Abstract
Bacteria inhabiting biofilms usually produce one or more polysaccharides that provide a hydrated scaffolding to stabilize and reinforce the structure of the biofilm, mediate cell-cell and cell-surface interactions, and provide protection from biocides and antimicrobial agents. Historically, alginate has been considered the major exopolysaccharide of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm matrix, with minimal regard to the different functions polysaccharides execute. Recent chemical and genetic studies have demonstrated that alginate is not involved in the initiation of biofilm formation in P. aeruginosa strains PAO1 and PA14. We hypothesized that there is at least one other polysaccharide gene cluster involved in biofilm development. Two separate clusters of genes with homology to exopolysaccharide biosynthetic functions were identified from the annotated PAO1 genome. Reverse genetics was employed to generate mutations in genes from these clusters. We discovered that one group of genes, designated psl, are important for biofilm initiation. A PAO1 strain with a disruption of the first two genes of the psl cluster (PA2231 and PA2232) was severely compromised in biofilm initiation, as confirmed by static microtiter and continuous culture flow cell and tubing biofilm assays. This impaired biofilm phenotype could be complemented with the wild-type psl sequences and was not due to defects in motility or lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis. These results implicate an as yet unknown exopolysaccharide as being required for the formation of the biofilm matrix. Understanding psl-encoded exopolysaccharide expression and protection in biofilms will provide insight into the pathogenesis of P. aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis and other infections involving biofilms.
Recurrent bacterial infections of the lower respiratory tract are the primary cause of morbidity and mortality in cystic fibrosis (CF) patients (17, 43). In the CF lung, mucociliary clearance is impaired, which results in persistent microbial colonization by a succession of pathogens, usually beginning with Staphylococcus aureus and nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae, followed by Burkholderia cepacia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa as the terminal pathogens recovered from the CF lung (17). P. aeruginosa is a versatile opportunistic pathogen that is capable of thriving in diverse environments ranging from water and soil to plant and animal tissues. This bacterium has an extensive arsenal of virulence factors that it uses to successfully colonize the lungs of CF patients (30, 43).
Several lines of evidence indicate that colonization of the CF lung by P. aeruginosa involves a biofilm mode of growth (7, 27, 51). Bacteria within biofilms are attached to either a substratum or each other and are embedded in a matrix of extracellular polymeric substance (EPS), which may consist of proteins, polysaccharides, nucleic acids, or combinations of these macromolecules (8, 39, 58). One of the most clinically significant characteristics of biofilm communities is that they are more resistant to antibiotics, biocides, and host-mediated clearance strategies than are their planktonic counterparts (33, 53). Since the EPS matrix, in certain cases, may play a critical role in the biofilm resistance phenotype (52, 53), a complete understanding of its organization and composition may assist in the development of therapeutics aimed at disrupting biofilms.
The exopolysaccharide alginate has traditionally been considered the major EPS of P. aeruginosa biofilms during CF pathogenesis. Initially, the CF lung is colonized by nonmucoid P. aeruginosa strains, but due to poorly understood selective pressures, these strains convert to a characteristic mucoid phenotype. The mucoid phenotype is caused by the overproduction of alginate, a linear copolymer of mannuronic and guluronic acid joined by β 1-4 linkages (12, 17). Despite the extensive work conducted on alginate biosynthesis and regulation (17), to date there is no direct evidence that alginate is required for the development of biofilms by nonmucoid P. aeruginosa strains, which are the first to colonize CF patients. In most CF patients, mucoid conversion occurs months or years after the initial colonization (17). There remain significant gaps in our understanding of how P. aeruginosa survives the harsh, inflammation-rich environment of the CF lung prior to converting to the alginate-producing phenotype. Recently published data strongly challenged the role of alginate in biofilm development by nonmucoid strains (19, 37, 62). An analysis of the EPS derived from biofilm-grown strain PAO1 revealed that the primary carbohydrate constituents are glucose, rhamnose, and mannose, not mannuronate or guluronate (62). This has led to the hypothesis that polysaccharides other than alginate may contribute to the formation of the biofilm matrix in nonmucoid strains. In this regard, annotation of the P. aeruginosa PAO1 genome revealed at least four novel putative polysaccharide biosynthetic gene clusters (14, 54).
For the present study, we identified a locus, psl, which may encode an alternative EPS that is essential for biofilm formation in P. aeruginosa PAO1. The disruption of psl generated a stable biofilm initiation-deficient phenotype in several assays. Significantly, most of the genes of the psl cluster are predicted to encode proteins with sequence homology to enzymes involved in the synthesis of polysaccharides from glucose, mannose, and rhamnose, which are the primary carbohydrate constituents of the EPS purified from biofilm-grown P. aeruginosa (62). This suggests that the relationship between the conversion from nonmucoid to mucoid strains and P. aeruginosa biofilms is not simply a change in the alginate levels present in the biofilm matrix, but a fundamental change in its carbohydrate constituents. This represents a new paradigm for P. aeruginosa biofilm development and pathogenesis that may reveal new avenues for immunological or chemotherapeutic interventions for infections caused by this organism. Two other groups have independently identified the psl locus and have shown its requirement for biofilm formation in P. aeruginosa in accompanying papers (15, 34).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Strains, plasmids, oligonucleotides, media, and antibiotics.
P. aeruginosa PAO, its isogenic pslAB mutant, WFPA60 (see below), and MS2, an insertion mutant inactivating PA1389-1391 (see below) were used for this study. Other P. aeruginosa strains used included PA103 (29), PAK (50), PA388 (4), and FRD1 (38), as well as a collection of CF-derived mucoid and nonmucoid strains (3, 61). WFPA50 is PAO1 fliC::xylE-aacC1 (63) and PAO AWO is PAO1 pilA::tet (J. Mattick); J. Goldberg supplied the PAO1 algC mutant. Escherichia coli strain JM109 (Promega) was used for all cloning experiments, while strains SM10 and HB101/pRK2013 (13) were used to transfer plasmids to P. aeruginosa. PAO1 Smr was a spontaneous mutant generated by plating an overnight culture of PAO1 onto a selective medium (100 μg of streptomycin/ml) and screening for spontaneous streptomycin-resistant mutants. PAO1, WFPA60, and MS2 were tagged with the green fluorescent protein (GFP)-expressing plasmid pMRP9 via a linear transformation protocol (11). PCR was used to amplify a 2.5-kb fragment, which included pslA (PA2231) and a portion of pslB (PA2232) (54), with the primers psl1 and psl2 (Table 1). The amplicon was cloned into pALTER1 (Promega) to generate pKDJ1. Huang and colleagues used the PAO1 cosmid library and the PAO1 genome sequence to map a minimal tiling path (22). This library was used to identify two overlapping cosmids, pMO011305 and pMO013305, that span the entire psl cluster. Luria broth (LB; 10 g of tryptone/liter, 5 g of yeast extract/liter, 5 g of sodium chloride/liter), LB lacking sodium chloride (LBNS), and Jensen's, a chemically defined medium (23), were used throughout the study. Unless otherwise indicated, the carbon sources were used at 0.4%. The plasmids were maintained in E. coli by antibiotic selection with 15 μg of tetracycline and gentamicin/ml, 100 μg of ampicillin/ml, and 30 μg of kanamycin or streptomycin/ml. In P. aeruginosa, antibiotics were used at 100 μg/ml for tetracycline, streptomycin, and gentamicin and 300 μg/ml for carbenicillin. Sucrose (5%) and irgasan (25 μg/ml) were utilized for counterselection. All oligonucleotides used for this study are depicted in Table 1.
