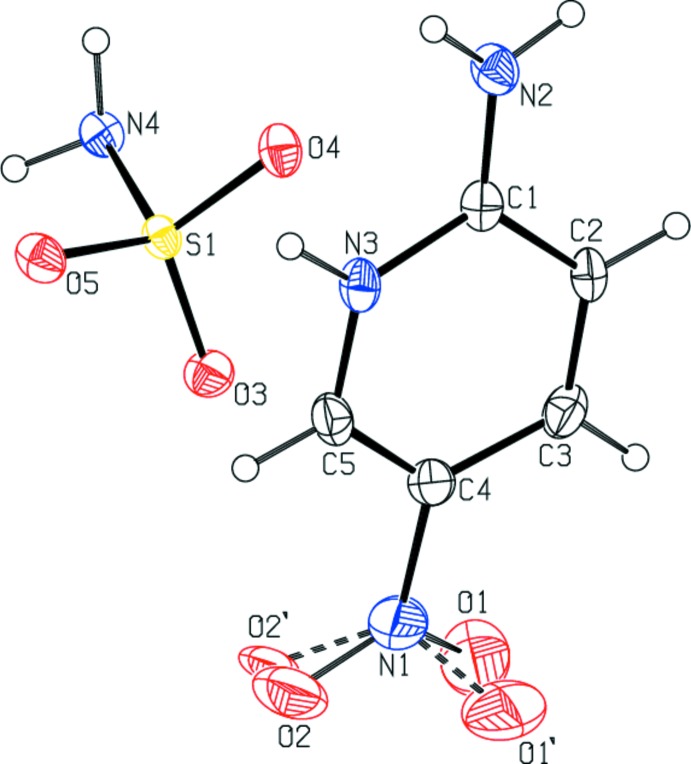
The title molecular salt, obtained by the reaction of sulfamic acid with 2-amino-5-nitropyridine, is the result of a proton transfer from sulfamic acid to the N atom of the pyridine ring. In the crystal, the cations and anions are linked by a number of N—H⋯O and N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming sheets lying parallel to (100).
Keywords: crystal structure, sulfamic acid, 2-amino-5-nitropyridine, sulfamate, 2-amino-5-pyridinium, molecular salt, hydrogen bonding.
Abstract
The title molecular salt, C5H6N3O2 + ·H2NO3S−, was obtained from the reaction of sulfamic acid with 2-amino-5-nitropyridine. A proton transfer from sulfamic acid to the pyridine N atom occurred, resulting in the formation of a salt. As expected, this protonation leads to the widening of the C—N—C angle of the pyridine ring, to 122.9 (3)°, with the pyridinium ring being essentially planar (r.m.s. deviation = 0.025 Å). In the crystal, the ion pairs are joined by three N—H⋯O and one N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds in which the pyridinium N atom and the amino N atom act as donors, and are hydrogen bonded to the carboxylate O atoms and the N atom of the sulfamate anion, thus generating an R 3 3(22) ring motif. These motifs are linked by further N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds enclosing R 3 3(8) loops, forming sheets parallel to (100). The sheets are linked via weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a three-dimensional structure. The O atoms of the nitro group are disordered over two sets of sites with a refined occupancy ratio of 0.737 (19):0.263 (19).
