Abstract
Objectives
The interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R) blocker tocilizumab (TCZ) reduces inflammatory disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) but elevates lipid concentrations in some patients. We aimed to characterise the impact of IL-6R inhibition on established and novel risk factors in active RA.
Methods
Randomised, multicentre, two-part, phase III trial (24-week double-blind, 80-week open-label), MEASURE, evaluated lipid and lipoprotein levels, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particle composition, markers of coagulation, thrombosis and vascular function by pulse wave velocity (PWV) in 132 patients with RA who received TCZ or placebo.
Results
Median total-cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C) and triglyceride levels increased in TCZ versus placebo recipients by week 12 (12.6% vs 1.7%, 28.1% vs 2.2%, 10.6% vs −1.9%, respectively; all p<0.01). There were no significant differences in mean small LDL, mean oxidised LDL or total HDL-C concentrations. However, HDL-associated serum amyloid A content decreased in TCZ recipients. TCZ also induced reductions (>30%) in secretory phospholipase A2-IIA, lipoprotein(a), fibrinogen and D-dimers and elevation of paraoxonase (all p<0.0001 vs placebo). The ApoB/ApoA1 ratio remained stable over time in both groups. PWV decreases were greater with placebo than TCZ at 12 weeks (adjusted mean difference 0.79 m/s (95% CI 0.22 to 1.35; p=0.0067)).
Conclusions
These data provide the first detailed evidence for the modulation of lipoprotein particles and other surrogates of vascular risk with IL-6R inhibition. When compared with placebo, TCZ induced elevations in LDL-C but altered HDL particles towards an anti-inflammatory composition and favourably modified most, but not all, measured vascular risk surrogates. The net effect of such changes for cardiovascular risk requires determination.
Keywords: Cardiovascular Disease, Lipids, Inflammation, Rheumatoid Arthritis, DMARDs (biologic)
Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disease associated with clinically important comorbidities, including accelerated cardiovascular risk.1 The latter is not explained by conventional risk factors (eg, hypertension, obesity), suggesting that additional pathways contribute to adverse outcomes. These may reflect common genetic or environmental aetiological factors or the impact of chronic inflammation on underlying atherosclerotic disease burden, operating through circulating cytokines, immune complexes, complement factors and acute-phase reactants.2–4 Furthermore, it is recognised that absolute circulating lipid concentrations are modified in RA, likely reflecting regulatory integration of metabolic and inflammatory molecular networks.5 In general, high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) and low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C) levels are reduced in active disease6 and may increase on the initiation of effective therapeutics regardless of modality.7 Moreover, interpretation of lipid particle concentrations may be further complicated by changes in size and composition associated with inflammation. For example, small LDL-C particles may confer more atherogenic risk than larger LDL-C particles.8 In inflammatory conditions, HDL particles are associated with increased serum amyloid A (SAA) content, representing a potentially proatherogenic phenotype.9 The impact of therapy on subparticle components in RA has not been well characterised. Similarly, the effect of therapy on other lipid particles causally associated with vascular disease, such as lipoprotein(a) (Lp[a]),10 and on clotting factors, such as fibrinogen or markers of activated clotting such as D-dimer,11 is poorly understood.
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) plays an important role in various inflammatory effector pathways in RA through B-cell, fibroblast and osteoclast activation. Additionally, it mediates systemic manifestations of disease operating through hepatic and central neurological pathways.12 Intriguingly, elevated IL-6 levels are independently associated with increased cardiovascular risk, including fatal myocardial infarction and cerebrovascular accident, in the general population.13 14 The mechanisms mediating such epidemiological observations are poorly understood but are likely to be commensurate with the fundamental role played by inflammatory pathways in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis, the systemic functional activities of IL-6 conferred by widespread gp130 receptor membrane expression and the existence of soluble IL-6 receptor (IL-6R).15 Moreover, loss-of-function IL-6R polymorphisms are associated with reduced vascular risk.16 17
Tocilizumab (TCZ) is a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-6R (membrane-bound and soluble) that reduces inflammation and articular damage in patients with RA. In phase II and III trials, moderate elevations of LDL-C, HDL-C and triglycerides were apparent in RA patients treated with TCZ.7 The atherogenic implications of these changes are unknown. Similarly, the effect of IL-6R blockade on vascular physiology parameters (eg, as assessed by pulse wave velocity (PWV)) has been minimally explored. PWV is a measure of early structural vascular changes and has been shown to respond within 3 months to changes in vascular inflammation.18 Thus, given its mode of action, TCZ provides a highly specific molecular intervention with which to dissect the role of IL-6 in the modulation of lipid particles and the regulation of other vascular risk factors in patients with chronic inflammation. We report herein the results of a placebo-controlled trial that sought to define the effects of TCZ on a range of vascular risk surrogates in patients with RA. Our primary hypotheses were that PWV and small LDL particles would be significantly reduced by TCZ.
