The mixed solvated salt 4-(2-chlorodibenzo[b,f][1,4]oxazepin-11-yl)piperazin-1-ium acetate–acetic acid–cyclohexane (2/2/1), crystallizes with one molecule of protonated amoxapine (AXPN), an acetate anion and a molecule of acetic acid together with half a molecule of cyclohexane. In the crystal, the various components are linked via N—H⋯O and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a layered structure with the solvent molecules occupying the spaces between the layers.
Keywords: crystal structure, amoxapine, oxazepine, mixed solvate, hydrogen bonding.
Abstract
The mixed solvated salt 4-(2-chlorodibenzo[b,f][1,4]oxazepin-11-yl)piperazin-1-ium acetate–acetic acid–cyclohexane (2/2/1), C17H17ClN3O+·C2H3O2 −·C2H4O2·0.5C6H12, crystallizes with one molecule of protonated amoxapine (AXPN), an acetate anion and a molecule of acetic acid together with half a molecule of cyclohexane. In the centrosymmetric crystal, both enantiomers of the protonated AXPN molecule stack alternatively along [001]. Acetate anions connect the AXPN cations through N—H⋯O hydrogen bonding in the [010] direction, creating a sheet lying parallel to (100). The acetic acid molecules are linked to the acetate anions via O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds within the sheets. Within the sheets there are also a number of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds present. The cyclohexane solvent molecules occupy the space between the sheets.
Chemical context
2-Chloro-11-(piperazin-1-yl)dibenzo[b,f][1,4]oxazepine (Amoxapine, AXPN) is a benzodiazepine derivative and exhibits anti-depressant properties (Greenbla & Osterber, 1968 ▸) with one reported crystal structure (CSD refcode: AMOXAP; Cosulich & Lovell, 1977 ▸). AXPN acetate acetic acid cyclohexane was obtained as a part of a wider investigation that couples experimental crystallization techniques with computational methods in order to obtain a better understanding of the factors underpinning the solid-state structure and diversity of structurally related compounds, i.e. olanzapine, clozapine, loxapine and AXPN (Bhardwaj & Florence, 2013 ▸; Bhardwaj, Johnston et al., 2013 ▸; Bhardwaj, Price et al., 2013 ▸). The sample of AXPN acetate acetic acid cyclohexane was isolated during an experimental physical form screen of AXPN. The sample was identified as a novel form using multi-sample foil transmission X-ray powder diffraction analysis (Florence et al., 2003 ▸). A suitable sample for single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis was obtained from slow evaporation of a saturated solution of AXPN in a 1:1 molar ratio of acetic acid and cyclohexane at room temperature.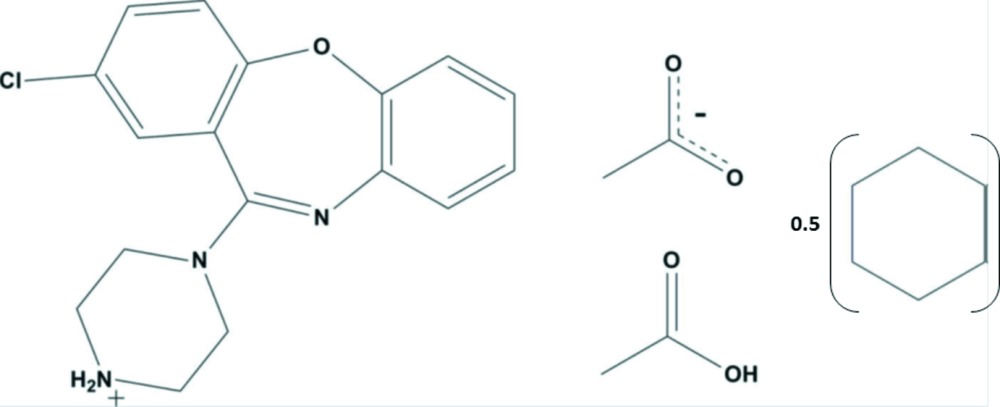
Structural commentary
The title compound crystallizes with one molecule of protonated AXPN and an acetate anion each with a molecule of acetic acid and a half molecule of cyclohexane (which lies across a center of inversion) as solvent of crystallization in the asymmetric unit (Fig. 1 ▸). The dioxazepine ring of AXPN exists in a puckered conformation between the planes of the benzene rings [the benzene rings fused to the central ring make a dihedral angle of 58.63 (6)°], and the piperazine ring adopts a chair conformation, as observed in the AXPN free base (CSD refcode: AMOXAP; Cosulich and Lovell, 1977 ▸) and structurally related analogues (Bhardwaj & Florence, 2013 ▸; Bhardwaj, Johnston et al., 2013 ▸; Bhardwaj, Price et al., 2013 ▸).