Chemical context
Pyridine heterocycles and their derivatives are present in many large molecules having photo-chemical, electro-chemical and catalytic applications. Some pyridine derivatives possess non-linear optical (NLO) properties (Babu et al., 2014a
▸,b
▸). Simple organic–inorganic salts containing strong intermolecular hydrogen bonds have attracted attention as materials which display ferroelectric–paraelectric phase transitions (Sethuram, et al., 2013a
▸,b
▸; Huq et al., 2013 ▸; Shihabuddeen Syed et al., 2013 ▸; Showrilu et al., 2013 ▸). We have recently reported the crystal structures of 2-amino-6-methylpyridinium 2,2,2-trichloroacetate (Babu et al., 2014a
▸), 2-amino-6-methylpyridinium 4-methylbenzenesulfonate (Babu et al., 2014b
▸) and 2-amino-5-nitropyridinium hydrogen oxalate (Rajkumar et al., 2014 ▸). In a continuation of our studies of pyridinium salts, we report herein on the crystal structure of the title molecular salt, obtained by the reaction of 2-amino-5-nitropyridine with sulfamic acid.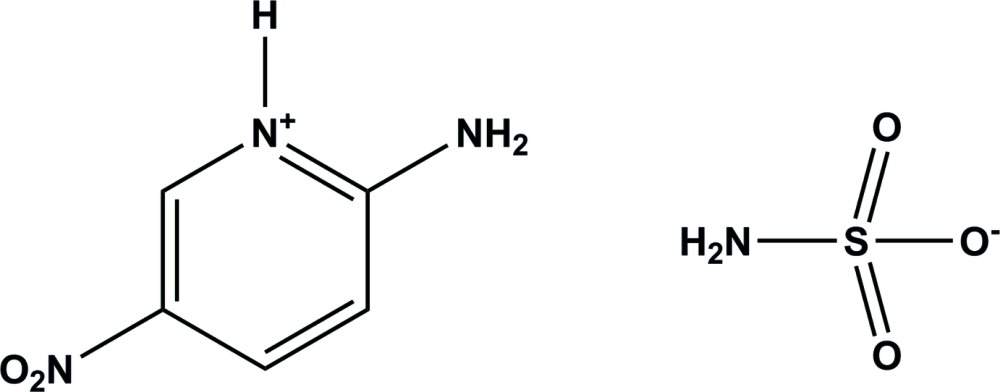
Structural commentary
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, Fig. 1 ▸, consists of a 2-amino-5-nitropyridin-1-ium cation and a sulfamate anion. The bond lengths and angles are within normal ranges and comparable with those in closely related structures (Babu et al., 2014a ▸,b ▸; Rajkumar et al., 2014 ▸). A proton transfer from the sulfamic acid to the pyridine atom N3 resulted in the formation of a salt. This protonation leads to the widening of the C5—N3—C1 angle of the pyridine ring to 122.9 (3)°, compared with 115.25 (13)° in unprotonated aminopyridine (Anderson et al., 2005 ▸). This type of protonation is observed in various aminopyridine acid complexes (Babu et al., 2014a ▸,b ▸; Rajkumar et al., 2014 ▸). In the sulfamate anion the S—O distances vary from 1.440 (3) to 1.460 (2) Å, and O—S—O angles vary from 111.59 (15) to 114.22 (15) °.
Figure 1.
View of the molecular structure of the title molecular salt, with atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
In the cation, the N2—C1 [1.317 (5) Å] bond is shorter than the N3—C1 [1.357 (4) Å] and N3—C5 [1.340 (5) Å] bonds, and the C1—C2 [1.411 (5) Å] and C3—C4 [1.402 (6) Å] bonds lengths are significantly longer than bonds C2—C3 [1.348 (5) Å] and C4—C5 [1.338 (6) Å], similar to those observed previously for the aminopyridinium cation (Babu et al., 2014a ▸,b ▸; Rajkumar et al., 2014 ▸). In contrast, in the solid-state structure of aminopyridinium, the C—N(H2) bond is clearly longer than that in the ring (Nahringbauer & Kvick, 1977 ▸). The geometrical features of the aminopyridinium cation (N1/N3/C1–C5) resemble those observed in other 2-aminopyridinium structures (Babu et al., 2014a ▸,b ▸; Rajkumar et al., 2014 ▸) that are believed to be involved in amine–imine tautomerism (Ishikawa et al., 2002 ▸). However, previous studies have shown that a pyridinium cation always possesses an expanded C—N—C angle in comparison with pyridine itself (Jin et al., 2005 ▸).
