N—H⋯O=C bonded molecules of the title compound are linked into a inversion dimer with an  (8) motif.
(8) motif.
Keywords: crystal structure, barbiturate, hydrogen bonding, anaesthetic
Abstract
Molecules of the title compound, C14H18N2O3 [systematic name: 5-allyl-5-(hex-3-yn-2-yl)-1-methylpyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione in the (RbSh)/(SbRh) racemic form], are connected by mutual N—H⋯O=C hydrogen bonds in which the carbonyl group at the 2-position of the pyrimidinetrione ring is employed. These interactions result in an inversion dimer which displays a central R 2 2(8) ring motif. This dimer is topologically distinct from that of the previously reported (SbRh) form, which is, however, also based on an R 2 2(8) motif. The methyl group at the 1-position of the pyrimidinetrione ring in the title structure is disordered over two sets of sites in a 0.57 (2):0.43 (2) ratio.
Chemical context
The title compound is a barbiturate derivative, the Na salt of which (trade name Brevimytal, Eli Lilly) is a widely used short-acting anaesthetic with a rapid onset of action. The molecule contains two asymmetric centres and can exist as two diastereomeric enantiomer pairs. Its stereoisomerism is known to affect the anaesthetic activity and possible side effects of the drug (Gibson et al., 1959 ▸). The crystal structure of the (SbRh) form of methohexital was previously reported by Brunner et al. (2003 ▸), who also established that the commercial product (α-racemate) consists of the (RbSh) and (SbRh) isomers.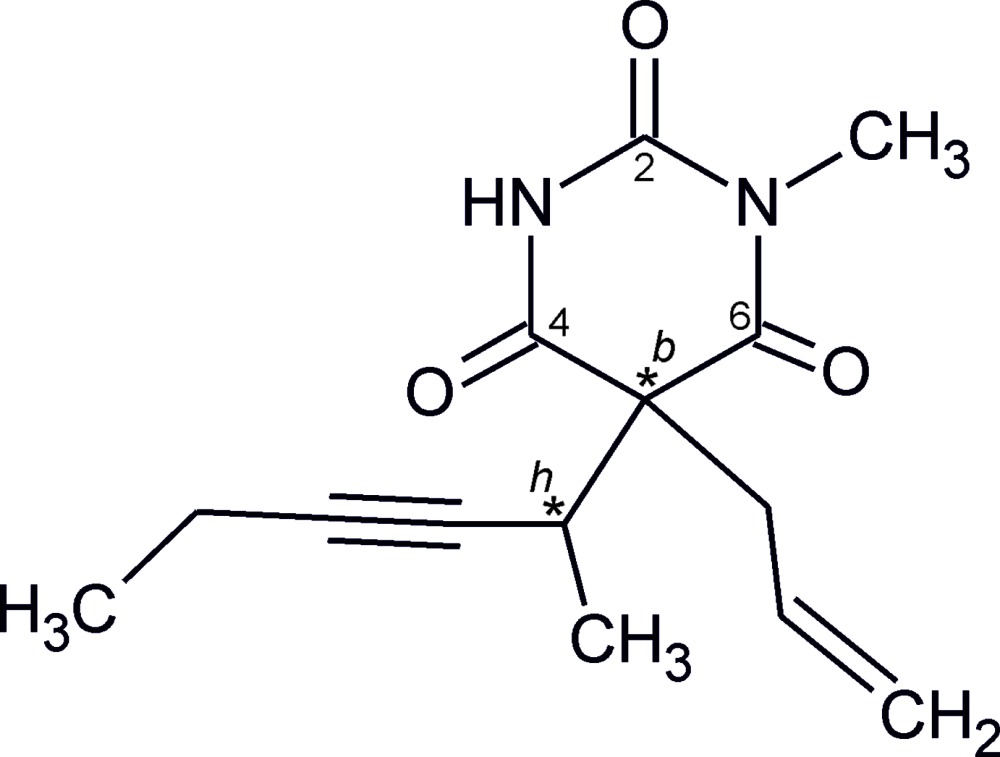
