Experimentation with inhaled bronchodilators and corticosteroids. Int J Pharm 2014;461:411-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bai C, Huang H, Yao X, et al. Application of flexible bronchoscopy in inhalation lung injury. Diagn Pathol 2013;8:174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zarogoulidis P, Kioumis I, Porpodis K, et al. Clinical experimentation with aerosol antibiotics: current and future methods of administration. Drug Des Devel Ther 2013;7:1115-34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Zarogoulidis P, Pataka A, Terzi E, et al. Intensive care unit and lung cancer: when should we intubate? J Thorac Dis 2013;5Suppl 4:S407-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Hohenforst-Schmidt W, Petermann A, Visouli A, et al. Successful application of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation due to pulmonary hemorrhage secondary to granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Drug Des Devel Ther 2013;7:627-33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zarogoulidis P, Kontakiotis T, Tsakiridis K, et al. Difficult airway and difficult intubation in postintubation tracheal stenosis: a case report and literature review. Ther Clin Risk Manag 2012;8:279-86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Zarogoulidis P, Tsakiridis K, Kioumis I, et al. Cardiothoracic diseases: basic treatment. J Thorac Dis 2014;6Suppl 1:S1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kolettas A, Grosomanidis V, Kolettas V, et al. Influence of apnoeic oxygenation in respiratory and circulatory system under general anaesthesia. J Thorac Dis 2014;6Suppl 1:S116-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Turner JF, Quan W, Zarogoulidis P, et al. A case of pulmonary infiltrates in a patient with colon carcinoma. Case Rep Oncol 2014;7:39-42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Machairiotis N, Stylianaki A, Dryllis G, et al. Extrapelvic endometriosis: a rare entity or an under diagnosed condition? Diagn Pathol 2013;8:194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Tsakiridis K, Zarogoulidis P.An interview between a pulmonologist and a thoracic surgeon-Pleuroscopy: the reappearance of an old definition. J Thorac Dis 2013;5Suppl 4:S449-51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Huang H, Li C, Zarogoulidis P, et al. Endometriosis of the lung: report of a case and literature review. Eur J Med Res 2013;18:13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