In this atomic arrangement, one can distinguish the intercation-to-anion contact C5—H5⋯O3 (H5⋯O5 = 2.41 Å), which induces the aggregation of the independent organic cation 2-amino-5-nitropyridinium. This kind of arrangement is also observed in the related structure of 2-amino-5-nitropyridinium hydrogen selenate (Akriche & Rzaigui, 2009 ▸). These pairs are located between the anionic layers to link them by various interactions. The geometric features of the organic cation are usual and comparable with values observed for other 2-amino nitropyridinium compounds (Akriche & Rzaigui, 2009 ▸). It is worth noticing that the C—NH2 [1.317 (5) Å] and C—NO2 [1.449 (6) Å] distances in the cations are, respectively, shortened and lengthened with respect to the same bond lengths [1.337 (4) and 1.429 (4) Å] observed for 2-amino-nitropyridine (Aakeroy et al., 1998 ▸). All the 2-amino-nitropyridinium cations encapsulated in various anionic sub-networks show the same changes in the C—NH2 and C—NO2 distances, revealing a weak increase of π bond character in the bond C—NH2 and a decrease in the bond C—NO2.
Supramolecular features
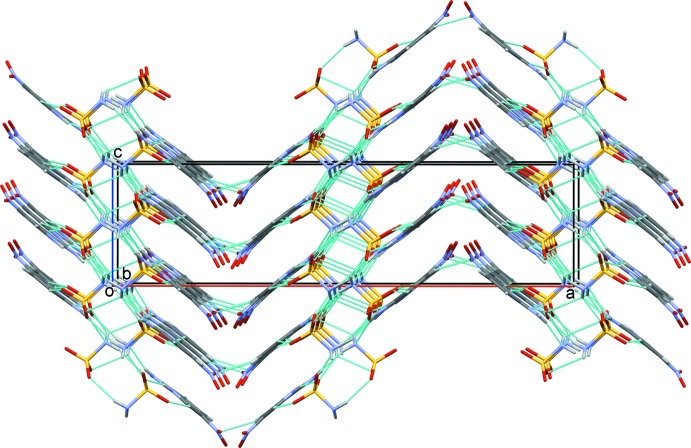
In the crystal, the ion pairs are linked by the N—H⋯O and N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 2 ▸). The protonated atom (N3) and the 2-amino group (N2) of the cation are hydrogen bonded to the carboxylate oxygen atoms (O5 and O4) and the nitrogen atom (N4) of the sulfamate anion via a pair of N—H⋯O and N—H⋯N (N3—H3A⋯O5, N2—H2B⋯O4 and N2—H2A⋯N4) hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸), forming an 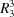 (22)ring motif. These motifs are further linked by N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, enclosing
(22)ring motif. These motifs are further linked by N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, enclosing 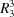 (8) loops, and forming sheets lying parallel to (100). Weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the sheets, forming a three-dimensional structure (Fig. 2 ▸ and Table 1 ▸). The identification of such supramolecular patterns will help us design and construct preferred hydrogen-bonding patterns of drug-like molecules.
(8) loops, and forming sheets lying parallel to (100). Weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the sheets, forming a three-dimensional structure (Fig. 2 ▸ and Table 1 ▸). The identification of such supramolecular patterns will help us design and construct preferred hydrogen-bonding patterns of drug-like molecules.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2H2BO4i | 0.88(2) | 1.98(2) | 2.861(4) | 176(4) |
| N2H2AN4ii | 0.88(2) | 2.18(2) | 3.044(4) | 169(4) |
| N3H3AO5iii | 0.89(2) | 1.91(2) | 2.766(4) | 163(4) |
| N4H4BO4iv | 0.89(2) | 2.20(2) | 3.073(4) | 166(3) |
| N4H4AO5v | 0.89(2) | 2.20(2) | 2.960(4) | 143(3) |
| C2H2O3i | 0.93 | 2.57 | 3.469(4) | 163 |
| C3H3O2vi | 0.93 | 2.46 | 3.328(13) | 155 |
| C5H5O3iii | 0.93 | 2.41 | 3.187(4) | 141 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 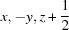 ; (ii)
; (ii) 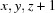 ; (iii)
; (iii) 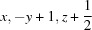 ; (iv)
; (iv) 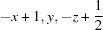 ; (v)
; (v) 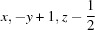 ; (vi)
; (vi) 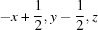 .
