Abstract
Despite much effort, pancreatic cancer survival rates are still dismally low. Novel therapeutics may hold the key to improving survival. YM155 is a small molecule inhibitor which has shown anti-tumor activity in a number of cancers by reducing the expression of survivin. The aim of our study is to understand the mechanisms by which YM155 functions in pancreatic cancer cells. We established the anti-tumor effect of YM155 with in vitro studies in the cultured cells, and in vivo studies using a mouse xenograft model. Our data demonstrated that YM155 reduced the expression of survivin; however down-regulation of survivin itself is insufficient to induce apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. We showed for the first time that treatment with YM155 increased death receptor 5 (DR5) expression in pancreatic cancer cells. We found that YM155 induced apoptosis by broad-spectrum inhibition of IAP family member proteins (e.g. CIAP1/2 and FLIP) and induced pro-apoptotic Bak protein up-regulation and activation; the anti-tumor effect of YM155 treatment with either the DR5 agonist lexatumumab or gemcitabine on pancreatic cancer cells was synergistic. Our data also revealed that YM155 inhibit tumor growth in vivo, whilst had no apparent toxicity to the non-cancerous human pancreatic ductal epithelial cell line (HPDE). Together, these findings suggest that YM155 could be a novel therapeutic agent for pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: Pancreatic cancer, Apoptosis, YM155, Death receptor 5, survivin
Introduction
Pancreatic cancer has a 5 year survival rate of less than 5% and is the fourth leading cause of cancer related death in the United States (1, 2). Recent increases in patient survival are due to improvements in surgical procedures and the development of adjuvant chemotherapy (3). Only 20% of pancreatic cancer patients have operable tumors and only 15–20% of those patients survive (2). New and effective systemic chemotherapeutic strategies are urgently needed for the treatment of advanced stage pancreatic cancer.
Apoptosis plays an important role in the maintenance of homeostasis, and elimination of damaged cells in multi-cellular organisms (4). Evasion of apoptosis is a characteristic feature of cancer (5). Currently, induction of apoptosis is one of the most attractive strategies for cancer therapy (6). Of note, tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL/Apo2L) is a member of the TNF super family able to specifically induce programmed death in cancer cells. TRAIL mediates apoptosis via the binding two death receptors, TRAIL-R1 (DR4) and/or TRAIL-R2 (DR5) (7). We have previously reported that the human anti-DR5 monoclonal antibody lexatumumab (Lexa) induced cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the activation of Bcl-2 associated X protein (Bax) (8). Targeting death receptors to trigger apoptosis in tumor cells without causing toxicity to normal healthy tissue is a very promising concept for cancer therapy including pancreatic cancer, where there is a clear unmet need (9, 10).
YM155 (sepantronium bromide) is a novel small molecule (chemical structure, see Figure 1A) that has been reported to specifically suppress survivin expression at the transcriptional level (11–13). YM155 shows potent antitumor activity in non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) xenograft models, and induces in-vivo antitumor activity without systemic toxicity in mice. Patient clinical trials also suggest beneficial applications of YM155 (14, 15). YM155 sensitizes tumors to radiation and other chemotherapeutics such as platinum compounds or taxanes, to induce apoptosis in human NSCLC (16, 17). YM155 is also a broad-spectrum anti-tumor agent among a wide variety of human cancer cell lines (11). It has been previously reported that YM155 induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells, but the molecular mechanisms have yet to be fully elucidated (18, 19).
Figure 1. Survivin down-regulation is not sufficient to trigger apoptosis.

(A), Chemical structure of YM155. (B), Panc-1 cells were treated with YM155 and cell lysates were prepared for Western blotting to detect survivin. β-actin were assessed as the control for equal loading of protein. (C), Panc-1 cells were transfected with either survivin-specific siRNA or scramble-siRNA as negative control. 48 h post-transfection, cell lysates were prepared for Western blotting to examine survivin. β-actin were assessed as the control for equal loading of protein. (D), Panc-1 cells were initially transfected with survivin-specific siRNA. 48 h post-transfection, cells were either treated with YM155 (10 nM) for an additional 24 h or not, control cells had neither YM155 treatment nor transfection with siRNA. Apoptosis was assessed by Hoechst 33258 staining (cells exemplifying apoptotic nuclei are demarcated by white arrows). (E), Panc-1 cells were treated as in Figure 1C, and the ratio of apoptotic cells was assessed by counting the number of cells with apoptotic nuclei. Each experiment was conducted in triplicate and repeated twice independently (*p<0.05). (F), Panc-1 cells were treated as in Figure 1C. Apoptosis was assessed by a DNA ladder assay. (G), Panc-1 cells were treated as in Figure 1C and cell lysates were prepared for Western blotting to detect survivin and cleaved Caspase 3. β-actin were assessed as the control for equal loading of protein.
Recognizing that YM155 may be acting as a broad-spectrum anti-tumor agent, the present study sought to characterize the effects of YM155 on pancreatic cancer cells, and to identify the molecular pathways involved, by the use of a cell culture model of pancreatic cancer and a murine xenograft model. The results of our study reveal that YM155-induced apoptosis is associated with DR5 up-regulation and Bak activation; YM155 enhances the therapeutic effect of either Lexa or gemcitabine in a synergistic manner; YM155 exhibits tumor growth inhibition in vivo, but has no significant toxicity to normal pancreatic cells.