Figure 1.
A view of the molecular structure of the asymmetric unit of the title molecular salt, showing the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Supramolecular features
In the crystal, opposite enantiomers of protonated AXPN molecules stack along the c-axis direction. Each protonated AXPN molecule forms two N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds with two acetate anions, which connect it to an adjacent protonated AXPN molecule along the b axis, creating a sheet-like structure parallel to (100); see Fig. 2 ▸ and Table 1 ▸. The acetic acid molecules act as hydrogen-bond donors to acetate anions and are present between the protonated AXPN molecules along the c-axis direction. There are also C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds present within the sheets (Table 1 ▸). These sheets stack along the a axis and the cyclohexane molecules occupy the space between the sheets (Fig. 2 ▸).
Figure 2.
The crystal packing of the title molecular salt, viewed down the b axis. The cyclohexane molecules are shown as a blue space-fill model. Hydrogen bonds are shown as green lines (see Table 1 ▸ for details; atom colour code: C, N, O, Cl and H are blue, violet, red, green and black, respectively; H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N3H1N3O1S | 0.91(2) | 1.86(2) | 2.7664(13) | 175(2) |
| O3SH1SO2S i | 0.94(2) | 1.61(2) | 2.5375(13) | 171(2) |
| N3H2N3O1S ii | 0.94(2) | 1.82(2) | 2.7292(14) | 162(1) |
| C1SH1S1O3S ii | 0.96 | 2.42 | 3.3778(18) | 172 |
| C14H14AO1iii | 0.97 | 2.59 | 3.2448(15) | 125 |
| C17H17AO4S iii | 0.97 | 2.32 | 3.2314(15) | 155 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Synthesis and crystallization
Rod-shaped crystals were grown from a saturated solution of AXPN in a 1:1 molar ratio of acetic acid and cyclohexane by isothermal solvent evaporation at 298 K.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. The N- and O-bound H atoms were located in a difference Fourier map and freely refined. The C-bound H atoms were placed in calculated positions and refined as riding atoms: C—H = 0.95–0.99 Å with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C) for methyl H atoms and = 1.2U eq(C) for other H atoms.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C17H17ClN3O+C2H3O2 C2H4O20.5C6H12 |
| M r | 475.96 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 150 |
| a, b, c () | 21.0726(12), 6.0393(3), 18.6087(10) |
| () | 92.096(2) |
| V (3) | 2366.6(2) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo K |
| (mm1) | 0.20 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.55 0.22 0.11 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2007 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.647, 0.745 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2(I)] reflections | 18828, 4860, 4177 |
| R int | 0.018 |
| (sin /)max (1) | 0.626 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.030, 0.082, 1.03 |
