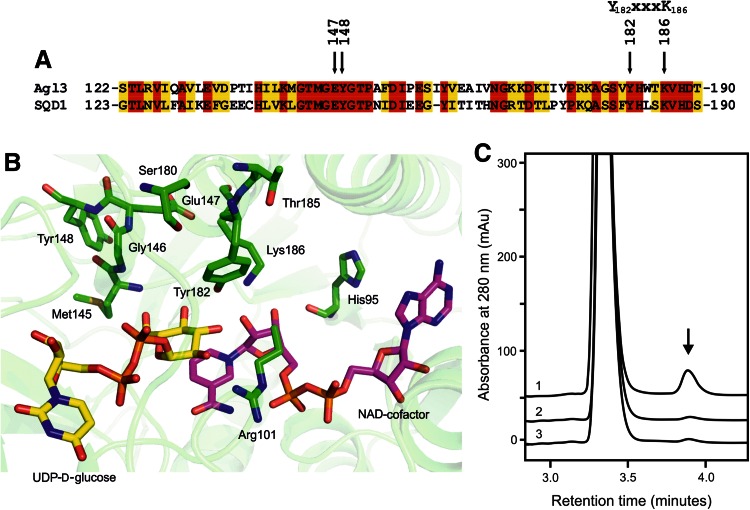
Fig. 2.
Partial amino acid comparison, close-up of the active site, and reactivity of wild-type and specific mutants of Agl3. a Selected region of the sequence alignment of Agl3 and SQD1 demonstrating a high degree of amino acid similarity of both enzymes. The positions of E147, Y148, and the characteristic Y-XXX-K motif of SDR proteins are indicated (Kavanagh et al. 2008). b Homology model of the active site of Agl3 with the critical amino acids drawn in green sticks, the NAD-cofactor in pink and the substrate in yellow. For clarity the backbone of residues 96–108 is not shown; (the figure was generated by pymol version 1.2r1). c In vitro conversion of UDP-d-glucose to UDP-d-glucose-5,6-ene (arrow) in absence of sulfite by the wild-type Agl3 (graph 1), Y148A mutant (graph 2), and E147A mutant (graph 3)