Abstract
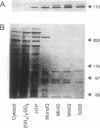
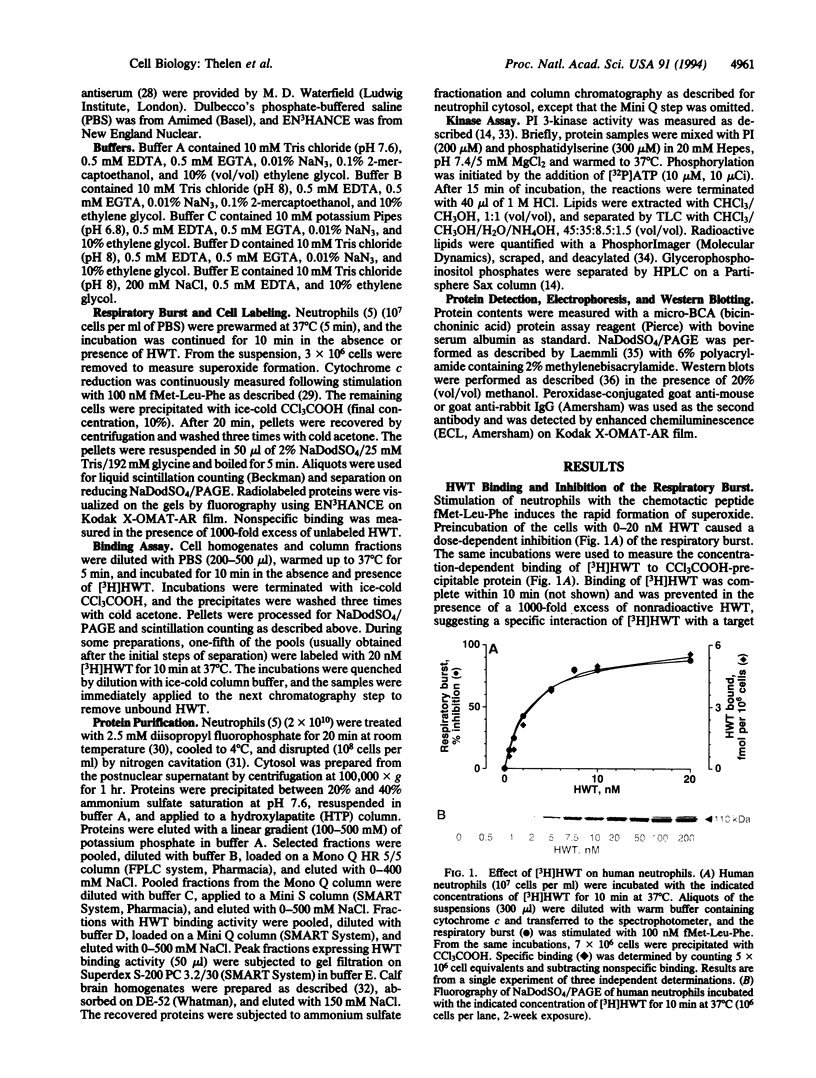
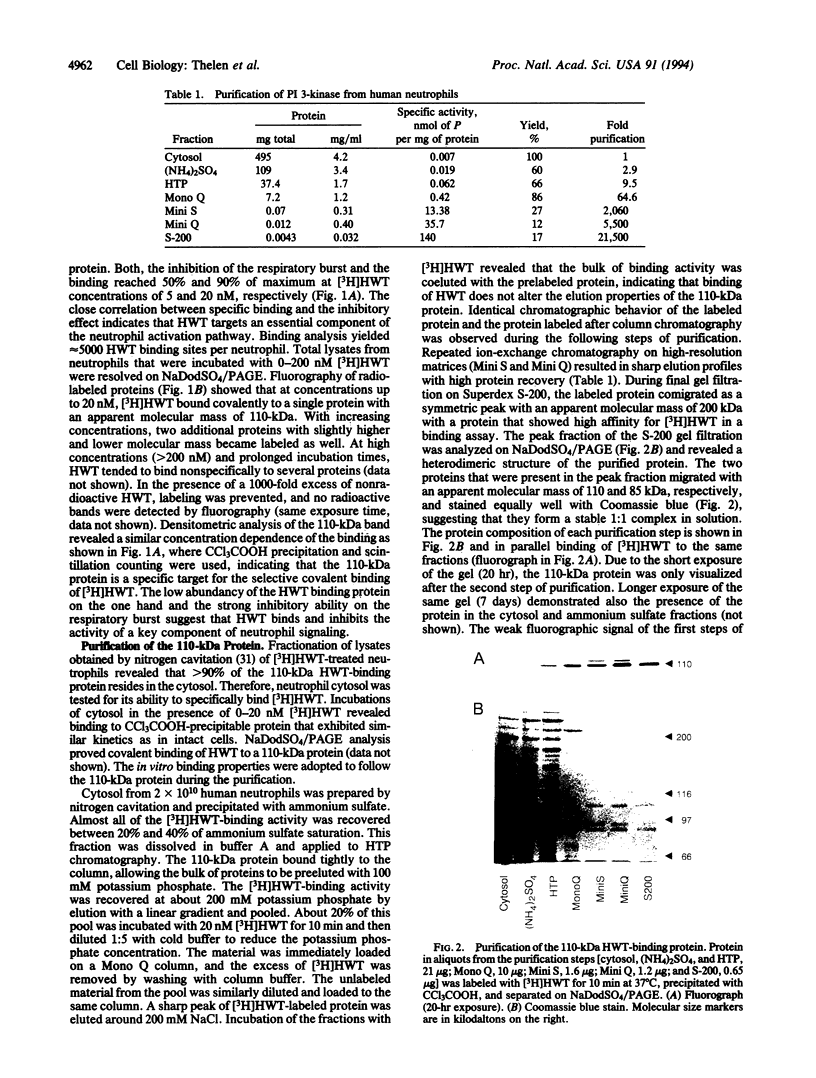
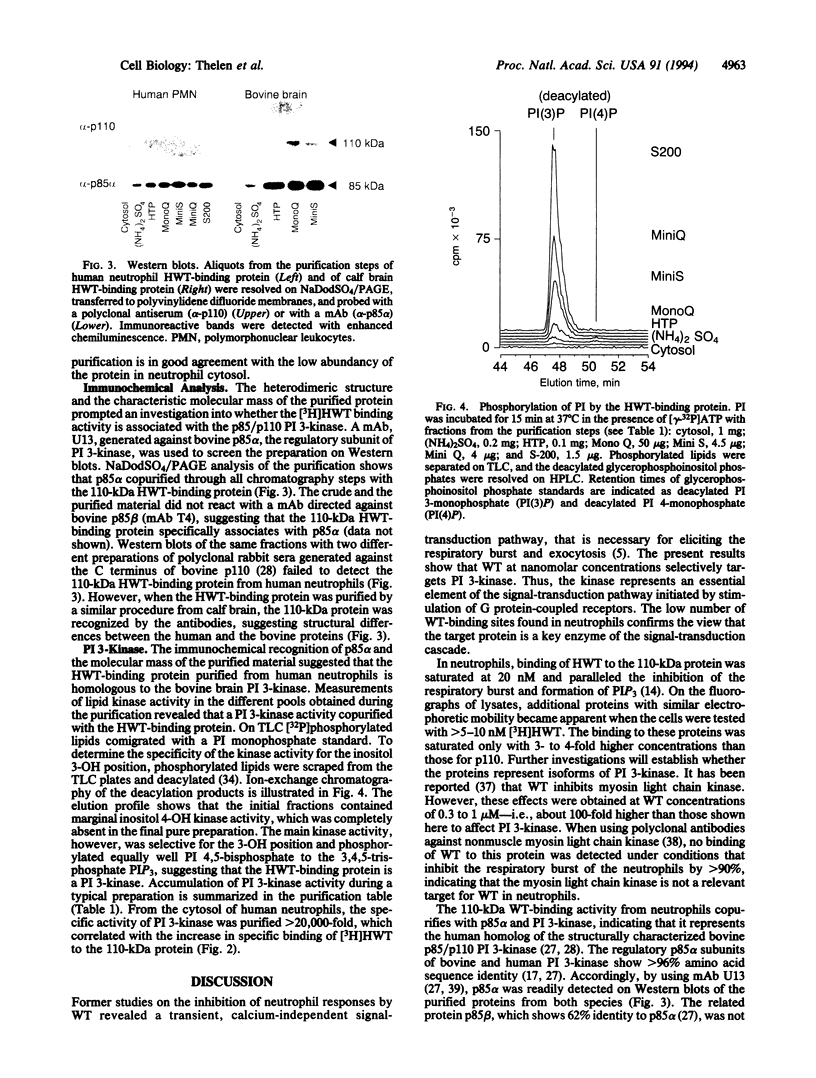
Wortmannin (WT) and its derivative 17-hydroxywortmannin (HWT) inhibit at nanomolar concentrations superoxide formation and exocytosis in neutrophils stimulated with chemotactic agonists. Treatment of neutrophils with radiolabeled [3H]HWT resulted in specific and saturable binding that paralleled the inhibition of the respiratory burst. Both half-maximal binding and half-maximal inhibition were observed at 5 nM, and > 90% of maximal binding and inhibition was observed at 20 nM HWT. Fluorography of subcellular fractions that were separated on NaDodSO4/PAGE showed that [3H]HWT binds covalently to a 110-kDa cytosolic protein. The WT-binding protein was purified from human neutrophils and bovine brain homogenates by column chromatography. The pure protein was eluted from gel filtration columns with an apparent molecular mass of 200 kDa and showed a heterodimeric structure on Coomassie-stained NaDodSO4/PAGE. In addition to the 110 kDa wortmannin binding protein an equally intense band was seen migrating at 85 kDa. This band was identified on Western blots as p85 alpha, the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase (ATP:1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 3-phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.137). The purified protein contained PI 3-kinase activity that was enriched > 20,000-fold from human neutrophil cytosol during preparation. The data impose a key role for PI 3-kinase-mediated signal transduction through guanine nucleotide-binding protein-coupled receptors and suggest that 3-phosphorylated inositol phospholipids are important second messengers for immediate responses in neutrophils. Furthermore, the results show that WT is a powerful and selective tool to study the function of PI 3-kinase.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert K. A., Wu W. C., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Inhibition by calmodulin of calcium/phospholipid-dependent protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3622–3625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arcaro A., Wymann M. P. Wortmannin is a potent phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor: the role of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate in neutrophil responses. Biochem J. 1993 Dec 1;296(Pt 2):297–301. doi: 10.1042/bj2960297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Boulay F., Badwey J. A., Curnutte J. T. Activation of neutrophil leukocytes: chemoattractant receptors and respiratory burst. FASEB J. 1993 Aug;7(11):1004–1010. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.11.8396540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Dewald B., Schnyder J., Ruch W., Cooper P. H., Payne T. G. Inhibition of the phagocytosis-induced respiratory burst by the fungal metabolite wortmannin and some analogues. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Apr;169(2):408–418. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonser R. W., Thompson N. T., Randall R. W., Tateson J. E., Spacey G. D., Hodson H. F., Garland L. G. Demethoxyviridin and wortmannin block phospholipase C and D activation in the human neutrophil. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 May;103(1):1237–1241. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12330.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booker G. W., Breeze A. L., Downing A. K., Panayotou G., Gout I., Waterfield M. D., Campbell I. D. Structure of an SH2 domain of the p85 alpha subunit of phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):684–687. doi: 10.1038/358684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camps M., Carozzi A., Schnabel P., Scheer A., Parker P. J., Gierschik P. Isozyme-selective stimulation of phospholipase C-beta 2 by G protein beta gamma-subunits. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):684–686. doi: 10.1038/360684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. L., Auger K. R., Chanudhuri M., Yoakim M., Schaffhausen B., Shoelson S., Cantley L. C. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase is activated by phosphopeptides that bind to the SH2 domains of the 85-kDa subunit. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9478–9483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. L., Duckworth B. C., Auger K. R., Cohen B., Schaffhausen B. S., Cantley L. C. Purification and characterization of phosphoinositide 3-kinase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19704–19711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke N. G., Dawson R. M. Alkaline O leads to N-transacylation. A new method for the quantitative deacylation of phospholipids. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):301–306. doi: 10.1042/bj1950301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewald B., Thelen M., Baggiolini M. Two transduction sequences are necessary for neutrophil activation by receptor agonists. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16179–16184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- End P., Gout I., Fry M. J., Panayotou G., Dhand R., Yonezawa K., Kasuga M., Waterfield M. D. A biosensor approach to probe the structure and function of the p85 alpha subunit of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10066–10075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry M. J., Panayotou G., Dhand R., Ruiz-Larrea F., Gout I., Nguyen O., Courtneidge S. A., Waterfield M. D. Purification and characterization of a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex from bovine brain by using phosphopeptide affinity columns. Biochem J. 1992 Dec 1;288(Pt 2):383–393. doi: 10.1042/bj2880383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry M. J., Waterfield M. D. Structure and function of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: a potential second messenger system involved in growth control. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1993 Jun 29;340(1293):337–344. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1993.0076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher P. J., Herring B. P., Griffin S. A., Stull J. T. Molecular characterization of a mammalian smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23936–23944. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig J. H., Thelen M., Rosen A., Janmey P. A., Nairn A. C., Aderem A. MARCKS is an actin filament crosslinking protein regulated by protein kinase C and calcium-calmodulin. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):618–622. doi: 10.1038/356618a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiles I. D., Otsu M., Volinia S., Fry M. J., Gout I., Dhand R., Panayotou G., Ruiz-Larrea F., Thompson A., Totty N. F. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: structure and expression of the 110 kd catalytic subunit. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):419–429. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90166-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P., Margolis B., Skolnik E. Y., Lammers R., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Interaction of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-associated p85 with epidermal growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):981–990. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones O. T., Jones S. A., Hancock J. T., Topley N. Composition and organization of the NADPH oxidase of phagocytes and other cells. Biochem Soc Trans. 1993 May;21(2):343–346. doi: 10.1042/bst0210343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai F., Ito K., Todaka M., Hayashi H., Kamohara S., Ishii K., Okada T., Hazeki O., Ui M., Ebina Y. Insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation is relevant to the phosphorylation of IRS-1 and the activity of PI3-kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Sep 15;195(2):762–768. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A., Wu D., Simon M. I. Subunits beta gamma of heterotrimeric G protein activate beta 2 isoform of phospholipase C. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):686–689. doi: 10.1038/360686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudanna C., Rossi F., Berton G. Effect of inhibitors of distinct signalling pathways on neutrophil Q2- generation in response to tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and antibodies against CD18 and CD11a: evidence for a common and unique pattern of sensitivity to wortmannin and protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Feb 15;190(3):935–940. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Caon A. C., Gilbert C., Gaudry M., Roberge C. J., Poubelle P. E., Bourgoin S. Inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation by wortmannin in human neutrophils. Dissociation from its inhibitory effects on phospholipase D. Lab Invest. 