| No. of reflections | 4860 |
| No. of parameters | 312 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| max, min (e 3) | 0.28, 0.22 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014028096/su5039sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014028096/su5039Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014028096/su5039Isup3.mol
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014028096/su5039Isup4.cml
CCDC reference: 1040948
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the UK Research Councils for funding under the project Control and Prediction of the Organic Solid State (www.cposs.org.uk). RMB thanks the Commonwealth Scholarship Commission for providing a scholarship.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C17H17ClN3O+·C2H3O2−·C2H4O2·0.5C6H12 | F(000) = 1008 |
| Mr = 475.96 | Dx = 1.336 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 9940 reflections |
| a = 21.0726 (12) Å | θ = 2.9–26.4° |
| b = 6.0393 (3) Å | µ = 0.20 mm−1 |
| c = 18.6087 (10) Å | T = 150 K |
| β = 92.096 (2)° | Rod, colourless |
| V = 2366.6 (2) Å3 | 0.55 × 0.22 × 0.11 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 4860 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 4177 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.018 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 26.4°, θmin = 1.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2007) | h = −26→26 |
| Tmin = 0.647, Tmax = 0.745 | k = −6→7 |
| 18828 measured reflections | l = −23→21 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.030 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.082 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0383P)2 + 1.089P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4860 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 312 parameters | Δρmax = 0.28 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| H2N3 | 0.0503 (7) | −0.014 (3) | 0.3171 (8) | 0.029 (4)* | |
| H1N3 | 0.0584 (7) | 0.167 (3) | 0.2658 (9) | 0.025 (4)* | |
| H1S | 0.1043 (10) | 0.564 (4) | 0.5635 (12) | 0.064 (6)* | |
| Cl | 0.276361 (16) | 0.39554 (6) | 0.594267 (17) | 0.02772 (10) | |
| O1 | 0.30157 (4) | 0.90957 (15) | 0.32837 (5) | 0.0225 (2) | |
| O2S | 0.07221 (4) | 0.03016 (16) | 0.13430 (5) | 0.0259 (2) | |
| O1S | 0.01425 (4) | 0.28471 (16) | 0.18632 (5) | 0.0234 (2) | |
| N3 | 0.07793 (5) | 0.09975 (18) | 0.30430 (6) | 0.0161 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.19325 (5) | 0.34168 (17) | 0.31916 (5) | 0.0160 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.27645 (5) | 0.48819 (18) | 0.25813 (6) | 0.0196 (2) | |
| C4 | 0.33285 (6) | 0.6088 (2) | 0.25098 (7) | 0.0198 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.25997 (5) | 0.4584 (2) | 0.45099 (6) | 0.0177 (2) | |
| H6 | 0.2404 | 0.3204 | 0.4501 | 0.021* | |
| C2S | 0.03703 (5) | 0.1974 (2) | 0.13128 (6) | 0.0175 (2) | |
