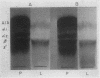
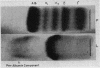
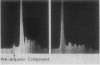
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLASIUS R., SEITZ W. Die Beeinflussung der Elektrophoretischen Wanderungsgeschwindigkeit von Serumglobulinen durch Zusatz von Heparin. Klin Wochenschr. 1952 Oct 1;30(37-38):905–906. doi: 10.1007/BF01471486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYLE E., BRAGDON J. H., BROWN R. K. Role of heparin in in vitro production of alpha1 lipoproteins in human plasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1952 Nov;81(2):475–477. doi: 10.3181/00379727-81-19915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN R. K., BOYLE E., ANFINSEN C. B. The enzymatic transformation of lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1953 Sep;204(1):423–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FASOLI A. Electrophoresis of serum lipoproteins on filter-paper. Acta Med Scand. 1953;145(3):233–235. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1953.tb07014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON R. S., Jr, BOYLE E., BROWN R. K., CHERKES A., ANFINSEN C. B. Role of serum albumin in lipemia clearing reaction. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Oct;84(1):168–170. doi: 10.3181/00379727-84-20579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRASSMANN W., HANNIG K. Ein quantitatives Verfahren zur Analyse der Serumproteine durch Papierelektrophorese. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1952;290(1-2):1–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOCH H., CHANUTIN A. Effects of anticoagulants on serum and plasma. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;197(2):503–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVER W. F., SMITH P. A., HURLEY N. A. Idiopathic hyperlipemia and primary hypercholesteremic xanthomatosis. III. Effects of intravenously administered heparin on the plasma proteins and lipids. J Invest Dermatol. 1954 Jan;22(1):71-84; discussion, 84-7. doi: 10.1038/jid.1954.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIKKILA E. A. The effect of heparin on serum lipoproteins. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1952;4(4):369–370. doi: 10.3109/00365515209060690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBERG I. N. Serum lipids studied by electrophoresis on paper. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1952 Aug-Sep;80(4):751–756. doi: 10.3181/00379727-80-19752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHORE B., NICHOLS A. V., FREEMAN N. K. Evidence for lipolytic action by human plasma obtained after intravenous administration of heparin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Jun;83(2):216–220. doi: 10.3181/00379727-83-20312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPITZER J. J. Properties of heparin-produced lipemia clearing factor. Am J Physiol. 1952 Nov;171(2):492–498. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.171.2.492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWAHN B. A method for localization and determination of serum lipids after electrophoretical separation on filter paper. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1952;4(2):98–103. doi: 10.3109/00365515209060643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]