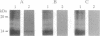Abstract
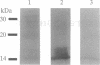
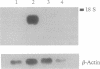
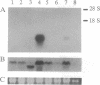
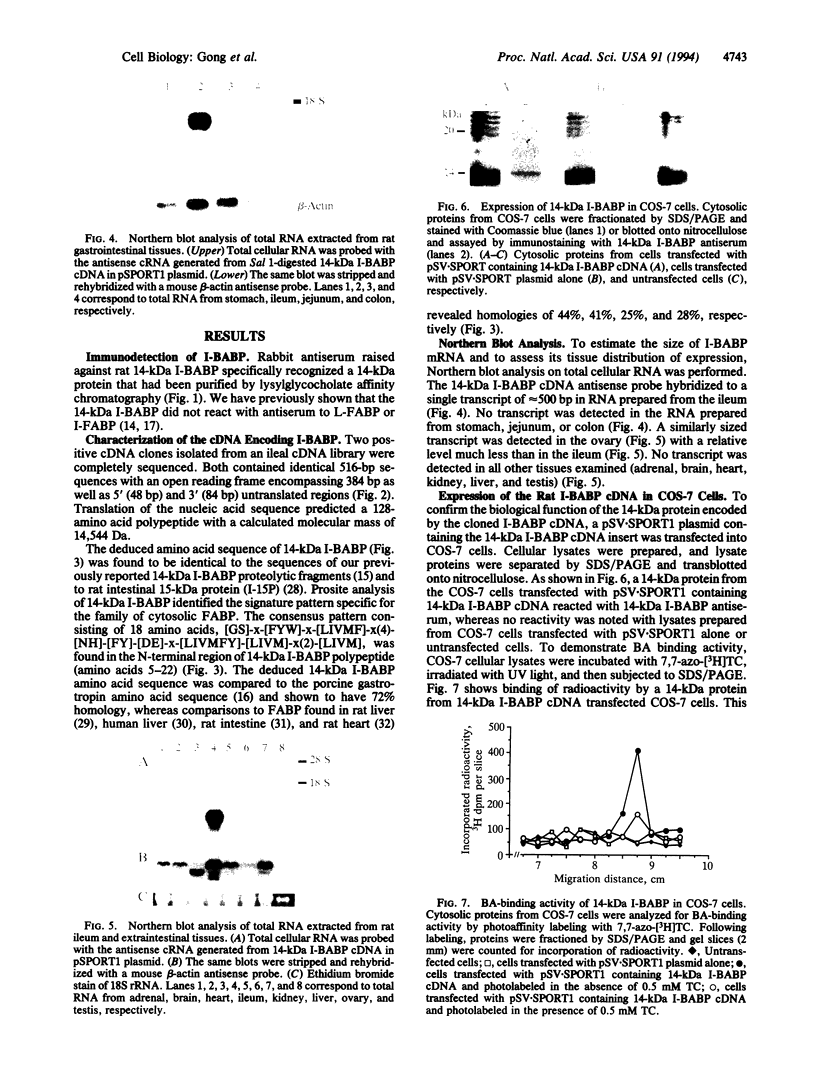
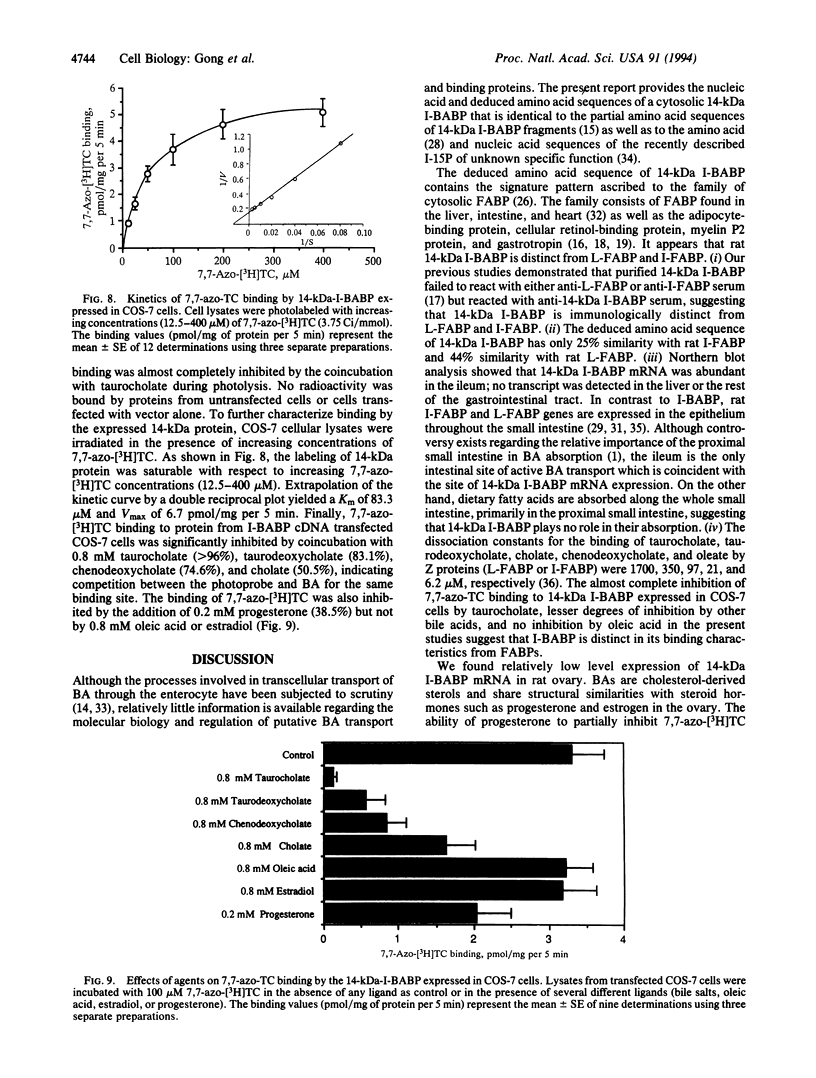
A cDNA clone encoding the major intestinal cytosolic 14-kDa bile acid-binding protein (14-kDa I-BABP) was isolated from a rat ileal lambda gt22A library following immunoscreening using a monospecific antiserum raised against a 14-kDa polypeptide found in the rat ileal cytosol. One clone of 516 bp encoded a 128-amino acid protein with a predicted molecular mass of 14,544 Da. The deduced amino acid sequence of 14-kDa I-BABP showed 100% homology to rat intestinal 15-kDa protein (I-15P) and 72% homology to porcine 15-kDa gastrotropin, whereas comparison of I-BABP to rat 14-kDa fatty acid-binding proteins of liver, intestine, and heart revealed homologies of 44%, 25%, and 28%, respectively. Northern blot analysis revealed a single transcript of approximately 0.5 kb in ileum and ovary; however, the abundance of I-BABP mRNA was much greater in ileum than in ovary. No transcript was seen in RNA extracted from stomach, jejunum, colon, liver, adrenal, brain, heart, kidney, or testis. Transfection of the I-BABP cDNA into COS-7 cells resulted in the expression of a 14-kDa protein that was identical to the ileal cytosolic I-BABP as determined by immunoblotting. Photoaffinity labeling of expressed 14-kDa protein was saturable with respect to increasing concentrations of 7,7-azo[3H]taurocholate (Km, 83.3 microM; Vmax, 6.7 pmol/mg per 5 min). Taurocholate inhibited 7,7-azotaurocholate labeling by > 96% with lesser inhibition by taurochenodeoxycholate (83.1%), chenodeoxycholate (74.6%), cholate (50.5%), and progesterone (38.5%), whereas oleic acid and estradiol did not inhibit binding.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpers D. H., Strauss A. W., Ockner R. K., Bass N. M., Gordon J. I. Cloning of a cDNA encoding rat intestinal fatty acid binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):313–317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bairoch A. PROSITE: a dictionary of sites and patterns in proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19 (Suppl):2241–2245. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.suppl.2241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beesley R. C., Faust R. G. Sodium ion-coupled uptake of taurocholate by intestinal brush-border membrane vesicles. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 15;178(2):299–303. doi: 10.1042/bj1780299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernier I., Jollès P. A survey on cytosolic non-enzymic proteins involved in the metabolism of lipophilic compounds: from organic anion binders to new protein families. Biochimie. 1987 Nov-Dec;69(11-12):1127–1152. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90140-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan L., Wei C. F., Li W. H., Yang C. Y., Ratner P., Pownall H., Gotto A. M., Jr, Smith L. C. Human liver fatty acid binding protein cDNA and amino acid sequence. Functional and evolutionary implications. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2629–2632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claffey K. P., Herrera V. L., Brecher P., Ruiz-Opazo N. Cloning and tissue distribution of rat heart fatty acid binding protein mRNA: identical forms in heart and skeletal muscle. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7900–7904. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii H., Nomura M., Kanda T., Amano O., Iseki S., Hatakeyama K., Ono T. Cloning of a cDNA encoding rat intestinal 15 kDa protein and its tissue distribution. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jan 15;190(1):175–180. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantz I., Nothwehr S. F., Lucey M., Sacchettini J. C., DelValle J., Banaszak L. J., Naud M., Gordon J. I., Yamada T. Gastrotropin: not an enterooxyntin but a member of a family of cytoplasmic hydrophobic ligand binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20248–20254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong Y. Z., Zwarych P. P., Jr, Lin M. C., Wilson F. A. Effect of antiserum to a 99 kDa polypeptide on the uptake of taurocholic acid by rat ileal brush border membrane vesicles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 30;179(1):204–209. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91355-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Alpers D. H., Ockner R. K., Strauss A. W. The nucleotide sequence of rat liver fatty acid binding protein mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3356–3363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Lowe J. B. Analyzing the structures, functions and evolution of two abundant gastrointestinal fatty acid binding proteins with recombinant DNA and computational techniques. Chem Phys Lipids. 1985 Aug 30;38(1-2):137–158. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(85)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J. H., Stratowa C., Rutter W. J. Isolation of full-length putative rat lysophospholipase cDNA using improved methods for mRNA isolation and cDNA cloning. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 24;26(6):1617–1625. doi: 10.1021/bi00380a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignment on a microcomputer. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda T., Odani S., Tomoi M., Matsubara Y., Ono T. Primary structure of a 15-kDa protein from rat intestinal epithelium. Sequence similarity to fatty-acid-binding proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1991 May 8;197(3):759–768. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Burckhardt G., Wilson F. A., Kurz G. Bile salt-binding polypeptides in brush-border membrane vesicles from rat small intestine revealed by photoaffinity labeling. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3623–3627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Kurz G. Photolabile derivatives of bile salts. Synthesis and suitability for photoaffinity labeling. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jul;24(7):910–923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lack L., Walker J. T., Hsu C. Y. Taurocholate uptake by membrane vesicles prepared from ileal brush borders. Life Sci. 1977 May 1;20(9):1607–1611. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90455-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. C., Gong Y. Z., Geoghegan K. F., Wilson F. A. Characterization of a novel 14 kDa bile acid-binding protein from rat ileal cytosol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jul 12;1078(3):329–335. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(91)90152-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. C., Kramer W., Wilson F. A. Identification of cytosolic and microsomal bile acid-binding proteins in rat ileal enterocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14986–14995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. C., Mullady E., Wilson F. A. Timed photoaffinity labeling and characterization of bile acid binding and transport proteins in rat ileum. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jul;265(1 Pt 1):G56–G62. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1993.265.1.G56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. C., Weinberg S. L., Kramer W., Burckhardt G., Wilson F. A. Identification and comparison of bile acid-binding polypeptides in ileal basolateral membrane. J Membr Biol. 1988 Nov;106(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF01871762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lücke H., Stange G., Kinne R., Murer H. Taurocholate--sodium co-transport by brush-border membrane vesicles isolated from rat ileum. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 15;174(3):951–958. doi: 10.1042/bj1740951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwenk M., Hegazy E., Lopez Del Pino V. Kinetics of taurocholate uptake by isolated ileal cells of guinea pig. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 15;131(2):387–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takikawa H., Arai S., Yamanaka M. Binding of bile acids, organic anions, and fatty acids by bovine intestinal Z protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Jan;292(1):151–155. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90063-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veerkamp J. H., Peeters R. A., Maatman R. G. Structural and functional features of different types of cytoplasmic fatty acid-binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 4;1081(1):1–24. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(91)90244-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodenlich A. D., Jr, Gong Y. Z., Geoghegan K. F., Lin M. C., Lanzetti A. J., Wilson F. A. Identification of the 14 kDa bile acid transport protein of rat ileal cytosol as gastrotropin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jun 28;177(3):1147–1154. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90659-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg S. L., Burckhardt G., Wilson F. A. Taurocholate transport by rat intestinal basolateral membrane vesicles. Evidence for the presence of an anion exchange transport system. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):44–50. doi: 10.1172/JCI112571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wider M. D., Duhaime P. M., Weisman R. L. Chemical characterization of circulating porcine ileal polypeptide in plasma from normal adult pigs. Endocrinology. 1986 Apr;118(4):1546–1550. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-4-1546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson F. A., Dietschy J. M. Characterization of bile acid absorption across the unstirred water layer and brush border of the rat jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1972 Dec;51(12):3015–3025. doi: 10.1172/JCI107129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson F. A., Dietschy J. M. The intestinal unstirred layer: its surface area and effect on active transport kinetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 21;363(1):112–126. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson F. A., Treanor L. L. Characterization of the passive and active transport mechanisms for bile acid uptake into rat isolated intestinal epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 6;406(2):280–293. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson F. A., Treanor L. L. Glycodeoxycholate transport in brush border membrane vesicles isolated from rat jejunum and ileum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 5;554(2):430–440. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90382-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]