TABLE 1.
Oligonucleotides used for this study
| Oligonucleotide | Sequence (5′ - 3′) |
|---|---|
| psl1 | GGAATTCCTCGCAGAAGGTCCAGTCCCGCGCCT |
| psl2 | CGGGATCCGGCGCGCTCCGGGGGATGCCGAA |
| algD17 | CGCAGAGAAAACATCCTATC |
| algD20 | TGAAGTCGGTGGTGCCGACA |
| PA1389A | GGTCTAGAGCCACTACCATTCTCTCG |
| PA1391A | GCCAGAGTTGCCTGTCC |
| PA1390A | CGGATGACTGGCTGGCGTCC |
| PA1390B | TGATCAGCCTGCCTCGCACC |
| PA2231A | CATGTACCAGGGCCTGGGCC |
| PA2231B | CCGCGGTAGCCGTTGATCTG |
| PA3059A | GTTGATCCTCGGTCTCCCCG |
| PA3059B | CGATCAGTTCGCGGCAGGAG |
| PA3559A | GCTGTTCGAACGCATCCGGG |
| PA3559B | TCAGGCCTGGCGCAACAGGC |
Genomic DNA isolation and PCR assays.
Genomic DNAs were purified from P. aeruginosa strains with Wizard genomic DNA isolation reagents (Promega). PCR assays were performed with 100 ng of genomic DNA, the primer pairs indicated in Table 1, and Taq polymerase according to the manufacturer's recommendations (Promega).
Creation of WFPA60 and MS2.
A restriction digest of pKDJ1 with BamHI and EcoRI generated a 2.5-kb fragment which was cloned into the gene replacement vector pEX18Ap (21) and designated pDJW630. Plasmid pDJW630 was subsequently digested with the restriction enzyme XmaI, and a 2.2-kb xylE-aacC1 cassette from pX1918G (21) was cloned in the plasmid to create pDJW634, which carries pslAB::xylE-aacC1. The digestion of pDJW630 with XmaI removes the 3′ end of pslA and the 5′ end of pslB (54). The aacC1 marker of pX1918G is reported to create nonpolar insertions during gene disruptions (21). We utilized standard reverse genetics strategies with strain SM10/pDJW634 to disrupt pslAB (PA2231-2232) (21, 31, 60). The successful disruption of pslAB was confirmed by PCR assays. MS2 construction proceeded as follows. A 7.0-kb region of the PAO1 genome containing open reading frames (ORFs) PA1389 to PA1391 was amplified by using primers PA1389A and PA1391A (Table 1). The PCR product was digested with EcoRI and XbaI and ligated into the corresponding restriction sites of pUC18 (57). A 1.6-kb SmaI fragment from pGMΩ1 (48), containing a marker for gentamicin resistance, was ligated into the EcoRV sites of the construct. The PvuII fragment of the resulting plasmid was ligated into pEX18Ap (21). The MS2 mutant was generated in PAO1 via standard allelic exchange and was verified by PCR (21). The growth kinetics of WFPA60 and MS2 were determined in both LBNS and Jensen's defined medium.
Microtiter dish assay.
For biofilm initiation assays, LBNS was inoculated (1:100) with an overnight culture of each strain, and the diluted bacterial suspensions were added to a 96-well microtiter dish (40). The microtiter dish was incubated at 30°C for the indicated times. At each time point, the nonattached and loosely adherent bacteria were removed by discarding the medium and the cells. The wells were rinsed thoroughly with water. Next, 100 μl of a 0.1% solution of crystal violet was added to each well and the plates were incubated at 25°C for 30 min. The washing process was repeated, the crystal violet staining the attached cells was solubilized with 200 μl of 95% ethanol, and 125 μl was removed and place in a fresh polystyrene microtiter dish to determine the A540.
Motility and LPS assays.
For twitching motility assays (50), the strains were stab inoculated into a thin layer of 1% LANS (LBNS plus 1% agar), incubated overnight at 37°C, and incubated an additional 24 h at 25°C to allow motility zones to become more prominent. Flagellum-mediated motility assays were performed by inoculating a single colony onto 0.3% LANS. After overnight growth at 37°C, the motility was assessed by examining the distance the colonies spread beyond the point of inoculation (1). Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was extracted, resolved by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), and silver stained according to previously published methods (20).
Confocal laser scanning microscopy.
Bacteria were cultured in Jensen's medium in a flowthrough biofilm culturing system at 30°C (5, 23). For visualization, each strain was tagged with the GFP-containing plasmid pMRP9 (11). Biofilm growth was assessed at 12-h time points up to 72 h with a Zeiss LSM 510 confocal laser scanning microscope.
Quantitative analysis of biofilm formation by silicone tubing continuous-flow model.
To quantitatively analyze biofilm populations of the wild type and the pslAB mutants, we used a biofilm tubing assay as previously described (47). The tubing was aseptically inoculated with 200 μl of a cell suspension from a mid-logarithmic-phase culture (A600 = 0.5, or ∼107 cells) of strain PAO1 or WFPA60 by use of a 25 5/8-gauge needle. The bacteria were allowed to adhere to the inner surface of the tubing for 30 min before the flow of the culture medium was resumed (flow rate, ∼0.7 ml/min). At designated time points, a 15.0-cm-long section of tubing was excised 7.5 cm from the inoculation point. This length of tubing was longitudinally sectioned, and biofilm-grown cells were harvested into 1 ml of medium. The bacteria were serially diluted and enumerated by viable plate counts on LANS. Data are expressed as the log CFU recovered at each time point examined.
Coinoculation assays.
For coinoculation experiments (see Table 3), ∼107 PAO1 Smr and WFPA60 bacteria were coinoculated into the same biofilm tubing system. The experiments were conducted as described above, except that the cells were enumerated by plate counts on a selective medium containing streptomycin for PAO1 Smr and gentamicin for WFPA60. In sequential coinoculation experiments, ∼107 PAO1 Smr bacteria were introduced into the tubing system and allowed to establish a biofilm for 24 h, at which time ∼107 WFPA60 cells were inoculated 0.5 cm upstream of the PAO1 Smr inoculation point. WFPA60 was allowed to attach for 30 min, and then the medium flow was resumed for an additional 24 h. Biofilm cells were then harvested, resuspended, and enumerated by plating onto selective medium. Data are presented as fractions of the total bacteria recovered.
TABLE 3.