Structural commentary
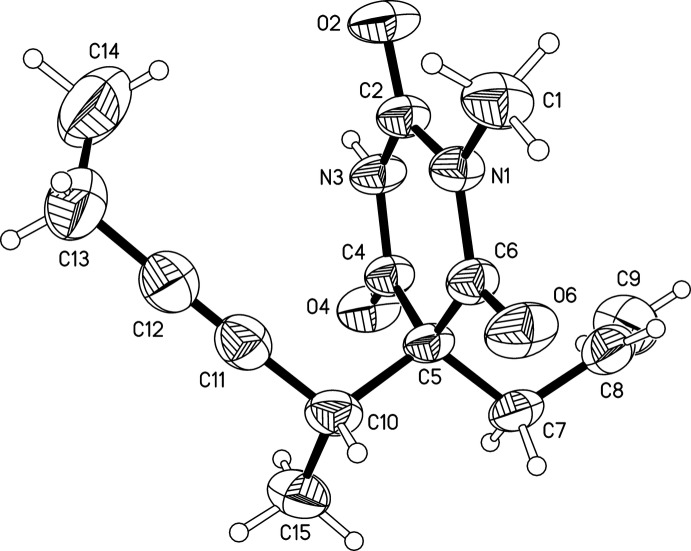
This study confirmed the presence of the (RbSh)/(SbRh) racemate. The molecule (Fig. 1 ▸) displays an approximately planar pyrimidinetrione unit in which the oxygen atoms of the C2 and C4 carbonyl groups lie at distances of −0.160 (2) and 0.156 (2) Å from the mean plane of the six-membered ring (r.m.s. deviation = 0.046 Å). The conformation of the two 5-substituents of the ring is characterized by three parameters, the torsion angles C5—C7—C8—C9 of −103.3 (2) and C10—C5—C7—C8 of −171.51 (13)° and the pseudo-torsion angle C5—C10⋯C13–C14 of 23.2 (2)°.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level; hydrogen atoms are drawn as spheres of arbitrary size.
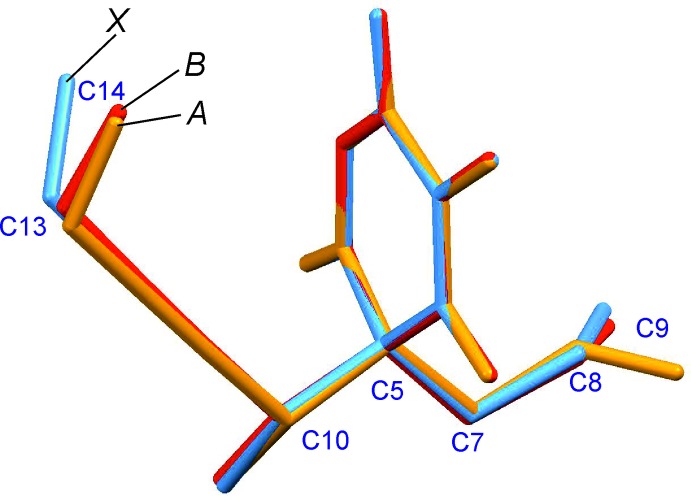
The previously reported (SbRh) form contains two independent molecules (denoted A and B), which differ from the molecule of the title structure in the conformation adopted by the terminal groups of both 5-substituents (Fig. 2 ▸). Specifically, in molecule A, the torsion angle analogous to C5—C7—C8—C9 in the present α-racemate is 125.3°, and the pseudo-torsion angles analogous to C5—C10⋯C13—C14 of the title structure are −15.4° (A) and −26.3° (B).
Figure 2.
