Abstract
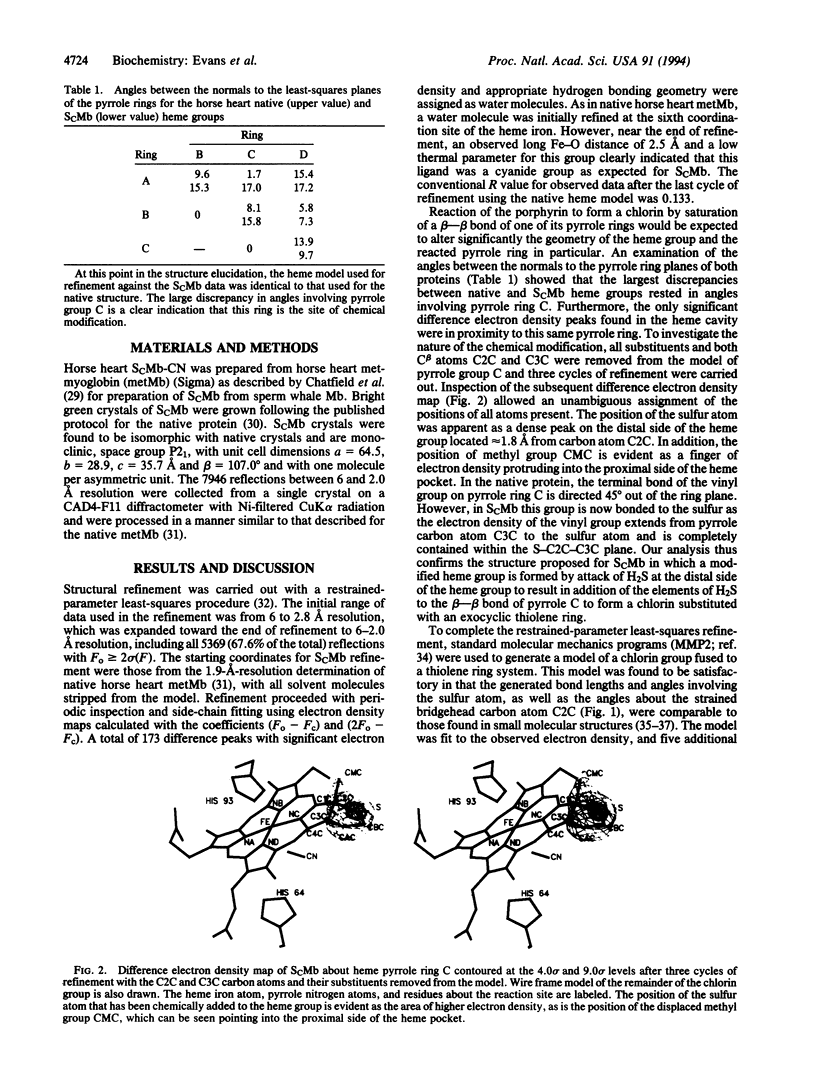
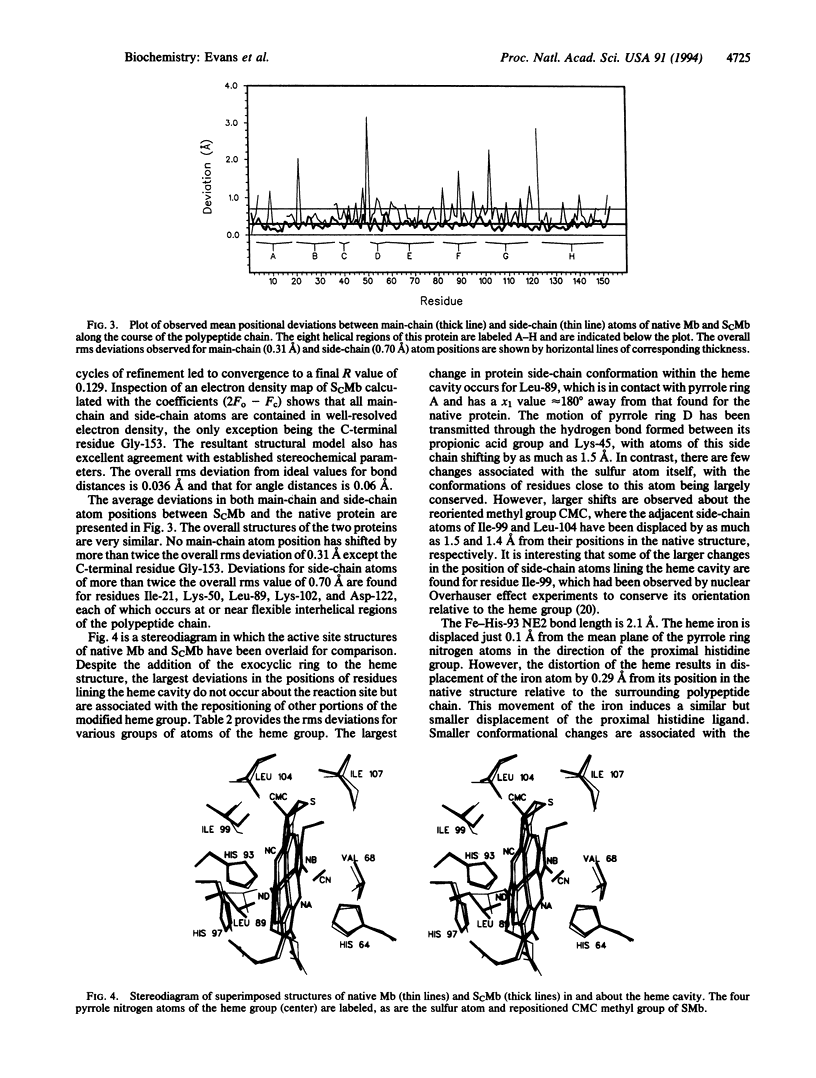
The atomic structure of horse heart cyanomet-sulfmyoglobin C has been established by x-ray crystallographic techniques to a resolution of 2.0 A with an R value of 0.129. The protoheme IX prosthetic group of this thermodynamically stable sulfmyoglobin derivative has been converted to a chlorin in which the pyrrole ring bearing the 4-vinyl group is saturated and possesses an exocyclic thiolene ring. This study provides the three-dimensional structure of a protein with an iron-chlorin prosthetic group. The overall conformation of the surrounding polypeptide chain of the modified protein is very similar to that of the native protein. However, the addition of the sulfur atom has caused a distortion of the prosthetic group from that in the native protein to result in the repositioning of the side chains of some residues in the heme pocket.
Full text
PDF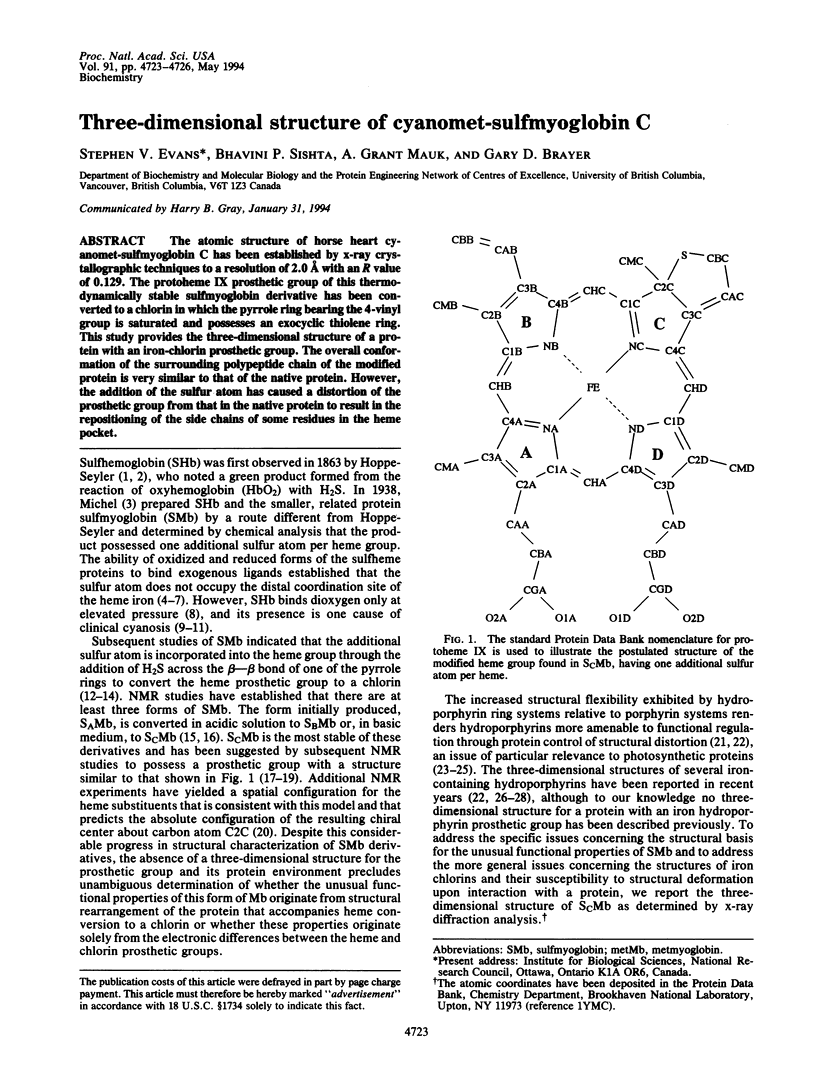

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson L. A., Loehr T. M., Lim A. R., Mauk A. G. Sulfmyoglobin. Resonance Raman spectroscopic evidence for an iron-chlorin prosthetic group. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15340–15349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRANDENBURG R. O., SMITH H. L. Sulfhemoglobinemia; a study of 62 clinical cases. Am Heart J. 1951 Oct;42(4):582–588. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(51)90153-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berzofsky J. A., Peisach J., Blumberg W. E. Sulfheme proteins. I. Optical and magnetic properties of sulfmyoglobin and its derivatives. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3367–3377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berzofsky J. A., Peisach J., Blumberg W. E. Sulfheme proteins. II. The reversible oxygenation of ferrous sulfmyoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7366–7372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondoc L. L., Chau M. H., Price M. A., Timkovich R. Structure of a stable form of sulfheme. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 30;25(26):8458–8466. doi: 10.1021/bi00374a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrico R. J., Peisach J., Alben J. O. The preparation and some physical properties of sulfhemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2386–2391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatfield M. J., La Mar G. N., Balch A. L., Lecomte J. T. Multiple forms of sulfmyoglobin as detected by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 26;135(1):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90978-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatfield M. J., La Mar G. N., Balch A. L., Smith K. M., Parish D. W., LePage T. J. Proton NMR study of the influence of heme vinyl groups on the formation of the isomeric forms of sulfmyoglobin. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 6;206(2):343–346. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatfield M. J., La Mar G. N., Kauten R. J. Proton NMR characterization of isomeric sulfmyoglobins: preparation, interconversion, reactivity patterns, and structural features. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 3;26(22):6939–6950. doi: 10.1021/bi00396a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans S. V., Brayer G. D. High-resolution study of the three-dimensional structure of horse heart metmyoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):885–897. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans S. V., Brayer G. D. Horse heart metmyoglobin. A 2.8-A resolution three-dimensional structure determination. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4263–4268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyan J., Wilz S., Karplus M., Petsko G. A. X-ray structure and refinement of carbon-monoxy (Fe II)-myoglobin at 1.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 5;192(1):133–154. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90470-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magliozzo R. S., Peisach J. A proton nuclear magnetic resonance study of sulfmyoglobin cyanide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jul 25;872(1-2):158–162. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90160-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel H., Epp O., Deisenhofer J. Pigment-protein interactions in the photosynthetic reaction centre from Rhodopseudomonas viridis. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2445–2451. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLLS P. The formation and properties of sulphmyoglobin and sulphcatalase. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:374–383. doi: 10.1042/bj0810374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C. M., Nagel R. L. Sulfhemoglobinemia. Clinical and molecular aspects. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jun 14;310(24):1579–1584. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198406143102407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker W. O., Jr, Chatfield M. J., La Mar G. N. Determination of the chirality of the saturated pyrrole in sulfmyoglobin using the nuclear Overhauser effect. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 21;28(4):1517–1525. doi: 10.1021/bi00430a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. E. Structure and refinement of oxymyoglobin at 1.6 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 5;142(4):531–554. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90262-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. E. Structure of oxymyoglobin. Nature. 1978 May 18;273(5659):247–248. doi: 10.1038/273247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS T. B., WARE A. G. Sulphemo-globinemia following habitual use of acetanild. J Am Med Assoc. 1952 Aug 23;149(17):1538–1541. doi: 10.1001/jama.1952.02930340022008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood C., Mauk A. G., Brayer G. D. Crystallization and preliminary diffraction data for horse heart metmyoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 5;193(1):227–227. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90641-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronrud D. E., Schmid M. F., Matthews B. W. Structure and X-ray amino acid sequence of a bacteriochlorophyll A protein from Prosthecochloris aestuarii refined at 1.9 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 5;188(3):443–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90167-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