Methods
Patients
This trial, conducted independently of the pivotal RA trials, was approved by an independent ethics committee or institutional review board, and all patients gave written informed consent for participation in the trial. Adult patients with moderately to severely active RA (diagnosed per American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria) of more than 6 months’ duration were recruited. Enrolment criteria included inadequate response to stable methotrexate (MTX) therapy, exemplified by a swollen joint count (SJC) ≥6 and a tender joint count (TJC) ≥6, together with C-reactive protein (CRP) >10 mg/L or erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) >28 mm/h. Patients with inadequate response to an antitumour necrosis factor-α (aTNF) agent during the 6 months before baseline or to more than two previous aTNF agents were ineligible. MTX therapy was continued during the study. Initiation of lipid-lowering, oral antidiabetic or antihypertensive medications or change in dose within 12 weeks of baseline was prohibited, and glucocorticoid doses (≤10 mg) had to remain stable. Patients were stratified at randomisation by age (<52 vs ≥52 years), mean arterial blood pressure (<93.3 vs ≥93.3 mm Hg) and CRP (<1.66 vs ≥1.66 mg/dL).
Procedures
This two-arm, randomised, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, phase III study was conducted in the USA, Canada and the UK (figure 1) at 34 sites (the MEASURE study). Patients were randomly assigned using an interactive voice response system to blinded (patient and treating clinical team) intravenous treatment with TCZ 8 mg/kg or placebo in a 1:1 ratio, both in combination with oral MTX, every 4 weeks for 6 months between November 2007 and June 2008. Patients who, despite scheduled infusions of double-blind study medication at weeks 8 and 12, did not achieve ≥20% improvement from baseline in SJC and TJC at week 16 were offered escape therapy with open-label TCZ 8 mg/kg. At completion of the 24-week randomised treatment period, all patients were offered open-label treatment with TCZ 8 mg/kg plus MTX. Assessments during part 1 (randomised phase) of the study were performed at day 1 and at weeks 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 16, 20 and 24. Open-label assessments were performed every 12 weeks to week 104 (ClinicalTrials.gov number NCT00535782). The study protocol (version C, 22 June 2009 (original protocol published 10 May 2007)) is available as online supplementary material.
Figure 1.
Study design. MTX, methotrexate; TCZ, tocilizumab. (A) *Patients who did not achieve ≥20% improvement from baseline in swollen and tender joint counts at week 16 were offered escape therapy with open-label TCZ 8 mg/kg. †60 placebo+MTX and 65 TCZ+MTX patients completed 12 weeks. ‡59 placebo+MTX and 65 TCZ+MTX patients completed 24 weeks. (B) *TCZ 8 mg/kg every 4 weeks+background MTX (7.5–25 mg weekly). †Escape therapy, open-label TCZ (8 mg/kg every 4 weeks+background MTX). ‡Patients who received at least one dose of TCZ (double-blind or open-label).
Lipid and biomarker assays
Commercial assays were used to measure cholesterol, triglycerides, apolipoproteins A1 and B (ApoA1 and ApoB), CRP (by high-sensitivity assay) and ESR (all assays conducted or facilitated by Covance Laboratories, Greenfield, Indiana, USA). Serum lipid subclasses were characterised by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR; LipoScience, Raleigh, North Carolina, USA). Assays for HDL-associated SAA and serum paraoxonase, secretory phospholipase A2-IIA (sPLA2-IIA), oxidised LDL, d-dimer, fibrinogen, Lp(a) and haptoglobin were performed at Pacific Biomarkers, Inc. (Seattle, Washington, USA). Specific details are provided as online supplementary material.
