Abstract
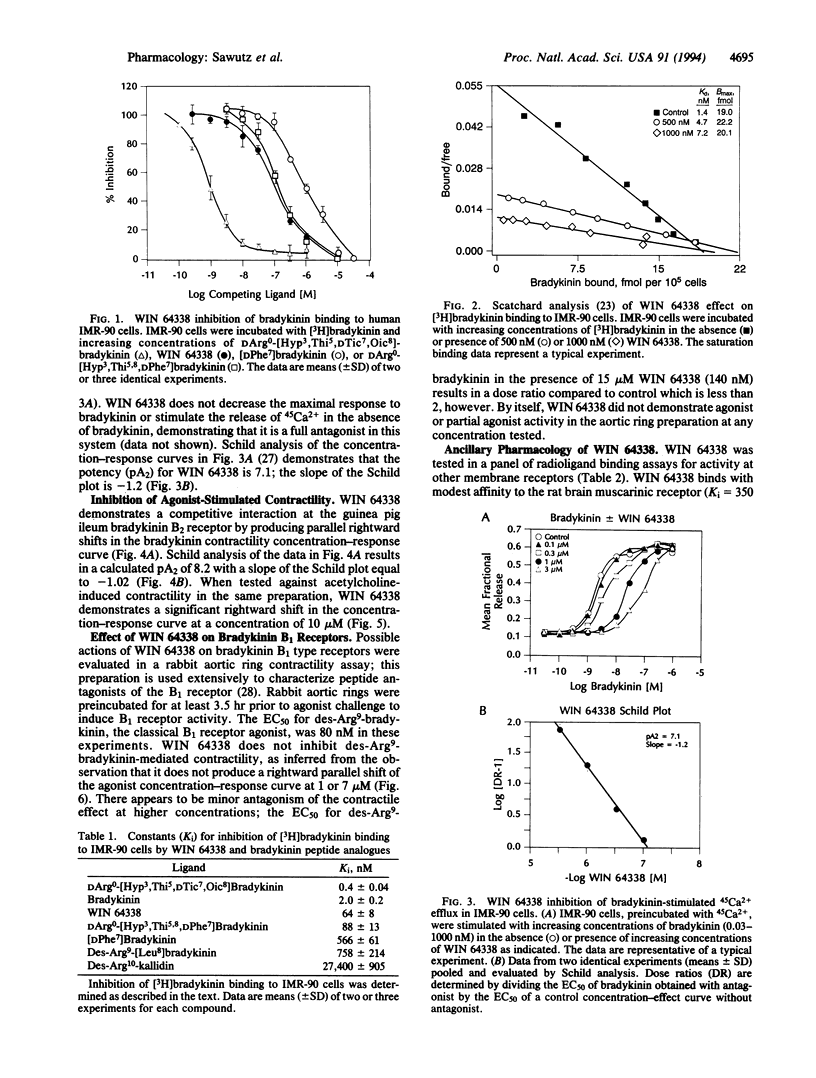
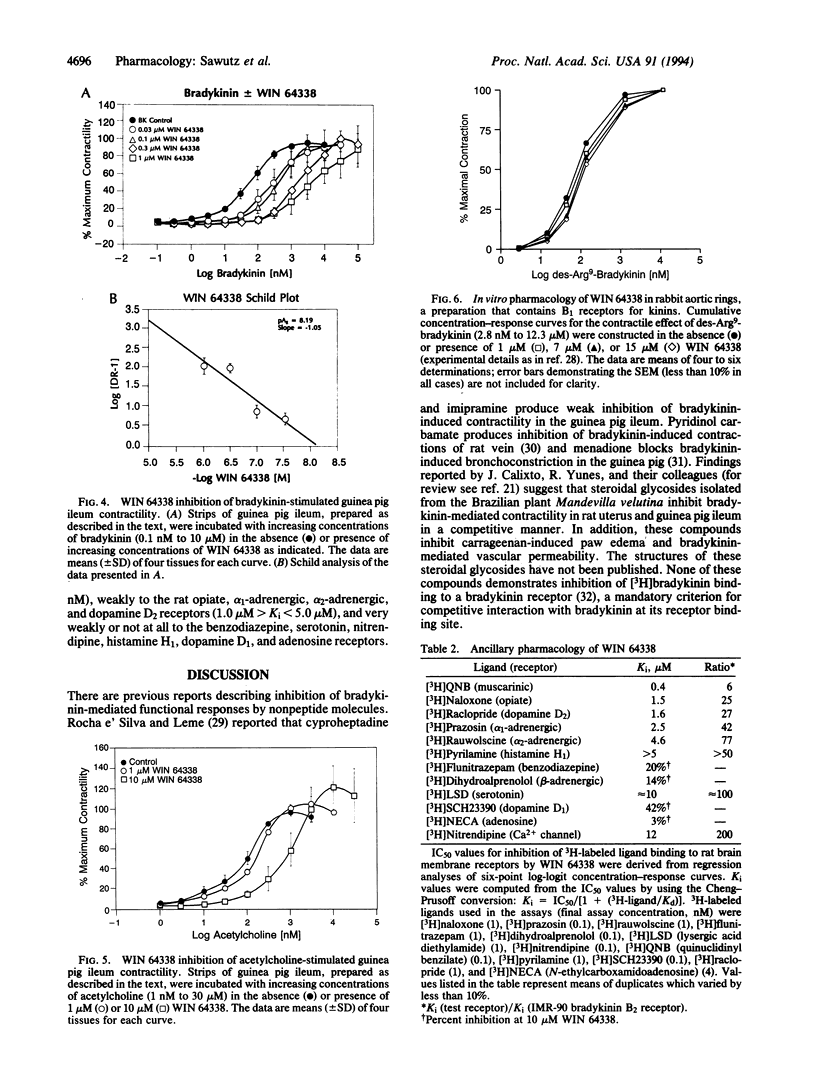
We report the synthesis and in vitro biological activity of the nonpeptide bradykinin receptor antagonist WIN 64338, [[4-[[2-[[bis(cyclohexylamino)methylene]amino]-3-(2- naphthyl)-1-oxopropyl]amino]phenyl]methyl]tributylphosphonium chloride monohydrochloride. WIN 64338 inhibits [3H]-bradykinin binding to the bradykinin B2 receptor on human IMR-90 cells with a binding inhibition constant (Ki) of 64 +/- 8 nM and demonstrates competitive inhibition of bradykinin-stimulated 45Ca2+ efflux from IMR-90 cells (pA2 = 7.1). The antagonist inhibits bradykinin-mediated guinea pig ileum contractility (pA2 = 8.2) and has significantly weaker activity against acetylcholine-induced contractility in the same preparation. WIN 64338 is not active in a rabbit aorta bradykinin B1 receptor assay, demonstrating that it is a selective bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist. The compound inhibits [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate binding to the rat brain muscarinic receptor (Ki = 350 nM) but is 25- to 100-fold more selective for the bradykinin receptor compared with other receptors against which it has been tested. Synthesis of WIN 64338 has provided a nonpeptide competitive bradykinin B2 antagonist active in both bradykinin radioligand binding and functional assays.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altinkurt O., Kanzik I. Effects of vitamin K3 on the hypotensive and bronchoconstrictor responses to bradykinin and histamine in the guinea pig. Arzneimittelforschung. 1980;30(2):286–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bathon J. M., Proud D. Bradykinin antagonists. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1991;31:129–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.31.040191.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M., Farmer S. G., Steranka L. R. Bradykinin receptor antagonists. Med Res Rev. 1990 Apr-Jun;10(2):237–269. doi: 10.1002/med.2610100204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., MacVinish L. J., Pickles R. J. Antagonism of kinin effects on epithelial by Hoe 140: apparently competitive and non-competitive interactions. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;107(3):797–802. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLean A., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E97–102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G., Audet R., Levesque L., Godin D., Marceau F. Development and in vivo evaluation of metabolically resistant antagonists of B1 receptors for kinins. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Jul;266(1):192–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Burch R. M., Kyle D. J., Martin J. A., Meeker S. N., Togo J. D-Arg[Hyp3-Thi5-D-Tic7-Tic8]-bradykinin, a potent antagonist of smooth muscle BK2 receptors and BK3 receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;102(4):785–787. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12251.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Burch R. M., Meeker S. A., Wilkins D. E. Evidence for a pulmonary B3 bradykinin receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;36(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griesbacher T., Lembeck F. Analysis of the antagonistic actions of HOE 140 and other novel bradykinin analogues on the guinea-pig ileum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb 18;211(3):393–398. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90397-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves K. M., Troullos E. S., Dionne R. A., Schmidt E. A., Schafer S. C., Joris J. L. Bradykinin is increased during acute and chronic inflammation: therapeutic implications. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1988 Dec;44(6):613–621. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1988.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hock F. J., Wirth K., Albus U., Linz W., Gerhards H. J., Wiemer G., Henke S., Breipohl G., König W., Knolle J. Hoe 140 a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: in vitro studies. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):769–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenakin T. P. The Schild regression in the process of receptor classification. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1982 Mar;60(3):249–265. doi: 10.1139/y82-036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lembeck F., Griesbacher T., Eckhardt M., Henke S., Breipohl G., Knolle J. New, long-acting, potent bradykinin antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;102(2):297–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marceau F., Lussier A., Regoli D., Giroud J. P. Pharmacology of kinins: their relevance to tissue injury and inflammation. Gen Pharmacol. 1983;14(2):209–229. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(83)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevin R., Owen P. J. Multiple B2 kinin receptors in mammalian tissues. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Nov;9(11):387–389. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proud D., Kaplan A. P. Kinin formation: mechanisms and role in inflammatory disorders. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:49–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.000405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROCHAESILVA M., LEME J. G. ANTAGONISTIS OF BRADYKININ. Med Exp Int J Exp Med. 1963;8:287–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Barabé J. Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Mar;32(1):1–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Drapeau G., Rovero P., Dion S., Rhaleb N. E., Barabé J., D'Orléans-Juste P., Ward P. Conversion of kinins and their antagonists into B1 receptor activators and blockers in isolated vessels. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Aug 15;127(3):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90367-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhaleb N. E., Rouissi N., Jukic D., Regoli D., Henke S., Breipohl G., Knolle J. Pharmacological characterization of a new highly potent B2 receptor antagonist (HOE 140: D-Arg-[Hyp3,Thi5,D-Tic7,Qic8]bradykinin). Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 14;210(2):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90661-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. A. Bradykinin receptors: characterization, distribution and mechanisms of signal transduction. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1989;1(4):237–252. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(89)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvino J. M., Seoane P. R., Douty B. D., Awad M. M., Dolle R. E., Houck W. T., Faunce D. M., Sawutz D. G. Design of potent non-peptide competitive antagonists of the human bradykinin B2 receptor. J Med Chem. 1993 Aug 20;36(17):2583–2584. doi: 10.1021/jm00069a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawutz D. G., Faunce D. M., Houck W. T., Haycock D. Characterization of bradykinin B2 receptors on human IMR-90 lung fibroblasts: stimulation of 45Ca2+ efflux by D-Phe substituted bradykinin analogues. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov 2;227(3):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(92)90009-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawutz D. G., Singh S. S., Tiberio L., Koszewski E., Johnson C. G., Johnson C. L. The effect of TNFa on bradykinin receptor binding, phosphatidylinositol turnover and cell growth in human A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. Immunopharmacology. 1992 Jul-Aug;24(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(92)90063-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. M., Vavrek R. J. Kinin antagonists: design and activities. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1990;15 (Suppl 6):S69–S74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Togo J., Burch R. M., DeHaas C. J., Connor J. R., Steranka L. R. D-Phe7-substituted peptide bradykinin antagonists are not substrates for kininase II. Peptides. 1989 Jan-Feb;10(1):109–112. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vavrek R. J., Stewart J. M. Competitive antagonists of bradykinin. Peptides. 1985 Mar-Apr;6(2):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth K., Hock F. J., Albus U., Linz W., Alpermann H. G., Anagnostopoulos H., Henk S., Breipohl G., König W., Knolle J. Hoe 140 a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: in vivo studies. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):774–777. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12249.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