Materials and methods
Cell culture and reagents
Human pancreatic cancer cells Panc-1, PC-3 and immortalized HPDE cells were provided by Dr. Steve Hochwald (Roswell Park Cancer Center, Buffalo, New York) in April 2010. Pancreatic cancer cells and HPDE cells were authenticated by using short tandem repeat analysis and amelogenin analysis. Panc-1 and PC-3 cells were grown in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) with 10% fetal bovine serum (Sigma, St. Louis, MO) and antibiotics (100 U/ml penicillin and 100 μg/ml streptomycin) at 37°C in 5% CO2. HPDE cells were grown in Keratinocyte serum free media and supplemented with bovine pituitary extract and EGF as per the manufacturer’s instructions (Life technologies, Carlsbad, CA). Anti-Caspase 9, anti-Caspase 8, anti-Caspase 3, anti-Bid, anti-PARP, anti-FLIP, anti-CIAP1/2, anti-survivin, anti-Bcl-2, anti-Mcl-1, anti-Bak, anti-Bim, anti-DR5, and anti-DR4 primary antibodies were obtained from Cell Signaling Technology (Beverly, MA); anti-β-actin monoclonal antibody, Hoechst 33258 and disuccinimidyl suberate (DSS) were obtained from Sigma (St. Louis, MO); RNAiso Plus, PrimeScript™ RT Master Mix and SYBR® Premix Ex Taq™ (Tli RNaseH Plus) were purchased from Takara Biotechnology; goat anti-rabbit/mouse horseradish peroxidase (HRP) conjugated secondary antibody was purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA); YM155 and gemcitabine were purchased from Selleck Chemicals (Houston, TX). Lexatumumab was kindly provided by Human Genome Science Inc. YM155 and gemcitabine were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and stored at −20 °C. Lexatumumab was dissolved in water and stored at −80 °C.
SiRNA-mediated knockdown
SiRNA knockdown was performed as previously described (20). Panc-1 cells were transfected with survivin siRNA duplex mixtures in the presence of lipo-fectamine RNAiMax (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). A non-specific scramble siRNA (Cell Signaling Biotechnology, Beverly, MA) was also transfected at the same concentration as a control.
Hoechst staining
For Hoechst 33258 staining, cells were plated at a density of 5×104 cells per milliliter in a 6-well plate and treated with YM155. After treatment, cells were stained with Hoechst 33258 for 15 min at room temperature in the dark. Cells were then analyzed using a fluorescence microscope. For quantitative analysis, the cell death ratio was assessed by counting the number of apoptotic cells with condensed nuclei in six to eight randomly selected areas.
DNA ladder assays
A DNA ladder assay was performed as previously described with modification (21). Briefly, cells were treated under different experimental conditions and then washed twice in PBS and harvested. Genomic DNA was then separated by electrophoresis.
Western blotting analysis
Western blotting was performed as previously described (22). Cells were washed twice with sterile PBS and harvested. Cell lysates were prepared and samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE on 12% gels. Bands were detected using enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL). Protein molecular weight was determined by comparison with pre-stained protein markers.
Crosslinking of Bak protein
The Bak crosslinking assay was performed as described previously (23, 24). Following treatment with YM155, cells were washed with conjugating buffer and DSS was added to a final concentration of 2 mM. After incubating at room temperature for 30 min, the crosslinker was quenched by Tris-HCl. Bak was detected by Western blotting with anti-Bak polyclonal antibody.
MTS assays
Cell viability assays were performed as previously described (25). Briefly, cells were treated with gemcitabine with or without YM155. Cell viability was determined using the CellTiter®96 Aqueous One Solution Cell proliferation assay kit according to the supplier’s protocol.
Colony formation assays
Cells were seeded in 6-well plates at a density of 1×103 cells. Cells were untreated or treated with interested conditions for 48 h. After being rinsed with fresh medium, cells were allowed to grow to form colonies, which were then stained with 0.4 g/L crystal violet (Sigma, St. Louis, MO). Clonogenic assay was used to elucidate the possible differences in long-term effects the combination on human pancreatic cancer cells.
Tumor growth inhibition
Mice were managed humanely in line with criteria outlined in the “Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals” (NIH publication 86-23, revised 1985). 8 week old male SCID mice were divided into two groups. Each mouse (5 per group) was inoculated subcutaneously with Panc-1 cells in PBS in the right flank. Treatment with YM155 was initiated by daily tail vein injection of YM155 or vehicle only when tumors were palpable, each for a total of 7 days. The effect of drug treatment on tumor growth was analyzed statistically with individual group comparison and evaluated by student’s paired t-test by SPSS 15.0.
Results
Down regulation of survivin in pancreatic cancer cells does not induce apoptosis
It has been reported that YM155 induces apoptosis through the inhibition of survivin expression in a number of cancer cells (26, 27). We tested the effects of YM155 on pancreatic cancer cells. Cells were treated with YM155 for 48 h and apoptosis was measured by Hoechst 33258 staining, DNA ladder assay and Western blot analysis. Our data showed that YM155 induced apoptosis in Panc-1 cells (Figure S1A and S1B). The treatment induced apoptosis in Panc-1 cells in both time and dose-dependent manners as determined by treatment with different concentrations of YM155 or by treatment over a time course (Figure S1C and S1D). To assess intracellular apoptotic events, Panc-1 cells were treated and Western blotting was performed. The results showed that YM155 induced activation of Caspase 8, Bid, Caspase 3 and Caspase 9 (Figure S1E and S1F). Cleaved PARP was also detected in YM155 treated Panc-1 cells (Figure S1E and S1F). We also treated PC-3 pancreatic cancer cells with YM155, in order to identify if YM155 had the same effect in other pancreatic cancer cell lines. Treatment of PC-3 cells with YM155 induced apoptosis as observed by nuclear condensation detected by Hoechst staining (Figure S2A). Treatment of PC-3 cells over 24 hours with different doses of YM155 down regulated expression of survivin and increased expression of DR5 (Figure S2B). These data suggest that YM155 induces apoptosis via activation of components of the extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis signaling pathways in pancreatic cancer cells.
