Abstract
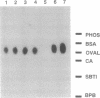
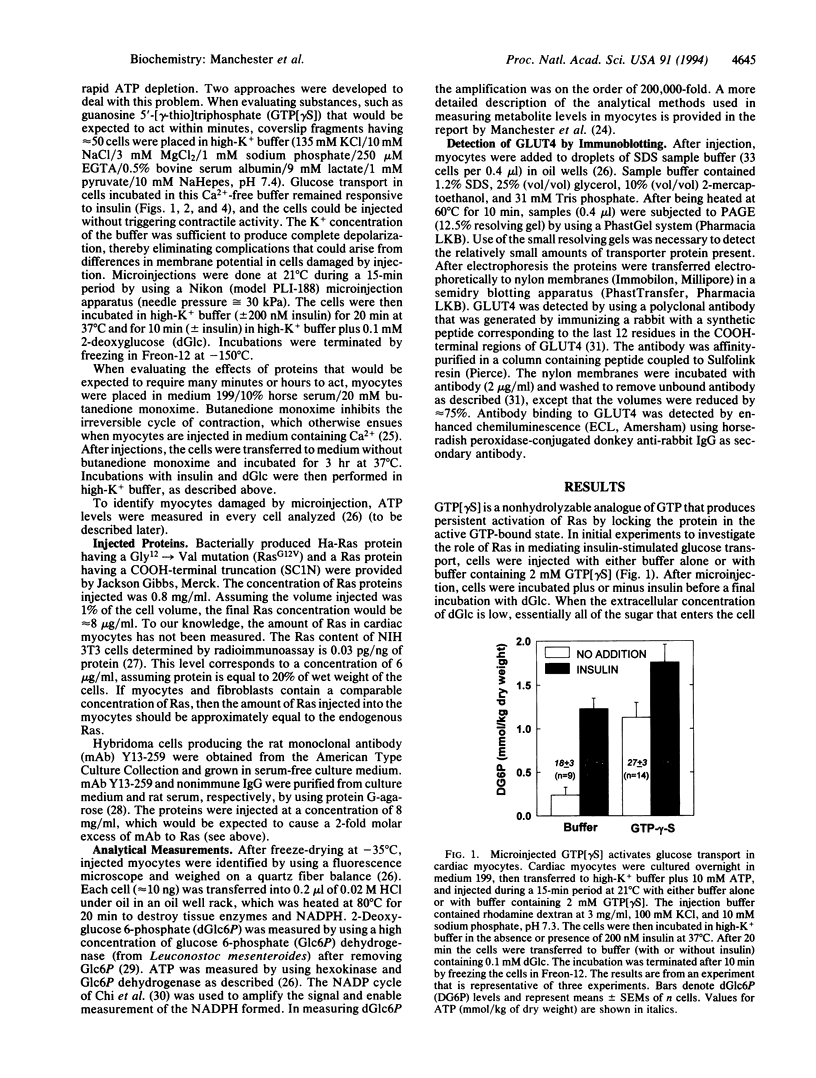
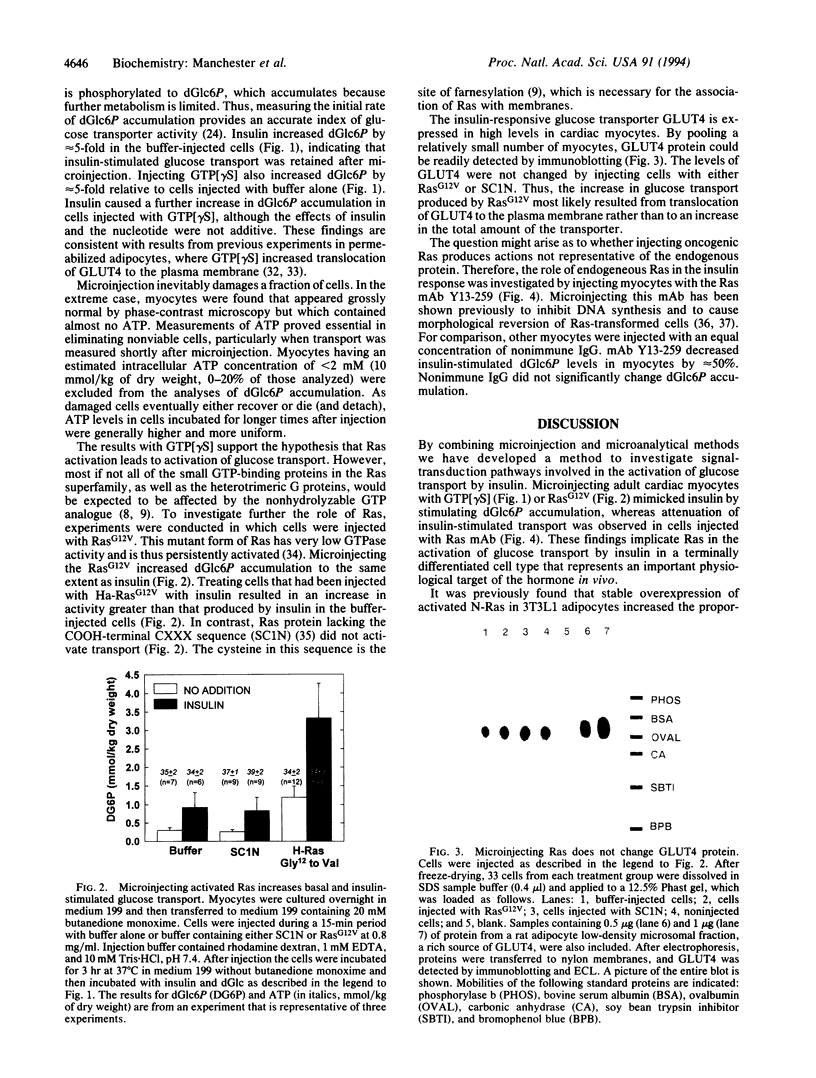
An approach involving microinjection and microanalysis has been developed to investigate signal-transduction pathways involved in the hormonal control of metabolism. We have applied this strategy to investigate the role of Ras signaling in the acute activation of glucose transport by insulin in cardiac myocytes. Glucose transport activity was assessed by measuring the initial rate of accumulation of 2-deoxyglucose 6-phosphate (dGlc6P) in individual cells after incubation in 2-deoxyglucose. Insulin increased accumulation of dGlc6P by 3- to 4-fold, consistent with its stimulatory effect on glucose transport. Accumulation of dGlc6P was increased severalfold by microinjecting the nonhydrolyzable GTP analogue, guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate, which activates members of the Ras superfamily of GTP-binding proteins. Injecting activated Ha-Ras protein also mimicked insulin by increasing dGlc6P; whereas, injecting a Ras protein lacking the COOH-terminal site of fatty acylation required for Ras function was without effect. Introducing the neutralizing Ras antibody Y13-259 into cells attenuated the effect of insulin. These findings implicate Ras in the acute regulation of metabolism by insulin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldini G., Hohman R., Charron M. J., Lodish H. F. Insulin and nonhydrolyzable GTP analogs induce translocation of GLUT 4 to the plasma membrane in alpha-toxin-permeabilized rat adipose cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4037–4040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltensperger K., Kozma L. M., Cherniack A. D., Klarlund J. K., Chawla A., Banerjee U., Czech M. P. Binding of the Ras activator son of sevenless to insulin receptor substrate-1 signaling complexes. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1950–1952. doi: 10.1126/science.8391166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J. Signal transduction via the MAP kinases: proceed at your own RSK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5889–5892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgering B. M., Medema R. H., Maassen J. A., van de Wetering M. L., van der Eb A. J., McCormick F., Bos J. L. Insulin stimulation of gene expression mediated by p21ras activation. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1103–1109. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caruso A., Schlom J., Vilasi V., Weeks M. O., Hand P. H. Development of quantitative liquid competition radioimmunoassays for the ras oncogene and proto-oncogene p21 products. Int J Cancer. 1986 Oct 15;38(4):587–595. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910380420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi M. M., Lowry C. V., Lowry O. H. An improved enzymatic cycle for nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate. Anal Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):119–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90732-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi M. M., Manchester J. K., Carter J. G., Pusateri M. E., McDougal D. B., Lowry O. H. A refinement of the Akabayashi-Saito-Kato modification of the enzymatic methods for 2-deoxyglucose and 2-deoxyglucose 6-phosphate. Anal Biochem. 1993 Mar;209(2):335–338. doi: 10.1006/abio.1993.1130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E. Glucose counterregulation: prevention and correction of hypoglycemia in humans. Am J Physiol. 1993 Feb;264(2 Pt 1):E149–E155. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1993.264.2.E149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M. Early events in insulin actions. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1986;20:293–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbrink J., Bihler I. Membrane transport: its relation to cellular metabolic rates. Science. 1975 Jun 20;188(4194):1177–1184. doi: 10.1126/science.1096301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Siebel C. W., McCormick F., Roth R. A. Ras p21 as a potential mediator of insulin action in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):840–843. doi: 10.1126/science.3554510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozma L., Baltensperger K., Klarlund J., Porras A., Santos E., Czech M. P. The ras signaling pathway mimics insulin action on glucose transporter translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4460–4464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung H. F., Smith M. R., Bekesi E., Manne V., Stacey D. W. Reversal of transformed phenotype by monoclonal antibodies against Ha-ras p21 proteins. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Feb;162(2):363–371. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90341-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., App H., Zhang X. F., Banerjee P., Brautigan D. L., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Raf-1 activates MAP kinase-kinase. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):417–421. doi: 10.1038/358417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. C., Jr Signal transduction and protein phosphorylation in the regulation of cellular metabolism by insulin. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:177–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.001141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Willumsen B. M. Function and regulation of ras. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:851–891. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.004223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakafuku M., Satoh T., Kaziro Y. Differentiation factors, including nerve growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, and interleukin-6, induce an accumulation of an active Ras.GTP complex in rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19448–19454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterop A. P., Medema R. H., Bos J. L., vd Zon G. C., Moller D. E., Flier J. S., Möller W., Maassen J. A. Relation between the insulin receptor number in cells, autophosphorylation and insulin-stimulated Ras.GTP formation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14647–14653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessin J. E., Bell G. I. Mammalian facilitative glucose transporter family: structure and molecular regulation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:911–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.004403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porras A., Nebreda A. R., Benito M., Santos E. Activation of Ras by insulin in 3T3 L1 cells does not involve GTPase-activating protein phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):21124–21131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell T., Twist V. W. A rapid technique for the isolation and purification of adult cardiac muscle cells having respiratory control and a tolerance to calcium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Sep 7;72(1):327–333. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90997-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson L. J., Pang S., Harris D. S., Heuser J., James D. E. Translocation of the glucose transporter (GLUT4) to the cell surface in permeabilized 3T3-L1 adipocytes: effects of ATP insulin, and GTP gamma S and localization of GLUT4 to clathrin lattices. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(6):1181–1196. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.6.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson L. J., Razzack Z. F., Lawrence J. C., Jr, James D. E. Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation is not sufficient for stimulation of glucose transport or glycogen synthase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26422–26427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson L. J., Razzack Z. F., Lawrence J. C., Jr, James D. E. Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation is not sufficient for stimulation of glucose transport or glycogen synthase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26422–26427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose D. W., Saltiel A. R., Majumdar M., Decker S. J., Olefsky J. M. Insulin receptor substrate 1 is required for insulin-mediated mitogenic signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):797–801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H., Colby W. W., Capon D. J., Goeddel D. V., Levinson A. D. Biological properties of human c-Ha-ras1 genes mutated at codon 12. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):71–75. doi: 10.1038/312071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth A., Alvarez E., Gupta S., Davis R. J. A phosphorylation site located in the NH2-terminal domain of c-Myc increases transactivation of gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23521–23524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sevetson B. R., Kong X., Lawrence J. C., Jr Increasing cAMP attenuates activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10305–10309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Hormonal regulation of mammalian glucose transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1059–1089. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Batzer A., Li N., Lee C. H., Lowenstein E., Mohammadi M., Margolis B., Schlessinger J. The function of GRB2 in linking the insulin receptor to Ras signaling pathways. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1953–1955. doi: 10.1126/science.8316835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Lee C. H., Batzer A., Vicentini L. M., Zhou M., Daly R., Myers M. J., Jr, Backer J. M., Ullrich A., White M. F. The SH2/SH3 domain-containing protein GRB2 interacts with tyrosine-phosphorylated IRS1 and Shc: implications for insulin control of ras signalling. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1929–1936. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., DeGudicibus S. R., Smith M. R. Cellular ras activity and tumor cell proliferation. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Jul;171(1):232–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temeles G. L., Gibbs J. B., D'Alonzo J. S., Sigal I. S., Scolnick E. M. Yeast and mammalian ras proteins have conserved biochemical properties. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):700–703. doi: 10.1038/313700a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorburn A., Thorburn J., Chen S. Y., Powers S., Shubeita H. E., Feramisco J. R., Chien K. R. HRas-dependent pathways can activate morphological and genetic markers of cardiac muscle cell hypertrophy. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):2244–2249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Kahn C. R. The insulin signaling system. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]