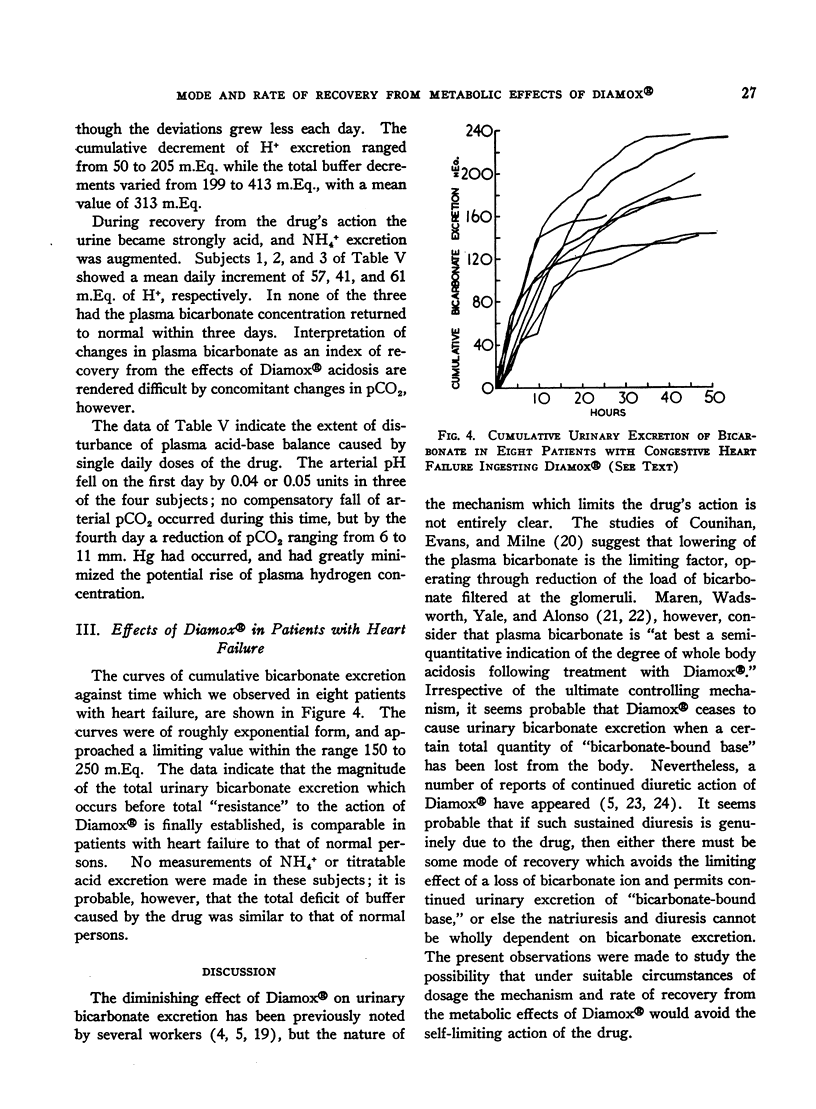
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BELSKY H. Use of a new oral diuretic, diamox, in congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 1953 Jul 23;249(4):140–143. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195307232490404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COUNIHAN T. B., EVANS B. M., MILNE M. D. Observations on the pharmacology of the carbonic anhydrase inhibitor diamox. Clin Sci. 1954 Nov;13(4):583–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDBERG C. K., TAYMOR R., MINOR J. B., HALPERN M. The use of diamox, a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, as an oral diuretic in patients with congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 1953 May 21;248(21):883–889. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195305212482102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILMAN A., BRAZEAU P. Role of the kidney in the regulation of acid-base metabolism. Am J Med. 1953 Dec;15(6):765–770. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(53)90167-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner R. J. Colorimetric determination of magnesium in plasma or serum by means of titan yellow. Biochem J. 1946;40(5-6):828–831. doi: 10.1042/bj0400828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAF A., SCHWARTZ W. B., RELMAN A. S. Oral administration of a potent carbonic anhydrase inhibitor (diamox). I. Changes in electrolyte and acid-base balance. N Engl J Med. 1954 May 6;250(18):759–764. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195405062501803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAREN T. H., WADSWORTH B. C., YALE E. K., ALONSO L. G. Carbonic anhydrase inhibition. III. Effects of diamox on electrolyte metabolism. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1954 Dec;95(6):277–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NADELL J. The effects of the carbonic anhydrase inhibitor 6063 on electrolytes and acid-base balance in two normal subjects and two patients with respiratory acidosis. J Clin Invest. 1953 Jul;32(7):622–629. doi: 10.1172/JCI102773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECTOR F. C., Jr, SELDIN D. W., COPENHAVER J. H. The mechanism of ammonia excretion during ammonium chloride acidosis. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jan;34(1):20–26. doi: 10.1172/JCI103058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDERSON P. H. Potentiometric determination of chloride in biological fluids. Biochem J. 1952 Nov;52(3):502–505. doi: 10.1042/bj0520502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ W. B., RELMAN A. S., LEAF A. Oral administration of a potent carbonic anhydrase inhibitor (diamox). III. Its use as a diuretic in patients with severe congestive heart failure due to cor pulmonale. Ann Intern Med. 1955 Jan;42(1):79–89. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-42-1-79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartorius O. W., Roemmelt J. C., Pitts R. F., Calhoon D., Miner P. THE RENAL REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE IN MAN. IV. THE NATURE OF THE RENAL COMPENSATIONS IN AMMONIUM CHLORIDE ACIDOSIS. J Clin Invest. 1949 May;28(3):423–439. doi: 10.1172/JCI102087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