To determine whether YM155-induced apoptosis is indeed mediated by survivin down-regulation, Panc-1 or PC-3 cells were treated with YM155 for up to 48 h, followed by Western blot analysis of survivin expression. Survivin expression was almost completely ablated after treatment for 48 h (Figure 1B and Figure S2B). To establish the causal relationship between survivin suppression and apoptosis, a survivin-specific siRNA was used to knockdown survivin in Panc-1 cells. As shown in Figure 1C, survivin expression was effectively depleted by the siRNA knockdown. Induction of apoptosis was then assessed by siRNA knockdown. Cells were either treated by survivin-siRNA transfection or with YM155. Untreated Panc-1 cells were used as the control. Hoechst staining demonstrated that there was no overt apoptosis in Panc-1 cells transfected with survivin siRNA (Figure 1D and 1E). We also compared the effect of survivin knockdown and YM155-mediated survivin down-regulation on apoptosis using the DNA ladder assay. Consistent with the Hoechst staining test, genomic DNA extracted from control cells or cells transfected with survivin-siRNA had no DNA fragmentation, whilst cells treated with YM155 did (Figure 1F). Similarly, Caspase 3 cleavage was only detected in cells treated with YM155, but neither control cells nor cells transfected with survivin-siRNA showed cleavage of Caspase 3 (Figure 1G).
YM155 induces death receptor 5 up-regulation
We first examined functional expression of the death receptors DR4 and DR5 at the protein level. We found that YM155 treatment significantly increased the expression of DR5 in Panc-1 cells (Figure 2A and 2B) or PC-3 cells (Figure S2B). YM155 treatment decreased expression of DR4 in Panc-1 cells (Figure 2A and 2B). We next tested whether YM155 is able to regulate DR5 and DR4 expression at the mRNA level in Panc-1 cells. As shown in Figure 2C and 2D, YM155 treatment increased DR5 mRNA and decreased DR4 mRNA, which is consistent with the protein expression pattern. To determine whether the effect of YM155 on DR5 and DR4 is related to survivin expression, we knocked down survivin expression using a siRNA approach. Western blotting results showed that siRNA-mediated survivin gene silencing had no effect on DR4 or DR5 expression (Figure 2E). To evaluate the role of DR5 over-expression in YM155-induced apoptotic signaling in pancreatic cancer cells, a known DR5 monoclonal antibody lexatumumab (Lexa) which can activate DR5 to induce apoptosis was used to co-treat cells with YM155. Pre-treatment of cells with YM155 for 1 h followed by Lexa for another 12 h induced significant apoptosis, while treatment with either YM155 for 1 h or Lexa for 12 h did not cause apoptosis as assessed by Hoechst 33258 staining and DNA ladder assay (Figure 2F and 2G). The synergistic effect of Lexa and YM155 is further confirmed by Western blot analysis of Caspase 3, Caspase 8 and Bid (Figure 2H). Combined treatment with Lexa induced the most potent apoptosis in 30% of cells as observed by Hoechst staining (Figure 2I). These data suggest that DR5 up-regulation plays a role in YM155-induced apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells; the detection of tBid in treated cells indicates that the apoptosis is likely through intrinsic pathway (Figure 2H). This led us to investigate the role of Bak activation in YM155 induced apoptosis.
Figure 2. YM155 induces death receptor 5 up-regulation.

(A), Panc-1 cells were treated with YM155 for 48 h and cell lysates were prepared for Western blotting to detect DR4 and DR5. β-actin were assessed as the control for equal loading of protein. Band density was qualified by Image J software. (B), Panc-1 cells treated with YM155 and cell lysates were prepared for Western blotting to detect DR4 and DR5 expression. β-actin were used for equal total protein amounts loading control. Band density was qualified by Image J software. (C), Panc-1 cells treated with YM155 for 48 h were harvested and total mRNA was extracted. Reverse transcription PCR and quantitative real-time PCR were performed to examine DR5 mRNA levels with specific primers. Statistical analysis was performed to show the effects of YM155 on DR5 mRNA levels. Each experiment was conducted in triplicate and repeated twice independently (#p<0.05). (D), Panc-1 cells were treated and DR4 mRNA levels were examined as in Figure 2C (*p<0.05). (E), Panc-1 cells were transfected with survivin specific siRNA. 48 h post-transfection, cell lysates were prepared for Western blotting to detect survivin, DR4 and DR5 expression. β-actin were used for an equal protein loading control. (F), Cells were treated with DMSO (control), YM155 (10 nM), Lexa (1 μg/ml), or pre-treated with YM155 (10 nM) for 1 h followed by Lexa (1 μg/ml) for 12 h. Apoptosis was measured by Hoechst 33258 staining (representative apoptotic cells are demarcated by open arrows). (G), Cells were treated as in Figure 2F and apoptosis was tested by a DNA ladder assay. (H), Cells were treated as in Figure 2F and apoptosis was measured by Western blotting to detect Caspase 8, Bid, and Caspase 3 activation. (I), Cells were treated as in Figure 2F and apoptosis was measured. Statistical analysis was performed to determine the ratio of apoptotic cells by counting the number of apoptotic cells with condensed nuclei. Each experiment was conducted in triplicate and repeated twice independently (* p<0.05).