.
Figure 2.
The crystal packing of the title salt, viewed along the b axis. The hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 ▸ for details; only the major components of the disordered nitro O atoms are shown).
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, Version 5.35, May 2014; Groom & Allen, 2014 ▸) for the cation 2-amino-5-nitropyridinium gave 42 hits for which there were 36 hits with atomic coordinates present. For these structures, the average C—N—C bond angle is ca 123°, while the average C—N(H2) and C—N(O2) bond lengths are ca 1.32 and 1.45 Å, respectively. A search for the anion aminosulfamate gave 23 hits but only 17 contained atomic coordinates. Here the S—O bond lengths vary from ca 1.399 to 1.469 Å, while the N—S bond length varies from ca 1.63 to 1.80 Å. The bond lengths and angles in the title salt are very similar to those reported for the various structures in the CSD.
Synthesis and crystallization
The starting material 2-amino-5-nitropyridine was obtained by treating 3-nitropyridine with ammonia in the presence of KMnO4. Colourless block-like crystals of the title salt were obtained by slow evaporation of a 1:1 equimolar mixture of 2-amino-5-nitropyridine and sulfamic acid in methanol at room temperature.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. The N-bound H atoms were located in a difference Fourier map and refined with distance restraints: N—H = 0.89 (2) Å. The C-bound H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model: C—H = 0.93 Å with U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C). The O atoms of the nitro group are disordered over two sets of sites (O1/O1′ and O2/O2′) with a refined occupancy ratio of 0.737 (19):0.263 (19).
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C5H6N3O2 +H2NO3S |
| M r | 236.21 |
| Crystal system, space group | Orthorhombic, P b c n |
| Temperature (K) | 293 |
| a, b, c () | 28.0866(10), 9.0052(3), 7.4023(2) |
| V (3) | 1872.23(10) |
| Z | 8 |
| Radiation type | Mo K |
| (mm1) | 0.36 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.35 0.30 0.25 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.887, 0.917 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2(I)] reflections | 15358, 1653, 1557 |
| R int | 0.024 |
| (sin /)max (1) | 0.594 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.055, 0.111, 1.28 |
| No. of reflections | 1653 |
| No. of parameters | 175 |
| No. of restraints | 50 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| max, min (e 3) | 0.27, 0.45 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015000365/su5048sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015000365/su5048Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015000365/su5048Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1042506
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
MAR, PAD and SSJX would like to thank the Board of Research in the Nuclear Sciences Department of Atomic Energy (BRNS–DAE) (File No. 2012/34/63/BRNS/2865; date: 01 March 2013) for funding this major research project.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C5H6N3O2+·H2NO3S− | F(000) = 976 |
| Mr = 236.21 | Dx = 1.676 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pbcn | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2n 2ab | Cell parameters from 1653 reflections |