Vascular physiology
Arterial stiffness was assessed by PWV according to the manufacturer's instructions using a pulse wave analysis apparatus (SphygmoCor; AtCor, San Jose, California, USA).19 Blinded assessors from all centres underwent training with an expert assessor, and certification was provided by AtCor. All PWV scans were reviewed by AtCor, and only those meeting predetermined quality control measures were accepted for analysis (details in online supplementary material).
Statistical analysis
The primary objective was to investigate the effect of 12 weeks of treatment with TCZ on PWV and on small LDL particle number assessed by NMR compared with placebo. The secondary objective was to investigate the effect of TCZ compared with placebo on these measurements at week 24. All other analyses, including lipid and lipoprotein parameters, were exploratory. A sample size of 120 patients (60 per arm), calculated based on previous results in patients with RA,5 18 was expected to provide sufficient power to detect a difference at week 12 in PWV (−1.14 m/s) and small LDL (−5.51 mg/dL (30% reduction)) in patients treated with TCZ compared with placebo.
The co-primary efficacy end points of change from baseline in PWV and small LDL particle number were analysed by parametric analysis of covariance. The 12-week and 24-week efficacy analyses of primary and secondary end points were performed on the intent-to-treat (ITT) population using last-observation-carried-forward to impute missing data at the analysis time point. Only measurements recorded before escape therapy were carried forward. All other exploratory end points were summarised for the ITT population observed cases, without imputation of missing data and excluding escape data. All laboratory parameter values were converted to SI units; for lipid parameters, only the latest fasted values within the time window were included. Assumptions of normality and homogeneity of the variance were assessed by inspecting normal probability plots, plots of standardised residual versus predicted values and plots of standardised residual versus continuous covariates. Primary end points in the study were analysed based on a normal distribution; however, because baseline values for several laboratory assessments in this study demonstrated non-normal distributions, values for exploratory serum analytes are presented as medians or median percentage changes from baseline. Exploratory analyses, based on observed cases, were performed using the non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis test. Hodges–Lehmann estimates of location shift and 95% CIs are presented. No adjustments for multiplicity were performed.
Results
Sixty-nine patients were randomly assigned to receive TCZ+MTX and sixty-three to receive placebo+MTX (figure 1). Sixty-five and sixty patients, respectively, completed 12 weeks of therapy. One patient in each arm withdrew because of an adverse event; one patient on placebo withdrew because of insufficient therapeutic response, three patients in the TCZ arm refused treatment and one patient in the TCZ arm was withdrawn because of a protocol violation. Two patients in the TCZ arm had their lipid-lowering medications changed; though included in the ITT analyses, they were excluded from the per-protocol analyses. Of 124 patients who completed blinded treatment, 117 elected to continue to the open-label phase; 92 completed treatment for 96 weeks. Demographic and baseline disease characteristics (table 1) were similar to those of the TCZ phase III cohort.20 Moreover, 30% and 39% of the patients in the placebo and TCZ arms, respectively, had previously received aTNFs. TCZ efficacy, assessed by change in disease activity score at 28 joints (DAS28) at weeks 12 and 24 or by ACR 20/50/70 proportional changes at week 24, was similar to that previously observed and differed significantly from that of placebo (see online supplementary figure S1). Adverse events and serious adverse events occurring during the trial were similar to those observed in previous TCZ studies (see online supplementary table S1).
Table 1.
Demographic and disease factors at baseline
| Placebo+MTX (n=63)* |
TCZ+MTX (n=69) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Female, n (%) | 47 (75) | 57 (83) |
| Age, years | 57.0 (50.0–64.0) | 57.0 (49.0–62.0) |
| Weight, kg | 82.0 (65.0–92.1) | 77.4 (67.0–86.5) |
| BMI, kg/m2, median (range) | 29.2 (18.5–49.6) | 29.2 (19.4–57.3) |
| Current smoker, n (%) | 14 (22) | 19 (28) |
| History of diabetes, n (%) | 4 (6) | 6 (9) |
| Duration of RA, years | 6.8 (2.4–9.9) | 7.0 (2.0–16.2) |
| DAS28 | 6.6 (5.8–7.3) | 6.8 (5.9–7.4) |
| CRP, mg/dL | 0.88 (0.39–1.86) | 0.94 (0.52–2.65) |
| Statin use, n (%) | 10 (16) | 10 (14) |
| Previous aTNF, n (%) | 19 (30) | 27 (39) |
| Oral steroid use, n (%) | 17 (27) | 20 (29) |
| Baseline MTX dose, mg/week | 15.0 (15.0–20.0) | 15.0 (15.0–20.0) |
Data are presented as median (IQR) unless otherwise indicated.