Overlay of the molecule of the α-racemate (denoted X) with the two independent molecules (A, B) of the previously reported (SbRh) form, generated by least-squares fits of their 1-methyl-2,4,6-pyrimidinetrione units (ten non-H atomic positions).
Supramolecular features
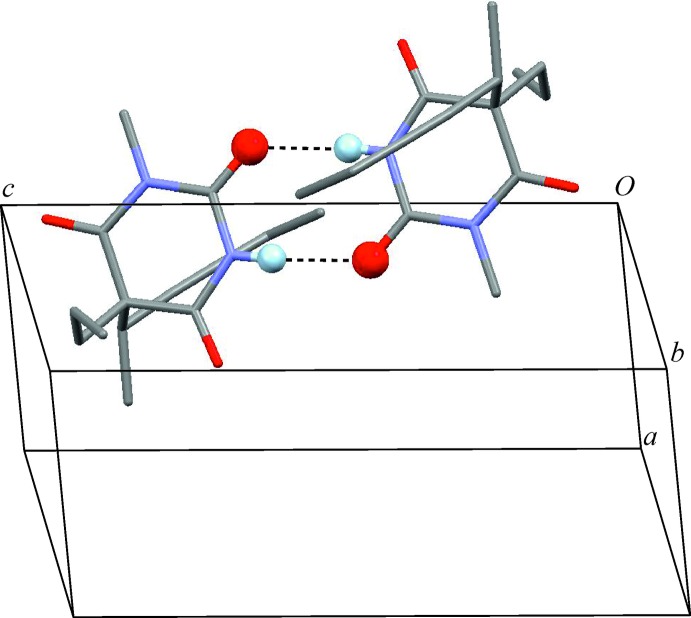
Two molecules are linked to one another by two mutual antiparallel N—H⋯O=C bonds so that an inversion dimer is formed (Table 1 ▸, Fig. 3 ▸), which displays a central 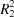 (8) ring motif (Etter et al., 1990 ▸; Bernstein et al., 1995 ▸). This interaction involves the carbonyl group at the 2-position of the ring. The
(8) ring motif (Etter et al., 1990 ▸; Bernstein et al., 1995 ▸). This interaction involves the carbonyl group at the 2-position of the ring. The 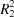 (8) ring motif is also present in the (SbRh) form (Brunner et al., 2003 ▸) where it connects the two crystallographically independent molecules. However, in this case the dimer is based on two topologically distinct N—H⋯O=C interactions which involve the carbonyl groups at the 4-position of the ring of molecule A and at the 2-position of molecule B.
(8) ring motif is also present in the (SbRh) form (Brunner et al., 2003 ▸) where it connects the two crystallographically independent molecules. However, in this case the dimer is based on two topologically distinct N—H⋯O=C interactions which involve the carbonyl groups at the 4-position of the ring of molecule A and at the 2-position of molecule B.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N3H3O2i | 0.85(2) | 2.03(2) | 2.8826(17) | 173.2(17) |
Symmetry code: (i) 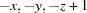 .
.
Figure 3.
The N—H⋯O=C hydrogen-bonded inversion dimer displaying a central 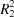 (8) ring. These interactions (dotted lines) involve the carbonyl group at the 2-position of the six-membered ring. O and H atoms engaged in hydrogen bonding are drawn as spheres.
(8) ring. These interactions (dotted lines) involve the carbonyl group at the 2-position of the six-membered ring. O and H atoms engaged in hydrogen bonding are drawn as spheres.
Database survey
The Cambridge Structural Database (Groom & Allen, 2014 ▸; Version 3.35) contains 11 unique entries for derivatives of barbituric acid which are analogous to the title compound and substituted at the 1-position, but not at the 3-position of the six-membered ring. A common characteristic of these compounds is the presence of one hydrogen-bond donor group (NH) and three potential acceptor groups, viz. the carbonyl groups at the ring positions 2, 4 and 6. Thus, three topologically distinct hydrogen-bonding acceptor interactions are possible. Additionally, there is a competition between possible dimer and catemer motifs, which is similar to the competition between hydrogen-bonded dimer and catemer motifs between carboxyl groups (Beyer & Price; 2000 ▸) or carboxamide groups (Arlin et al., 2010 ▸, 2011 ▸).
