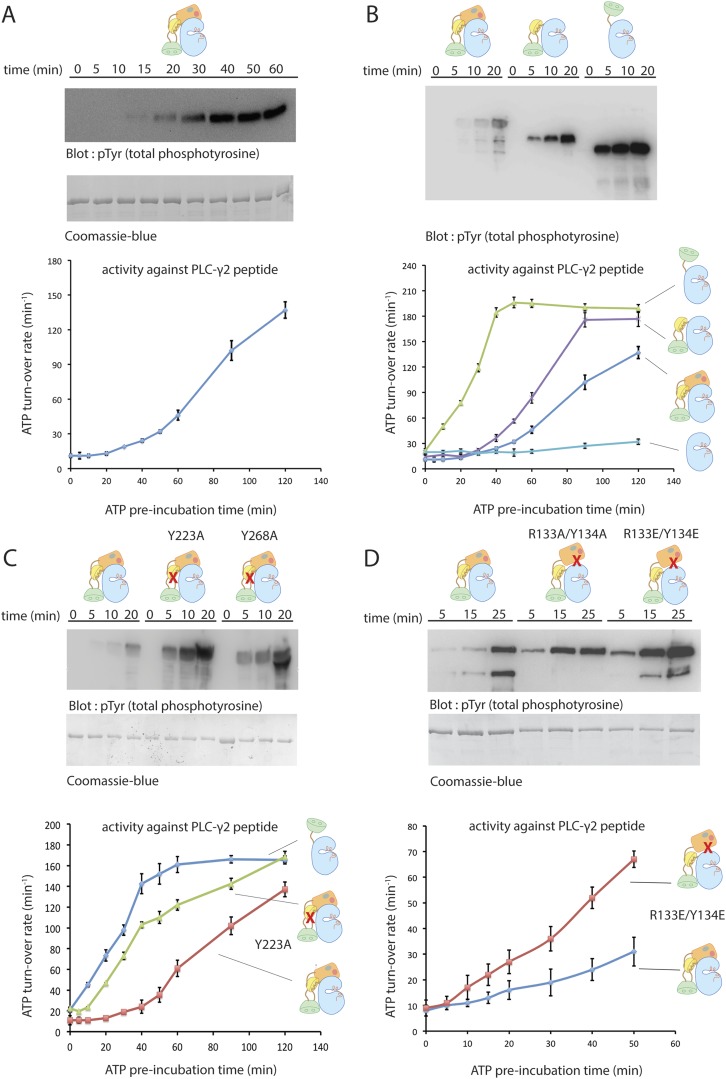
Figure 4. Autoinhibition of Btk.
(A) Activation of full-length bovine Btk (residues 1 to 659, 2 μM). Reactions are carried out in the presence of 10 mM Mg2+, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM ATP, 25 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0. The level of autophosphorylation is assayed by immunoblotting an SDS-PAGE gel with a non-specific, anti-phosphotyrosine antibody (4G10, EMD Millipore) (upper panel). The amount of total protein loaded on the gel is measured by coomassie-blue staining. The kinase activity of Btk is assayed by a continuous kinase-coupled colorimetric assay, in the presence of 1 mM PLC-γ2 peptide substrate. See methods for detailed experimental procedures. (B) Comparison of the activation of the Btk Src-like module (residues 217 to 659), SH2-kinase (residues 270 to 659), and the kinase domain (residues 394 to 659). The SH2-kinase construct activates substantially faster than full-length Btk and the Src-like module of Btk. Activated full-length Btk degrades to a small extent over time, which results in some lower molecule-weight bands being detected on the western blot. (C) Activation of full-length Btk with mutations Y223A and Y268A. Tyr 223 and Tyr 268 are on the SH3/SH2-linker interface, and the two mutants activate faster than wild-type Btk. (D) Activation of full-length Btk with a double mutation (R134E/Y133E). Arg 134 and Tyr 133 are located at the PH-TH/kinase interface.