Quantification of bacteria recovered during simultaneous and sequential coinoculation biofilm tubing assaysa
| Strain | Inoculation | Time of harvesting (h) | Fraction of bacteria recovered |
|---|---|---|---|
| PAO1 Smr | Simultaneous | 48 | 0.999 |
| WFPA60 | Simultaneous | 48 | 0.001 |
| PAO1 Smr | Sequential | 48 | 0.999999 |
| WFPA60 | Sequential | 24 | 0.000001 |
At 48 h, the biofilm cells were harvested, resuspended, plated onto selective media, enumerated, and expressed as a percentage of the total population of cells recovered.
RESULTS
Analysis of loci potentially involved in EPS production.
Recently published data suggest that polysaccharides other than alginate may contribute to the formation of the PAO1 biofilm matrix (19, 37, 62). A prior annotation of the P. aeruginosa genome suggested that PAO1 has at least three regions that are potentially involved in the synthesis of novel exopolysaccharides (see the supplemental data for reference 54). A recent report has implicated a fourth locus, designated pel, that is required for P. aeruginosa pellicle formation on liquid surfaces and that may be involved in the synthesis of an extracellular matrix (14). We determined whether the genes within these loci are conserved among P. aeruginosa strains. Chromosomal DNAs were purified from a variety of commonly used P. aeruginosa strains as well as from mucoid and nonmucoid isolates derived from CF patients (see Materials and Methods for a list of the strains analyzed). PCR assays were performed, using primers specific for one gene within each cluster (PA2231 [algD], PA1390, PA3059 [pelF], and PA3559) (Fig. 1). The algD gene was chosen as a control since earlier studies suggested that alginate genes are widely conserved among Pseudomonas isolates (16). With the exception of PA1390 and PA3059 (pelF), these genes were conserved in all strains examined (data not shown). This suggests that P. aeruginosa may utilize common pathways for biofilm matrix formation.
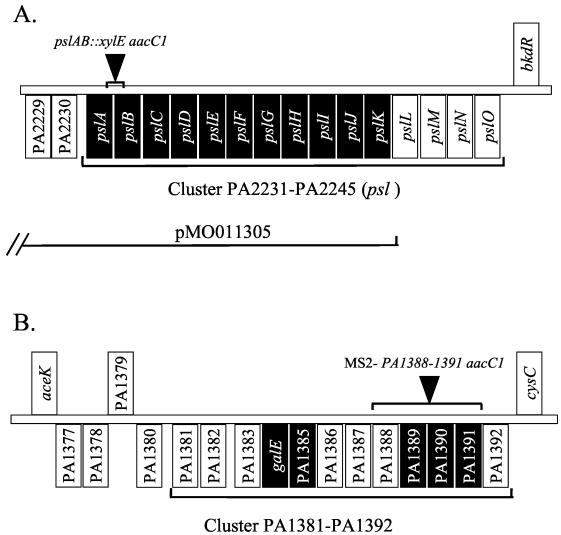
FIG. 1.
(A) Schematic of the psl gene cluster from the annotated P. aeruginosa PAO1 genome. The psl gene cluster is located between opdE and bkdR and contains 15 putative ORFs (∼18.7 kb), annotated PA2231 to PA2245 (54). The ORFs of this cluster are tightly linked in the same orientation, which implies an operon structure. The position of the xylE aacC1 insertion in pslAB, as well as a map of cosmid pMO011305, which complements the WFPA60 mutation, is indicated. Black boxes indicate ORFs that share homology with proteins involved in polysaccharide synthesis, modification, or transport. (B) Schematic of the PA1381-PA1392 gene cluster from the annotated P. aeruginosa PAO1 genome (54). This gene cluster is located between aceK and cysC and contains 12 putative ORFs (∼16.9 kb). The ORFs of this cluster are tightly linked in the same orientation, which implies an operon structure. The position of the aacC1 insertion of strain MS2, replacing the PA1388-PA1391 cluster, is indicated. Black boxes indicate ORFs that share homology with proteins involved in polysaccharide synthesis, modification, or transport.
Two clusters, PA1381-1392 and PA2231-2240 (which we and others have designated psl, for polysaccharide synthesis locus), were selected for further study because most of the genes within these clusters are predicted to encode proteins with sequence homology to enzymes involved in the synthesis of polysaccharides (Fig. 1). For the psl cluster, these biosynthetic genes were suggested to potentially use the carbohydrates glucose, mannose, and rhamnose, the primary constituents of the EPS purified from biofilm-grown P. aeruginosa (62). An analysis of the pslA and pslC genes suggested that they encode glucose and rhamnose glycosyl transferases, respectively. The pslB gene encodes a probable phosphomannose isomerase/GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase, and pslD encodes an exopolysaccharide transporter (Fig. 1A; Table 2). The psl gene cluster, annotated PA2231-PA2245, is located between opdE and bkdR and contains 15 putative ORFs (∼18.7 kb, designated pslA to pslO). The ORFs of this cluster are tightly linked in the same orientation, which implies an operon structure (Fig. 1A).
TABLE 2.
psl ORFs PA2231 to PA2245 with proposed roles in polysaccharide synthesis
| Gene | ORF | No. of amino acids, predicted mass (kDa) | % Similarity or homology to another protein |
|---|---|---|---|
| pslA | PA2231 | 478, 54.8 | 69, to colonic acid UDP-glucose lipid carrier, WcaJ (E. coli) |
| pslB | PA2232 | 488, 53.5 | 72, to PMI/GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase WbpW (P. aeruginosa) |
| pslC | PA2233 | 303, 33.6 | 59, to rhamnosyl transferase RfbN (Salmonella) |
| pslD | PA2234 | 256, 27.9 | 47, to amylovoran export protein AmsH (Erwinia) |
| pslE | PA2235 | 662, 74.5 | 40, to xanthan translocation protein GumC (Xanthomonas) |
| pslF | PA2236 | 395, 42.7 | 38, to beta-xylosidase (Caldicellulosiruptor) |
| pslG | PA2237 | 442, 50.0 | 43, to putative GlcNAc transferase (Bordetella) |
| pslH | PA2238 | 402, 44.6 | 43, to putative galactosyltransferase (Archaeoglobus) |
| pslI | PA2239 | 367, 40.6 | 42, to glycosyltransferase WbpY (P. aeruginosa) |
| pslJ | PA2240 | 478, 52.5 | 43, to putative polysaccharide polymerase (Streptococcus pneumoniae) |
| pslK | PA2241 | 469, 49.6 | 45, to putative membrane-associated virulence factor MviN (E. coli) |
| pslL | PA2242 | 355, 39.9 | Unknown (hypothetical protein) |
| pslM | PA2243 | 577, 61.5 | 49, to hypothetical protein Rv3537 (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) |
| pslN | PA2244 | 333, 38.0 | Unknown (hypothetical protein) |
| pslO | PA2245 | 101, 10.6 | Unknown (hypothetical protein) |
An analysis of the PA1381-PA1392 cluster revealed a collection of genes that also encode potential polysaccharide biosynthetic enzymes (Fig. 1B). This cluster harbors four genes, PA1385 and PA1389 to PA1391, that have homology to glycosyl transferases. PA1384, annotated as galE, is predicted to encode a UDP-glucose 4-epimerase. Interestingly, the genes of this cluster display a G+C content that is much lower (<60%) than that of the P. aeruginosa average (67%), suggesting that these genes may have been acquired through horizontal gene transfer. These genes also cluster fairly tightly, implying an operon structure.
