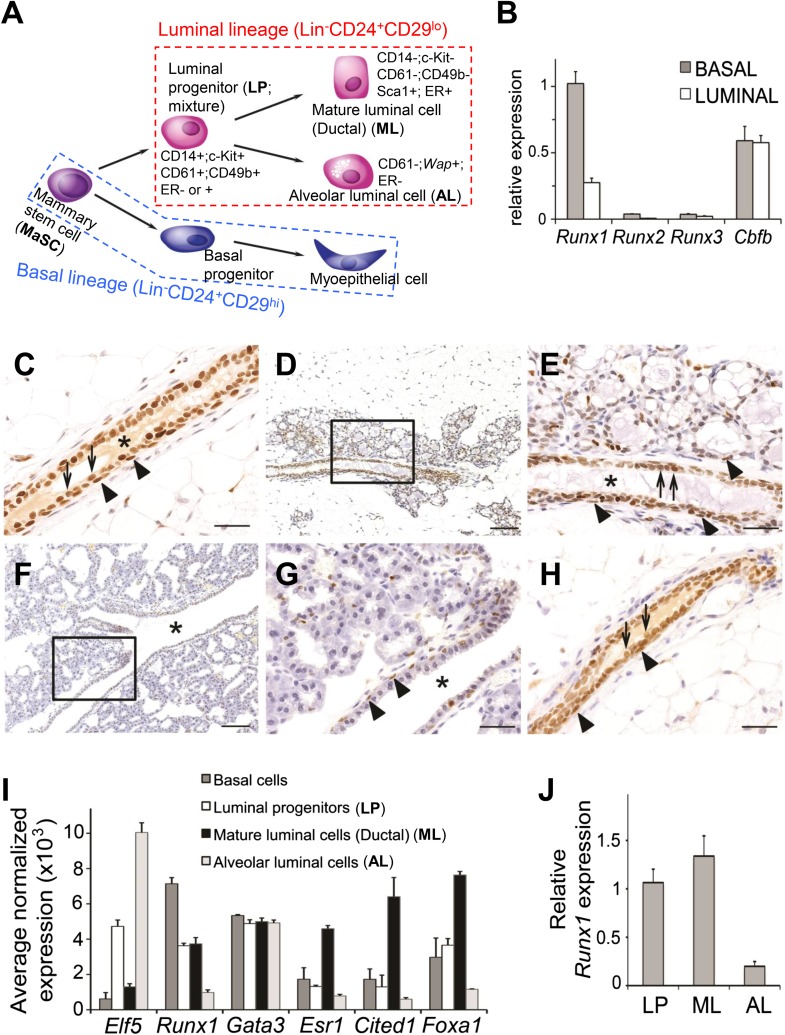
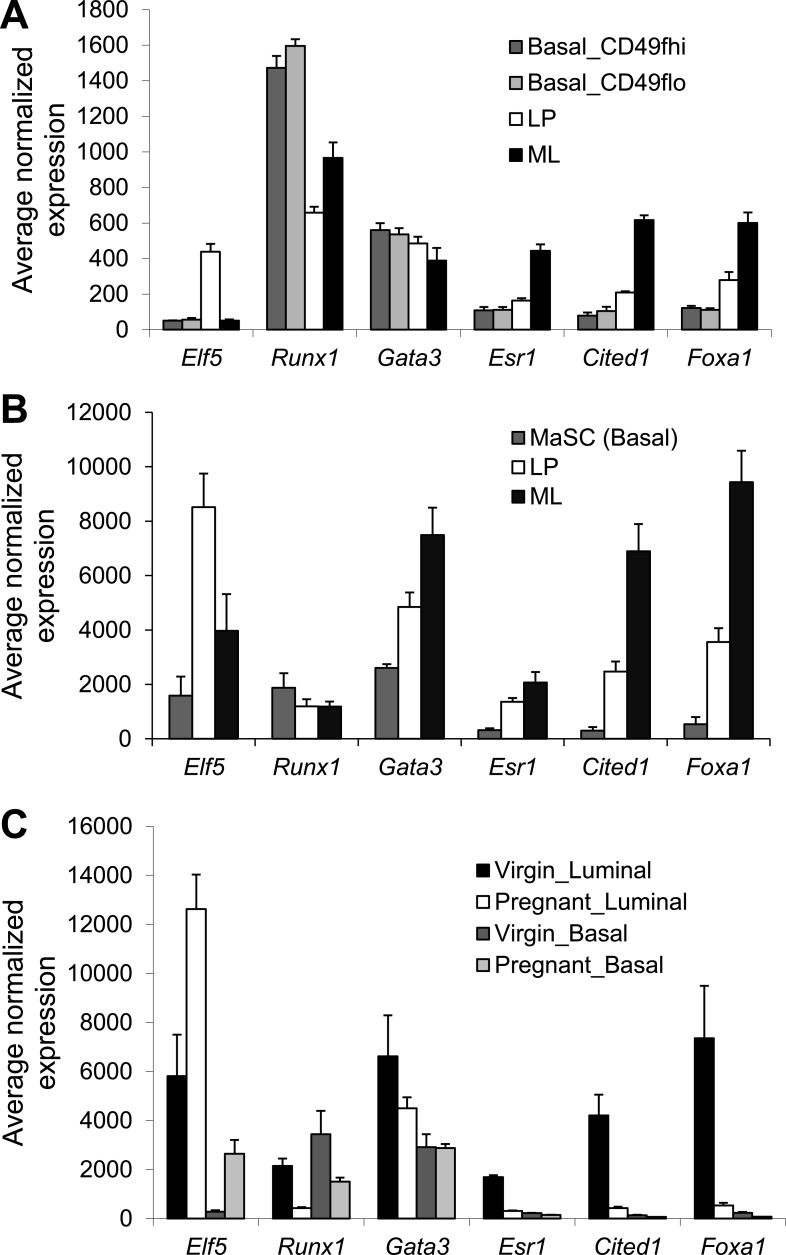
Figure 1. Expression pattern of Runx1 in murine MGs.
(A) Schematic diagram of a simplified version of the MEC hierarchy. MECs can be separated into the luminal and basal lineages. Major MEC subpopulations, their names and name abbreviations, as well as their marker expression patterns are shown. Note: ‘luminal progenitor (LP)’ has been used to refer to progenitor cells for the luminal lineage defined based on either CD61 (Asselin-Labat et al., 2007), or CD14 and c-Kit (Asselin-Labat et al., 2011), or CD49b (Li et al., 2009; Shehata et al., 2012), and is therefore a mixture of overlapping progenitor cell populations and may include common or separate progenitors for ductal and alveolar luminal cells. (B) qRT-PCR analysis of Runx1, Runx2, Runx3, and Cbfb transcripts isolated from luminal and basal cells of adult virgin female mice. (C–H) IHC staining for RUNX1 on sections of MGs at different developmental stages: (C) adult virgin, (D–E) mid-gestation (the region highlighted in D is shown in E), (F–G) lactation (the region highlighted in F is shown in G), and (H) after involution. Arrows and arrowheads indicate RUNX1-expressing luminal and basal cells, respectively; * indicates lumen. Scale bars = 20 μm. (I) Relative expression values of indicated genes determined by microarray analysis of the indicated MEC subpopulations isolated from the MGs of adult virgin female mice. ALs were isolated as YFP+ cells from Wap-Cre;R26Y females (i.e., MECs genetically marked by the Wap-Cre transgene) during mid-gestation. Affymetrix probes used to estimate expression of each indicated gene are 1419555_at, 1422864_at, 1448886_at, 1435663_at, 1449031_at, and 1418496_at for Elf5, Runx1, Gata3, Esr1, Cited1, and Foxa1, respectively. (J) Runx1 expression levels were confirmed in sorted LPs, MLs, and ALs (as in I) by qRT-PCR.