| C5 | 0.24619 (5) | 0.4789 (2) | 0.31684 (6) | 0.0170 (2) | |
| C2 | 0.29573 (5) | 0.7852 (2) | 0.39086 (7) | 0.0183 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.31125 (6) | 0.7556 (2) | 0.51865 (7) | 0.0228 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.3256 | 0.8140 | 0.5625 | 0.027* | |
| C15 | 0.13972 (6) | 0.0041 (2) | 0.28291 (6) | 0.0167 (2) | |
| H15A | 0.1326 | −0.1006 | 0.2439 | 0.020* | |
| H15B | 0.1596 | −0.0741 | 0.3233 | 0.020* | |
| C1 | 0.26655 (5) | 0.5783 (2) | 0.38728 (7) | 0.0168 (2) | |
| C17 | 0.08763 (5) | 0.2614 (2) | 0.36432 (6) | 0.0169 (2) | |
| H17A | 0.1044 | 0.1855 | 0.4068 | 0.020* | |
| H17B | 0.0473 | 0.3278 | 0.3757 | 0.020* | |
| C7 | 0.28300 (6) | 0.5483 (2) | 0.51529 (7) | 0.0200 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.31772 (6) | 0.8743 (2) | 0.45570 (7) | 0.0219 (3) | |
| H9 | 0.3368 | 1.0133 | 0.4569 | 0.026* | |
| C16 | 0.13360 (5) | 0.4404 (2) | 0.34257 (7) | 0.0164 (2) | |
| H16A | 0.1145 | 0.5276 | 0.3037 | 0.020* | |
| H16B | 0.1425 | 0.5384 | 0.3830 | 0.020* | |
| C10 | 0.39883 (6) | 0.9372 (2) | 0.26691 (7) | 0.0264 (3) | |
| H10 | 0.4059 | 1.0745 | 0.2884 | 0.032* | |
| C3 | 0.34532 (6) | 0.8156 (2) | 0.28257 (7) | 0.0208 (3) | |
| C13 | 0.37702 (6) | 0.5278 (2) | 0.20305 (7) | 0.0234 (3) | |
| H13 | 0.3701 | 0.3911 | 0.1811 | 0.028* | |
| C14 | 0.18287 (6) | 0.1887 (2) | 0.25899 (6) | 0.0167 (2) | |
| H14A | 0.2231 | 0.1280 | 0.2446 | 0.020* | |
| H14B | 0.1634 | 0.2660 | 0.2182 | 0.020* | |
| C12 | 0.43094 (6) | 0.6479 (3) | 0.18768 (7) | 0.0275 (3) | |
| H12 | 0.4600 | 0.5904 | 0.1562 | 0.033* | |
| C1S | 0.02027 (7) | 0.2996 (3) | 0.05945 (7) | 0.0298 (3) | |
| H1S1 | −0.0177 | 0.2323 | 0.0396 | 0.045* | |
| H1S2 | 0.0544 | 0.2763 | 0.0275 | 0.045* | |
| H1S3 | 0.0134 | 0.4556 | 0.0653 | 0.045* | |
| C11 | 0.44173 (6) | 0.8535 (3) | 0.21911 (8) | 0.0297 (3) | |
| H11 | 0.4776 | 0.9348 | 0.2082 | 0.036* | |
| O4S | 0.15853 (5) | 0.90631 (17) | 0.46941 (5) | 0.0285 (2) | |
| O3S | 0.11677 (5) | 0.61112 (17) | 0.51804 (5) | 0.0266 (2) | |
| C4S | 0.16200 (7) | 0.8869 (2) | 0.59805 (7) | 0.0292 (3) | |
| H4S1 | 0.1780 | 1.0354 | 0.5958 | 0.044* | |
| H4S2 | 0.1937 | 0.7926 | 0.6202 | 0.044* | |
| H4S3 | 0.1246 | 0.8849 | 0.6259 | 0.044* | |
| C3S | 0.14591 (6) | 0.8053 (2) | 0.52335 (7) | 0.0212 (3) | |
| C6S | 0.44669 (7) | 0.4352 (3) | 0.45153 (8) | 0.0347 (4) | |
| H6S1 | 0.4659 | 0.3259 | 0.4209 | 0.042* | |
| H6S2 | 0.4024 | 0.4505 | 0.4362 | 0.042* | |
| C5S | 0.45086 (7) | 0.3553 (3) | 0.52918 (9) | 0.0363 (4) | |
| H5S1 | 0.4317 | 0.2097 | 0.5322 | 0.044* | |
| H5S2 | 0.4274 | 0.4555 | 0.5591 | 0.044* | |
| C7S | 0.48016 (7) | 0.6561 (3) | 0.44293 (9) | 0.0370 (4) | |
| H7S1 | 0.4580 | 0.7693 | 0.4691 | 0.044* | |
| H7S2 | 0.4789 | 0.6974 | 0.3925 | 0.044* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl | 0.02984 (17) | 0.0361 (2) | 0.01704 (16) | 0.00076 (14) | −0.00169 (12) | 0.00358 (14) |
