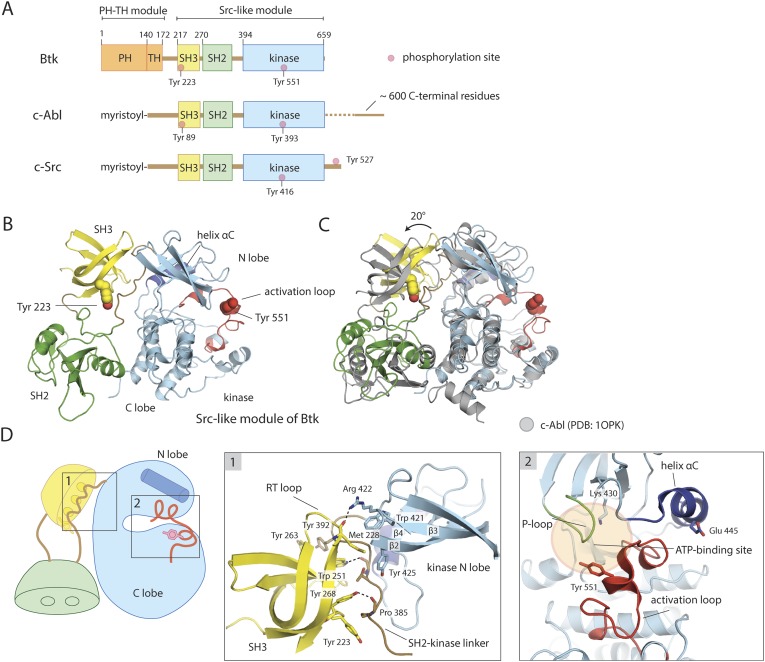
Figure 1. Crystal structure of the Src-like module of Btk.
(A) Domain architectures of Btk, c-Abl, and c-Src. (B) Model for the Src-like module of Btk, based on the crystal structure of the domain-swapped dimer. (C) Comparison of the Src-like modules of Btk and c-Abl (PDB: 1OPK) (Nagar et al., 2003), superimposed on the C lobes of the kinase domains. There is a relative rotation of about 15° for the SH2 domains and 20° for the SH3 domains for the two structures. (D) Details of the SH3/SH2-kinase linker interface and the kinase catalytic cleft in Btk. Left panel: a cluster of hydrophobic residues on the SH3 domain packs against the polyproline type-II helix formed by the SH2-kinase linker. This type of interaction is seen in most SH3-peptide ligand complexes. Right panel: the activation loop of Btk folds into the mouth of the catalytic cleft, blocking part of the ATP-binding cleft. Glu 445, in helix αC, forms an ion pair with Lys 430 in the active conformation but is prevented from doing so in this inactive conformation by the activation loop and helix αC.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.06074.003