YM155 exerts broad spectrum IAP inhibition and induces oligomerization of Bak
We examined the effect of YM155 on IAP family protein expression. Western blotting analysis showed that YM155 inhibit survivin expression in Panc-1 cells (Figure 3A) and PC-3 cells (Figure S2B). Treatment with YM155 also reduced CIAP1/2 and FLIP expression. Bcl-2 family protein expression analysis indicated that Bcl-2 and Bim were not affected by YM155, whereas Mcl-1 was decreased and Bak was up-regulated (Figure 3A). The oligomerization of Bak has previously been reported to occur only in apoptotic cells. Oligomerization of Bak is required for the formation of pores which release cytochrome c from the mitochondria (28). We next investigated whether YM155 could trigger Bak oligomerization. Following treatment with YM155, Panc-1 cells were exposed to the membrane-permeable crosslinking agent disuccinimidyl suberate (DSS) and subjected to Western blotting for the analysis of Bak oligomerization. The detection of a Bak band at 52~56 kDa indicates the presence of Bak homodimer. The elevation of Bak homodimer formation correlated with YM155 concentration increase (Figure 3B). Moreover, we performed non-reducing SDS-PAGE to confirm Bak dimerization. Bak homodimers were detected 48 h after treatment with YM155 (Figure 3C). Homodimerization of Bak correlated with the detection of tBid, the increase in Bak homodimerization indicates that YM155 induces apoptosis via the intrinsic pathway.
Figure 3. Altered expression of apoptotic proteins and oligomerization of Bak proteins.

(A), Panc-1 cells were treated with YM155 for 48 h. Cell lysates were prepared for Western blotting to detect CIAP1/2, FLIP, survivin, Bcl-2, Mcl-1, Bak, and Bim expression. β-actin was used for an equal loading of protein. Band density was qualified by Image J software. Representative bands are shown and every experiment was repeated three times. (B), Cells were treated with YM155 (10 nM) or untreated for 48 h. Proteins were then cross-linked using DSS as described in ‘Materials and methods’. Bak protein was detected by Western blotting. A 26~28kDa band represents Bak monomers, and bands at 52~56 kDa detected represent Bak homodimers. (C), Panc-1 cells were treated with YM155 for 48 h. Cell lysates were prepared for non-reducing SDS-PAGE. Bak protein was detected by Western blotting. A 26~28 kDa band represents Bak monomers, and bands at 52~56 kDa detected represent Bak homodimers.
YM155 enhances gemcitabine-induced apoptosis in Panc-1 cells
Gemcitabine is a common agent used in the clinical treatment of pancreatic cancer (29). We studied mono and combination treatment using YM155 and gemcitabine. Quantitative MTS assays showed that the presence of sub-lethal quantity of YM155 increased gemcitabine cyto-toxicity (Figure 4A); chromatin condensation assays indicated that gemcitabine and YM155 worked synergistically to induce apoptosis (Figure 4B); colony formation assays revealed that gemcitabine and YM155 combination treatment effectively inhibits cell proliferation (Figure 4C). These data suggest that YM155 enhanced the anti-tumor effects of gemcitabine.
Figure 4. YM155 enhances gemcitabine-induced apoptosis in Panc-1 cells.

(A), Cells grown in 96-well plate were treated with gemcitabine (4 mM) alone or in the presence or absence of YM155 (5 nM) for 24 h. Relative cell viability was measured via MTS assay (*P<0.05). (B), Cells were treated as in Figure 4A, and apoptosis was assessed by Hoechst 33258 staining. (C), Panc-1 cells grown in 6-well plate were either untreated (control) or treated with either: YM155 (5 nM), gemcitabine (4 mM), or a combination of YM155 (5 nM) with gemcitabine (4 mM) for 48 h. Cells were rinsed post treatment with fresh culture medium 3 times, cells were then cultured for another two weeks. Cell colony formation assays were performed with crystal violet staining.
YM155 has no apoptotic effects on non-cancerous pancreatic cells
HPDE cells are a model for non-cancerous pancreatic cells (30). HPDE cells were treated with YM155 and Hoechst 33258 staining was performed. YM155 treatment induced apoptosis in the Panc-1 cells (positive control), but not in HPDE cells (Figure 5A). To further assess YM155-induced apoptosis in HPDE and Panc-1 cells Western blotting were performed to measure Caspase 3 activation. Our results indicated that YM155 indeed induced no apoptotic toxicity in HPDE cells, whereas Panc-1 cells, as the positive control underwent apoptosis (Figure 5B). These data suggest that YM155 appears to be relatively safe to normal healthy pancreatic cells in vitro.
Figure 5. YM155 has no apparent apoptotic cyto-toxicity to normal pancreas cells.

(A), HPDE cells grown in 48-well plates were treated with YM155 (10 nM) for 48 h. Panc-1 cells treated under the same conditions were used as a positive control. Apoptosis was measured by Hoechst 33258 staining. (B), HPDE cells and Panc-1 cells (a positive control) grown in six-well plates were treated with YM155 for 48 h. Cell lysates were prepared for Western blotting to show Caspase 3 activation. β-actin were assessed as a control for equal protein loading.