| O1 | 0.0221 (4) | 0.0177 (4) | 0.0275 (5) | −0.0006 (4) | −0.0010 (4) | 0.0056 (4) |
| O2S | 0.0311 (5) | 0.0282 (5) | 0.0183 (5) | 0.0132 (4) | 0.0001 (4) | 0.0000 (4) |
| O1S | 0.0258 (5) | 0.0263 (5) | 0.0179 (4) | 0.0112 (4) | 0.0001 (4) | 0.0005 (4) |
| N3 | 0.0174 (5) | 0.0156 (5) | 0.0151 (5) | −0.0033 (4) | −0.0012 (4) | 0.0029 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0154 (5) | 0.0161 (5) | 0.0165 (5) | −0.0018 (4) | 0.0005 (4) | −0.0018 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0178 (5) | 0.0222 (5) | 0.0186 (5) | −0.0040 (4) | −0.0010 (4) | 0.0033 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0183 (6) | 0.0232 (7) | 0.0175 (6) | −0.0036 (5) | −0.0034 (5) | 0.0071 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0149 (5) | 0.0185 (6) | 0.0197 (6) | 0.0015 (5) | −0.0005 (4) | −0.0006 (5) |
| C2S | 0.0154 (5) | 0.0197 (6) | 0.0174 (6) | −0.0009 (5) | −0.0012 (4) | 0.0017 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0164 (5) | 0.0151 (6) | 0.0192 (6) | −0.0001 (5) | −0.0024 (4) | 0.0025 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0146 (5) | 0.0179 (6) | 0.0223 (6) | 0.0017 (5) | −0.0010 (5) | 0.0020 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0184 (6) | 0.0274 (7) | 0.0222 (6) | 0.0019 (5) | −0.0036 (5) | −0.0073 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0201 (6) | 0.0144 (6) | 0.0155 (6) | 0.0002 (5) | −0.0011 (4) | 0.0011 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0133 (5) | 0.0175 (6) | 0.0196 (6) | 0.0010 (4) | −0.0013 (4) | −0.0007 (5) |
| C17 | 0.0171 (5) | 0.0184 (6) | 0.0154 (6) | −0.0001 (5) | 0.0010 (4) | 0.0006 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0166 (6) | 0.0259 (7) | 0.0175 (6) | 0.0040 (5) | −0.0005 (5) | 0.0011 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0164 (6) | 0.0192 (6) | 0.0298 (7) | −0.0009 (5) | −0.0021 (5) | −0.0047 (5) |
| C16 | 0.0173 (6) | 0.0141 (6) | 0.0179 (6) | −0.0001 (4) | 0.0003 (4) | −0.0003 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0266 (7) | 0.0256 (7) | 0.0264 (7) | −0.0086 (6) | −0.0048 (5) | 0.0074 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0184 (6) | 0.0235 (7) | 0.0202 (6) | −0.0008 (5) | −0.0029 (5) | 0.0074 (5) |
| C13 | 0.0228 (6) | 0.0281 (7) | 0.0193 (6) | −0.0038 (5) | −0.0009 (5) | 0.0039 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0176 (5) | 0.0173 (6) | 0.0150 (6) | −0.0011 (5) | −0.0001 (4) | −0.0002 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0211 (6) | 0.0394 (8) | 0.0221 (7) | −0.0036 (6) | 0.0017 (5) | 0.0069 (6) |
| C1S | 0.0350 (7) | 0.0344 (8) | 0.0197 (7) | 0.0083 (6) | −0.0014 (6) | 0.0068 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0221 (6) | 0.0392 (8) | 0.0278 (7) | −0.0122 (6) | −0.0008 (5) | 0.0099 (6) |
| O4S | 0.0308 (5) | 0.0296 (5) | 0.0254 (5) | 0.0071 (4) | 0.0062 (4) | 0.0109 (4) |
| O3S | 0.0309 (5) | 0.0308 (5) | 0.0182 (5) | −0.0071 (4) | 0.0018 (4) | 0.0010 (4) |
