Abstract
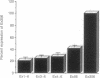
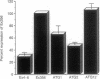
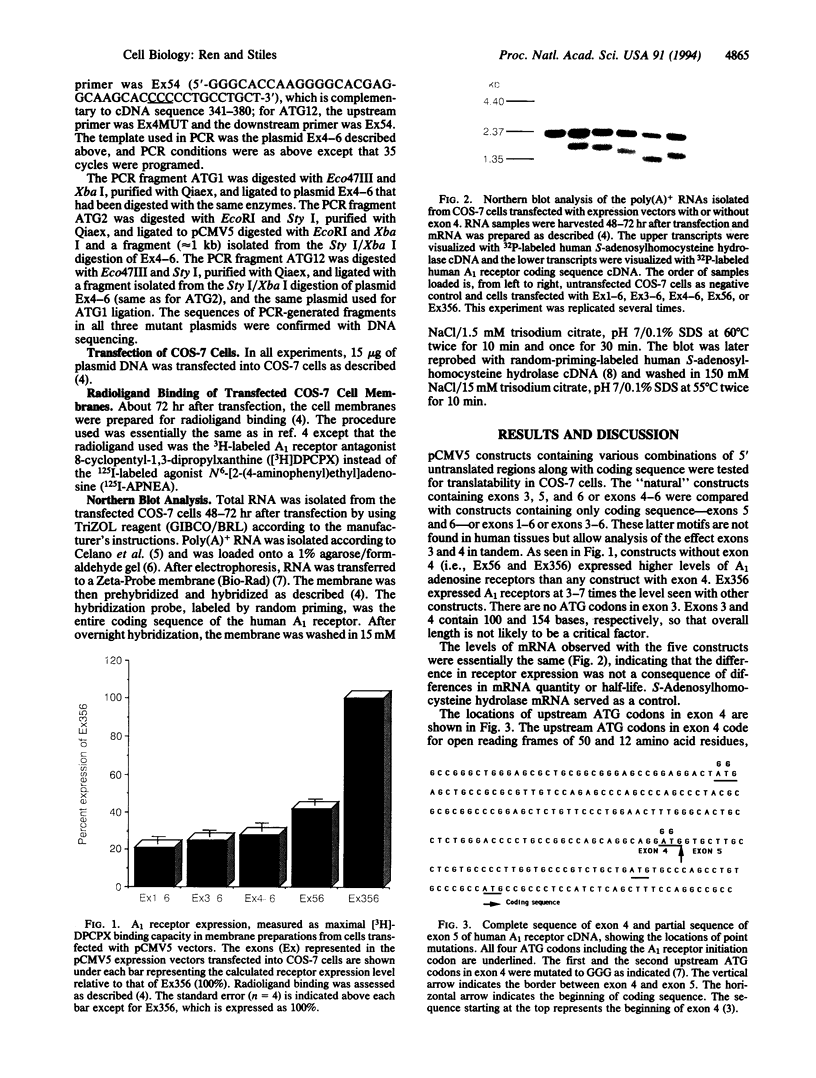
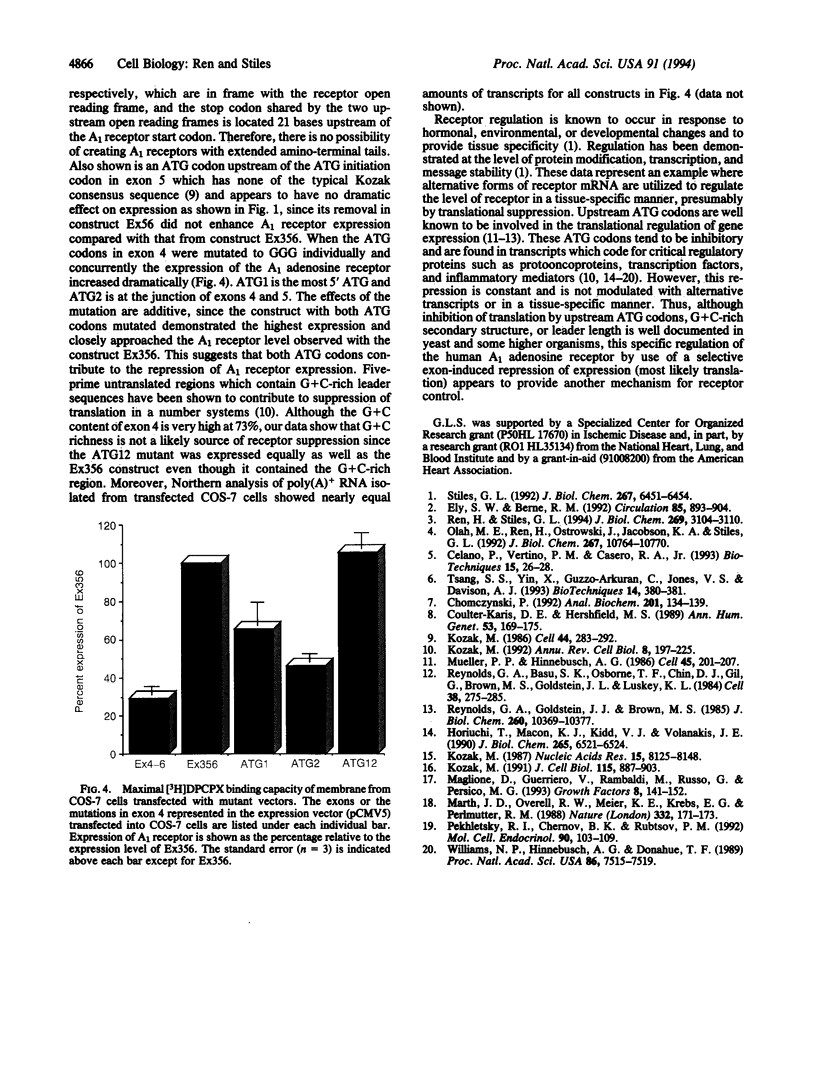
The human A1 adenosine receptor gene contains six exons with exons 1, 2, 3, 4, and part of 5 representing 5' untranslated regions. Reverse transcription-PCR with exon-specific primers showed two distinct transcripts containing either exons 3, 5, and 6 or exons 4, 5, and 6, with exons 3 and 4 being mutually exclusive. No mature mRNAs containing exons 1 and 2 have been detected. All human tissues that express any A1 receptors contain mRNA with exons 4, 5, and 6. Tissues which express high levels of A1 receptors contain mRNA with exons 3, 5, and 6. Exon 4 contains two upstream ATG codons whereas exon 3 contains none. COS cells transfected with expression vectors containing exon 4 (exons 1-6, 3-6, or Ex4-6) express much lower levels of A1 receptors than vectors without exon 4 (exons 3, 5, and 6). Mutation of upstream ATG codons in exon 4 leads to 3- to 7-fold increased A1 receptor expression, up to the level seen with the construct containing exons 3, 5, and 6. Thus, in human tissues "basal" levels of A1 receptors can be expressed by use of mRNA containing exons 4, 5, and 6, but when high levels are needed, alternative transcripts with exons 3, 5, and 6 are produced.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Celano P., Vertino P. M., Casero R. A., Jr Isolation of polyadenylated RNA from cultured cells and intact tissues. Biotechniques. 1993 Jul;15(1):26–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P. One-hour downward alkaline capillary transfer for blotting of DNA and RNA. Anal Biochem. 1992 Feb 14;201(1):134–139. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90185-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter-Karis D. E., Hershfield M. S. Sequence of full length cDNA for human S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. Ann Hum Genet. 1989 May;53(Pt 2):169–175. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1989.tb01781.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely S. W., Berne R. M. Protective effects of adenosine in myocardial ischemia. Circulation. 1992 Mar;85(3):893–904. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.85.3.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi T., Macon K. J., Kidd V. J., Volanakis J. E. Translational regulation of complement protein C2 expression by differential utilization of the 5'-untranslated region of mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6521–6524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of vertebrate mRNA sequences: intimations of translational control. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):887–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Regulation of translation in eukaryotic systems. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:197–225. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maglione D., Guerriero V., Rambaldi M., Russo G., Persico M. G. Translation of the placenta growth factor mRNA is severely affected by a small open reading frame localized in the 5' untranslated region. Growth Factors. 1993;8(2):141–152. doi: 10.3109/08977199309046934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Overell R. W., Meier K. E., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. Translational activation of the lck proto-oncogene. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):171–173. doi: 10.1038/332171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. P., Hinnebusch A. G. Multiple upstream AUG codons mediate translational control of GCN4. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90384-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olah M. E., Ren H., Ostrowski J., Jacobson K. A., Stiles G. L. Cloning, expression, and characterization of the unique bovine A1 adenosine receptor. Studies on the ligand binding site by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10764–10770. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekhletsky R. I., Chernov B. K., Rubtsov P. M. Variants of the 5'-untranslated sequence of human growth hormone receptor mRNA. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1992 Dec;90(1):103–109. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(92)90107-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren H., Stiles G. L. Characterization of the human A1 adenosine receptor gene. Evidence for alternative splicing. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):3104–3110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. A., Basu S. K., Osborne T. F., Chin D. J., Gil G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Luskey K. L. HMG CoA reductase: a negatively regulated gene with unusual promoter and 5' untranslated regions. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90549-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. A., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Multiple mRNAs for 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase determined by multiple transcription initiation sites and intron splicing sites in the 5'-untranslated region. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10369–10377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles G. L. Adenosine receptors. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6451–6454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang S. S., Yin X., Guzzo-Arkuran C., Jones V. S., Davison A. J. Loss of resolution in gel electrophoresis of RNA: a problem associated with the presence of formaldehyde gradients. Biotechniques. 1993 Mar;14(3):380–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N. P., Hinnebusch A. G., Donahue T. F. Mutations in the structural genes for eukaryotic initiation factors 2 alpha and 2 beta of Saccharomyces cerevisiae disrupt translational control of GCN4 mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7515–7519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]