Abstract
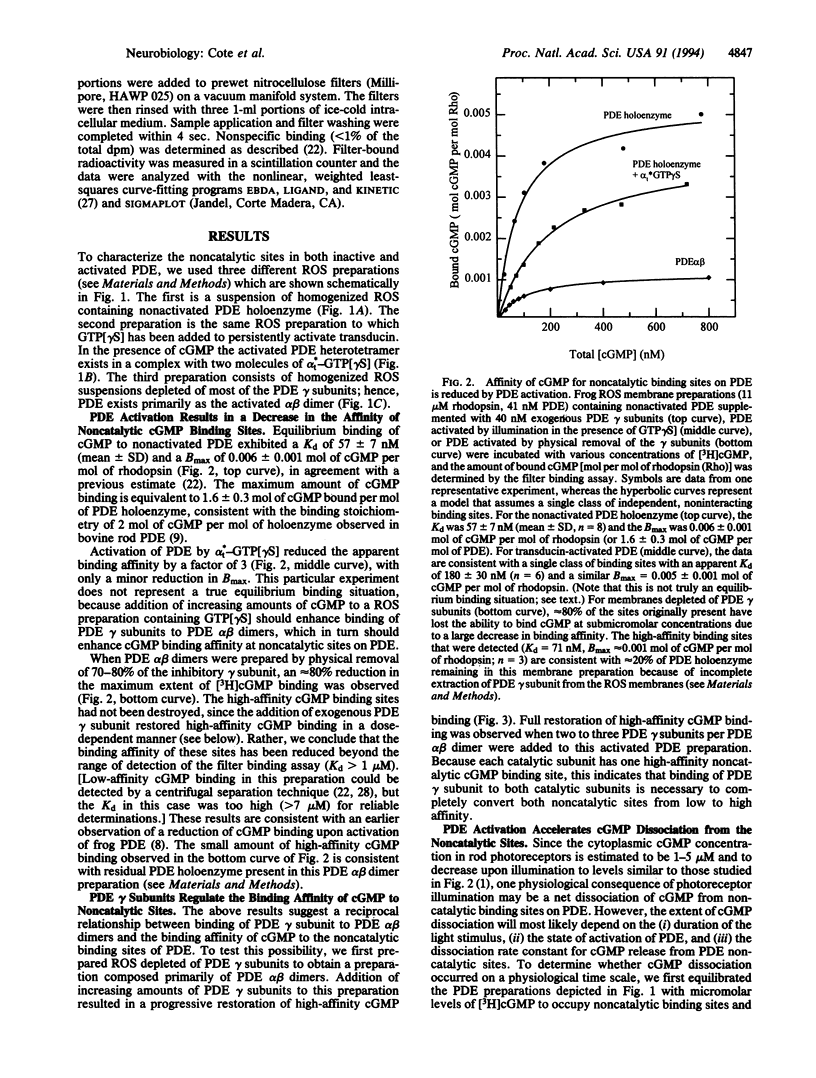
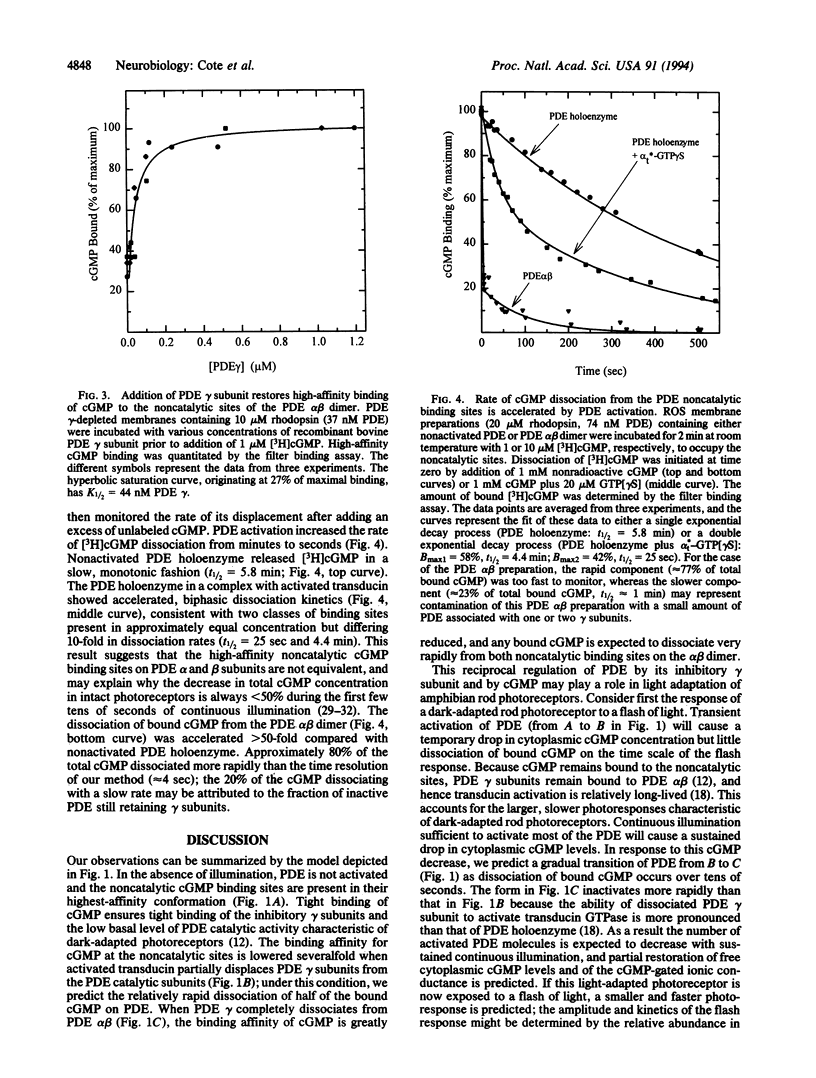
A central step in vertebrate visual transduction is the rapid drop in cGMP levels that causes cGMP-gated ion channels in the photoreceptor cell membrane to close. It has long been a puzzle that the cGMP phosphodiesterase (PDE) whose activation causes this decrease contains not only catalytic sites for cGMP hydrolysis but also noncatalytic cGMP binding sites. Recent work has shown that occupancy of these noncatalytic sites slows the rate of PDE inactivation. We report here that PDE activation induced by activated transduction lowers the cGMP binding affinity for noncatalytic sites on PDE and accelerates the dissociation of cGMP from these sites. These sites can exist in three states: high affinity (Kd = 60 nM) for the nonactivated PDE, intermediate affinity (Kd approximately 180 nM) when the enzyme is activated in a complex with transducin, and low affinity (Kd > 1 microM) when transducin physically removes the inhibitory subunits of PDE from the PDE catalytic subunits. Activation of PDE by transducin causes a 10-fold increase in the rate of cGMP dissociation from one of the two noncatalytic sites; physical removal of the inhibitory subunits from the PDE catalytic subunits further accelerates the cGMP dissociation rate from both sites > 50-fold. Because PDE molecules lacking bound cGMP inactivate more rapidly, this suggests that a prolonged cGMP decrease may act as a negative feedback regulator to generate the faster, smaller photoresponses characteristic of light-adapted photoreceptors.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arshavsky VYu, Bownds M. D. Regulation of deactivation of photoreceptor G protein by its target enzyme and cGMP. Nature. 1992 Jun 4;357(6377):416–417. doi: 10.1038/357416a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arshavsky VYu, Gray-Keller M. P., Bownds M. D. cGMP suppresses GTPase activity of a portion of transducin equimolar to phosphodiesterase in frog rod outer segments. Light-induced cGMP decreases as a putative feedback mechanism of the photoresponse. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18530–18537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arshavsky V. Y., Dumke C. L., Bownds M. D. Noncatalytic cGMP-binding sites of amphibian rod cGMP phosphodiesterase control interaction with its inhibitory gamma-subunits. A putative regulatory mechanism of the rod photoresponse. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24501–24507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biernbaum M. S., Bownds M. D. Frog rod outer segments with attached inner segment ellipsoids as an in vitro model for photoreceptors on the retina. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Jan;85(1):83–105. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blazynski C., Cohen A. I. Rapid declines in cyclic GMP of rod outer segments of intact frog photoreceptors after illumination. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14142–14147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bownds D., Gordon-Walker A., Gaide-Huguenin A. C., Robinson W. Characterization and analysis of frog photoreceptor membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Sep;58(3):225–237. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.3.