1993 Jul;69(1):19–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Kakita S., Takahashi I., Kawahara K., Tsukuda E., Sano T., Yamada K., Yoshida M., Kase H., Matsuda Y. Wortmannin, a microbial product inhibitor of myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2157–2163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu M., Hiles I., Gout I., Fry M. J., Ruiz-Larrea F., Panayotou G., Thompson A., Dhand R., Hsuan J., Totty N. Characterization of two 85 kd proteins that associate with receptor tyrosine kinases, middle-T/pp60c-src complexes, and PI3-kinase. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90411-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold S. L., Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A., McIntyre T. M. Activation of human neutrophil phospholipase D by three separable mechanisms. FASEB J. 1990 Feb 1;4(2):208–214. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.2.2105252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Lowenstein E., Fischer R., Drepps A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Cloning of PI3 kinase-associated p85 utilizing a novel method for expression/cloning of target proteins for receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90410-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltoff S. P., Carpenter C. L., Auger K. R., Kapeller R., Schaffhausen B., Cantley L. C. Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase and growth regulation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1992;57:75–80. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1992.057.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Hughes K. T., Irvine R. F. Pathway of phosphatidylinositol(3,4,5)-trisphosphate synthesis in activated neutrophils. Nature. 1991 May 2;351(6321):33–39. doi: 10.1038/351033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Jackson T. R., Hawkins P. T. Agonist-stimulated synthesis of phosphatidylinositol(3,4,5)-trisphosphate: a new intracellular signalling system? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Oct 7;1179(1):27–75. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(93)90072-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L., Eguinoa A., Corey S., Jackson T., Hawkins P. T. Receptor stimulated accumulation of phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate by G-protein mediated pathways in human myeloid derived cells. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2265–2273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05880.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L., Jackson T., Hawkins P. T. Synthesis of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate in permeabilized neutrophils regulated by receptors and G-proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):17162–17172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelen M., Baggiolini M. Reconstitution of cell-free NADPH-oxidase from human monocytes and comparison with neutrophils. Blood. 1990 Jun 1;75(11):2223–2228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelen M., Dewald B., Baggiolini M. Neutrophil signal transduction and activation of the respiratory burst. Physiol Rev. 1993 Oct;73(4):797–821. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1993.73.4.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelen M., Peveri P., Kernen P., von Tscharner V., Walz A., Baggiolini M. Mechanism of neutrophil activation by NAF, a novel monocyte-derived peptide agonist. FASEB J. 1988 Aug;2(11):2702–2706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelen M., Rosen A., Nairn A. C., Aderem A. Regulation by phosphorylation of reversible association of a myristoylated protein kinase C substrate with the plasma membrane. Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):320–322. doi: 10.1038/351320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelen M., Wolf M., Baggiolini M. Activation of monocytes by interferon-gamma has no effect on the level or affinity of the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-phosphate oxidase and on agonist-dependent superoxide formation. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1889–1895. doi: 10.1172/JCI113535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traynor-Kaplan A. E., Harris A. L., Thompson B. L., Taylor P., Sklar L. A. An inositol tetrakisphosphate-containing phospholipid in activated neutrophils. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):353–356. doi: 10.1038/334353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traynor-Kaplan A. E., Thompson B. L., Harris A. L., Taylor P., Omann G. M., Sklar L. A. Transient increase in phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate and phosphatidylinositol trisphosphate during activation of human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15668–15673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlahos C. J., Matter W. F. Signal transduction in neutrophil activation. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is stimulated without tyrosine phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 1992 Sep 14;309(3):242–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80781-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Downes C. P., Keeler M., Keller T., Cantley L. Type I phosphatidylinositol kinase makes a novel inositol phospholipid, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):644–646. doi: 10.1038/332644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Kaplan D. R., Schaffhausen B., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Association of phosphatidylinositol kinase activity with polyoma middle-T competent for transformation. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):239–242. doi: 10.1038/315239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wymann M. P., von Tscharner V., Deranleau D. A., Baggiolini M. The onset of the respiratory burst in human neutrophils. Real-time studies of H2O2 formation reveal a rapid agonist-induced transduction process. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12048–12053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]