*One patient randomly assigned to placebo+MTX actually received one dose of TCZ and was therefore included in the TCZ group for the safety analyses.
aTNF, anti-tumour necrosis factor α; BMI, body mass index; CRP, C-reactive protein; DAS28, disease activity score at 28 joints; MTX, methotrexate; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; TCZ, tocilizumab.
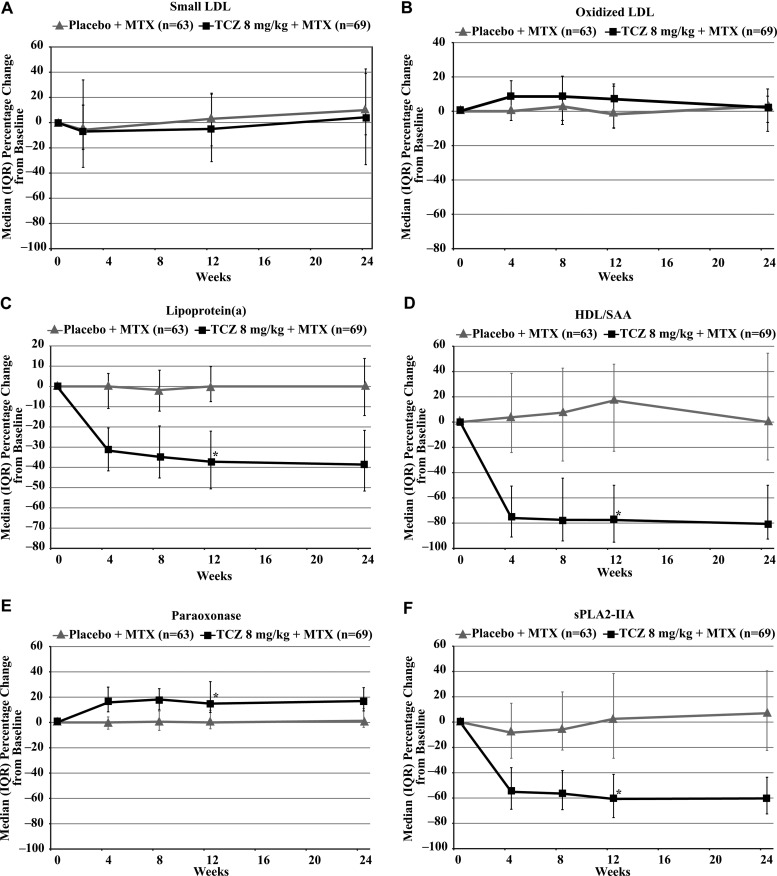
Consistent with results from TCZ phase III clinical trials, median total cholesterol and LDL-C levels increased in TCZ recipients but did not change in placebo patients (table 2). In contrast, no statistically significant difference in the co-primary outcome of concentration of small LDL particles was observed at either week 12 (adjusted mean difference −0.0 (95% CI −115.0 to 115.0) nmol/L) or week 24 (adjusted mean difference 11.2 (95% CI −106.7 to 129.1) nmol/L) after treatment with TCZ compared with placebo (figure 2A). Oxidised LDL exhibited a 7% increase on TCZ treatment that was not significantly different from the increase observed with placebo and did not persist at week 24 (figure 2B). By contrast, Lp(a) was reduced (by 37%) in TCZ recipients (figure 2C) compared with controls.
Table 2.