A pslAB mutant is deficient in the initiation of biofilm formation.
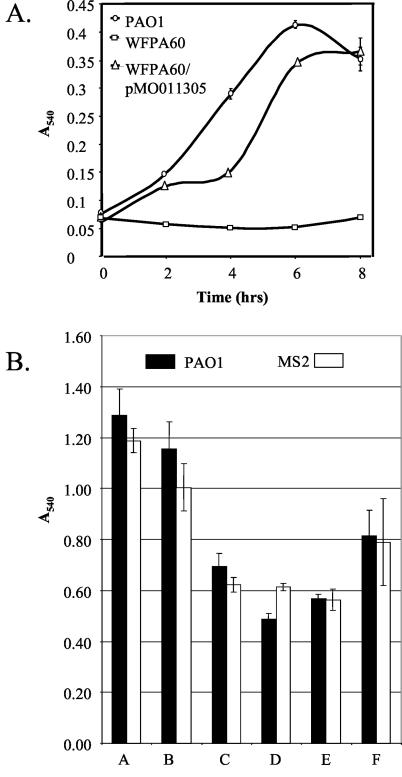
To test whether the psl or PA1381-PA1393 gene cluster plays a role in biofilm development, we utilized standard reverse genetics strategies to disrupt both pslA and pslB or PA1388-1391 in P. aeruginosa PAO1 (see Materials and Methods and Fig. 1). The pslAB mutant was generated with the aacC1 (gentamicin resistance) marker of pX1918G, which is reported to create nonpolar insertions during gene disruption (49). We compared the pslAB mutant, designated WFPA60, with the parental PAO1 strain for the ability to initiate biofilm formation by utilizing the biofilm microtiter dish assay (Fig. 2). This assay, which measures the early stages of biofilm formation, is based on the quantitation of bacterial cells attached at the medium-air interface of a well of a polyvinyl chloride (PVC) microtiter dish (41). In this assay, WFPA60 was severely deficient in the ability to initiate biofilm formation (Fig. 2A). This defect was not due to differences in the growth rate, as PAO1 and WFPA60 had similar growth rates (data not shown). The defect in biofilm initiation was clearly mediated by the disruption of pslAB, since the introduction of cosmid pMO011305, which harbors a 22.5-kb insert containing the majority of the psl locus (22) (Fig. 1A), into WFPA60 restored the biofilm initiation levels (Fig. 2A).
FIG. 2.
Biofilm formation by P. aeruginosa strains. (A) The biofilm formation of strains PAO1 (circles), WFPA50 (squares), and WFPA60/pMO011305 (triangles) was assayed at 2-h intervals in a static microtiter plate system (40). Surface-attached cells were stained with crystal violet, the stain was solubilized in ethanol, and the absorbance was analyzed at 540 nm. (B) Biofilm formation of PAO1 (black) and MS2 (white) at 10 h in a static microtiter plate system (40). Bacteria were cultured with the following carbon sources (0.4%): A, LB medium; B, LB medium with glucose; C, 10× glucose; D, succinate; E, glycerol; F, glutamate (F).
An analysis of strain MS2, which had a mutation in the other potential EPS biosynthetic gene cluster (PA1388-1391), showed no significant defect in biofilm initiation in the microtiter dish assay, even when tested under a variety of growth conditions (Fig. 2B). In flow cell assays, MS2 also produced a robust biofilm that was structurally similar to that of the wild-type strain (data not shown). Because the disruption of PA1388-1391 had no apparent effect on biofilm formation, the remainder of the study focused on the involvement of the psl gene cluster in biofilm development.
The pslAB mutant has no apparent defect in LPS synthesis or motility.
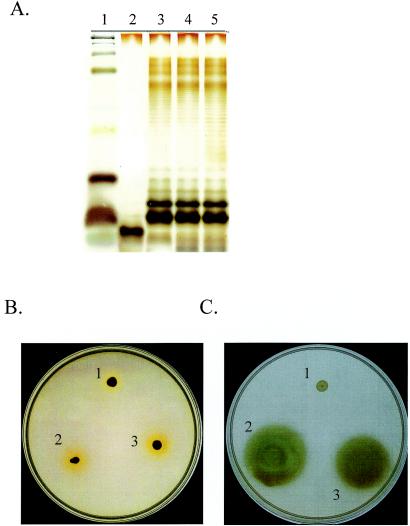
To our knowledge, a function for the psl gene cluster in biofilm formation has yet to be reported. Since many of the ORFs may encode enzymes involved in polysaccharide synthesis (Fig. 1; Table 2), psl may regulate or constitute a portion of the LPS synthesis pathway. LPS has been implicated in the architecture of P. aeruginosa biofilms (44), and a prior study suggested that pslB (designated ORF 488) may be involved in A-band LPS synthesis (45). To determine if the psl-dependent effects on biofilm formation are LPS related, we compared the LPS profiles of PAO1, WFPA60, a PAO1 algC mutant, and the corresponding algC complemented strain. P. aeruginosa algC mutants have a defect in LPS core oligosaccharide synthesis (9). The LPSs from these strains were extracted (20), resolved by SDS-15% PAGE, and silver stained. The silver-stained gel revealed identical LPS profiles for PAO1, WFPA60, and the complemented LPS-deficient mutant (Fig. 3A, lanes 3 to 5), whereas the PAO1 algC mutant clearly lacked core oligosaccharides (Fig. 3A, lane 2).
FIG. 3.
The pslAB mutant has no defects in LPS synthesis or motility. (A) LPS profiles of PAO1 (lane 5) or the following PAO1-derived strains: PAO1 algC (lane 2), PAO1 algC plus algC (lane 3), and WFPA60 (lane 4). LPS was extracted from these strains, separated by SDS-15% PAGE, and visualized by silver staining of the polyacrylamide gel. Lane 1 contains a protein standard. (B) Twitching motility assays of PAO1 AWO (pilA::tet) (spot 1), PAO1 (spot 2), and WFPA60 (spot 3). (C) Flagellum motility assays of WFPA50 (fliC::aacC1) (spot 1), PAO1 (spot 2), and WFPA60 (spot 3).
Since prior studies implicated flagellum (swimming)- and type IV fimbria (twitching)-mediated motility in P. aeruginosa biofilm development (25, 42), we conducted standard twitching and swimming motility assays (2, 50) and found no motility defects in WFPA60 (Fig. 3B and C, respectively). These data strongly suggest that the defect in biofilm formation described above for WFPA60 is not due to alterations in LPS biosynthesis or motility.
The pslAB mutant is severely compromised in biofilm formation in a flow cell reactor.