YM155 inhibits tumor growth in vivo
Finally we investigated the anti-tumor effects of YM155 in vivo. Pancreatic cancer xenografts were established in SCID mice. Mice were injected with Panc-1 cells to form xenograft tumors. One group of mice was treated with PBS buffer (control group) and other group was treated with YM155. The result showed that the control mice had developed much larger and more highly vascularized tumors than those mice treated with YM155 (Figure 6A). There was a significant difference in tumor mass with at least a ten-fold decrease in YM155-treated mice when compared with untreated control mice (Figure 6B). In order to identify whether or not the DR5 pathway was up-regulated by YM155 in tumor tissue, tumor tissues from untreated or treated groups were analyzed to examine DR5 protein levels. Our results indicated that, in comparison with control samples (N), tumor tissue from YM155 treated mice (T), had elevated expression of DR5 (Figure 6C). These data suggest that YM155 effectively inhibits malignant pancreatic tumor growth in vivo and the mode of action is similar to that which we have observed in the cell culture experiments.
Figure 6. YM155 induces tumor growth inhibition in vivo.
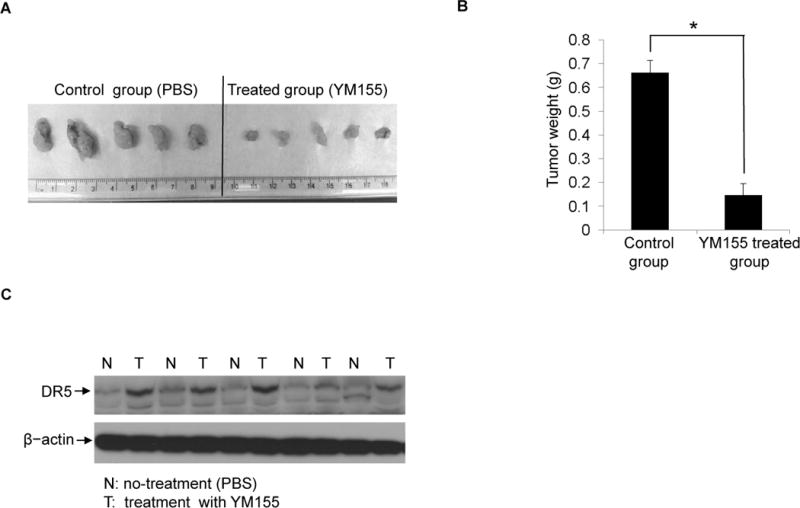
(A), BALB/c severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice were inoculated subcutaneously with 5×106 Panc-1 cells. The mice were treated with 10 mg/kg body weight of YM155 via tail vein injection until day 14. At the end point of the experiment, mice were euthanized and tumors were excised. Pictures of excised tumors from xenograft mice show larger tumors from untreated (control) mice and smaller tumors from YM155-treated mice. (B), The mass of tumors from the control group and the YM155-treated group were compared. Statistical analysis was performed to show inhibitory effects of YM155 on the mass of implanted tumors (*P<0.05). (C), Xenograft pancreatic tumors from untreated groups and YM155-treated groups were collected and lysates were prepared. Western blotting was performed to detect DR5 expression. β-actin were assessed as an equal protein loading control. The five pairs of tissues tested were randomly selected sample pairs, from untreated or YM155-treated tumor mice.
Discussion
Pancreatic cancer is a complex disease. Effective therapeutic strategies to treat this cancer require a more in-depth understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying survival and apoptotic pathways in pancreatic cancer cells. In this study, we have investigated the mechanism of YM155-induced apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells and tumors. We found that survivin down-regulation, accompanied with YM155 treatment, is insufficient to initiate apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. We showed that expression of a number of IAPs as well as survivin is suppressed by YM155. Surprisingly, YM155 treatment induces DR5 up-regulation. Our results suggest that YM155 has a much broader function on regulating pro- and anti-apoptotic proteins. Consistent with this notion, YM155 indeed enhances the therapeutic effect of gemcitabine and death receptor agonist Lexa.
YM155 was initially identified as a survivin inhibitor through high-throughput screening. In vitro studies consistently demonstrated its suppression on survivin expression. Previous reports showed that YM155 can induce apoptosis in prostate cancer cells and non-Hodgkin lymphoma cells (27, 31). YM155 has entered a few early stage clinical trials for the treatment of advanced cancers. The preliminary results have shown a potent anti-tumor growth activity (11, 12, 32, 33). However, YM155 has yet to be fully tested in human pancreatic cancer. In the present study, we demonstrate YM155 can induce apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells at clinically relevant doses. The reported plasma concentration is approximately 15 nM (12, 13, 34). Our study suggests that YM155 may have potential use as a systemic therapy for pancreatic cancer.
