Abstract
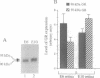
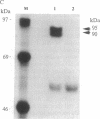
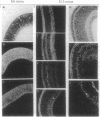
Inducibility by glucocorticoids of the glutamine synthetase gene in chicken embryo retina and the transcriptional activity of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) greatly increase between embryonic days 6 and 10 (E6, E10), although the level of GR does not markedly change during that time. This apparent discrepancy was investigated by examining the pattern of GR expression in undifferentiated E6 retina and in E10 retina, which consists mostly of differentiated cells. Two GR isoforms, 90 and 95 kDa, were found to be expressed at both of these ages at a similar total level but in different proportions: in E6 retina the level of the 90-kDa isoform was higher, whereas in E10 retina the 95-kDa receptor was higher. However, following treatment of the retinas with cortisol, the 95-kDa isoform became the predominant receptor at both ages. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed that the cellular localization of GR markedly changed in the course of development: in the undifferentiated E6 retina GR was expressed in virtually all cells, whereas in the more differentiated E10 and E12 retina, GR was detected only in Müller glia cells. The latter represent approximately 20% of the cells in this tissue and are the only cells in which glucocorticoid hormone induces the glutamine synthetase gene. We suggest that the compartmentalization of GR in Müller glia is a major aspect of the mechanism that modulates receptor activity during retina development and results in the temporal increase in the inducibility of glutamine synthetase and its specific localization in Müller glia cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagchi M. K., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Ligand and DNA-dependent phosphorylation of human progesterone receptor in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2664–2668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Dror I., Havazelet N., Vardimon L. Developmental control of glucocorticoid receptor transcriptional activity in embryonic retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):1117–1121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Or S., Okret S. Involvement of a C/EBP-like protein in the acquisition of responsiveness to glucocorticoid hormones during chick neural retina development. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):331–340. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berko-Flint Y., Levkowitz G., Vardimon L. Involvement of c-Jun in the control of glucocorticoid receptor transcriptional activity during development of chicken retinal tissue. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 1;13(3):646–654. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06303.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cidlowski J. A., Richon V. Evidence for microheterogeneity in the structure of human glucocorticoid receptors. Endocrinology. 1984 Oct;115(4):1588–1597. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-4-1588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobi E. T., Naya F. J., Hausman R. E. Distribution of R-cognin and choline acetyltransferase in the ganglion cell layer of developing chick neural retina. Cell Differ. 1988 Jan;22(2):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(88)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong Y., Poellinger L., Gustafsson J. A., Okret S. Regulation of glucocorticoid receptor expression: evidence for transcriptional and posttranslational mechanisms. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1256–1264. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman R., Fox L. E., Gorovits R., Ben-Dror I., Reisfeld S., Vardimon L. Molecular basis for differential expression of glutamine synthetase in retina glia and neurons. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1994 Feb;21(3-4):312–320. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(94)90262-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon J. M., Eisen H. J., Brower S. T., Simons S. S., Jr, Langley C. L., Thompson E. B. Identification of human leukemic glucocorticoid receptors using affinity labeling and anti-human glucocorticoid receptor antibodies. Cancer Res. 1984 Oct;44(10):4540–4547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon J. M., Smith A. C., Elsasser M. S. Use of high-resolution two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and affinity labeling to probe glucocorticoid receptor structure and function. Cancer Res. 1989 Apr 15;49(8 Suppl):2238s–2243s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeck W., Groner B. Hormone-dependent phosphorylation of the glucocorticoid receptor occurs mainly in the amino-terminal transactivation domain. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5403–5408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeck W., Rusconi S., Groner B. Down-regulation and phosphorylation of glucocorticoid receptors in cultured cells. Investigations with a monospecific antiserum against a bacterially expressed receptor fragment. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14396–14402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy A. J., Voaden M. J., Marshall J. Glutamate metabolism in the frog retina. Nature. 1974 Nov 1;252(5478):50–52. doi: 10.1038/252050a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehler D. E., Moscona A. A. Corticosteroid receptors in the neural retina and other tissues of the chick embryo. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Sep;170(1):102–113. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landers J. P., Spelsberg T. C. New concepts in steroid hormone action: transcription factors, proto-oncogenes, and the cascade model for steroid regulation of gene expression. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1992;2(1):19–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linser P., Moscona A. A. Induction of glutamine synthetase in embryonic neural retina: localization in Müller fibers and dependence on cell interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6476–6480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippman M. E., Wiggert B. O., Chader G. J., Thompson E. B. Glucocorticoid receptors. Characteristics, specificity, and ontogenesis in embryonic chick neural retina. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5916–5917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logeat F., Le Cunff M., Pamphile R., Milgrom E. The nuclear-bound form of the progesterone receptor is generated through a hormone-dependent phosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 30;131(1):421–427. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91819-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luppis B., Rutter W. J. Induction of tyrosine aminotransferase by triamcinolone during rat liver development in vitro. Dev Biol. 1973 Aug;33(2):482–486. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90154-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marie C. Ontogenesis of the adrenal glucocorticoids and of the target function of the enzymatic tyrosine transaminase activity in the chick embryo. J Endocrinol. 1981 Aug;90(2):193–200. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0900193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Rusconi S., Godowski P. J., Maler B. A., Okret S., Wikström A. C., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Genetic complementation of a glucocorticoid receptor deficiency by expression of cloned receptor cDNA. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90659-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscona A. A., Linser P. Developmental and experimental changes in retinal glia cells: cell interactions and control of phenotype expression and stability. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1983;18:155–188. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60582-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okret S., Dong Y., Tanaka H., Cairns B., Gustafsson J. A. The mechanism for glucocorticoid-resistance in a rat hepatoma cell variant that contains functional glucocorticoid receptor. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;40(1-3):353–361. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(91)90202-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortí E., Mendel D. B., Smith L. I., Munck A. Agonist-dependent phosphorylation and nuclear dephosphorylation of glucocorticoid receptors in intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9728–9731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patejunas G., Young A. P. Tissue-specific regulation of avian glutamine synthetase expression during development and in response to glucocorticoid hormones. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1070–1077. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piddington R., Moscona A. A. Precocious induction of retinal glutamine synthetase by hydrocortisone in the embryo and in culture. Age-dependent differences in tissue response. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jul 25;141(2):429–432. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pu H. F., Young A. P. Glucocorticoid-inducible expression of a glutamine synthetase-CAT-encoding fusion plasmid after transfection of intact chicken retinal explant cultures. Gene. 1990 May 14;89(2):259–263. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90014-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saad A. D., Moscona A. A. Cortisol receptors and inducibility of glutamine synthetase in embryonic retina. Cell Differ. 1985 Jun;16(4):241–250. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(85)90574-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan P. L., Francis M. D., Horwitz K. B. Synthesis of human progesterone receptors in T47D cells. Nascent A- and B-receptors are active without a phosphorylation-dependent post-translational maturation step. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):7054–7058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva C. M., Cidlowski J. A. The effect of oxidation/reduction on the charge heterogeneity of the human glucocorticoid receptor. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1992 Jan;41(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(92)90218-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons S. S., Jr, Thompson E. B. Dexamethasone 21-mesylate: an affinity label of glucocorticoid receptors from rat hepatoma tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3541–3545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. C., Harmon J. M. Multiple forms of the glucocorticoid receptor steroid binding protein identified by affinity labeling and high-resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 27;24(18):4946–4951. doi: 10.1021/bi00339a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder J. M., Mendelson C. R., Johnston J. M. The effect of cortisol on rabbit fetal lung maturation in vitro. Dev Biol. 1981 Jul 15;85(1):129–140. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90242-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takimoto G. S., Tasset D. M., Eppert A. C., Horwitz K. B. Hormone-induced progesterone receptor phosphorylation consists of sequential DNA-independent and DNA-dependent stages: analysis with zinc finger mutants and the progesterone antagonist ZK98299. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3050–3054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderbilt J. N., Miesfeld R., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. Intracellular receptor concentration limits glucocorticoid-dependent enhancer activity. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Jan;1(1):68–74. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-1-68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vardimon L., Ben-Dror I., Havazelet N., Fox L. E. Molecular control of glutamine synthetase expression in the developing retina tissue. Dev Dyn. 1993 Apr;196(4):276–282. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001960410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vardimon L., Fox L. E., Moscona A. A. Developmental regulation of glutamine synthetase and carbonic anhydrase II in neural retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9060–9064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vardimon L., Fox L. L., Degenstein L., Moscona A. A. Cell contacts are required for induction by cortisol of glutamine synthetase gene transcription in the retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5981–5985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal H. M., Moldenhauer G., Beato M. Monoclonal antibodies to the rat liver glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1467–1471. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01339.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Li Y. C., Young A. P. Protein kinase A activation of glucocorticoid-mediated signaling in the developing retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3880–3884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Young A. P. Exogenous, but not endogenous, glucocorticoid receptor induces glutamine synthetase gene expression in early stage embryonic retina. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2850–2856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]