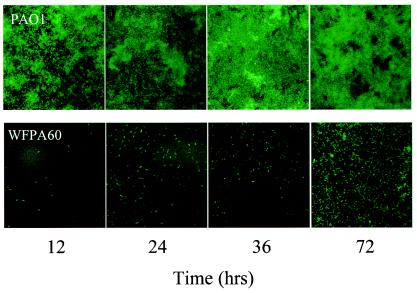
One limitation of the microtiter dish assay is that nutrients are diminished and waste products accumulate rapidly, making it difficult to examine biofilm development for extended periods of time. In addition, microtiter dish-grown biofilms are not amenable to microscopy. Therefore, we used flow cell devices to compare the biofilm development of PAO1 and WFPA60. In this system, nutrients are continually replenished, allowing for the long-term observation of living hydrated biofilms on a glass surface. We generated GFP-tagged derivatives of PAO1 and WFPA60 (11, 64) and combined flow cell culturing technology and confocal scanning laser microscopy to examine the architecture of these strains over time (Fig. 4). The parental strain PAO1 formed robust biofilms throughout the time course of this experiment (Fig. 4, top panels). However, when strain WFPA60 was examined, we discovered that it was severely compromised in biofilm development at all time points examined, even though an identical number of PAO1 and WFPA60 bacteria were initially inoculated into the flow cells (Fig. 4, bottom panels). At the latest time point examined (72 h), some of the WFPA60 bacteria began to develop into microcolonies, suggesting a severe attenuation in biofilm initiation.
FIG. 4.
Qualitative analysis of PAO1 and WFPA60 biofilm populations. Strains harboring pMRP9 were inoculated into respective flow devices and assayed at various time points postinoculation up to 72 h. WFPA60 is deficient in biofilm formation under laminar flow growth conditions compared to PAO1.
Quantitative analysis of PAO1 and pslAB biofilm-grown cells.
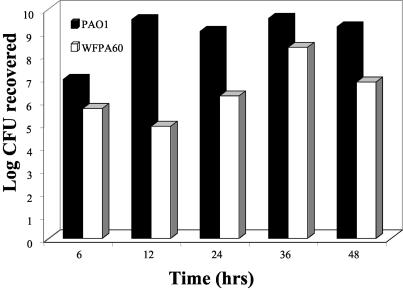
A quantitative assessment of the biofilm formation of WFPA60 further strengthened our assertion that the psl cluster plays a role in biofilm development. Therefore, we devised a tubing assay to quantify the population of biofilm-grown cells under continuous laminar flow conditions with a constant supply of fresh growth medium. Based on the above results, we hypothesized that there would be a significant difference in biofilm formation between the PAO1 and WFPA60 strains. The biofilms were grown in silicone tubes by first priming the substratum with medium and then inoculating the tubing with a culture of PAO1 or WFPA60, allowing the cells to attach for 1 h, and initiating a continuous flow of medium. At 6, 12, 24, 36, and 48 h, a defined section of tubing was longitudinally sectioned, and biofilm bacteria were harvested and enumerated by plate counting. WFPA60 exhibited a substantial defect in biofilm initiation (up to 105-fold) compared to the isogenic parental PAO1 strain (Fig. 5). Strain WFPA60, which was impaired in the initial stages of biofilm formation (Fig. 2), appeared unable to overcome the defect over an extended time period when it was incubated under continuous laminar flow conditions.
FIG. 5.
Quantitative analysis of PAO1 and WFPA60 biofilm populations in silicone tubing continuous flow devices. Overnight cultures of each strain (∼107 cells) were inoculated into a section of silicone tubing that had first been primed with medium. At designated endpoints (6, 12, 24, 36, and 48 h), the tubing was longitudinally sectioned and the biofilm-grown cells were harvested, resuspended, and enumerated by plate counts (see Materials and Methods). Data are expressed as the log CFU recovered at each time point examined and are the averages of three independent experiments.
Since WFPA60 was severely compromised in biofilm development, we reasoned that one or more factors (likely the EPS) that are required for cell-surface or cell-cell interactions are lacking in this strain. Assuming that this was the case, we hypothesized that the factor(s) may be supplied in trans by the parental strain in a coculture. To test this, we coinoculated an identical number of PAO1 and WFPA60 bacteria into the biofilm tubing system described above. After 48 h, the tubing was sectioned and the cells were harvested and plated onto a selective growth medium. To distinguish between WFPA60 and PAO1, we used a streptomycin-resistant PAO1 derivative (PAO1 Smr) and WFPA60, which is gentamicin resistant. When they were simultaneously cocultured, PAO1 Smr was unable to rescue the pslAB mutant phenotype (Table 3), suggesting that WFPA60 was unable to effectively compete with the wild-type strain for a shared substratum.
In the above assay, PAO1 and WFPA60 were inoculated simultaneously. We also examined whether WFPA60 could be recruited into an established biofilm formed by a wild-type strain. To test this, we inoculated PAO1 Smr into the continuous flow silicone tubing system and incubated it for 24 h. PAO1 Smr readily attached to the tubing and initiated biofilm development during this period (Table 3). After this initiation, an identical number of WFPA60 cells were introduced into the system and incubated for 30 min without flow, after which the flow was resumed. After 24 h, the numbers of PAO1 Smr and WFPA60 cells were determined. The results were consistent with those of the other biofilm assays; even when cocultured sequentially, WFPA60 was significantly impaired at biofilm initiation (Table 3). These data indicate that even when WFPA60 is deposited onto an established biofilm of wild-type cells, it is unable to establish a niche. Taken together, the data in Fig. 2, 4, and 5 and Table 3 suggest that the psl gene cluster contributes significantly to cell-surface interactions with abiotic surfaces (glass, PVC, and silicone) as well as to cell-cell interactions with certain biotic surfaces.
DISCUSSION
A critical aspect of P. aeruginosa pathogenesis is the ability to form biofilms in the lungs of CF patients and on many other surfaces. For some time, alginate has been considered the major polysaccharide of the biofilm EPS matrix. However, recent studies have indicated that alginate is not involved in the initiation of biofilm formation by nonmucoid P. aeruginosa strains, which are the first to colonize CF patients (19, 37, 62). Instead, there appear to be other EPS components that mediate biofilm formation. In this paper, we analyzed two gene clusters that appear to encode enzymes for the synthesis of novel polysaccharides. The inactivation of genes within one cluster (PA1381-PA1393) resulted in no discernible biofilm phenotype. Although we cannot rule out a role for this cluster in biofilm development or polysaccharide synthesis in P. aeruginosa, we concentrated our efforts on discerning the function of the psl gene cluster. The disruption of the first two genes within the psl cluster (strain WFPA60) led to a profound biofilm initiation deficiency. The pslAB mutant cells, which were impaired in the initial stages of biofilm formation, were unable to overcome this defect over an extended time period when they were incubated under continuous flow conditions. This impaired ability of WFPA60 to initiate biofilm formation was observed for several abiotic surfaces (PVC, glass, and silicone tubing) and was not due to defects in motility or LPS biosynthesis. Moreover, by using both qualitative and quantitative assays, we showed that WFPA60 is deficient in biofilm formation for up to 72 h. Finally, we report that either simultaneous or sequential coinoculation of wild-type P. aeruginosa cannot rescue the biofilm formation phenotype of WFPA60. Overall, our interpretation of these data is that the pslAB mutant is impaired in the initiation phase of biofilm formation. We propose that genes within the psl cluster play a critical role in cell-cell and/or cell-surface interactions. This is consistent with the findings in accompanying papers from two other groups (15, 34).