Consistent with previous reports that YM155 is an effective survivin suppressor (13, 14), YM155 indeed induced a dramatic survivin down-regulation in Panc-1 and PC-3 cells. However, our siRNA-mediated knockdown experiments provided evidence to support the notion that down-regulation of survivin protein expression alone is insufficient to trigger apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells, which raises interesting questions regarding the mechanisms by which YM155 induces robust apoptosis. In searching for answers, we analyzed the molecular events related to YM155-induced apoptosis. Our experiments demonstrated that Caspase 8, Bid and Caspase 9 were significantly activated in YM155-treated pancreatic cancer cells. This is similar to death receptor-mediated intrinsic or extrinsic apoptosis signal pathway activation (35–37). We then examined the death receptor DR4 and DR5 expression upon YM155 treatment. We found that YM155 induces expression of DR5 at both mRNA and protein levels and activates the DR5-mediated intrinsic apoptotic pathway in Panc-1 cells, while the DR4 expression is suppressed. This observation is confirmed in a xenograft pancreatic cancer mouse model. Further experiments confirmed that the effect on DR5 and DR4 is not caused directly by survivin, as knock-down of survivin did not affect DR5 or DR4 expression. There are previous reports showing that chemotherapeutic agents could result in DR5 up-regulation to induce apoptosis (38–40); ectopic over-expression of DR5 in cells has been shown to trigger apoptosis without additional stimuli (41–43). The role of DR5 over-expression in YM155-treated cells is further demonstrated by tests with the monoclonal antibody specifically against DR5 (Lexa). Neither YM155 nor Lexa single treatment, induced apoptosis as evidenced by the lack of Caspase 8, Caspase 3 and Bid activation, which are hallmarks of YM155 induced apoptosis. However combination treatment was able to induce apoptotic events in a similar pattern to YM155 induced apoptosis. These findings support the notion that DR5 activation may be a mechanism for YM155 induced apoptosis. Nevertheless, key questions remain: how does YM155 induce DR5 transcription and suppress DR4 transcription? Since the discovery of YM155, the detailed mechanisms by which YM155 down-regulates survivin RNA have not been defined. Our study indicates that the impact of YM155 on gene transcription machinery may be broader than survivin itself. The underlying mechanism of YM155 is likely to be complex and may involve the regulation of transcription at more genes than originally thought. This presents an opportunity for further investigation. We are currently working on the structural basis of YM155 interaction with DNA regulatory elements. We hope this effort will provide further insights into the specific mechanism by which YM155 regulates transcription of survivin and DR5 mRNA.
Our study also demonstrates the impact of YM155 on other genes expressed in pancreatic cancer cells. In addition to the inhibition of survivin expression in pancreatic and other cancers (11, 26, 44), YM155 down-regulates two additional IAP family members CIAP1/2 and FLIP, suggesting that YM155 may be an IAP family inhibitor. This is not in agreement with a previous study which reported selective inhibition of survivin by YM155 without affecting CIAP level. However this study only analyzed survivin expression inhibition and did not analyze the expression of other IAP family members (11). We also found that YM155 decreased the expression of Mcl-1. Moreover, YM155 treatment increased Bak expression but not Bim expression, suggesting some degree of Bak-specific activation by YM155. Both Bak and Bim are BH3 domain containing pro-apoptotic proteins. Bak activation in apoptosis has been reported to occur via the oligomerization of Bak dimers that plays a role in cytochrome c release (28, 45). Our experiments demonstrated dose-dependent Bak dimerization, which occurred in cells treated with YM155. Similar findings were reported in studies using small molecule compounds such as doxorubicin and gossypol that induce apoptosis by activating Bak/Bax (22, 46). We observed a decrease in Bak expression at 20 nM after 48 h, which may be caused by substantial cell death and subsequent protein degradation. All the data suggest that YM155 is a broad spectrum IAP family inhibitor and is not survivin-specific.
Because of the broader impact of YM155 on expression of genes related to apoptosis, it is conceivable that YM155 may have synergistic treatment effect on cancer cells when combined with other chemotherapeutic agents. Gemcitabine remains one of the most widely used agents in the treatment for various solid tumors, especially pancreatic cancer (47). We tested this idea using a cell culture model of pancreatic cancer in combination with gemcitabine. Our data demonstrate that YM155 exerts cell growth inhibition effects synergistically with gemcitabine. This is consistent with reports that YM155 enhances the anti-tumor effects of other chemotherapeutic agents including: cisplatin, rituximab and paclitaxel (14, 19, 34, 48, 49). Our study raises the potential prospect of using YM155 and gemcitabine in combination for pancreatic cancer therapy.
One concern for YM155 is its potential non-specific genotoxic effect. Thus, we tested the effect of YM155 on a normal cellular model for pancreatic epithelial cells using the HPDE cell line. Our experiments show that YM155 did not exert apparent apoptotic effects on HPDE. The underlying mechanisms for resistance to YM155-induced apoptosis in HPDE cells are unknown, but further investigation is important to elucidate the mode of action of YM155. Our study provides evidence which alleviate concerns relating the potential non-specific toxicity of YM155. These findings are in agreement with early stage clinical trials which also indicate that patients tolerate treatment with YM155 well.
In summary, our study reveals several novel findings: 1) YM155 effectively induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo; 2) YM155 has broad spectrum impact on the expression of genes that are related to pro- or anti-apoptotic pathways including up-regulation of DR5 and Bak; 3) YM155 exhibits synergistic therapeutic effects when combined with other chemotherapeutic agents including gemcitabine and Lexa. 4) Non-specific cyto-toxicity is not observed in non-cancerous pancreatic epithelial cells and treated animals. Based on our investigation, we believe YM155 has a potential for pancreatic cancer therapy either as mono-therapy agent or in combination with other agents. Moreover, through better understanding of the molecular mechanisms underpinning YM155 function, we may be able to design better small molecules for cancer therapy.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported, in part, by a National Institutes of Health grant (CA133086 and RR023976) to C. Liu; (R01AA019976) to K. Robertson and C. Liu. National Natural Science Foundation of China 31371425 to X. Zhao, and Liaoning Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China 2013023056 to X. Zhao.