Percentage change from baseline to week 12 in lipid parameters and lipid particles* (observed cases), ITT population
| Placebo+MTX (n=63) |
TCZ 8 mg/kg+MTX (n=69) |
Estimate* (95% CI) p for difference at week 12 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual values | Change from baseline (%) | Actual values | Change from baseline (%) | ||||||||||
| n | Median | IQR | n† | Median | IQR | n | Median | IQR | n† | Median | IQR | ||
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | |||||||||||||
| Baseline | 58 | 4.8 | 4.3–5.5 | 55 | – | – | 64 | 4.7 | 4.2–5.3 | 56 | – | – | |
| Week 12 | 60 | 4.8 | 4.4–5.8 | 55 | 1.7 | –9.0–11.6 | 60 | 5.3 | 4.6–6.1 | 56 | 12.6 | –0.5–23.9 | 10.4 (4.8 to 16.9) p=0.0004 |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | |||||||||||||
| Baseline | 55 | 3.1 | 2.5–3.5 | 50 | – | – | 56 | 2.8 | 2.4–3.4 | 48 | – | – | |
| Week 12 | 56 | 3.1 | 2.5–3.8 | 50 | –1.9 | –8.7–12.7 | 57 | 3.1 | 2.5–3.8 | 48 | 10.6 | 1.0–28.9 | 11.0(3.8 to 18.6) p=0.0076 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | |||||||||||||
| Baseline | 58 | 1.3 | 1.1–1.6 | 54 | – | – | 62 | 1.3 | 1.1–1.6 | 53 | – | – | |
| Week 12 | 60 | 1.4 | 1.1–1.6 | 54 | 2.4 | –10.2–9.3 | 60 | 1.5 | 1.2–1.6 | 53 | 3.1 | –6.6–12.7 | 3.0 (–2.4 to 8.6) p=0.2753 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | |||||||||||||
| Baseline | 58 | 1.3 | 1.1–1.9 | 55 | – | – | 64 | 1.2 | 1.0–1.8 | 56 | – | – | |
| Week 12 | 60 | 1.2 | 1.1–1.7 | 55 | 2.2 | –18.7–18.7 | 60 | 1.5 | 1.1–2.3 | 56 | 28.1 | –1.7–63.5 | 25.4 (10.1 to 40.8) p=0.0011 |
| Total cholesterol/HDL (ratio) | |||||||||||||
| Baseline | 58 | 3.8 | 3.2–4.4 | 55 | – | – | 62 | 3.6 | 2.8–4.5 | 54 | – | – | |
| Week 12 | 60 | 3.9 | 3.2–4.8 | 55 | 0.9 | –7.5–7.9 | 60 | 3.9 | 3.1–4.4 | 54 | 11.3 | 2.0–19.4 | 9.7 (4.3 to 14.5) p=0.0008 |
| ApoB/ApoA1 (ratio) | |||||||||||||
| Baseline | 58 | 0.67 | 0.57–0.77 | 55 | – | – | 64 | 0.68 | 0.49–0.80 | 56 | – | – | |
| Week 12 | 60 | 0.70 | 0.56–0.79 | 55 | 2.5 | –7.8–11.0 | 60 | 0.67 | 0.52–0.75 | 56 | 4.7 | –4.2–15.8 | 2.1(–4.1 to 7.9) p=0.5108 |
| Large VLDL/chylomicrons (nmol/L) | |||||||||||||
| Baseline | 59 | 1.1 | 0.5–2.8 | 53 | – | – | 63 | 1.3 | 0.20–4.30 | 51 | – | – | |
| Week 12 | 60 | 1.2 | 0.3–4.1 | 53 | 0.0 | –50.0–67.5 | 59 | 3.7 | 1.30–7.40 | 51 | 205.6 | 0.0–700.0 | 167.5 (68.5 to 280.6) p<0.0001 |
| Medium VLDL/chylomicrons (nmol/L) | |||||||||||||
| Baseline | 59 | 22.1 | 12.0–38.3 | 56 | – | – | 63 | 22.0 | 11.0–32.7 | 55 | – | – | |
| Week 12 | 60 | 21.9 | 12.1–30.5 | 56 | –2.1 | –31.8–56.0 | 59 | 28.2 | 17.2–47.4 | 55 | 57.7 | –19.1–123.6 | 41.3(9.2 to 77.5) p=0.0088 |
| Small VLDL/chylomicrons (nmol/L) | |||||||||||||
| Baseline | 59 | 35.6 | 29.1–48.1 | 56 | – | – | 63 | 30.4 | 18.7–40.0 | 55 | – | – | |
| Week 12 | 60 | 36.2 | 26.2–46.2 | 56 | –6.1 | –25.1–17.9 | 59 | 40.1 | 26.5–57.2 | 55 | 31.4 | 10.2–91.5 | 42.3 (24.1 to 60.5) p<0.0001 |
| IDL particles (nmol/L) | |||||||||||||
| Baseline | 59 | 33.0 | 9.0–57.0 | 51 | – | – | 63 | 31.0 | 7.0–71.0 | 46 | – | – | |