Although our present data do not directly address whether the psl locus encodes a novel exopolysaccharide, there are precedents for exopolysaccharides from other bacteria having roles similar to those proposed for P. aeruginosa psl. Exopolysaccharides have been shown to play an important role in bacterial plant and animal pathogenesis for a variety of bacterial species (24, 32, 36). Many of the infections caused by these organisms are believed to involve biofilms, and exopolysaccharide-negative strains are typically avirulent.
Exopolysaccharides are often implicated in either mediating attachment or providing protection. The properties of the exopolysaccharide matrix that confer protection depend upon the nature of the antimicrobial agent or stress being applied. In general, the exopolysaccharide can act as a physical barrier or function as a chemically reactive barrier. Future studies are aimed at determining if the psl locus does indeed encode a novel polysaccharide that plays a protective role in P. aeruginosa biofilms. Nonetheless, our observations support the conclusion that the psl cluster encodes gene products that are required for mediating cell-surface and cell-cell interactions. Initial attachment requires that a repulsion barrier between a negatively charged bacterial cell and a surface must be overcome (55, 56). Different exopolysaccharides, such as those from Vibrio sp., acidic polysaccharides of marine pseudomonads, and Staphylococcus epidermidis PIA and PS/A clearly promote adherence (6, 18, 32, 35, 65). The prosthecate marine bacterium Hyphomonas produces at least two developmentally regulated exopolysaccharides that serve as adhesins (28). Exopolysaccharides can also influence biofilm structure and function, as has been demonstrated for alginate (19, 37), Vibrio cholerae Vps (65), and E. coli colanic acid (10).
The pslAB mutant attaches poorly to abiotic and biotic surfaces under both static and dynamic culture conditions. This phenotype is most readily apparent for attachment to these surfaces under dynamic culture conditions. However, under extended static culture conditions (>36 h), WFPA60 eventually will form biofilms that are comparable to those formed by the wild-type strain (K. D. Jackson and D. J. Wozniak, unpublished data). When the WFPA60 cells are left undisturbed for extended periods, they begin the biofilm formation process, but this is substantially delayed in the dynamic flow tubing system. This assay was designed to mimic indwelling device biofilms such as those that form in catheters. Our interpretation of this is as follows. If WFPA60 is deficient at forming cell-surface and cell-cell interactions but is left undisturbed, it will eventually overcome these barriers. However, if it is subjected to laminar or turbulent flow, it is incapable of mediating such interactions. It is also possible that the growth conditions in these long-term static experiments result in the activation of another set of exopolysaccharide genes, such as pel or PA1388-1391, and that this can compensate for the loss of psl.
Sauer et al. proposed that during biofilm formation, cells undergo a two-step attachment process consisting of reversible and irreversible phases (see reference 46 and references therein). In the reversible attachment phase, the cells contact the surface via the cell pole and are transiently affixed to the substratum, contrasting with the irreversible attachment stage, in which the cells reorient to the longitudinal cell axis and begin cell cluster (microcolony) formation. In future experiments, it would be worthwhile to investigate more thoroughly at which stage WFPA60 is impaired (i.e., reversible versus irreversible attachment).
The biochemical composition of the P. aeruginosa biofilm matrix in mature nonmucoid biofilms has remained poorly defined. Until recently, it was assumed that the matrix is composed of alginate, but several reports have challenged this (14, 19, 37, 62). A recent study indicated the importance of extracellular DNA for the initial establishment of P. aeruginosa biofilms (58). More recently, Friedman and Kolter identified a seven-gene locus in P. aeruginosa strain PA14, designated pel, that is required for the formation of pellicles at the air-liquid interface (14). Most of the predicted proteins of the pel genes have amino acid sequence similarities with enzymes involved in carbohydrate processing. Carbohydrate and glycosyl linkage analysis of the matrix material derived from PA14 and PA14 pel mutants supported the conclusion that the matrix is composed of a glucose-rich component that is distinct from cellulose or LPS. Although we did not investigate the involvement of the pel locus in P. aeruginosa PAO1 biofilms, it was reported that the laboratory domestication of strain PAO1 may have precluded identification of the pel genes in PAO1 biofilm formation (14). Likewise, strain PA14 appears to lack the pslA to -D genes (15). A recent analysis examined the genomic contents of 18 P. aeruginosa isolates derived from diverse sources ranging from the environment to acute and chronic infections (59). The data from that analysis showed that the psl and pel loci were present in every strain analyzed, indicating that most P. aeruginosa genes possess the genetic potential to produce these putative EPS types. Interestingly, the putative EPS locus PA1381-1392 was present in only 11 of the isolates examined.
An earlier analysis of the P. aeruginosa PAO1 biofilm matrix revealed that the primary carbohydrate constituents are glucose, rhamnose, and mannose (62). A neutral extracellular polysaccharide containing d-glucose, d-mannose, and l-rhamnose was previously purified from a clinical P. aeruginosa immunotype 4 isolate (26). However, there have been no subsequent reports regarding the genetic basis for the production of this polysaccharide. Although carbohydrate analysis of the PA14 pellicle matrix did not identify mannose as a component (14), this sugar subunit is clearly present in the PAO1 biofilm matrix (62). Since the pslB gene product is a probable phosphomannose isomerase/GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase, it is tempting to speculate that the psl locus may be involved in the synthesis of a mannose-containing polysaccharide that contributes to biofilm formation. Data in one of the accompanying papers (15) support this hypothesis. It is also possible that P. aeruginosa has the capacity to synthesize several alternative polysaccharides that play a role in the biofilm matrix.
Because of their intrinsic resistance to antimicrobial agents, biofilms are significant in medicine and industry. The chemical structure of the biofilm matrix is believed to be composed of nucleic acids and exopolysaccharides. Our data indicate that a previously uncharacterized locus, psl, may encode a novel polysaccharide that is required for the formation of the biofilm matrix. Future experiments will include a thorough comparison of the carbohydrate constituents and the glycosyl linkages of polysaccharides purified from PAO1 and WFPA60. In addition, the role of the remaining psl genes (pslC to pslO) in biofilm formation requires further study. In this regard, data in an accompanying paper reveal that all 15 of the genes within the psl locus are cotranscribed, suggesting that there is a single operon (34).
Since mucoid conversion typically occurs months or years after initial colonization (17), we hypothesize that P. aeruginosa has the capacity to express alternative exopolysaccharides that are essential for biofilm formation and the persistence of P. aeruginosa infections. Further investigations of these early events in conjunction with data derived from genetic regulation studies of the psl cluster may open up new avenues for immunological or chemotherapeutic interventions for infections caused by this important opportunistic pathogen.
