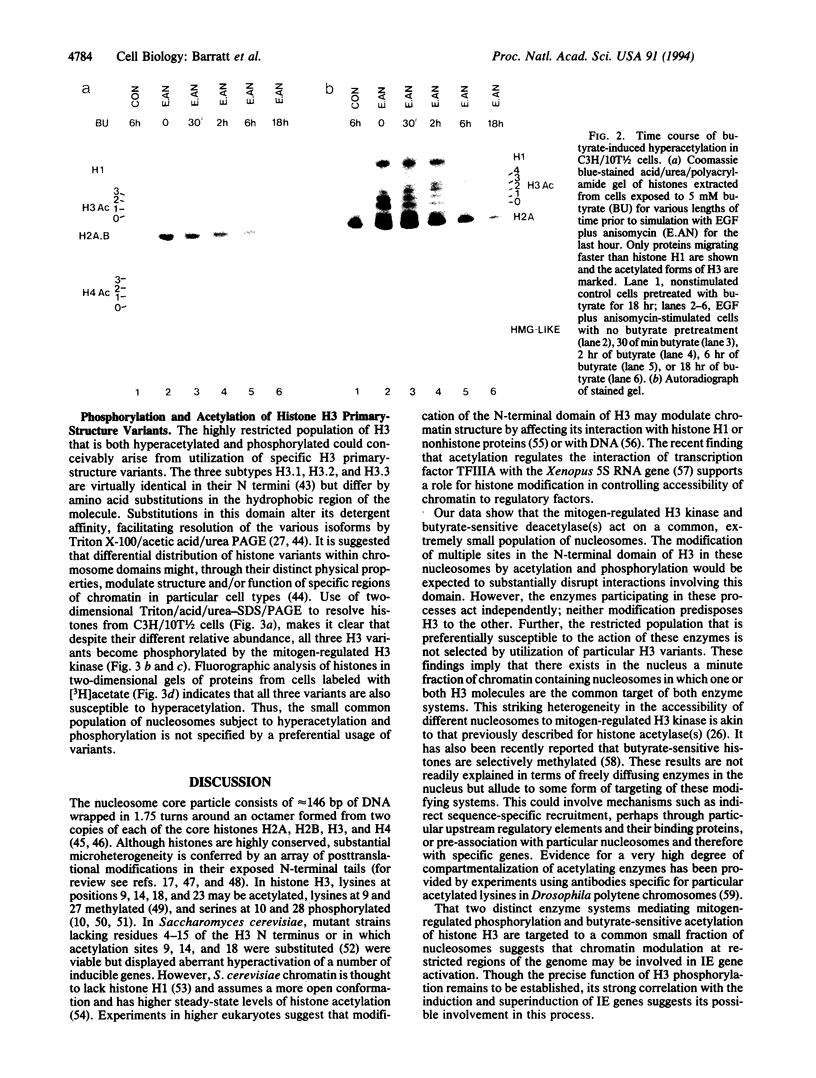
Abstract
Diverse agents, including growth factors and phorbol esters, induce rapid transcriptional activation of a subset of immediate-early (IE) genes that include the protooncogenes c-fos and c-jun. Among the earliest nuclear signaling events concomitant with IE gene activation is the phosphorylation of nucleosomal histone H3 in its basically charged N-terminal tail. This highly conserved domain is also subject to reversible posttranslational acetylation at specific lysine residues, a process implicated in transcriptional regulation. We show here that H3 phosphorylation associated with G0-G1 transition affects only a small fraction of this histone in the nucleus. Moreover, this fraction is biochemically distinct from bulk H3 in being extremely sensitive to sodium butyrate-induced hyperacetylation. However, acetylation itself does not predispose H3 to phosphorylation, nor does phosphorylation predispose H3 to enhanced acetylation. Further, selectivity is not based on preferential modification of particular histone H3 subtypes. Thus, the mitogen-regulated kinase that phosphorylates histone H3 is restricted to a small subset of nucleosomes that is especially susceptible to hyperacetylation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfageme C. R., Zweidler A., Mahowald A., Cohen L. H. Histones of Drosophila embryos. Electrophoretic isolation and structural studies. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3729–3736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan J., Harborne N., Rau D. C., Gould H. Participation of core histone "tails" in the stabilization of the chromatin solenoid. J Cell Biol. 1982 May;93(2):285–297. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.2.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almendral J. M., Sommer D., Macdonald-Bravo H., Burckhardt J., Perera J., Bravo R. Complexity of the early genetic response to growth factors in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2140–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boffa L. C., Gruss R. J., Allfrey V. G. Manifold effects of sodium butyrate on nuclear function. Selective and reversible inhibition of phosphorylation of histones H1 and H2A and impaired methylation of lysine and arginine residues in nuclear protein fractions. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9612–9621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candido E. P., Reeves R., Davie J. R. Sodium butyrate inhibits histone deacetylation in cultured cells. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90305-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cano E., Barratt M. J., Mahadevan L. C. Which histone kinase? Nature. 1992 Nov 12;360(6400):116–116. doi: 10.1038/360116a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Certa U., Colavito-Shepanski M., Grunstein M. Yeast may not contain histone H1: the only known 'histone H1-like' protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a mitochondrial protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):7975–7985. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.7975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabanas A., Khoury E., Goeltz P., Froussard P., Gjerset R., Dod B., Eisen H., Lawrence J. J. Effects of butyric acid on cell cycle regulation and induction of histone H1(0) in mouse cells and tissue culture. Inducibility of H1 (0)in the late S-G2 phase of the cell cycle. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 25;183(2):141–151. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. A., Allfrey V. G. Rapid and reversible changes in nucleosome structure accompany the activation, repression, and superinduction of murine fibroblast protooncogenes c-fos and c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5252–5256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran B. H., Reffel A. C., Stiles C. D. Molecular cloning of gene sequences regulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):939–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousens L. S., Gallwitz D., Alberts B. M. Different accessibilities in chromatin to histone acetylase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1716–1723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csordas A. On the biological role of histone acetylation. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 1;265(1):23–38. doi: 10.1042/bj2650023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. R., Mahadevan L. C. Protein synthesis inhibitors differentially superinduce c-fos and c-jun by three distinct mechanisms: lack of evidence for labile repressors. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2415–2424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fashena S. J., Reeves R., Ruddle N. H. A poly(dA-dT) upstream activating sequence binds high-mobility group I protein and contributes to lymphotoxin (tumor necrosis factor-beta) gene regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):894–903. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng J. L., Villeponteau B. Serum stimulation of the c-fos enhancer induces reversible changes in c-fos chromatin structure. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1126–1133. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. T., Lutter L. C., Rhodes D., Brown R. S., Rushton B., Levitt M., Klug A. Structure of nucleosome core particles of chromatin. Nature. 1977 Sep 1;269(5623):29–36. doi: 10.1038/269029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco R., Rosenfeld M. G. Hormonally inducible phosphorylation of a nuclear pool of ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4321–4325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin S. G., Zweidler A. Non-allelic variants of histones 2a, 2b and 3 in mammals. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):273–275. doi: 10.1038/266273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harootunian A. T., Kao J. P., Tsien R. Y. Agonist-induced calcium oscillations in depolarized fibroblasts and their manipulation by photoreleased Ins(1,4,5)P3, Ca++, and Ca++ buffer. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):935–943. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbes T. R., Thorne A. W., Crane-Robinson C. A direct link between core histone acetylation and transcriptionally active chromatin. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1395–1402. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02956.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendzel M. J., Davie J. R. Dynamically acetylated histones of chicken erythrocytes are selectively methylated. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 1;273(Pt 3):753–758. doi: 10.1042/bj2730753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschman H. R., Lim R. W., Brankow D. W., Fujiki H. The tumor promoters 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate and okadaic acid differ in toxicity, mitogenic activity and induction of gene expression. Carcinogenesis. 1989 Aug;10(8):1495–1498. doi: 10.1093/carcin/10.8.1495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip Y. T., Jackson V., Meier J., Chalkley R. The separation of transcriptionally engaged genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14044–14052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson V., Shires A., Tanphaichitr N., Chalkley R. Modifications to histones immediately after synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 25;104(2):471–483. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90282-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kardalinou E., Zhelev N., Hazzalin C. A., Mahadevan L. C. Anisomycin and rapamycin define an area upstream of p70/85S6k containing a bifurcation to histone H3-HMG-like protein phosphorylation and c-fos-c-jun induction. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1066–1074. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau L. F., Nathans D. Expression of a set of growth-related immediate early genes in BALB/c 3T3 cells: coordinate regulation with c-fos or c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1182–1186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. Y., Hayes J. J., Pruss D., Wolffe A. P. A positive role for histone acetylation in transcription factor access to nucleosomal DNA. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90051-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennox R. W., Cohen L. H. Analysis of histone subtypes and their modified forms by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1989;170:532–549. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)70063-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutter L. C., Judis L., Paretti R. F. Effects of histone acetylation on chromatin topology in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5004–5014. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan L. C., Edwards D. R. Signalling and superinduction. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):747–748. doi: 10.1038/349747c0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan L. C., Targett K., Heath J. K. 2-Aminopurine abolishes epidermal growth factor-stimulated phosphorylation of complexed and chromatin-associated forms of a 33 kDa phosphoprotein. Oncogene. 1989 Jun;4(6):699–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan L. C., Willis A. C., Barratt M. J. Rapid histone H3 phosphorylation in response to growth factors, phorbol esters, okadaic acid, and protein synthesis inhibitors. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):775–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90385-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan L. C., Wills A. J., Hirst E. A., Rathjen P. D., Heath J. K. 2-Aminopurine abolishes EGF- and TPA-stimulated pp33 phosphorylation and c-fos induction without affecting the activation of protein kinase C. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):327–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Ross T. S., Cunningham T. W., Caldwell K. K., Jefferson A. B., Bansal V. S. Recent insights in phosphatidylinositol signaling. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):459–465. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90442-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R. K., Grunstein M. Histone H3 N-terminal mutations allow hyperactivation of the yeast GAL1 gene in vivo. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3297–3306. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05408.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion C., Roux B., Coulet P. R. Role of histones H1 and H3 in the maintenance of chromatin in a compact conformation. Study with an immobilized enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jul 4;157(2):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80568-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazen A., Hacques M. F., Marion C. H3 phosphorylation-dependent structural changes in chromatin. Implications for the role of very lysine-rich histones. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 20;194(4):741–745. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90251-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. A. Histone acetylation in baker's yeast. Maintenance of the hyperacetylated configuration in log phase protoplasts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1565–1568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton V. G., Imai B. S., Yau P., Bradbury E. M. Histone acetylation reduces nucleosome core particle linking number change. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):449–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90920-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. R., Taylor S. S. Phosphorylation of histones 1 and 3 and nonhistone high mobility group 14 by an endogenous kinase in HeLa metaphase chromosomes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6064–6072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Tyrosine kinases and their interactions with signalling proteins. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Feb;2(1):4–12. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80314-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond T. J., Finch J. T., Rushton B., Rhodes D., Klug A. Structure of the nucleosome core particle at 7 A resolution. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):532–537. doi: 10.1038/311532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Carrillo A., Wangh L. J., Allfrey V. G. Processing of newly synthesized histone molecules. Science. 1975 Oct 10;190(4210):117–128. doi: 10.1126/science.1166303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Hirai S. I., Yaniv M., Bravo R. Transcriptional activation of c-jun during the G0/G1 transition in mouse fibroblasts. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):535–537. doi: 10.1038/334535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata K., Inagaki M., Ajiro K. Mitosis-specific histone H3 phosphorylation in vitro in nucleosome structures. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Aug 28;192(1):87–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Bird A. Alternative chromatin structure at CpG islands. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):909–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90339-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanos D., Maniatis T. The high mobility group protein HMG I(Y) is required for NF-kappa B-dependent virus induction of the human IFN-beta gene. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):777–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90554-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne A. W., Kmiciek D., Mitchelson K., Sautiere P., Crane-Robinson C. Patterns of histone acetylation. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):701–713. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19390.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. M., Birley A. J., Lavender J. Histone H4 isoforms acetylated at specific lysine residues define individual chromosomes and chromatin domains in Drosophila polytene nuclei. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):375–384. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90417-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. M. Histone acetylation and control of gene expression. J Cell Sci. 1991 May;99(Pt 1):13–20. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells D., McBride C. A comprehensive compilation and alignment of histones and histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989;17 (Suppl):r311–r346. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.suppl.r311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Augustine R., Schulman H. Calcium-dependent phosphorylation of histone H3 in butyrate-treated HeLa cells. Nature. 1980 Sep 4;287(5777):74–76. doi: 10.1038/287074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Galeazzi D., Schulman H. Acetylation and calcium-dependent phosphorylation of histone H3 in nuclei from butyrate-treated HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1299–1304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]