Abstract
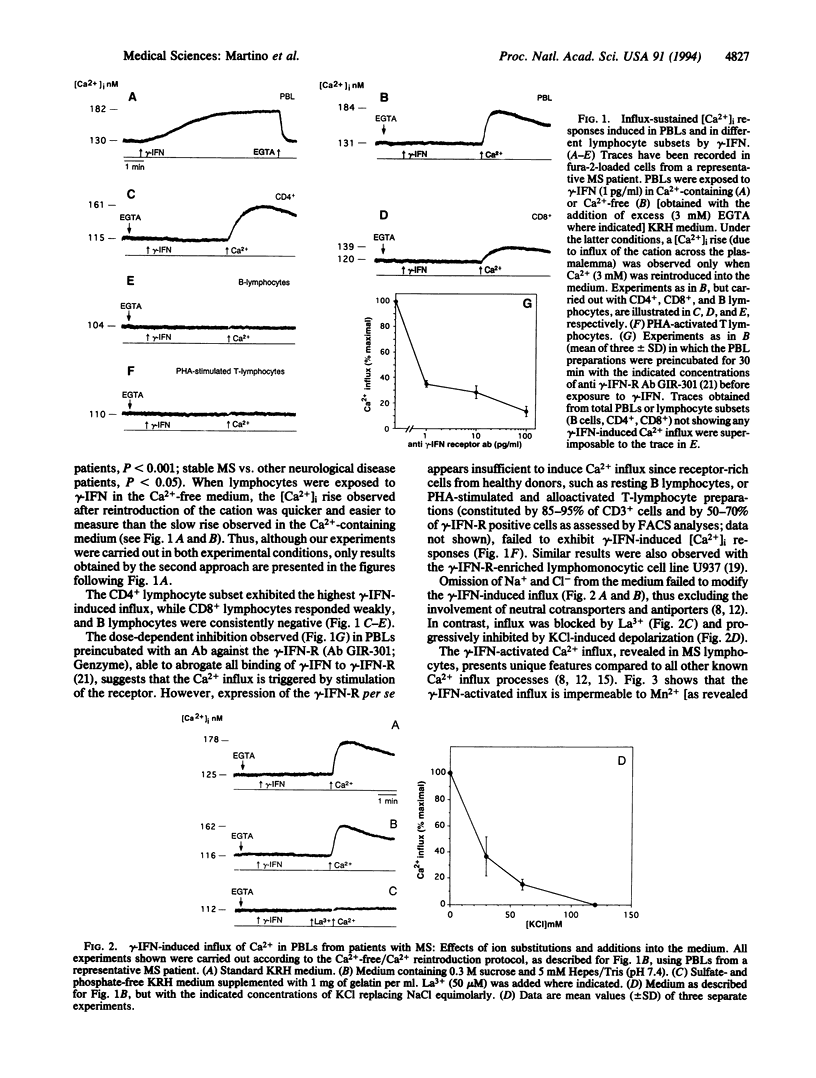
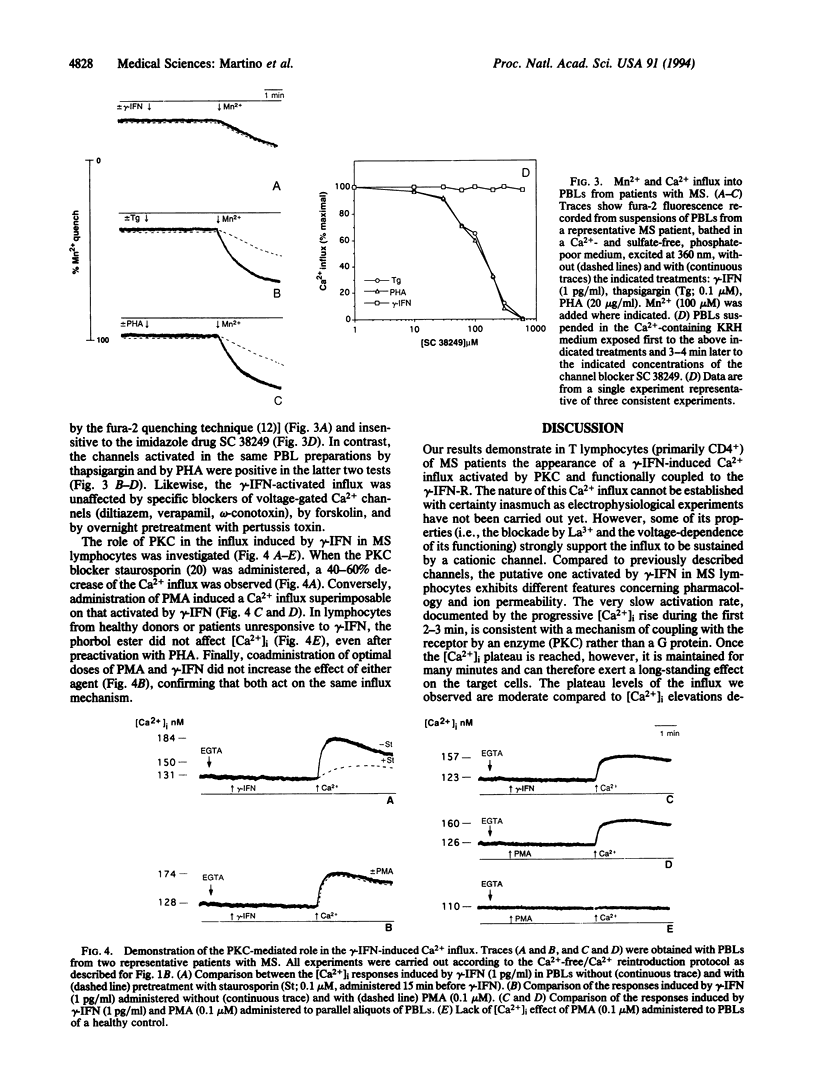
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an immune-mediated demyelinating disease of the central nervous system. The etiology of the disease is still unknown. Activated T lymphocytes are considered essential in mediating the inflammatory process leading to demyelination in MS. They operate through a complex network of cytokines among which gamma interferon (gamma-IFN) plays a key role. Here we report that exposure to gamma-IFN of T lymphocytes from patients with MS activates, by a protein kinase C-mediated pathway, a previously undescribed gamma-IFN-activated Ca2+ influx, functionally coupled to the gamma-IFN receptor. The influx mainly expressed by CD4+ T lymphocytes, was found in 12 of 15 (80%) patients with clinically active MS and in 14 of 30 (46%) patients with stable MS. The influx was found in only 3 of 24 (12%) control patients and in none of the 15 healthy subjects studied. Our results document the appearance in MS lymphocytes of a gamma-IFN-activated, protein kinase C-dependent, Ca2+ influx that might be due to the expression of a new cation-specific plasmalemma channel. This finding suggests that at least part of gamma-IFN's contribution to the pathogenesis of MS is exerted through a Ca(2+)-dependent regulation of T lymphocyte activity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cannella B., Raine C. S. Cytokines up-regulate Ia expression in organotypic cultures of central nervous system tissue. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Oct;24(3):239–248. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chofflon M., Juillard C., Juillard P., Gauthier G., Grau G. E. Tumor necrosis factor alpha production as a possible predictor of relapse in patients with multiple sclerosis. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1992 Nov-Dec;3(6):523–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciardo A., Meldolesi J. Multiple actions of SC 38249: the blocker of both voltage-operated and second messenger-operated Ca2+ channels also inhibits Ca2+ extrusion. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun 12;188(6):417–421. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(90)90204-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clementi E., Scheer H., Zacchetti D., Fasolato C., Pozzan T., Meldolesi J. Receptor-activated Ca2+ influx. Two independently regulated mechanisms of influx stimulation coexist in neurosecretory PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2164–2172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan X. D., Goldberg M., Bloom B. R. Interferon-gamma-induced transcriptional activation is mediated by protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5122–5125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. A., Becton D. L., Somers S. D., Gray P. W., Adams D. O. Interferon-gamma modulates protein kinase C activity in murine peritoneal macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1378–1381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy K. J., Sawada T. Human gamma interferon strongly upregulates its own gene expression in peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):1021–1026. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung H. P., Jung S., Stoll G., Zielasek J., Schmidt B., Archelos J. J., Toyka K. V. Inflammatory mediators in demyelinating disorders of the CNS and PNS. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Oct;40(2-3):197–210. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaziro Y., Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nakafuku M., Satoh T. Structure and function of signal-transducing GTP-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:349–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzke J. F. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology. 1983 Nov;33(11):1444–1452. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.11.1444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald W. I., Halliday A. M. Diagnosis and classification of multiple sclerosis. Br Med Bull. 1977 Jan;33(1):4–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. H., Rudge P., Johnson G., Kendall B. E., Macmanus D. G., Moseley I. F., Barnes D., McDonald W. I. Serial gadolinium enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis. Brain. 1988 Aug;111(Pt 4):927–939. doi: 10.1093/brain/111.4.927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J. Voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1403–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novelli F., Giovarelli M., Gentz R., Zucca M., di Pierro F., Garotta G., Forni G. Modulation of interferon-gamma receptor during human T lymphocyte alloactivation. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jun;23(6):1226–1231. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panitch H. S., Hirsch R. L., Haley A. S., Johnson K. P. Exacerbations of multiple sclerosis in patients treated with gamma interferon. Lancet. 1987 Apr 18;1(8538):893–895. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92863-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J. Receptor-mediated calcium entry. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 1;268(2):381–385. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81290-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudick R. A., Carpenter C. S., Cookfair D. L., Tuohy V. K., Ransohoff R. M. In vitro and in vivo inhibition of mitogen-driven T-cell activation by recombinant interferon beta. Neurology. 1993 Oct;43(10):2080–2087. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.10.2080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage S. O., Merritt J. E., Hallam T. J., Rink T. J. Receptor-mediated calcium entry in fura-2-loaded human platelets stimulated with ADP and thrombin. Dual-wavelengths studies with Mn2+. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 15;258(3):923–926. doi: 10.1042/bj2580923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selmaj K. W., Raine C. S. Tumor necrosis factor mediates myelin and oligodendrocyte damage in vitro. Ann Neurol. 1988 Apr;23(4):339–346. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan K. C., Calderon J., Schreiber R. D. Generation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific for the human IFN-gamma receptor. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4231–4237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Tsien R. Y. Calcium channels, stores, and oscillations. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:715–760. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