| a = 28.0866 (10) Å | θ = 2.4–31.1° |
| b = 9.0052 (3) Å | µ = 0.36 mm−1 |
| c = 7.4023 (2) Å | T = 293 K |
| V = 1872.23 (10) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.35 × 0.30 × 0.25 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 1653 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1557 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.024 |
| ω and φ scans | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.4° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004) | h = −33→33 |
| Tmin = 0.887, Tmax = 0.917 | k = −10→10 |
| 15358 measured reflections | l = −8→8 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.055 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.111 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.28 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0116P)2 + 5.4481P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1653 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 175 parameters | Δρmax = 0.27 e Å−3 |
| 50 restraints | Δρmin = −0.44 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| C1 | 0.38918 (12) | 0.1439 (4) | 0.6248 (5) | 0.0269 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.35730 (13) | 0.0484 (4) | 0.5342 (5) | 0.0292 (8) | |
| H2 | 0.3602 | −0.0538 | 0.5477 | 0.035* | |
| C3 | 0.32268 (13) | 0.1047 (4) | 0.4283 (5) | 0.0373 (9) | |
| H3 | 0.3014 | 0.0421 | 0.3693 | 0.045* | |
| C4 | 0.31924 (13) | 0.2591 (4) | 0.4085 (6) | 0.0371 (9) | |
| C5 | 0.34829 (13) | 0.3498 (4) | 0.4998 (5) | 0.0345 (9) | |
| H5 | 0.3453 | 0.4522 | 0.4880 | 0.041* | |
| N1 | 0.28526 (15) | 0.3204 (5) | 0.2816 (7) | 0.0721 (15) | |
| N2 | 0.42542 (12) | 0.0961 (4) | 0.7215 (4) | 0.0343 (8) | |
| N3 | 0.38170 (11) | 0.2922 (3) | 0.6083 (4) | 0.0298 (7) | |
| N4 | 0.47684 (11) | 0.3034 (3) | −0.0187 (4) | 0.0267 (7) | |
| O1 | 0.2679 (4) | 0.2322 (7) | 0.1676 (14) | 0.105 (4) | 0.737 (19) |
| O2 | 0.2783 (4) | 0.4550 (6) | 0.280 (2) | 0.078 (4) | 0.737 (19) |
| O1' | 0.2456 (5) | 0.258 (2) | 0.279 (4) | 0.089 (7) | 0.263 (19) |
| O2' | 0.2901 (9) | 0.4556 (11) | 0.254 (6) | 0.050 (6) | 0.263 (19) |
| O3 | 0.39040 (9) | 0.3227 (3) | 0.0338 (4) | 0.0330 (6) | |
| O4 | 0.44135 (9) | 0.2156 (3) | 0.2645 (3) | 0.0325 (6) | |
| O5 | 0.44161 (9) | 0.4796 (3) | 0.2125 (3) | 0.0336 (6) | |
| S1 | 0.43441 (3) | 0.33299 (9) | 0.13275 (11) | 0.0231 (2) | |
| H4B | 0.5038 (10) | 0.282 (4) | 0.038 (5) | 0.040 (12)* | |
| H4A | 0.4797 (12) | 0.384 (3) | −0.087 (4) | 0.040 (12)* | |
| H3A | 0.4008 (12) | 0.356 (4) | 0.663 (5) | 0.043 (12)* | |
| H2B | 0.4319 (13) | 0.001 (2) | 0.732 (6) | 0.046 (12)* | |
| H2A | 0.4435 (13) | 0.154 (3) | 0.787 (5) | 0.051 (14)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0336 (18) | 0.0247 (18) | 0.0225 (17) | −0.0018 (15) | 0.0077 (16) | −0.0052 (15) |
| C2 | 0.038 (2) | 0.0201 (17) | 0.0297 (19) | −0.0061 (15) | 0.0054 (17) | −0.0005 (16) |
| C3 | 0.034 (2) | 0.039 (2) | 0.039 (2) | −0.0128 (17) | −0.0037 (18) | 0.0011 (19) |
| C4 | 0.0303 (19) | 0.039 (2) | 0.042 (2) | −0.0001 (17) | 0.0015 (17) | 0.0127 (19) |
| C5 | 0.038 (2) | 0.0248 (18) | 0.040 (2) | 0.0018 (16) | 0.0134 (18) | 0.0053 (17) |