Acknowledgments
Public Health Service grants AI-35177 and HL-58334 (D.J.W.) supported this work. The David and Lucile Packard Foundation supported K.J. This work was also supported by grants to M.P. by the CF foundation (Parsek 02I0) and the National Science Foundation (MCB 0133833). NIH Biotechnology Training grant 5-T32-GM08449-09 supported M.S.
J. Mattick supplied PAO1 AWO and J. Goldberg supplied the PAO1 algC mutant. We thank J. Goldberg and Antonio DiGiandomenico for assistance with the P. aeruginosa LPS analyses.
REFERENCES
- 1.Arora, S. K., B. W. Ritchings, E. C. Almira, S. Lory, and R. Ramphal. 1998. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa flagellar cap protein, FliD, is responsible for mucin adhesion. Infect. Immun. 66:1000-1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Arora, S. K., B. W. Ritchings, E. C. Almira, S. Lory, and R. Ramphal. 1997. A transcriptional activator, FleQ, regulates mucin adhesion and flagellar gene expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a cascade manner. J. Bacteriol. 179:5574-5581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Baynham, P. J., and D. J. Wozniak. 1996. Identification and characterization of AlgZ, an AlgT-dependent DNA binding protein required for Pseudomonas aeruginosa algD transcription. Mol. Microbiol. 22:97-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bjorn, M. J., O. R. Pavloskis, M. R. Thompson, and B. H. Iglewski. 1979. Production of exoenzyme S during Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections of burned mice. Infect. Immun. 24:837-842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Christensen, B., C. Sternberg, J. B. Andersen, R. J. Palmer, A. T. Nielsen, M. Givskov, and S. Molin. 1999. Molecular tools to study biofilm physiology. Methods Enzymol. 310:20-42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Christensen, G., W. Simpson, J. Younger, L. Baddour, F. Barrett, D. Melton, and E. Beachey. 1985. Adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to plastic tissue culture plates: a quantitative model for adherence of staphylococci to medical devices. J. Clin. Microbiol. 22:996-1006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Costerton, J. W. 2001. Cystic fibrosis pathogenesis and the role of biofilms in persistent infection. Trends Microbiol. 9:50-52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Costerton, J. W., Z. Lewandowski, D. E. Caldwell, D. R. Korber, and H. M. Lappin-Scott. 1995. Microbial biofilms. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 49:711-745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Coyne, M. J., K. S. Russell, C. L. Coyle, and J. B. Goldberg. 1994. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa algC gene encodes phosphoglucomutase required for the synthesis of a complete lipopolysaccharide core. J. Bacteriol. 176:3500-3507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Danese, P. N., L. A. Pratt, and R. Kolter. 2000. Exopolysaccharide production is required for development of Escherichia coli K-12 biofilm architecture. J. Bacteriol. 182:3593-3596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Davies, D. G., M. R. Parsek, J. P. Pearson, B. H. Iglewski, J. W. Costerton, and E. P. Greenberg. 1998. The involvement of cell-to-cell signals in the development of a bacterial biofilm. Science 280:295-298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Evans, L. R., and A. Linker. 1973. Production and characterization of the slime polysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 116:915-924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Figurski, D., and D. R. Helinski. 1979. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76:1648-1652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Friedman, L., and R. Kolter. 2004. Genes involved in matrix formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14 biofilms. Mol. Microbiol. 51:675-690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Friedman, L., and R. Kolter. 2004. Two genetic loci produce distinct carbohydrate-rich structural components of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm matrix. J. Bacteriol. 186:4457-4465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Goldberg, J. B., W. L. Gorman, J. L. Flynn, and D. E. Ohman. 1993. A mutation in algN permits transactivation of alginate production by algT in Pseudomonas species. J. Bacteriol. 175:1303-1308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Govan, J. R. W., and V. Deretic. 1996. Microbial pathogenesis in cystic fibrosis: mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cepacia. Microbiol. Rev. 60:539-574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Guvener, Z. T., and L. L. McCarter. 2003. Multiple regulators control capsular polysaccharide production in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J. Bacteriol. 185:5431-5441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hentzer, M., G. M. Teitzel, G. J. Balzer, A. Heydorn, S. Molin, M. Givskov, and M. R. Parsek. 2001. Alginate overproduction affects Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm structure and function. J. Bacteriol. 183:5395-5401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hitchcock, P. J., and T. M. Brown. 1983. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide types in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J. Bacteriol. 154:269-277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hoang, T. T., R. R. Karkhoff-Schweizer, A. J. Kutchma, and H. Schweizer. 1998. A broad-host-range Flp-FRT recombination system for site-specific excision of chromosomally-located DNA sequences: applications for isolation of unmarked Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants. Gene 212:77-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Huang, B., C. B. Whitchurch, L. Croft, S. A. Beatson, and J. S. Mattick. 2000. A minimal tiling path cosmid library for functional analysis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 genome. Microb. Comp. Genomics 5:189-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jensen, S. E., I. T. Facycz, and J. N. Campbell. 1980. Nutritional factors controlling exocellular protease production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 144:844-847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kao, C. C., E. Barlow, and L. Sequeira. 1992. Extracellular polysaccharide is required for wild-type virulence of Pseudomonas solanacearum. J. Bacteriol. 174:1068-1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Klausen, M., A. Heydorn, P. Ragas, L. Lambertsen, A. Aaes-Jorgensen, S. Molin, and T. Tolker-Nielsen. 2003. Biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa wild type, flagella and type IV pili mutants. Mol. Microbiol. 48:1511-1524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kocharova, N., K. Hatano, A. Shaskov, Y. Knirel, N. Kochetkov, and G. Pier. 1989. The structure and serologic distribution of an extracellular neutral polysaccharide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa immunotype 3. J. Biol. Chem. 264:15569-15573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lam, J., R. Chan, K. Lam, and J. R. W. Costerton. 1980. Production of mucoid microcolonies by Pseudomonas aeruginosa within infected lungs in cystic fibrosis. Infect. Immun. 28:546-556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Langille, S. E., and R. M. Weiner. 1998. Spatial and temporal deposition of Hyphomonas strain VP-6 capsules involved in biofilm formation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64:2906-2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Liu, P. V. 1966. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on its pathogenesis. II. Effects of lecithinase and protease. J. Infect. Dis. 116:481-489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lyczak, J. B., C. Cannon, and G. B. Pier. 2000. Establishment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection: lessons from a versatile opportunist. Microbes Infect. 2:1051-1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ma, S., U. Selvaraj, D. E. Ohman, R. Quarless, D. J. Hassett, and D. J. Wozniak. 1998. Phosphorylation-independent activity of the response regulators AlgB and AlgR in promoting alginate biosynthesis in mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 180:956-968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mack, D., W. Fischer, A. Krokotsch, K. Leopold, R. Hartmann, H. Egge, and R. Laufs. 