Closer inspection of the geometric possibilities (Fig. 4 ▸) shows that dimer formation is feasible for N—H⋯O=C2 and N—H⋯O=C4 connections only, whereas N—H⋯O=C6 should be the preferred connection mode for chain formation. Indeed, five crystal structures containing N—H⋯O=C6 chain motifs are known and their CSD refcodes are DMCYBA01 (Nichol & Clegg, 2005 ▸), DULMED (Gelbrich et al., 2010 ▸), MDEBAR (Wunderlich, 1973 ▸), MIBABA (Wilhelm & Fischer, 1976 ▸), OBIPUM (Gelbrich & Griesser, 2009 ▸). So far, the crystal structure with refcode VEMQUB (Savechenkov et al., 2012 ▸) is the only example in the set where another chain type, viz. N—H⋯O=C2, is present.
Figure 4.
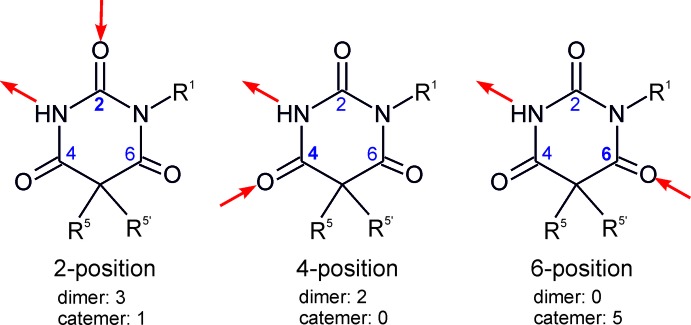
The three fundamental connection modes for the formation of N—H⋯O=C bonds in 1-substituted derivatives of barbituric acid arising from the involvement of different carbonyl groups, and the corresponding numbers of observed dimer and catemer isomers. The (SbRh) form of methohexithal contains a dimer with mixed N—H⋯O=C2/N—H⋯O=C4 connectivity and was therefore not included.
Apart from the title structure, two analogues with refcodes CXALBA (Dideberg et al., 1975 ▸) and DULMAZ (Gelbrich et al., 2010 ▸) also form N—H⋯O=C2 bonded dimers. The alternative N—H⋯O=C4 dimer was observed in the two structures with refcodes ALLBTC (Pyżalska et al., 1980 ▸) and MEPBAB01 (Lewis et al., 2005 ▸). The (SbRh) form of methohexital provides the only case of a dimer based on a mixed N—H⋯O=C2/N—H⋯O=C4 connectivity.
Synthesis and crystallization
The crystals investigated in this study were obtained at room temperature, by slow evaporation from an aqueous solution of the α-racemate of methohexital (Lilly Research Centre Ltd., Windlesham, England).