| N1 | 0.046 (2) | 0.070 (3) | 0.100 (4) | −0.007 (2) | −0.023 (3) | 0.039 (3) |
| N2 | 0.0415 (19) | 0.0261 (17) | 0.0353 (19) | −0.0004 (15) | −0.0064 (15) | −0.0048 (15) |
| N3 | 0.0382 (18) | 0.0210 (15) | 0.0303 (17) | −0.0046 (13) | 0.0038 (14) | −0.0074 (14) |
| N4 | 0.0323 (17) | 0.0268 (16) | 0.0211 (15) | 0.0009 (13) | −0.0010 (13) | 0.0003 (13) |
| O1 | 0.097 (7) | 0.089 (5) | 0.129 (7) | −0.034 (4) | −0.080 (6) | 0.036 (4) |
| O2 | 0.055 (6) | 0.073 (5) | 0.105 (8) | 0.032 (3) | 0.014 (5) | 0.029 (4) |
| O1' | 0.062 (10) | 0.099 (11) | 0.106 (14) | 0.002 (9) | −0.043 (9) | 0.003 (11) |
| O2' | 0.032 (10) | 0.050 (10) | 0.068 (11) | 0.023 (6) | 0.008 (10) | 0.026 (7) |
| O3 | 0.0326 (13) | 0.0323 (14) | 0.0340 (14) | −0.0008 (11) | −0.0074 (12) | −0.0047 (12) |
| O4 | 0.0407 (15) | 0.0289 (13) | 0.0277 (13) | −0.0039 (12) | 0.0010 (12) | 0.0047 (11) |
| O5 | 0.0415 (14) | 0.0245 (13) | 0.0349 (14) | 0.0030 (12) | −0.0083 (12) | −0.0085 (11) |
| S1 | 0.0293 (4) | 0.0191 (4) | 0.0210 (4) | −0.0007 (3) | −0.0026 (4) | −0.0015 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—N2 | 1.317 (5) | N1—O2' | 1.243 (8) |
| C1—N3 | 1.357 (4) | N1—O1' | 1.246 (8) |
| C1—C2 | 1.411 (5) | N1—O1 | 1.257 (6) |
| C2—C3 | 1.348 (5) | N2—H2B | 0.884 (18) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | N2—H2A | 0.877 (18) |
| C3—C4 | 1.402 (6) | N3—H3A | 0.886 (19) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | N4—S1 | 1.657 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.338 (6) | N4—H4B | 0.889 (18) |
| C4—N1 | 1.449 (6) | N4—H4A | 0.890 (18) |
| C5—N3 | 1.340 (5) | O3—S1 | 1.440 (3) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | O4—S1 | 1.451 (3) |
| N1—O2 | 1.228 (6) | O5—S1 | 1.460 (2) |
| N2—C1—N3 | 119.3 (3) | O1'—N1—O1 | 50.3 (11) |
| N2—C1—C2 | 123.4 (3) | O2—N1—C4 | 119.1 (8) |
| N3—C1—C2 | 117.3 (3) | O2'—N1—C4 | 114.0 (14) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.3 (3) | O1'—N1—C4 | 115.3 (10) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.8 | O1—N1—C4 | 116.7 (5) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.8 | C1—N2—H2B | 122 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 118.9 (4) | C1—N2—H2A | 124 (3) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.5 | H2B—N2—H2A | 114 (3) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.5 | C5—N3—C1 | 122.9 (3) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.7 (4) | C5—N3—H3A | 116 (3) |
| C5—C4—N1 | 119.8 (4) | C1—N3—H3A | 120 (3) |
| C3—C4—N1 | 119.4 (4) | S1—N4—H4B | 109 (3) |
| C4—C5—N3 | 119.6 (3) | S1—N4—H4A | 108 (2) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.2 | H4B—N4—H4A | 112 (3) |
| N3—C5—H5 | 120.2 | O3—S1—O4 | 114.22 (15) |
| O2—N1—O2' | 17.8 (19) | O3—S1—O5 | 112.50 (15) |
| O2—N1—O1' | 107.6 (12) | O4—S1—O5 | 111.59 (15) |
| O2'—N1—O1' | 122.5 (12) | O3—S1—N4 | 105.26 (16) |
| O2—N1—O1 | 123.8 (8) | O4—S1—N4 | 103.93 (15) |
| O2'—N1—O1 | 123.5 (19) | O5—S1—N4 | 108.63 (15) |
| N2—C1—C2—C3 | −175.9 (4) | C5—C4—N1—O2' | 8 (2) |
| N3—C1—C2—C3 | 3.6 (5) | C3—C4—N1—O2' | −169 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.6 (6) | C5—C4—N1—O1' | −141.5 (16) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −3.2 (6) | C3—C4—N1—O1' | 41.3 (16) |
| C2—C3—C4—N1 | 174.0 (4) | C5—C4—N1—O1 | 162.1 (8) |