Footnotes
Conflicts of interest: The authors disclose no conflicts
References
- 1.Pavlidis TE, Psarras K, Symeonidis NG, Pavlidis ET, Sakantamis AK. Current surgical management of pancreatic endocrine tumor liver metastases. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2011;10:243–7. doi: 10.1016/s1499-3872(11)60040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Castellanos EH, Cardin DB, Berlin JD. Treatment of early-stage pancreatic cancer. Oncology (Williston Park) 2011;25:182–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Paulson AS, Tran Cao HS, Tempero MA, Lowy AM. Therapeutic advances in pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology. 2013;144:1316–26. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pennarun B, Meijer A, de Vries EG, Kleibeuker JH, Kruyt F, de JS. Playing the DISC: turning on TRAIL death receptor-mediated apoptosis in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1805:123–40. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2009.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Schulze-Bergkamen H, Weinmann A, Moehler M, Siebler J, Galle PR. Novel ways to sensitise gastrointestinal cancer to apoptosis. Gut. 2009;58:1010–24. doi: 10.1136/gut.2008.164350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Reed JC. Apoptosis mechanisms: implications for cancer drug discovery. Oncology (Williston Park) 2004;18:11–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wang S. The promise of cancer therapeutics targeting the TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and TRAIL receptor pathway. Oncogene. 2008;27:6207–15. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zhao X, Cao M, Liu JJ, Zhu H, Nelson DR, Liu C. Reactive oxygen species is essential for cycloheximide to sensitize lexatumumab-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 2011;6:e16966. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yuan K, Sun Y, Zhou T, McDonald J, Chen Y. PARP-1 regulates resistance of pancreatic cancer to TRAIL therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:4750–9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gallmeier E, Bader DC, Kriegl L, Berezowska S, Seeliger H, Goke B, et al. Loss of TRAIL-receptors is a recurrent feature in pancreatic cancer and determines the prognosis of patients with no nodal metastasis after surgery. PLoS One. 2013;8:e56760. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nakahara T, Kita A, Yamanaka K, Mori M, Amino N, Takeuchi M, et al. Broad spectrum and potent antitumor activities of YM155, a novel small-molecule survivin suppressant, in a wide variety of human cancer cell lines and xenograft models. Cancer Sci. 2011;102:614–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Tolcher AW, Mita A, Lewis LD, Garrett CR, Till E, Daud AI, et al. Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of YM155, a small-molecule inhibitor of survivin. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:5198–203. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.17.2064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Satoh T, Okamoto I, Miyazaki M, Morinaga R, Tsuya A, Hasegawa Y, et al. Phase I study of YM155, a novel survivin suppressant, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:3872–80. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nakahara T, Yamanaka K, Hatakeyama S, Kita A, Takeuchi M, Kinoyama I, et al. YM155, a novel survivin suppressant, enhances taxane-induced apoptosis and tumor regression in a human Calu 6 lung cancer xenograft model. Anticancer Drugs. 2011;22:454–62. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0b013e328344ac68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Giaccone G, Zatloukal P, Roubec J, Floor K, Musil J, Kuta M, et al. Multicenter phase II trial of YM155, a small-molecule suppressor of survivin, in patients with advanced, refractory, non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:4481–6. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.21.1862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Iwasa T, Okamoto I, Suzuki M, Nakahara T, Yamanaka K, Hatashita E, et al. Radiosensitizing effect of YM155, a novel small-molecule survivin suppressant, in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:6496–504. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Iwasa T, Okamoto I, Takezawa K, Yamanaka K, Nakahara T, Kita A, et al. Marked anti-tumour activity of the combination of YM155, a novel survivin suppressant, and platinum-based drugs. Br J Cancer. 2010;103:36–42. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Na YS, Yang SJ, Kim SM, Jung KA, Moon JH, Shin JS, et al. YM155 induces EGFR suppression in pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS One. 2012;7:e38625. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yoon DH, Shin JS, Jin DH, Hong SW, Jung KA, Kim SM, et al. The survivin suppressant YM155 potentiates chemosensitivity to gemcitabine in the human pancreatic cancer cell line MiaPaCa-2. Anticancer Res. 2012;32:1681–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tian C, Murrin LC, Zheng JC. Mitochondrial fragmentation is involved in methamphetamine-induced cell death in rat hippocampal neural progenitor cells. PLoS One. 2009;4:e5546. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Herrmann M, Lorenz HM, Voll R, Grunke M, Woith W, Kalden JR. A rapid and simple method for the isolation of apoptotic DNA fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994;22:5506–07. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.24.5506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lei X, Chen Y, Du G, Yu W, Wang X, Qu H, et al. Gossypol induces Bax/Bak-independent activation of apoptosis and cytochrome c release via a conformational change in Bcl-2. FASEB J. 2006;20:2147–49. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-5665fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Makin GW, Corfe BM, Griffiths GJ, Thistlethwaite A, Hickman JA, Dive C. Damage-induced Bax N-terminal change, translocation to mitochondria and formation of Bax dimers/complexes occur regardless of cell fate. EMBO J. 2001;20:6306–15. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.22.6306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gross A, Jockel J, Wei MC, Korsmeyer SJ. Enforced dimerization of BAX results in its translocation, mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. EMBO J. 1998;17:3878–85. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.14.3878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zheng D, Cho YY, Lau AT, Zhang J, Ma WY, Bode AM, et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase 3-mediated activating transcription factor 1 phosphorylation enhances cell transformation. Cancer Res. 2008;68:7650–60. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rauch A, Hennig D, Schafer C, Wirth M, Marx C, Heinzel T, et al. Survivin and YM155: how faithful is the liaison? Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1845:202–20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2014.