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. H atoms were identified in difference maps. The H atoms of the C14 methyl group and disordered C1 methyl group [occupancy ratio 0.57 (2):0.43 (2)] were idealized and included as rigid groups allowed to rotate but not tip (C—H = 0.96 Å) and refined with U iso set to 1.5U eq(C) of the parent carbon atom. H atoms bonded to secondary CH2 (C—H = 0.97 Å), tertiary CH (C—H = 0.98 Å) carbon and aromatic CH carbon atoms (C—H = 0.93 Å) were positioned geometrically and refined with U iso set to 1.2U eq(C) of the parent carbon atom. The NH hydrogen atom was refined with a restrained distance [N—H = 0.86 (2) Å] and its U iso parameter was freely refined.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C14H18N2O3 |
| M r | 262.30 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P

|
| Temperature (K) | 293 |
| a, b, c () | 7.7502(6), 7.9792(5), 12.6881(10) |
| , , () | 93.713(6), 96.226(6), 113.314(7) |
| V (3) | 711.32(10) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo K |
| (mm1) | 0.09 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.35 0.20 0.20 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Agilent Xcalibur (Ruby, Gemini ultra) |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2012 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.883, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2(I)] reflections | 6896, 3363, 2462 |
| R int | 0.022 |
| (sin /)max (1) | 0.690 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.049, 0.135, 1.05 |
| No. of reflections | 3363 |
| No. of parameters | 180 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| max, min (e 3) | 0.22, 0.20 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901500105X/wm5105sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901500105X/wm5105Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901500105X/wm5105Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1044166
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
We thank Volker Kahlenberg for access to the X-ray diffraction instrument used in this study.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C14H18N2O3 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 262.30 | F(000) = 280 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.225 Mg m−3 |
| a = 7.7502 (6) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 7.9792 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 1814 reflections |
| c = 12.6881 (10) Å | θ = 4.4–28.8° |
| α = 93.713 (6)° | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| β = 96.226 (6)° | T = 293 K |
| γ = 113.314 (7)° | Prism, colourless |
| V = 711.32 (10) Å3 | 0.35 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm |
Data collection
| Agilent Xcalibur (Ruby, Gemini ultra) diffractometer | 3363 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 2462 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.022 |
| Detector resolution: 10.3575 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 29.4°, θmin = 2.8° |
| ω scans | h = −9→10 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2012) | k = −11→9 |
| Tmin = 0.883, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −16→15 |
| 6896 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.049 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.135 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0572P)2 + 0.1234P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.05 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3363 reflections | Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3 |