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. L., Stryer L. Expression in bacteria of functional inhibitory subunit of retinal rod cGMP phosphodiesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4922–4926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc A., Bennett N. Activated cGMP phosphodiesterase of retinal rods. A complex with transducin alpha subunit. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6620–6627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles J. A., Yamane S. Effects of adapting lights on the time course of the receptor potential of the anuran retinal rod. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(1):189–207. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cote R. H., Biernbaum M. S., Nicol G. D., Bownds M. D. Light-induced decreases in cGMP concentration precede changes in membrane permeability in frog rod photoreceptors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9635–9641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cote R. H., Brunnock M. A. Intracellular cGMP concentration in rod photoreceptors is regulated by binding to high and moderate affinity cGMP binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):17190–17198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deterre P., Bigay J., Robert M., Pfister C., Kühn H., Chabre M. Activation of retinal rod cyclic GMP-phosphodiesterase by transducin: characterization of the complex formed by phosphodiesterase inhibitor and transducin alpha-subunit. Proteins. 1986 Oct;1(2):188–193. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detwiler P. B., Gray-Keller M. P. Some unresolved issues in the physiology and biochemistry of phototransduction. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1992 Aug;2(4):433–438. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(92)90176-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson M. A., Robinson P., Lisman J. Deactivation of visual transduction without guanosine triphosphate hydrolysis by G protein. Science. 1992 Aug 28;257(5074):1255–1258. doi: 10.1126/science.1519062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forget R. S., Martin J. E., Cote R. H. A centrifugal separation procedure detects moderate affinity cGMP binding sites in membrane-associated proteins and permeabilized cells. Anal Biochem. 1993 Nov 15;215(1):159–161. doi: 10.1006/abio.1993.1570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K., Griswold-Prenner I. G protein-effector coupling: binding of rod phosphodiesterase inhibitory subunit to transducin. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3133–3137. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie P. G., Beavo J. A. Inhibition and stimulation of photoreceptor phosphodiesterases by dipyridamole and M&B 22,948. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;36(5):773–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie P. G., Beavo J. A. cGMP is tightly bound to bovine retinal rod phosphodiesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4311–4315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govardovskii V. I., Berman A. L. Light-induced changes of cyclic GMP content in frog retinal rod outer segments measured with rapid freezing and microdissection. Biophys Struct Mech. 1981;7(3):125–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00539174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B. Signal transduction enzymes of vertebrate photoreceptors. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Apr;24(2):219–226. doi: 10.1007/BF00762680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbride P., Ebrey T. G. Light-initiated changes of cyclic guanosine monophosphate levels in the frog retina measured with quick-freezing techniques. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Sep;74(3):415–426. doi: 10.1085/jgp.74.3.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagnado L., Baylor D. Signal flow in visual transduction. Neuron. 1992 Jun;8(6):995–1002. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90122-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li T. S., Volpp K., Applebury M. L. Bovine cone photoreceptor cGMP phosphodiesterase structure deduced from a cDNA clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):293–297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. Analysis of radioligand binding experiments. A collection of computer programs for the IBM PC. J Pharmacol Methods. 1985 Nov;14(3):213–228. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(85)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagès F., Deterre P., Pfister C. Enhanced GTPase activity of transducin when bound to cGMP phosphodiesterase in bovine retinal rods. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22018–22021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh E. N., Jr, Lamb T. D. Cyclic GMP and calcium: the internal messengers of excitation and adaptation in vertebrate photoreceptors. Vision Res. 1990;30(12):1923–1948. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(90)90013-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroop S. D., Beavo J. A. Sequence homology and structure--function studies of the bovine cyclic-GMP-stimulated and retinal phosphodiesterases. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1992;25:55–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Visual excitation and recovery. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10711–10714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensel T. G., Stryer L. Reciprocal control of retinal rod cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase by its gamma subunit and transducin. Proteins. 1986 Sep;1(1):90–99. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen M. M., Bitensky M. W. Comparison of the phosphodiesterase inhibitory subunit interactions of frog and bovine rod outer segments. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 1;259(1):13–19. doi: 10.1042/bj2590013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki A., Bartucca F., Ting A., Bitensky M. W. Reciprocal effects of an inhibitory factor on catalytic activity and noncatalytic cGMP binding sites of rod phosphodiesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3702–3706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki A., Hayashi F., Tatsumi M., Bitensky M. W., George J. S. Interactions between the subunits of transducin and cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase in Rana catesbiana rod photoreceptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11539–11548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki A., Sen I., Bitensky M. W., Casnellie J. E., Greengard P. Cyclic GMP-specific, high affinity, noncatalytic binding sites on light-activated phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11619–11624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