| Week 12 | 60 | 36.0 | 9.0–59.5 | 51 | –9.4 | –49.6–133.3 | 59 | 39.0 | 11.0–92.0 | 46 | 33.5 | –60.9–222.6 | 14.3 (–37.3 to 70.0) p=0.5853 |
| Large LDL particles (nmol/L) | |||||||||||||
| Baseline | 59 | 396.0 | 261.0–508.0 | 56 | – | – | 63 | 405.0 | 253.0–535.0 | 55 | – | – | |
| Week 12 | 60 | 479.5 | 331.5–544.5 | 56 | 13.2 | –9.4–35.3 | 59 | 495.0 | 306.0–605.0 | 55 | 18.6 | –18.6–46.9 | –0.16 (–17.9 to 17.2) p=0.9718 |
| Large HDL particles (µmol/L) | |||||||||||||
| Baseline | 59 | 6.9 | 4.7–9.9 | 56 | – | – | 63 | 7.0 | 4.6–10.6 | 55 | – | – | |
| Week 12 | 60 | 7.8 | 5.5–11.0 | 56 | 1.8 | –15.5–13.4 | 59 | 8.4 | 5.3–11.6 | 55 | 5.6 | –8.6–23.7 | 4.8 (–5.9 to 15.1) p=0.4140 |
| Medium HDL particles (µmol/L) | |||||||||||||
| Baseline | 59 | 3.0 | 0.5–6.4 | 46 | – | – | 63 | 4.8 | 1.9–7.6 | 52 | – | – | |
| Week 12 | 60 | 3.2 | 1.5–7.4 | 46 | 2.0 | –30.4–56.5 | 59 | 4.2 | 1.2–7.5 | 52 | –25.0 | –71.5–25.8 | –30.7 (–61.3 to –0.23) p=0.0454 |
| Small HDL particles (µmol/L) | |||||||||||||
| Baseline | 59 | 19.9 | 14.9–24.0 | 56 | – | – | 63 | 17.4 | 13.0–21.1 | 55 | – | – | |
| Week 12 | 60 | 20.7 | 13.1–23.1 | 56 | 2.8 | –10.8–21.9 | 59 | 20.9 | 18.2–25.7 | 55 | 23.0 | 0.0–55.4 | 20.3 (7.9 to 34.0) p=0.0012 |
Data were missing at time points (including baseline) for some parameters. All values have been converted to SI units. No imputation was used for missing values. Only the latest fasted values within the time window are included.
*Hodges–Lehmann estimate of location shift (pseudo-median). p was calculated from Kruskal–Wallis test.
†Percentage change from baseline values includes only patients with both baseline and 12-week values.
Apo, apolipoprotein; C, cholesterol; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; IDL, intermediate-density lipoprotein; ITT, intent-to-treat; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; MTX, methotrexate; TCZ, tocilizumab; VLDL, very low-density lipoprotein.
Figure 2.
(A–F) Effects on lipoproteins (TCZ vs placebo). HDL, high-density lipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; MTX, methotrexate; SAA, serum amyloid A; sPLA2-IIA, secretory phospholipase A2-IIA; TCZ, tocilizumab. *p<0.0001 (TCZ vs placebo).
Measurement of change in PWV (second co-primary outcome) over 12 weeks revealed a significant difference between groups (adjusted mean difference 0.79 m/s (95% CI 0.22 to 1.35; p=0.0067)), constituting a greater relative reduction in PWV in placebo compared with TCZ-treated patients (−0.99 vs −0.21 m/s). The group difference was not sustained to week 24 (−0.47 vs −0.17 m/s; adjusted mean difference 0.30 m/s (95% CI −0.27 to 0.87; p=0.30)) (table 3). Technical challenges across sites were recorded in a substantial number of case report forms. There was no evidence of change in blood pressure by treatment arm before or after infusions (data available on request). Ten (17.5%) patients who received placebo and nine (15.5%) who received TCZ did not meet the quality control standards established for all measured PWV parameters.
Table 3.
