Abstract
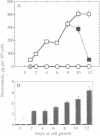
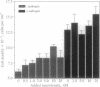
After therapeutic hormone deprivation, prostate cancer cells often develop androgen-insensitive growth through mechanisms thus far undefined. Neuropeptides have been previously implicated as growth factors in some prostate cancers. Here, we demonstrate that androgen-sensitive LNCaP human prostate cancer cells produce and secrete neurotensin following androgen withdrawal. We show that while LNCaP cells express the neurotensin receptor, only androgen-deprived cells exhibit a growth response to exogenous neurotensin. We further demonstrate that androgen-stimulated cells may be refractory to exogenous neurotensin due to androgen induction of a metalloprotease active toward neurotensin. Thus, prostate cancer cells deprived of androgen develop an alternative autocrine growth mechanism involving neurotensin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahamsson P. A., Falkmer S., Fält K., Grimelius L. The course of neuroendocrine differentiation in prostatic carcinomas. An immunohistochemical study testing chromogranin A as an "endocrine marker". Pathol Res Pract. 1989 Sep;185(3):373–380. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(89)80016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrahamsson P. A., Wadström L. B., Alumets J., Falkmer S., Grimelius L. Peptide-hormone- and serotonin-immunoreactive tumour cells in carcinoma of the prostate. Pathol Res Pract. 1987 Jun;182(3):298–307. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(87)80065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns E. M., de Boer W., Mulder E. Androgen-dependent growth regulation of and release of specific protein(s) by the androgen receptor containing human prostate tumor cell line LNCaP. Prostate. 1986;9(3):247–259. doi: 10.1002/pros.2990090305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boring C. C., Squires T. S., Tong T. Cancer statistics, 1993. CA Cancer J Clin. 1993 Jan-Feb;43(1):7–26. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.43.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R. E., Mitra S. P., Feurle G. E., Hacki W. H. Presence of neurotensin and neuromedin-N within a common precursor from a human pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Jun;66(6):1323–1328. doi: 10.1210/jcem-66-6-1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuttitta F., Carney D. N., Mulshine J., Moody T. W., Fedorko J., Fischler A., Minna J. D. Bombesin-like peptides can function as autocrine growth factors in human small-cell lung cancer. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):823–826. doi: 10.1038/316823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauch P., Barelli H., Vincent J. P., Checler F. Fluorimetric assay of the neurotensin-degrading metalloendopeptidase, endopeptidase 24.16. Biochem J. 1991 Dec 1;280(Pt 2):421–426. doi: 10.1042/bj2800421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis T. P., Burgess H. S., Crowell S., Moody T. W., Culling-Berglund A., Liu R. H. Beta-endorphin and neurotensin stimulate in vitro clonal growth of human SCLC cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb 28;161(2-3):283–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90862-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis T. P., Crowell S., McInturff B., Louis R., Gillespie T. Neurotensin may function as a regulatory peptide in small cell lung cancer. Peptides. 1991 Jan-Feb;12(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(91)90160-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evers B. M., Beauchamp R. D., Ishizuka J., Townsend C. M., Jr, Alam T., Papaconstantinou J., Thompson J. C. Posttranscriptional regulation of neurotensin in the gut. Surgery. 1991 Aug;110(2):247–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evers B. M., Ishizuka J., Townsend C. M., Jr, Rajaraman S., Thompson J. C. Expression of neurotensin messenger RNA in a human carcinoid tumor. Ann Surg. 1991 Oct;214(4):448–455. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199110000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. P. Prostate cancer. Chemotherapy. Cancer. 1987 Aug 1;60(3 Suppl):586–588. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19870801)60:3+<586::aid-cncr2820601525>3.0.co;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. A., McCormick D. J., Pfenning M. A., Kanba K. S., Enloe L. J., Moore A., Richelson E. Neurotensin(8-13): comparison of novel analogs for stimulation of cyclic GMP formation in neuroblastoma clone N1E-115 and receptor binding to human brain and intact N1E-115 cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Oct 1;38(19):3377–3382. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90637-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayhack J. T., Keeler T. C., Kozlowski J. M. Carcinoma of the prostate. Hormonal therapy. Cancer. 1987 Aug 1;60(3 Suppl):589–601. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19870801)60:3+<589::aid-cncr2820601526>3.0.co;2-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu J., Polak J. M., Probert L., Islam K. N., Marangos P. J., Mina S., Adrian T. E., McGregor G. P., O'Shaughnessy D. J., Bloom S. R. Peptidergic innervation of the human male genital tract. J Urol. 1983 Aug;130(2):386–391. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)51174-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez D. E., Richardson C. M., Nemeroff C. B., Orlando R. C., St-Pierre S., Rioux F., Prange A. J., Jr Evidence for biological activity of two N-terminal fragments of neurotensin, neurotensin1-8 and neurotensin1-10. Brain Res. 1984 May 28;301(1):153–156. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90414-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez D. E., Simons K. B., Spampinato D., Rioux F., St-Pierre S. Pupillary effects of neurotensin: structure-activity relationships. Neuropeptides. 1985 Dec;6(6):561–568. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(85)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horoszewicz J. S., Leong S. S., Kawinski E., Karr J. P., Rosenthal H., Chu T. M., Mirand E. A., Murphy G. P. LNCaP model of human prostatic carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1983 Apr;43(4):1809–1818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapuscinski M., Shulkes A., Read D., Hardy K. J. Expression of neurotensin in endocrine tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Jan;70(1):100–106. doi: 10.1210/jcem-70-1-100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi P., Poustis C., Granier C., Van Rietschoten J., Rivier J., Morgat J. L., Freychet P. Neurotensin binding to extraneural and neural receptors: comparison with biological activity and structure--activity relationships. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Jul;18(1):11–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knabbe C., Kellner U., Schmahl M., Voigt K. D. Growth factors in human prostate cancer cells: implications for an improved treatment of prostate cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;40(1-3):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(91)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyprianou N., English H. F., Isaacs J. T. Programmed cell death during regression of PC-82 human prostate cancer following androgen ablation. Cancer Res. 1990 Jun 15;50(12):3748–3753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizokami A., Saiga H., Matsui T., Mita T., Sugita A. Regulation of androgen receptor by androgen and epidermal growth factor in a human prostatic cancer cell line, LNCaP. Endocrinol Jpn. 1992 Jun;39(3):235–243. doi: 10.1507/endocrj1954.39.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. J., Field J. K., Everett N. P., Green C. D. Serum regulation of the estrogen responsiveness of the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Cancer Res. 1983 Mar;43(3):1244–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Przedborski S., Levivier M., Cadet J. L. Neurotensin receptors in human meningiomas. Ann Neurol. 1991 Nov;30(5):650–654. doi: 10.1002/ana.410300504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read D., Shulkes A., Fernley R., Simpson R. Characterization of neurotensin(6-13) from an hepatic fibrolamellar carcinoma. Peptides. 1991 Jul-Aug;12(4):887–892. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(91)90152-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuurmans A. L., Bolt J., Mulder E. Androgens stimulate both growth rate and epidermal growth factor receptor activity of the human prostate tumor cell LNCaP. Prostate. 1988;12(1):55–63. doi: 10.1002/pros.2990120108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipp M. A., Tarr G. E., Chen C. Y., Switzer S. N., Hersh L. B., Stein H., Sunday M. E., Reinherz E. L. CD10/neutral endopeptidase 24.11 hydrolyzes bombesin-like peptides and regulates the growth of small cell carcinomas of the lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10662–10666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternfeld M. D., Hendrickson J. E., Keeble W. W., Rosenbaum J. T., Robertson J. E., Pittelkow M. R., Shipley G. D. Differential expression of mRNA coding for heparin-binding growth factor type 2 in human cells. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Aug;136(2):297–304. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041360212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Masu M., Nakanishi S. Structure and functional expression of the cloned rat neurotensin receptor. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):847–854. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vita N., Laurent P., Lefort S., Chalon P., Dumont X., Kaghad M., Gully D., Le Fur G., Ferrara P., Caput D. Cloning and expression of a complementary DNA encoding a high affinity human neurotensin receptor. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 8;317(1-2):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81509-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., Hoang H. D., Bussjaeger L. J., Solomon T. E. Neurotensin stimulates growth of small intestine in rats. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 1):G813–G817. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.255.6.G813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L., Michener S. R., Bailey J. E., Harty G. J., Lucas D. L., Nelson D. K., Roddy D. R., Go V. L. Survey of distribution of substance P, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, cholecystokinin, neurotensin, Met-enkephalin, bombesin and PHI in the spinal cord of cat, dog, sloth and monkey. Peptides. 1988 Mar-Apr;9(2):357–372. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(88)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young C. Y., Andrews P. E., Montgomery B. T., Tindall D. J. Tissue-specific and hormonal regulation of human prostate-specific glandular kallikrein. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 28;31(3):818–824. doi: 10.1021/bi00118a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young C. Y., Montgomery B. T., Andrews P. E., Qui S. D., Bilhartz D. L., Tindall D. J. Hormonal regulation of prostate-specific antigen messenger RNA in human prostatic adenocarcinoma cell line LNCaP. Cancer Res. 1991 Jul 15;51(14):3748–3752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuck B., Goepfert C., Nedlin-Chittka A., Sohrt K., Voigt K. D., Knabbe C. Regulation of fibroblast growth factor-like protein(s) in the androgen-responsive human prostate carcinoma cell line LNCaP. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1992 Mar;41(3-8):659–663. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(92)90400-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Sant'Agnese P. A. Neuroendocrine differentiation in carcinoma of the prostate. Diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic implications. Cancer. 1992 Jul 1;70(1 Suppl):254–268. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19920701)70:1+<254::aid-cncr2820701312>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]