Full text
PDF

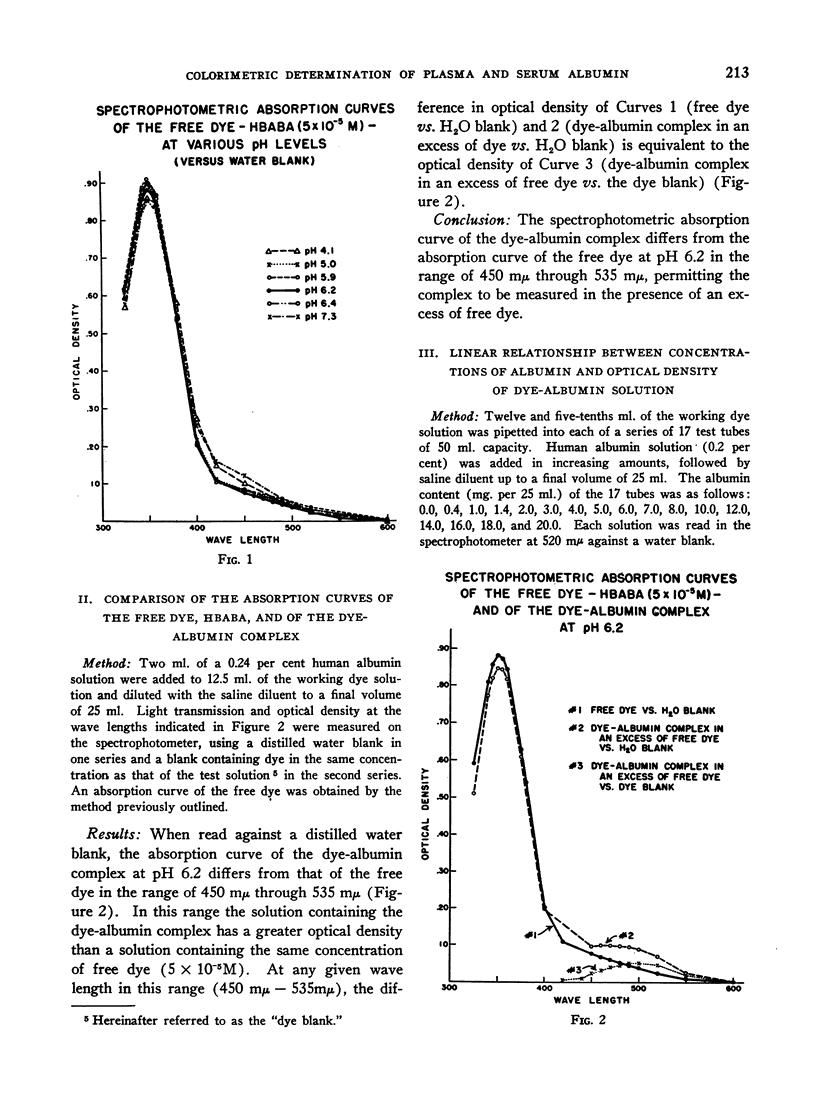
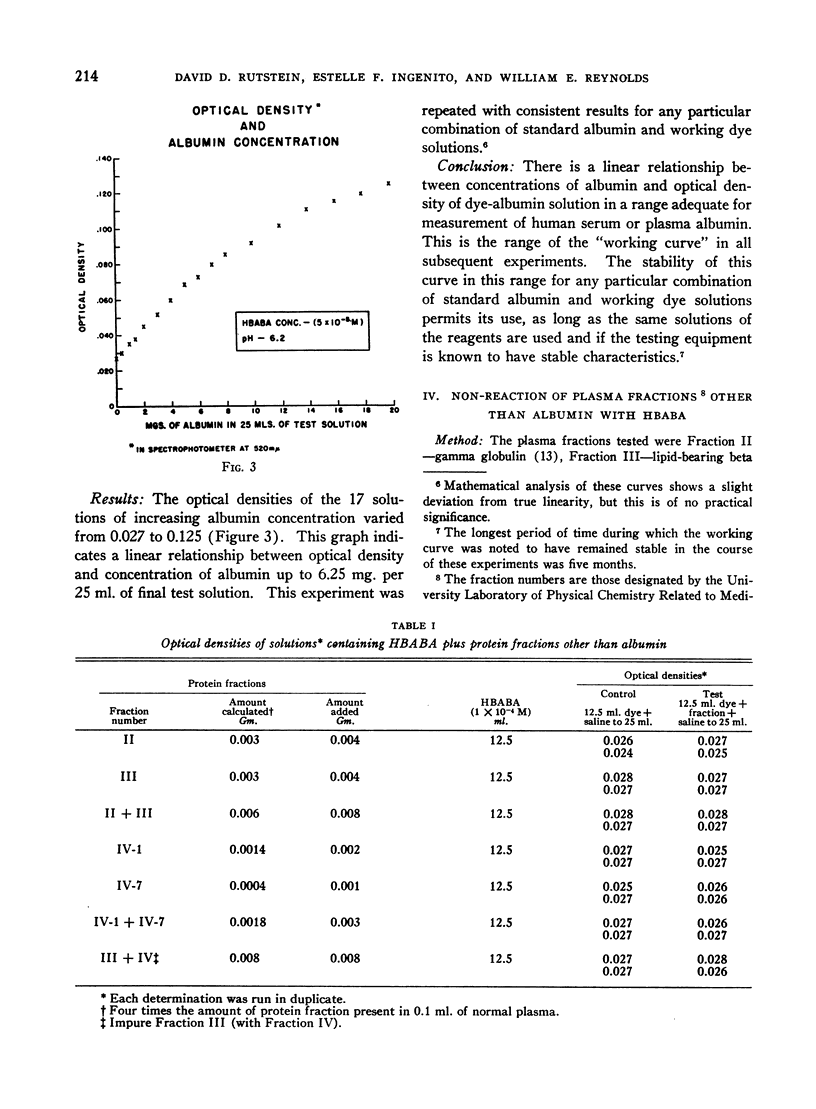

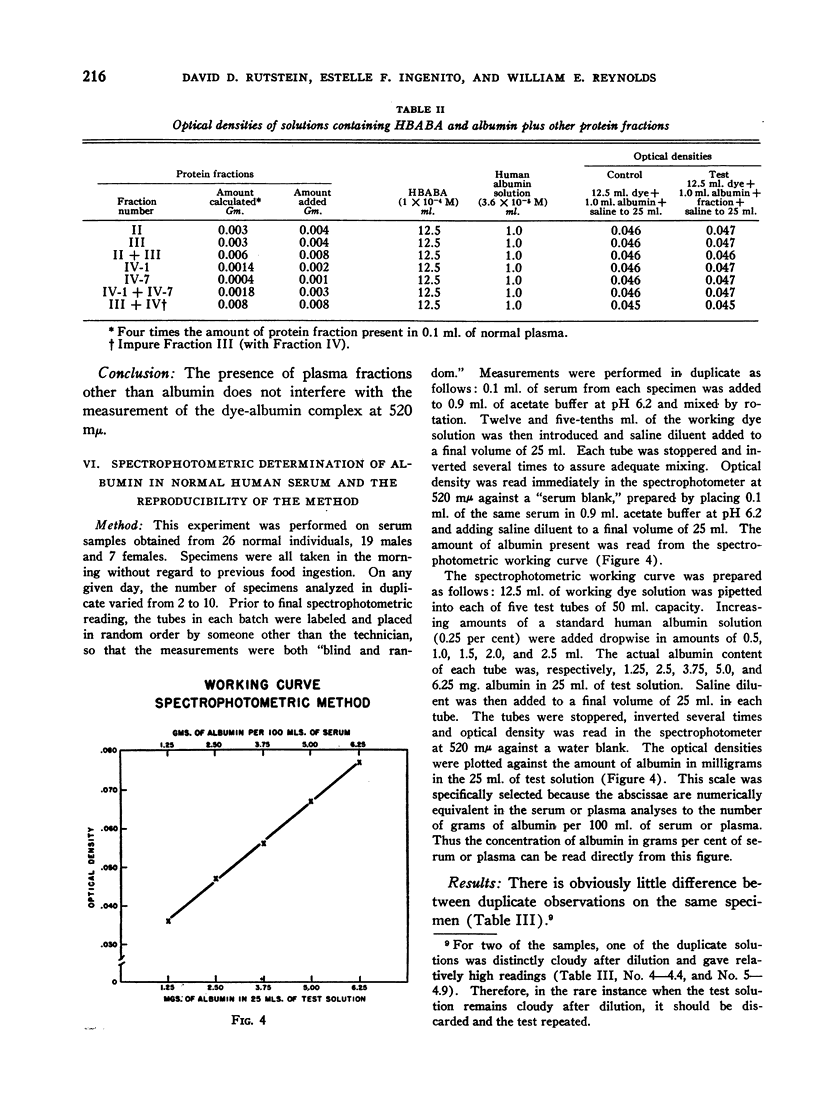
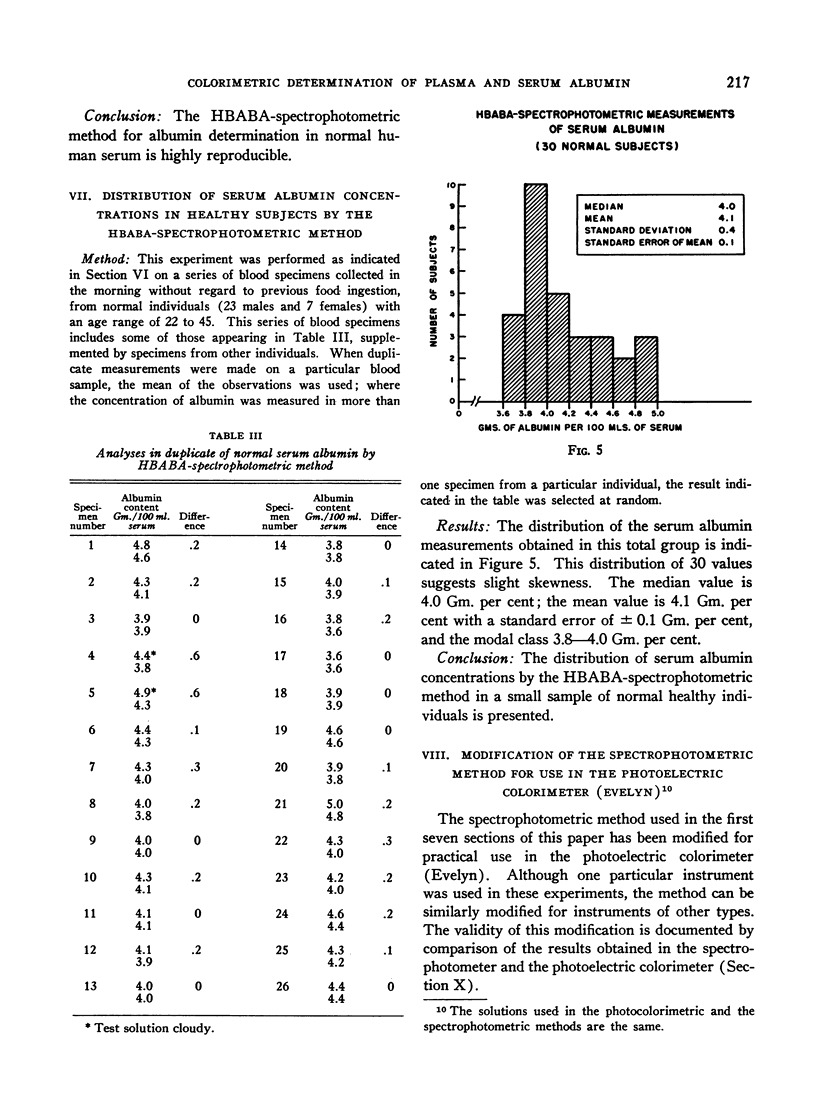



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dole V. P., Braun E. THE ELECTROPHORETIC PATTERNS OF NORMAL PLASMA. J Clin Invest. 1944 Sep;23(5):708–713. doi: 10.1172/JCI101542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GITLIN D., DAVIDSON C. S., WETTERLOW L. H. The quantitative estimation of serum albumin in human body fluids by direct titration with specific horse at tiserum. J Immunol. 1949 Dec;63(4):415–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAGER B. V., SCHWARTZ T. B. Comparative electrophoretic and chemical estimations of of human serum albumin; an evaluation of six methods. J Lab Clin Med. 1950 Jan;35(1):76–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENFELD M., SURGENOR D. M. The hematin-binding reaction as a basis for serum albumin determination. J Biol Chem. 1952 Dec;199(2):911–921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