Change from baseline in PWV (LOCF), ITT population
| Placebo+MTX (n=63) |
TCZ 8 mg/kg+MTX (n=69) |
95% CI (p) for difference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | |||
| n | 59 | 69 | |
| Mean (SD) PWV, m/s | 9.0 (2.5) | 9.0 (2.0) | |
| Week 12 | |||
| n | 62 | 69 | |
| Mean (SD) PWV, m/s | 8.4 (1.8) | 8.9 (2.5) | |
| Mean change from baseline in PWV, m/s | –0.99 | –0.21 | 0.22 to 1.35 (p=0.0067) |
| Week 24 | |||
| n | 62 | 69 | |
| Mean (SD) PWV, m/s | 8.9 (2.0) | 9.0 (2.3) | |
| Mean change from baseline in PWV, m/s | –0.47 | –0.17 | –0.27 to 0.87 (p=0.3042) |
LOCF was used for missing values. Only postbaseline and pre-escape therapy scores were carried forward. All assessments were set to missing from the time of escape therapy. Mean change from baseline was adjusted for baseline age, C-reactive protein level and mean arterial pressure.
ITT, intent-to-treat; LOCF, last-observation-carried-forward; MTX, methotrexate; PWV, pulse wave velocity; TCZ, tocilizumab.
No statistically significant changes occurred in total serum HDL-C levels in the study. NMR evaluation of HDL, however, revealed differential effects of TCZ versus placebo across particle sizes, with observed elevations in small HDL concentration and reductions in medium HDL (table 2). A significant reduction (by 78%) was observed in the TCZ arm for HDL-associated SAA. In contrast, a significant increase (by 16%) was noted in the antioxidative enzyme paraoxonase I, which is almost exclusively carried in serum HDL (figure 2D–F). sPLA2-IIA was reduced (by 61%) in TCZ recipients. No changes were observed in the control population in these biomarkers. Alterations occurred rapidly (by week 2) and were sustained throughout therapy.
Results of NMR subfractionation of other lipoprotein subclasses are shown in table 2. In patients treated with TCZ, changes in very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) subclasses were elevated compared with placebo, with changes in the largest components of the VLDL subclasses most notable, though they constituted a small proportion of the total VLDL particles. Similarly, no significant changes in the concentrations of intermediate, buoyant particles (large LDL and intermediate-density lipoprotein) occurred in TCZ-treated patients compared with placebo patients. Median triglyceride levels increased in TCZ-treated patients but did not change in placebo patients.
Markers of inflammation, including CRP and haptoglobin, were elevated at baseline and markedly reduced within the first week of TCZ treatment (figure 3). Similarly, rapid and sustained reductions in fibrinogen (by 47% from baseline) and d-dimer (by 62% from baseline) were observed in recipients of TCZ, whereas no changes were observed in the control arm (figure 3). All changes remained stable throughout TCZ treatment. Finally, the ApoB/ApoA1 ratio did not change throughout the study in either group (table 2).
Figure 3.
(A–D) Effects on inflammatory and thrombotic markers (TCZ vs placebo). hs-CRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; MTX, methotrexate; TCZ, tocilizumab. *p<0.0001 (TCZ vs placebo).
Discussion
We herein tested the primary hypotheses that TCZ in comparison to placebo would significantly lower PWV and the amount of small, dense LDL. However, neither hypothesis was supported. There was no change in the amount of small, dense LDL, and though PWV declined in both groups it did so more in placebo recipients. We also performed extensive additional analyses to investigate the wider impact of IL-6R inhibition on a range of vascular risk factors. Thus, we report that TCZ did modulate lipid particle levels (LDL, HDL, VLDL) and composition (HDL-associated SAA), together with a number of other inflammatory (CRP, paraoxonase) and vascular (Lp(a), D-dimer, fibrinogen) risk factors, suggesting potential modulation of the net atherogenic risk profile.
Consistent with results from other TCZ phase III clinical trials, total cholesterol, LDL-C and triglyceride levels increased in TCZ-treated patients but were minimally changed in placebo patients. In contrast, small LDL particle concentrations, considered proatherogenic, remained similar in TCZ-treated and placebo patients. Moreover, we observed a decrease (>30%) in Lp(a), a risk factor independently associated with vascular events.10 NMR assessment of lipoprotein subclasses revealed clear and sizeable changes in all classes of VLDL particles, the functional significance of which is yet unclear.