| 180 parameters | Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. The C1 methyl group is disordered over two positions. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| N1 | −0.00769 (16) | −0.12155 (16) | 0.75511 (9) | 0.0382 (3) | |
| N3 | 0.15035 (17) | 0.08665 (17) | 0.63981 (10) | 0.0412 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.145 (2) | 0.115 (2) | 0.5763 (16) | 0.055 (5)* | |
| O2 | −0.12784 (15) | −0.15309 (16) | 0.58085 (9) | 0.0582 (4) | |
| O4 | 0.42793 (15) | 0.32706 (15) | 0.69135 (9) | 0.0546 (3) | |
| O6 | 0.12730 (17) | −0.09825 (17) | 0.92461 (9) | 0.0589 (3) | |
| C1 | −0.1759 (2) | −0.2810 (2) | 0.77286 (14) | 0.0550 (4) | |
| H1A | −0.1624 | −0.3036 | 0.8461 | 0.082* | 0.43 (2) |
| H1B | −0.2871 | −0.2566 | 0.7570 | 0.082* | 0.43 (2) |
| H1C | −0.1881 | −0.3870 | 0.7272 | 0.082* | 0.43 (2) |
| H1D | −0.2627 | −0.3279 | 0.7074 | 0.082* | 0.57 (2) |
| H1E | −0.1380 | −0.3749 | 0.7965 | 0.082* | 0.57 (2) |
| H1F | −0.2370 | −0.2445 | 0.8263 | 0.082* | 0.57 (2) |
| C2 | −0.0015 (2) | −0.06791 (19) | 0.65385 (11) | 0.0393 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.30668 (19) | 0.18923 (19) | 0.71322 (11) | 0.0376 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.32002 (19) | 0.11774 (19) | 0.82021 (11) | 0.0368 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.1393 (2) | −0.04093 (19) | 0.83867 (11) | 0.0383 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.3687 (2) | 0.2764 (2) | 0.90965 (12) | 0.0460 (4) | |
| H7A | 0.3993 | 0.2375 | 0.9775 | 0.055* | |
| H7B | 0.4802 | 0.3803 | 0.8970 | 0.055* | |
| C8 | 0.2092 (2) | 0.3359 (2) | 0.91640 (13) | 0.0527 (4) | |
| H8 | 0.1068 | 0.2623 | 0.9479 | 0.063* | |
| C9 | 0.2045 (3) | 0.4828 (3) | 0.88144 (18) | 0.0759 (6) | |
| H9A | 0.3047 | 0.5594 | 0.8496 | 0.091* | |
| H9B | 0.1010 | 0.5118 | 0.8882 | 0.091* | |
| C10 | 0.4766 (2) | 0.0383 (2) | 0.82568 (12) | 0.0463 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.4680 | −0.0253 | 0.8897 | 0.057 (5)* | |
| C11 | 0.4322 (2) | −0.1006 (2) | 0.73331 (14) | 0.0510 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.3973 (3) | −0.2041 (3) | 0.65519 (17) | 0.0620 (5) | |
| C13 | 0.3521 (4) | −0.3299 (3) | 0.55608 (19) | 0.0882 (7) | |
| H13A | 0.4699 | −0.3204 | 0.5319 | 0.106* | |
| H13B | 0.2858 | −0.4551 | 0.5716 | 0.106* | |
| C14 | 0.2356 (5) | −0.2930 (4) | 0.4700 (2) | 0.1143 (10) | |
| H14A | 0.2091 | −0.3809 | 0.4086 | 0.171* | |
| H14B | 0.3027 | −0.1714 | 0.4518 | 0.171* | |
| H14C | 0.1185 | −0.3025 | 0.4931 | 0.171* | |
| C15 | 0.6801 (2) | 0.1819 (3) | 0.83485 (16) | 0.0640 (5) | |
| H15A | 0.7656 | 0.1217 | 0.8353 | 0.096* | |
| H15B | 0.7106 | 0.2628 | 0.8999 | 0.096* | |
| H15C | 0.6922 | 0.2517 | 0.7751 | 0.096* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0343 (6) | 0.0402 (6) | 0.0336 (6) | 0.0085 (5) | 0.0022 (5) | 0.0091 (5) |
| N3 | 0.0409 (7) | 0.0458 (7) | 0.0270 (6) | 0.0083 (5) | −0.0027 (5) | 0.0108 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0463 (6) | 0.0661 (7) | 0.0372 (6) | −0.0001 (5) | −0.0087 (5) | 0.0094 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0494 (6) | 0.0501 (6) | 0.0469 (7) | 0.0019 (5) | 0.0011 (5) | 0.0168 (5) |