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wang Q, Chen Z, Diao X, Huang S. Induction of autophagy-dependent apoptosis by the survivin suppressant YM155 in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2011;302:29–36. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2010.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Dewson G, Kratina T, Sim HW, Puthalakath H, Adams JM, Colman PM, et al. To trigger apoptosis, Bak exposes its BH3 domain and homodimerizes via BH3:groove interactions. Mol Cell. 2008;30:369–80. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bold RJ, Chandra J, McConkey DJ. Gemcitabine-induced programmed cell death (apoptosis) of human pancreatic carcinoma is determined by Bcl-2 content. Ann Surg Oncol. 1999;6:279–85. doi: 10.1007/s10434-999-0279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ouyang H, Mou L, Luk C, Liu N, Karaskova J, Squire J, et al. Immortal human pancreatic duct epithelial cell lines with near normal genotype and phenotype. Am J Pathol. 2000;157:1623–31. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64800-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kita A, Nakahara T, Yamanaka K, Nakano K, Nakata M, Mori M, et al. Antitumor effects of YM155, a novel survivin suppressant, against human aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk Res. 2011;35:787–92. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2010.11.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lewis KD, Samlowski W, Ward J, Catlett J, Cranmer L, Kirkwood J, et al. A multi-center phase II evaluation of the small molecule survivin suppressor YM155 in patients with unresectable stage III or IV melanoma. Invest New Drugs. 2011;29:161–6. doi: 10.1007/s10637-009-9333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Aoyama Y, Kaibara A, Takada A, Nishimura T, Katashima M, Sawamoto T. Population pharmacokinetic modeling of sepantronium bromide (YM155), a small molecule survivin suppressant, in patients with non-small cell lung cancer, hormone refractory prostate cancer, or unresectable stage III or IV melanoma. Invest New Drugs. 2013;31:443–51. doi: 10.1007/s10637-012-9867-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kelly RJ, Thomas A, Rajan A, Chun G, Lopez-Chavez A, Szabo E, et al. A phase I/II study of sepantronium bromide (YM155, survivin suppressor) with paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2013;24:2601–6. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zhang H, Song LC, Liu YY, Ma Y, Lu YL. Pinacidil reduces neuronal apoptosis following cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats through both mitochondrial and death-receptor signal pathways. Neurosci Bull. 2007;23:145–50. doi: 10.1007/s12264-007-0021-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yin XM. Signal transduction mediated by Bid, a pro-death Bcl-2 family proteins, connects the death receptor and mitochondria apoptosis pathways. Cell Res. 2000;10:161–67. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7290045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wilson NS, Dixit V, Ashkenazi A. Death receptor signal transducers: nodes of coordination in immune signaling networks. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:348–55. doi: 10.1038/ni.1714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Baritaki S, Huerta-Yepez S, Sakai T, Spandidos DA, Bonavida B. Chemotherapeutic drugs sensitize cancer cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis: up-regulation of DR5 and inhibition of Yin Yang 1. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:1387–99. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kim H, Kim EH, Eom YW, Kim WH, Kwon TK, Lee SJ, et al. Sulforaphane sensitizes tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-resistant hepatoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through reactive oxygen species-mediated up-regulation of DR5. Cancer Res. 2006;66:1740–50. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Thomas SA, Vasudevan S, Thamkachy R, Lekshmi SU, Santhoshkumar TR, Rajasekharan KN, et al. Upregulation of DR5 receptor by the diaminothiazole DAT1 [4-amino-5-benzoyl-2-(4-methoxy phenyl amino) thiazole] triggers an independent extrinsic pathway of apoptosis in colon cancer cells with compromised pro and antiapoptotic proteins. Apoptosis. 2013;18:713–26. doi: 10.1007/s10495-013-0826-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zhang HG, Xie J, Xu L, Yang P, Xu X, Sun S, et al. Hepatic DR5 induces apoptosis and limits adenovirus gene therapy product expression in the liver. J Virol. 2002;76:5692–700. doi: 10.1128/JVI.76.11.5692-5700.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Schneider P, Thome M, Burns K, Bodmer JL, Hofmann K, Kataoka T, et al. TRAIL receptors 1 (DR4) and 2 (DR5) signal FADD-dependent apoptosis and activate NF-kappaB. Immunity. 1997;7:831–6. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80401-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Wu GS, Burns TF, Zhan Y, Alnemri ES, El-Deiry WS. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of the mouse homologue of the KILLER/DR5 tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) death receptor. Cancer Res. 1999;59:2770–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yamanaka K, Nakata M, Kaneko N, Fushiki H, Kita A, Nakahara T, et al. YM155, a selective survivin suppressant, inhibits tumor spread and prolongs survival in a spontaneous metastatic model of human triple negative breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 2011;39:569–75. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2011.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Dewson G, Kratina T, Czabotar P, Day CL, Adams JM, Kluck RM. Bak activation for apoptosis involves oligomerization of dimers via their alpha6 helices. Mol Cell. 2009;36:696–703. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Panaretakis T, Pokrovskaja K, Shoshan MC, Grander D. Activation of Bak, Bax, and BH3-only proteins in the apoptotic response to doxorubicin. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:44317–26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M205273200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Liao ZJ, Guo YH, Zhao Z, Yao JT, Xu R, Nan KJ. Gemcitabine inhibits the micrometastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting the EpCAM-positive circulating tumor cells via the HGF/cMET pathway. Int J Oncol. 2014;45:651–8. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kaneko N, Mitsuoka K, Amino N, Yamanaka K, Kita A, Mori M, et al. Combination of YM155, a survivin suppressant, with bendamustine and rituximab: a new combination therapy to treat relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:1814–22. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kumar B, Yadav A, Lang JC, Cipolla MJ, Schmitt AC, Arradaza N, et al. YM155 reverses cisplatin resistance in head and neck cancer by decreasing cytoplasmic survivin levels. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11:1988–98. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