1996. The intercellular adhesin involved in biofilm accumulation of Staphylococcus epidermidis is a linear β-1,6-linked glucosaminoglycan: purification and structural analysis. J. Bacteriol. 178:175-183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mah, T. C., and G. A. O'Toole. 2001. Mechanisms of biofilm resistance to antimicrobial agents. Trends Microbiol. 9:34-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Matsukawa, M., and E. P. Greenberg. 2004. Putative exopolysaccharide synthesis genes influence Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm development. J. Bacteriol. 186:4449-4456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.McKenney, D., J. Hubner, E. Muller, Y. Wang, D. A. Goldmann, and G. Pier. 1998. The ica locus of Staphylococcus epidermidis encodes production of the capsular polysaccharide/adhesin. Infect. Immun. 66:4711-4720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Nimtz, M., A. Mort, T. Domke, V. Wray, Y. Zhang, F. Qiu, D. Coplin, and K. Geider. 1996. Structure of amylovoran, the capsular exopolysaccharide from the fire blight pathogen Erwinia amylovora. Carbohydr. Res. 287:59-76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nivens, D. E., D. E. Ohman, J. Williams, and M. J. Franklin. 2001. Role of alginate and its O acetylation in formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa microcolonies and biofilms. J. Bacteriol. 183:1047-1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ohman, D. E., and A. M. Chakrabarty. 1981. Genetic mapping of chromosomal determinants for the production of the exopolysaccharide alginate in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa cystic fibrosis isolate. Infect. Immun. 33:142-148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.O'Toole, G., H. B. Kaplan, and R. Kolter. 2000. Biofilm formation as microbial development. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 54:49-79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.O'Toole, G., L. A. Pratt, P. I. Watnick, D. K. Newman, V. B. Weaver, and R. Kolter. 1999. Genetic approaches to study biofilms. Methods Enzymol. 310:91-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.O'Toole, G. A. 1998. Initiation of biofilm formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens WCS365 proceeds via multiple convergent signalling pathways: a genetic analysis. Mol. Microbiol. 28:449-461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.O'Toole, G. A., and R. Kolter. 1998. Flagellar and twitching motilities are necessary for Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm development. Mol. Microbiol. 30:295-304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Pier, G. B. 1998. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a key problem in cystic fibrosis. ASM News 6:339-347. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Rocchetta, H. L., L. L. Burrows, and J. S. Lam. 1999. Genetics of O-antigen biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 63:523-553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Rocchetta, H. L., J. C. Pacan, and J. S. Lam. 1998. Synthesis of the A-band polysaccharide sugar d-rhamnose requires Rmd and WbpW: identification of multiple AlgA homologues, WbpW and ORF488, in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 29:1419-1434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sauer, K., A. K. Camper, G. D. Ehrlich, J. W. Costerton, and D. G. Davies. 2002. Pseudomonas aeruginosa displays multiple phenotypes during development as a biofilm. J. Bacteriol. 184:1140-1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Schaefer, A. L., E. P. Greenberg, and M. R. Parsek. 2001. Acylated homoserine lactone detection in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms by radiolabel assay, p. 41-47. In R. J. Doyle (ed.), Microbial growth in biofilms, part A: developmental and molecular biological aspects. Academic Press, New York, N.Y. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 48.Schweizer, H. P. 1993. Small broad-host-range gentamycin resistance cassettes for site-specific insertion and deletion mutagenesis. BioTechniques 15:831-833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Schweizer, H. P., and T. T. Hoang. 1995. An improved system for gene replacement and xylE fusion analysis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Gene 158:15-22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Semmler, A., C. B. Whitchurch, and J. S. Mattick. 1999. A re-examination of twitching motility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology 145:2863-2873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Singh, P. K., A. L. Schaefer, M. R. Parsek, T. O. Moninger, M. J. Welsh, and E. P. Greenberg. 2000. Quorum-sensing signals indicate that cystic fibrosis lungs are infected with bacterial biofilms. Nature 407:762-764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Stephens, C. 2002. Microbiology: breaking down biofilms. Curr. Biol. 12:R132-R134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Stewart, P. S., and J. W. Costerton. 2001. Antibiotic resistance of bacteria in biofilms. Lancet 358:135-138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Stover, C. K., X. Q. Pham, A. L. Erwin, S. D. Mizoguchi, P. Warrener, M. J. Hickey, F. S. L. Brinkman, W. O. Hufnagle, D. J. Kowalik, M. Lagrou, R. L. Garber, L. Goltry, E. Tolentino, S. Westbrock-Wadman, Y. Yuan, L. L. Brody, S. N. Coulter, K. R. Folger, A. Kas, K. Larbig, R. Lim, K. Smith, D. Spencer, G. K.-S. Wong, Z. Wu, I. T. Paulsenk, J. Reizer, M. H. Saier, R. E. W. Hancock, S. Lory, and M. V. Olson. 2000. Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, an opportunistic pathogen. Nature 406:959-964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Strevett, K., and G. Chen. 2003. Microbial surface thermodynamics and applications. Res. Microbiol. 154:329-335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Tsuneda, S., H. Aikawa, H. Hayaski, A. Yuasa, and A. Hirata. 2003. Extracellular polymeric substances responsible for bacterial adhesion onto solid surface. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 223:287-292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Vieira, J., and J. Messing. 1991. New pUC-derived cloning vectors with different selectable markers and DNA replication origins. Gene 100:189-194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Whitchurch, C. B., T. Tolker-Nielsen, P. C. Ragas, and J. S. Mattick. 2002. Extracellular DNA required for bacterial biofilm formation. Science 295:1487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Wolfgang, M. C., B. R. Kulasekara, X. Liang, D. Boyd, K. Wu, Q. Yang, C. G. Miyada, and S. Lory. 2003. Conservation of genome content and virulence determinants among clinical and environmental isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100:8484-8489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Woolwine, S., and D. J. Wozniak. 1999. Identification of an Escherichia coli pepA homolog and its involvement in suppression of the algB phenotype in mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 181:107-116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Wozniak, D. J., A. B. Sprinkle, and P. J. Baynham. 2003. Control of Pseudomonas aeruginosa algZ expression by the alternative sigma factor AlgT. J. Bacteriol. 185:7297-7300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Wozniak, D. J., T. J. O. Wyckoff, M. Starkey, R. Keyser, P. Azadi, G. A. O'Toole, and M. R. Parsek. 2003. Alginate is not a significant component of the extracellular polysaccharide matrix of PA14 and PAO1 Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100:7907-7912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Wyckoff, T. J. O., B. Thomas, D. J. Hassett, and D. J. Wozniak. 2002. Static growth of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa selects for non-mucoid variants that have acquired flagellum-dependent motility. Microbiology 148:3423-3430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Wyckoff, T. J. O., and D. J. Wozniak. 2001. Transcriptional analysis of genes involved in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Methods Enzymol. 336:144-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Yildiz, F. H., and G. K. Schoolnik. 1999. Vibrio cholerae O1 El Tor: identification of a gene cluster required for the rugose colony type, exopolysaccharide production, chlorine resistance, and biofilm formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96:4028-4033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]