| O6 | 0.0592 (7) | 0.0696 (8) | 0.0345 (6) | 0.0109 (6) | 0.0028 (5) | 0.0210 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0428 (8) | 0.0541 (9) | 0.0541 (10) | 0.0037 (7) | 0.0054 (7) | 0.0182 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0366 (7) | 0.0430 (8) | 0.0328 (8) | 0.0117 (6) | −0.0010 (6) | 0.0069 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0357 (7) | 0.0389 (7) | 0.0326 (7) | 0.0100 (6) | 0.0014 (6) | 0.0072 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0351 (7) | 0.0424 (7) | 0.0276 (7) | 0.0115 (6) | −0.0017 (5) | 0.0054 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0396 (7) | 0.0429 (8) | 0.0302 (7) | 0.0143 (6) | 0.0026 (6) | 0.0081 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0433 (8) | 0.0508 (9) | 0.0329 (8) | 0.0110 (7) | −0.0046 (6) | −0.0011 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0504 (9) | 0.0550 (10) | 0.0433 (9) | 0.0138 (8) | 0.0031 (7) | −0.0034 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0711 (13) | 0.0635 (12) | 0.0904 (16) | 0.0273 (10) | 0.0032 (11) | 0.0041 (11) |
| C10 | 0.0434 (8) | 0.0571 (9) | 0.0387 (8) | 0.0215 (7) | −0.0007 (6) | 0.0112 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0491 (9) | 0.0562 (10) | 0.0533 (10) | 0.0268 (8) | 0.0064 (8) | 0.0122 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0633 (11) | 0.0639 (11) | 0.0663 (12) | 0.0352 (9) | 0.0044 (9) | 0.0051 (9) |
| C13 | 0.1023 (18) | 0.0897 (16) | 0.0816 (16) | 0.0565 (14) | −0.0012 (14) | −0.0187 (13) |
| C14 | 0.146 (3) | 0.130 (2) | 0.0667 (16) | 0.064 (2) | 0.0027 (17) | −0.0222 (15) |
| C15 | 0.0396 (9) | 0.0777 (12) | 0.0671 (12) | 0.0194 (9) | −0.0034 (8) | 0.0029 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| N1—C2 | 1.3800 (18) | C7—H7A | 0.9700 |
| N1—C6 | 1.3804 (17) | C7—H7B | 0.9700 |
| N1—C1 | 1.4687 (18) | C8—C9 | 1.292 (3) |
| N3—C2 | 1.3648 (18) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| N3—C4 | 1.3701 (17) | C9—H9A | 0.9300 |
| N3—H3 | 0.85 (2) | C9—H9B | 0.9300 |
| O2—C2 | 1.2140 (16) | C10—C11 | 1.471 (2) |
| O4—C4 | 1.2032 (17) | C10—C15 | 1.526 (2) |
| O6—C6 | 1.2083 (17) | C10—H10 | 0.9800 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9600 | C11—C12 | 1.182 (2) |
| C1—H1B | 0.9600 | C12—C13 | 1.474 (3) |
| C1—H1C | 0.9600 | C13—C14 | 1.460 (3) |
| C1—H1D | 0.9600 | C13—H13A | 0.9700 |
| C1—H1E | 0.9600 | C13—H13B | 0.9700 |
| C1—H1F | 0.9600 | C14—H14A | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.5151 (18) | C14—H14B | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.5248 (19) | C14—H14C | 0.9600 |
| C5—C7 | 1.541 (2) | C15—H15A | 0.9600 |
| C5—C10 | 1.574 (2) | C15—H15B | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.498 (2) | C15—H15C | 0.9600 |
| C2—N1—C6 | 123.81 (12) | O6—C6—C5 | 120.29 (12) |
| C2—N1—C1 | 117.84 (12) | N1—C6—C5 | 119.14 (12) |
| C6—N1—C1 | 118.24 (12) | C8—C7—C5 | 112.61 (12) |
| C2—N3—C4 | 127.42 (12) | C8—C7—H7A | 109.1 |
| C2—N3—H3 | 113.2 (12) | C5—C7—H7A | 109.1 |
| C4—N3—H3 | 119.3 (12) | C8—C7—H7B | 109.1 |
| N1—C1—H1A | 109.5 | C5—C7—H7B | 109.1 |
| N1—C1—H1B | 109.5 | H7A—C7—H7B | 107.8 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C9—C8—C7 | 124.36 (18) |
| N1—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C9—C8—H8 | 117.8 |
| H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C7—C8—H8 | 117.8 |
| H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C8—C9—H9A | 120.0 |
| N1—C1—H1D | 109.5 | C8—C9—H9B | 120.0 |
| H1A—C1—H1D | 141.1 | H9A—C9—H9B | 120.0 |
| H1B—C1—H1D | 56.3 | C11—C10—C15 | 110.95 (15) |
| H1C—C1—H1D | 56.3 | C11—C10—C5 | 109.25 (12) |
| N1—C1—H1E | 109.5 | C15—C10—C5 | 114.96 (14) |
| H1A—C1—H1E | 56.3 | C11—C10—H10 | 107.1 |
| H1B—C1—H1E | 141.1 | C15—C10—H10 | 107.1 |
| H1C—C1—H1E | 56.3 | C5—C10—H10 | 107.1 |
| H1D—C1—H1E | 109.5 | C12—C11—C10 | 176.00 (18) |
| N1—C1—H1F | 109.5 | C11—C12—C13 | 178.4 (2) |
| H1A—C1—H1F | 56.3 | C14—C13—C12 | 113.7 (2) |
| H1B—C1—H1F | 56.3 | C14—C13—H13A | 108.8 |
| H1C—C1—H1F | 141.1 | C12—C13—H13A | 108.8 |
