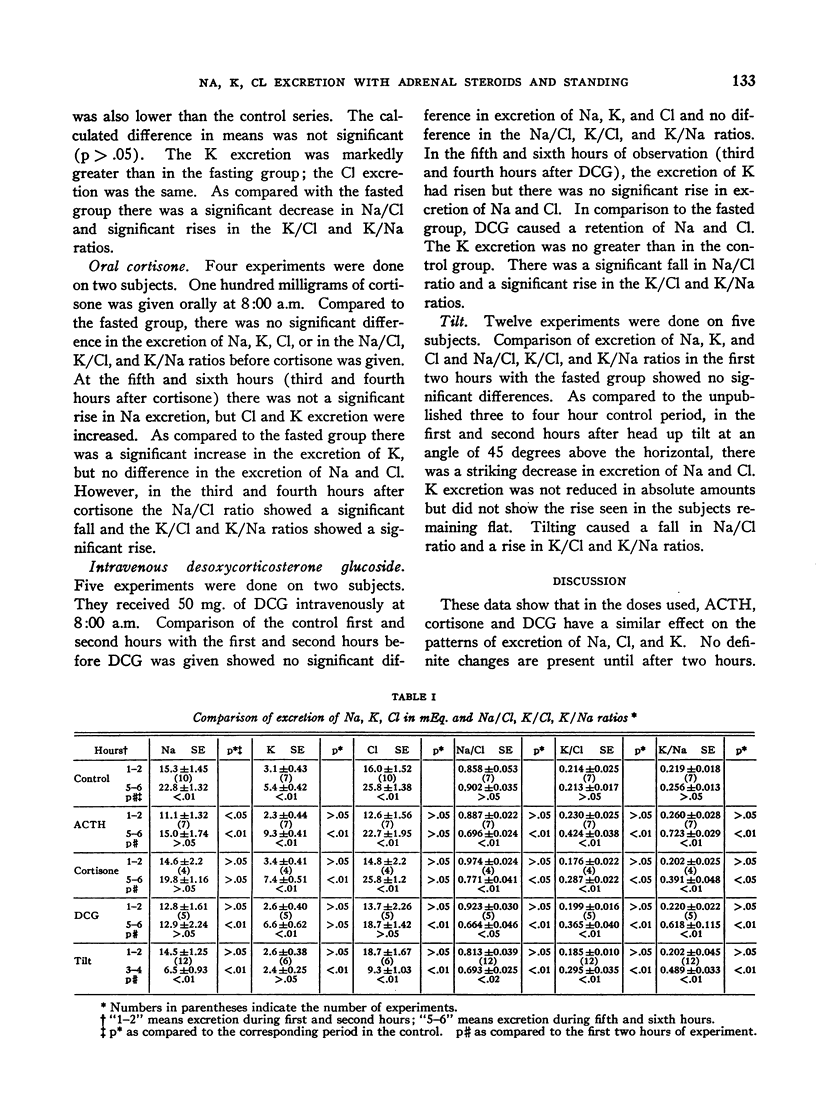
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- JACOBSON W. E., HAMMARSTEN J. F., HELLER B. I. The effects of adrenaline upon renal function and electrolyte excretion. J Clin Invest. 1951 Dec;30(122):1503–1506. doi: 10.1172/JCI102560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCUS F., ROMANOFF L. P., PINCUS G. The electrolyte-excreting activity of adrenocortical substances. Endocrinology. 1952 Mar;50(3):286–293. doi: 10.1210/endo-50-3-286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMYTHE C. M., NICKEL J. F., BRADLEY S. E. The effect of epinephrine (USP), l-epinephrine, and l-norepinephrine on glomerular filtration rate, renal plasma flow, and the urinary excretion of sodium, potassium, and water in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1952 May;31(5):499–506. doi: 10.1172/JCI102634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STANBURY S. W., THOMSON A. E. Diurnal variation in electrolyte excretion. Clin Sci. 1951 Aug;10(3):267–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