| C4S | 0.0341 (7) | 0.0292 (8) | 0.0244 (7) | −0.0058 (6) | 0.0035 (6) | −0.0020 (6) |
| C3S | 0.0188 (6) | 0.0233 (7) | 0.0215 (6) | 0.0054 (5) | 0.0027 (5) | 0.0031 (5) |
| C6S | 0.0226 (7) | 0.0481 (9) | 0.0332 (8) | 0.0057 (6) | −0.0017 (6) | −0.0085 (7) |
| C5S | 0.0256 (7) | 0.0440 (9) | 0.0394 (9) | 0.0011 (6) | 0.0031 (6) | −0.0021 (7) |
| C7S | 0.0302 (8) | 0.0467 (9) | 0.0341 (8) | 0.0076 (7) | −0.0009 (6) | 0.0030 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl—C7 | 1.7450 (13) | C16—H16A | 0.9700 |
| O1—C2 | 1.3936 (15) | C16—H16B | 0.9700 |
| O1—C3 | 1.3985 (16) | C10—C3 | 1.3856 (18) |
| O2S—C2S | 1.2529 (15) | C10—C11 | 1.387 (2) |
| O1S—C2S | 1.2623 (15) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| N3—C15 | 1.4918 (15) | C13—C12 | 1.3866 (18) |
| N3—C17 | 1.4919 (16) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| N3—H2N3 | 0.938 (17) | C14—H14A | 0.9700 |
| N3—H1N3 | 0.908 (16) | C14—H14B | 0.9700 |
| N2—C5 | 1.3916 (15) | C12—C11 | 1.388 (2) |
| N2—C14 | 1.4618 (15) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C16 | 1.4716 (15) | C1S—H1S1 | 0.9600 |
| N1—C5 | 1.2863 (16) | C1S—H1S2 | 0.9600 |
| N1—C4 | 1.4044 (16) | C1S—H1S3 | 0.9600 |
| C4—C13 | 1.4006 (19) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C3 | 1.4010 (19) | O4S—C3S | 1.2125 (16) |
| C6—C7 | 1.3852 (17) | O3S—C3S | 1.3256 (16) |
| C6—C1 | 1.4005 (17) | O3S—H1S | 0.94 (2) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C4S—C3S | 1.5019 (19) |
| C2S—C1S | 1.5027 (17) | C4S—H4S1 | 0.9600 |
| C5—C1 | 1.4905 (17) | C4S—H4S2 | 0.9600 |
| C2—C9 | 1.3854 (18) | C4S—H4S3 | 0.9600 |
| C2—C1 | 1.3929 (17) | C6S—C7S | 1.520 (2) |
| C8—C9 | 1.3845 (19) | C6S—C5S | 1.523 (2) |
| C8—C7 | 1.3867 (19) | C6S—H6S1 | 0.9700 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9300 | C6S—H6S2 | 0.9700 |
| C15—C14 | 1.5156 (16) | C5S—C7Si | 1.527 (2) |
| C15—H15A | 0.9700 | C5S—H5S1 | 0.9700 |
| C15—H15B | 0.9700 | C5S—H5S2 | 0.9700 |
| C17—C16 | 1.5164 (16) | C7S—C5Si | 1.527 (2) |
| C17—H17A | 0.9700 | C7S—H7S1 | 0.9700 |
| C17—H17B | 0.9700 | C7S—H7S2 | 0.9700 |
| C9—H9 | 0.9300 | ||
| C2—O1—C3 | 111.72 (9) | C3—C10—C11 | 119.77 (13) |
| C15—N3—C17 | 110.86 (9) | C3—C10—H10 | 120.1 |
| C15—N3—H2N3 | 110.0 (10) | C11—C10—H10 | 120.1 |
| C17—N3—H2N3 | 111.0 (10) | C10—C3—O1 | 118.21 (12) |
| C15—N3—H1N3 | 109.7 (9) | C10—C3—C4 | 121.72 (13) |
| C17—N3—H1N3 | 110.1 (10) | O1—C3—C4 | 119.99 (11) |
| H2N3—N3—H1N3 | 105.1 (13) | C12—C13—C4 | 121.16 (13) |
| C5—N2—C14 | 116.76 (10) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.4 |
| C5—N2—C16 | 117.53 (10) | C4—C13—H13 | 119.4 |
| C14—N2—C16 | 112.18 (9) | N2—C14—C15 | 108.33 (9) |
| C5—N1—C4 | 123.41 (11) | N2—C14—H14A | 110.0 |
| C13—C4—C3 | 117.37 (12) | C15—C14—H14A | 110.0 |
| C13—C4—N1 | 117.62 (12) | N2—C14—H14B | 110.0 |
| C3—C4—N1 | 124.68 (12) | C15—C14—H14B | 110.0 |