| H1D—C1—H1F | 109.5 | C14—C13—H13B | 108.8 |
| H1E—C1—H1F | 109.5 | C12—C13—H13B | 108.8 |
| O2—C2—N3 | 121.50 (13) | H13A—C13—H13B | 107.7 |
| O2—C2—N1 | 121.22 (13) | C13—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| N3—C2—N1 | 117.27 (12) | C13—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| O4—C4—N3 | 120.57 (12) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| O4—C4—C5 | 122.59 (12) | C13—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| N3—C4—C5 | 116.82 (12) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 114.41 (11) | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C7 | 108.82 (12) | C10—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C7 | 108.29 (12) | C10—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C10 | 108.59 (12) | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C10 | 105.19 (11) | C10—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C7—C5—C10 | 111.55 (11) | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| O6—C6—N1 | 120.54 (13) | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C10—C5—C7—C8 | −171.51 (13) | C5—C7—C8—C9 | −103.3 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N3—H3···O2i | 0.85 (2) | 2.03 (2) | 2.8826 (17) | 173.2 (17) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x, −y, −z+1.
References
- Agilent (2012). CrysAlis PRO. Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
- Arlin, J.-B., Johnston, A., Miller, G. J., Kennedy, A. R., Price, S. L. & Florence, A. J. (2010). CrystEngComm 12, 64–66.
- Arlin, J.-B., Price, L. S., Price, S. L. & Florence, A. J. (2011). Chem. Commun. 47, 7074–7076. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Beyer, T. & Price, S. L. (2000). J. Phys. Chem. B, 104, 2647–2655.
- Brunner, H., Ittner, K.-P., Lunz, D., Schmatloch, S., Schmidt, T. & Zabel, M. (2003). Eur. J. Org. Chem. pp. 855–862.
- Dideberg, O., Dupont, L. & Pyzalska, D. (1975). Acta Cryst. B31, 685–688.
- Etter, M. C., MacDonald, J. C. & Bernstein, J. (1990). Acta Cryst. B46, 256–262. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gelbrich, T. & Griesser, U. (2009). Private communication (refcode OBIPUM). CCDC, Cambridge, England.
- Gelbrich, T., Zencirci, N. & Griesser, U. J. (2010). Acta Cryst. C66, o55–o58. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gibson, W. R., Doran, W. J., Wood, W. C. & Swanson, E. E. (1959). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 125, 23–27. [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R. & Allen, F. H. (2014). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 115–121.
- Lewis, W., McKeown, R. H. & Robinson, W. T. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o799–o800.
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 453–457.
- Nichol, G. S. & Clegg, W. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o1004–o1006.
- Pyżalska, D., Pyżalski, R. & Borowiak, T. (1980). Acta Cryst. B36, 1672–1675.
- Savechenkov, P. Y., Zhang, X., Chiara, D. C., Stewart, D. S., Ge, R., Zhou, X., Raines, D. E., Cohen, J. B., Forman, S. A., Miller, K. W. & Bruzik, K. S. (2012). J. Med. Chem. 55, 6554–6565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
- Wilhelm, E. & Fischer, K. F. (1976). Cryst. Struct. Commun. 5, 507–510.
- Wunderlich, H. (1973). Acta Cryst. B29, 168–173.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901500105X/wm5105sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901500105X/wm5105Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901500105X/wm5105Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1044166
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report