| C3—C4—C5—N3 | 1.4 (6) | C3—C4—N1—O1 | −15.1 (9) |
| N1—C4—C5—N3 | −175.7 (4) | C4—C5—N3—C1 | 3.1 (6) |
| C5—C4—N1—O2 | −11.3 (11) | N2—C1—N3—C5 | 174.0 (3) |
| C3—C4—N1—O2 | 171.4 (9) | C2—C1—N3—C5 | −5.5 (5) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2B···O4i | 0.88 (2) | 1.98 (2) | 2.861 (4) | 176 (4) |
| N2—H2A···N4ii | 0.88 (2) | 2.18 (2) | 3.044 (4) | 169 (4) |
| N3—H3A···O5iii | 0.89 (2) | 1.91 (2) | 2.766 (4) | 163 (4) |
| N4—H4B···O4iv | 0.89 (2) | 2.20 (2) | 3.073 (4) | 166 (3) |
| N4—H4A···O5v | 0.89 (2) | 2.20 (2) | 2.960 (4) | 143 (3) |
| C2—H2···O3i | 0.93 | 2.57 | 3.469 (4) | 163 |
| C3—H3···O2vi | 0.93 | 2.46 | 3.328 (13) | 155 |
| C5—H5···O3iii | 0.93 | 2.41 | 3.187 (4) | 141 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y, z+1/2; (ii) x, y, z+1; (iii) x, −y+1, z+1/2; (iv) −x+1, y, −z+1/2; (v) x, −y+1, z−1/2; (vi) −x+1/2, y−1/2, z.
References
- Aakeroy, C. B., Beatty, A. M., Nieuwenhuyzen, M. & Zou, M. (1998). J. Mater. Chem. pp. 1385–1389.
- Akriche, S. & Rzaigui, M. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Anderson, F. P., Gallagher, J. F., Kenny, P. T. M. & Lough, A. J. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o1350–o1353.
- Babu, K. S. S., Dhavamurthy, M., NizamMohideen, M., Peramaiyan, G. & Mohan, R. (2014b). Acta Cryst. E70, o600–o601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Babu, K. S. S., Peramaiyan, G., NizamMohideen, M. & Mohan, R. (2014a). Acta Cryst. E70, o391–o392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2004). APEX2, SAINT, XPREP and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Groom, C. R. & Allen, F. H. (2014). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 662–671. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Huq, C. A. M. A., Fouzia, S. & NizamMohideen, M. (2013). Acta Cryst. E69, o1766–o1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, H., Iwata, K. & Hamaguchi, H. (2002). J. Phys. Chem. A, 106, 2305–2312.
- Jin, Z.-M., Shun, N., Lü, Y.-P., Hu, M.-L. & Shen, L. (2005). Acta Cryst. C61, m43–m45. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Nahringbauer, I. & Kvick, Å. (1977). Acta Cryst. B33, 2902–2905.
- Rajkumar, M. A., Xavier, S. S. J., Anbarasu, S., Devarajan, P. A. & NizamMohideen, M. (2014). Acta Cryst. E70, o473–o474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sethuram, M., Bhargavi, G., Dhandapani, M., Amirthaganesan, G. & NizamMohideen, M. (2013a). Acta Cryst. E69, o1301–o1302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sethuram, M., Rajasekharan, M. V., Dhandapani, M., Amirthaganesan, G. & NizamMohideen, M. (2013b). Acta Cryst. E69, o957–o958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shihabuddeen Syed, A., Rajarajan, K. & NizamMohideen, M. (2013). Acta Cryst. E69, i33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Showrilu, K., Rajarajan, K. & NizamMohideen, M. (2013). Acta Cryst. E69, m469–m470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015000365/su5048sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015000365/su5048Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015000365/su5048Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1042506
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report