| C7—C6—C1 | 119.10 (12) | H14A—C14—H14B | 108.4 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 120.4 | C13—C12—C11 | 120.26 (13) |
| C1—C6—H6 | 120.4 | C13—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| O2S—C2S—O1S | 122.84 (11) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| O2S—C2S—C1S | 119.38 (11) | C2S—C1S—H1S1 | 109.5 |
| O1S—C2S—C1S | 117.79 (11) | C2S—C1S—H1S2 | 109.5 |
| N1—C5—N2 | 118.38 (11) | H1S1—C1S—H1S2 | 109.5 |
| N1—C5—C1 | 126.41 (11) | C2S—C1S—H1S3 | 109.5 |
| N2—C5—C1 | 114.71 (10) | H1S1—C1S—H1S3 | 109.5 |
| C9—C2—C1 | 121.55 (12) | H1S2—C1S—H1S3 | 109.5 |
| C9—C2—O1 | 118.71 (11) | C10—C11—C12 | 119.73 (13) |
| C1—C2—O1 | 119.72 (11) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.1 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 119.01 (12) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.1 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 120.5 | C3S—O3S—H1S | 110.1 (14) |
| C7—C8—H8 | 120.5 | C3S—C4S—H4S1 | 109.5 |
| N3—C15—C14 | 109.42 (10) | C3S—C4S—H4S2 | 109.5 |
| N3—C15—H15A | 109.8 | H4S1—C4S—H4S2 | 109.5 |
| C14—C15—H15A | 109.8 | C3S—C4S—H4S3 | 109.5 |
| N3—C15—H15B | 109.8 | H4S1—C4S—H4S3 | 109.5 |
| C14—C15—H15B | 109.8 | H4S2—C4S—H4S3 | 109.5 |
| H15A—C15—H15B | 108.2 | O4S—C3S—O3S | 119.90 (12) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 118.71 (11) | O4S—C3S—C4S | 123.51 (13) |
| C2—C1—C5 | 121.06 (11) | O3S—C3S—C4S | 116.59 (11) |
| C6—C1—C5 | 120.13 (11) | C7S—C6S—C5S | 111.54 (13) |
| N3—C17—C16 | 109.77 (9) | C7S—C6S—H6S1 | 109.3 |
| N3—C17—H17A | 109.7 | C5S—C6S—H6S1 | 109.3 |
| C16—C17—H17A | 109.7 | C7S—C6S—H6S2 | 109.3 |
| N3—C17—H17B | 109.7 | C5S—C6S—H6S2 | 109.3 |
| C16—C17—H17B | 109.7 | H6S1—C6S—H6S2 | 108.0 |
| H17A—C17—H17B | 108.2 | C6S—C5S—C7Si | 110.96 (13) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 121.92 (12) | C6S—C5S—H5S1 | 109.4 |
| C6—C7—Cl | 118.96 (10) | C7Si—C5S—H5S1 | 109.4 |
| C8—C7—Cl | 119.13 (10) | C6S—C5S—H5S2 | 109.4 |
| C8—C9—C2 | 119.70 (12) | C7Si—C5S—H5S2 | 109.4 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 120.2 | H5S1—C5S—H5S2 | 108.0 |
| C2—C9—H9 | 120.2 | C6S—C7S—C5Si | 111.37 (13) |
| N2—C16—C17 | 110.55 (10) | C6S—C7S—H7S1 | 109.4 |
| N2—C16—H16A | 109.5 | C5Si—C7S—H7S1 | 109.4 |
| C17—C16—H16A | 109.5 | C6S—C7S—H7S2 | 109.4 |
| N2—C16—H16B | 109.5 | C5Si—C7S—H7S2 | 109.4 |
| C17—C16—H16B | 109.5 | H7S1—C7S—H7S2 | 108.0 |
| H16A—C16—H16B | 108.1 | ||
| C5—N1—C4—C13 | 148.72 (12) | C9—C8—C7—Cl | 178.58 (9) |
| C5—N1—C4—C3 | −38.18 (18) | C7—C8—C9—C2 | 0.34 (18) |
| C4—N1—C5—N2 | −175.55 (11) | C1—C2—C9—C8 | 0.53 (18) |
| C4—N1—C5—C1 | −4.1 (2) | O1—C2—C9—C8 | 178.70 (11) |
| C14—N2—C5—N1 | 10.69 (16) | C5—N2—C16—C17 | −162.34 (10) |
| C16—N2—C5—N1 | −127.00 (12) | C14—N2—C16—C17 | 58.13 (12) |
| C14—N2—C5—C1 | −161.70 (10) | N3—C17—C16—N2 | −54.59 (12) |
| C16—N2—C5—C1 | 60.61 (14) | C11—C10—C3—O1 | −177.05 (11) |
| C3—O1—C2—C9 | 111.88 (12) | C11—C10—C3—C4 | −0.4 (2) |
| C3—O1—C2—C1 | −69.92 (13) | C2—O1—C3—C10 | −117.96 (12) |
| C17—N3—C15—C14 | −59.51 (12) | C2—O1—C3—C4 | 65.30 (14) |
| C9—C2—C1—C6 | −0.46 (17) | C13—C4—C3—C10 | 0.51 (18) |
| O1—C2—C1—C6 | −178.62 (10) | N1—C4—C3—C10 | −172.60 (12) |
| C9—C2—C1—C5 | −176.70 (11) | C13—C4—C3—O1 | 177.14 (11) |
| O1—C2—C1—C5 | 5.14 (17) | N1—C4—C3—O1 | 4.02 (18) |
| C7—C6—C1—C2 | −0.46 (17) | C3—C4—C13—C12 | 0.09 (18) |
| C7—C6—C1—C5 | 175.81 (11) | N1—C4—C13—C12 | 173.70 (12) |
| N1—C5—C1—C2 | 38.92 (18) | C5—N2—C14—C15 | 159.85 (10) |
| N2—C5—C1—C2 | −149.41 (11) | C16—N2—C14—C15 | −60.29 (12) |
| N1—C5—C1—C6 | −137.27 (13) | N3—C15—C14—N2 | 60.12 (12) |
| N2—C5—C1—C6 | 34.41 (16) | C4—C13—C12—C11 | −0.8 (2) |
| C15—N3—C17—C16 | 56.29 (12) | C3—C10—C11—C12 | −0.4 (2) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | 1.35 (18) | C13—C12—C11—C10 | 1.0 (2) |
| C1—C6—C7—Cl | −178.52 (9) | C7S—C6S—C5S—C7Si | −55.20 (19) |
| C9—C8—C7—C6 | −1.29 (18) | C5S—C6S—C7S—C5Si | 55.42 (18) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N3—H1N3···O1S | 0.91 (2) | 1.86 (2) | 2.7664 (13) | 175 (2) |
| O3S—H1S···O2Sii | 0.94 (2) | 1.61 (2) | 2.5375 (13) | 171 (2) |
| N3—H2N3···O1Siii | 0.94 (2) | 1.82 (2) | 2.7292 (14) | 162 (1) |
| C1S—H1S1···O3Siii | 0.96 | 2.42 | 3.3778 (18) | 172 |
| C14—H14A···O1iv | 0.97 | 2.59 | 3.2448 (15) | 125 |
| C17—H17A···O4Siv | 0.97 | 2.32 | 3.2314 (15) | 155 |
Symmetry codes: (ii) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (iii) −x, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (iv) x, y−1, z.
References
- Allen, F. H., Johnson, O., Shields, G. P., Smith, B. R. & Towler, M. (2004). J. Appl. Cryst. 37, 335–338.
- Bhardwaj, R. M. & Florence, A. J. (2013). Acta Cryst. E69, o752–o753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, R. M., Johnston, B. F., Oswald, I. D. H. & Florence, A. J. (2013). Acta Cryst. C69, 1273–1278. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, R. M., Price, L. S., Price, S. L., Reutzel-Edens, S. M., Miller, G. J., Oswald, I. D. H., Johnston, B. & Florence, A. J. (2013). Cryst. Growth Des. 13, 1602–1617.
- Bruker (2007). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cosulich, D. B. & Lovell, F. M. (1977). Acta Cryst. B33, 1147–1154.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Florence, A. J., Baumgartner, B., Weston, C., Shankland, N., Kennedy, A. R., Shankland, K. & David, W. I. F. (2003). J. Pharm. Sci. 92, 1930–1938. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Greenbla, E. & Osterber, A. (1968). Fed. Proc. 27, 438.
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014028096/su5039sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014028096/su5039Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014028096/su5039Isup3.mol
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014028096/su5039Isup4.cml
CCDC reference: 1040948
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