By contrast, we did not see a reduction in PWV with TCZ but rather a significant reduction in the placebo group at 12 weeks relative to TCZ recipients, though this pattern was not sustained to the 24-week measurement. This finding, therefore, contradicts our original hypothesis. It should be noted, however, that technical challenges during the conduct of this multicentre trial led to approximately 15% of the measurements being substandard. Because of the severity of disease in study participants who had reduced mobility, contractures and joint pain, the procedure proved more difficult than anticipated. Nevertheless, it appears that PWV is not necessarily reduced with TCZ, though further studies with other vascular function measures not influenced by limited mobility (eg, peripheral arterial tonometry as a measure of endothelial function) would be useful. Our findings contrast with those of Kume et al,21 who observed similar reductions in cardio-ankle vascular index and aortic augmentation index for patients treated with TCZ, adalimumab or etanercept. Speculatively, it remains possible that disease-related vascular changes in patients in the present study (in which mean DAS28 was high) were much more progressed (and, thus, less reversible) than in patients studied in other trials.18 21
Increases in HDL particle number, measured by NMR, occurred primarily in small particles. Our demonstration of a significant increase in the concentration of small HDL particles with TCZ treatment is consistent with a potential ‘normalisation’ of small HDL particle levels. Small HDL particle numbers, measured by NMR, in two independent studies were lower in RA patients than in controls despite similar HDL-C concentrations.5 6 Furthermore, the observed significant reduction in medium HDL and HDL-SAA concentrations, along with the increase in paraoxonase, an antioxidant enzyme associated with HDL, suggests remodelling of HDL particles from a pro-inflammatory to an anti-inflammatory phenotype in response to TCZ treatment. Overall, such changes in HDL particle composition with TCZ are consistent with the results of a recent study of aTNFs in patients with ankylosing spondylitis.22 Although it is unclear to what extent small HDL particles measured by NMR corroborate with those measured by other methods, small HDL particles may be more active in cholesterol efflux and anti-inflammatory functions,23 though this observation remains debated.
Previous studies have demonstrated lower levels of LDL-C in patients with active RA than in controls.6 Such decreases may result from increased catabolism (including by scavenger receptors), increased particle retention in tissue, or both, rather than from decreased lipid production. Increased cholesterol retention under conditions of elevated IL-6/IL-6R levels have been hypothesised to result from increased surface density on multiple tissues of LDL receptor, VLDL receptor and scavenger receptors, leading to excess internalisation of VLDL and LDL.24–26 Furthermore, sPLA2-IIA expression, augmented by IL-6, leads to phospholipid hydrolysis of LDL and increases LDL uptake in tissues.27 Consistent with our results and the TCZ phase III programme,7 the TCZ-based IL-6 signal inhibition may reduce various receptor surface levels and sPLA2-IIA levels, leading to both decreased LDL and VLDL tissue retention and elevated circulating levels.
Decreased thrombotic potential in TCZ-treated RA patients is indicated by declines in circulating fibrinogen and D-dimer levels. Although the reduction in fibrinogen, an acute-phase protein, with TCZ is predictable, the reduction of D-dimer is of particular interest because it represents the most widely used clinical marker of activated blood coagulation. Moreover, several prospective studies28 29 have linked elevated D-dimer levels to heightened risk for vascular events independently of established risk factors. Similarly, the sizeable reduction in Lp(a) observed with TCZ is of considerable interest because recent genetic and epidemiological evidence suggests Lp(a) is causally linked to cardiovascular events in the general population.10 30 Our Lp(a) observations also extend findings from an earlier randomised, placebo-controlled study linking aTNF blockade to dose-dependent reductions in Lp(a) in patients with psoriatic arthritis.31 Collectively, these changes suggest a reduction in thrombotic potential with TCZ in patients with active RA. Of course, the net effect of TCZ-induced changes to vascular outcomes can be robustly tested only in the context of vascular outcomes in prospective studies.
In summary, the results of this randomised, placebo-controlled study suggest that IL-6R blockade with TCZ in patients with active RA not only reduces markers of inflammation but also affects quantitative and qualitative changes in lipids and lipoproteins. Such changes include a global increase in LDL-C concentration, in line with findings from other biological studies,7 and apparently favourable changes to HDL particle composition, rendering them less pro-inflammatory. In addition, marked reductions in haemostatic and Lp(a) markers were observed, though PWV did not change favourably. Future determination of the net vascular effect of such changes in RA patients—and potentially other groups of patients— is of major interest, particularly given the recent data from large-scale (>130 000 subjects, >25 000 coronary heart disease cases) genome-wide association studies16 17 that suggest a potentially detrimental effect of IL-6R signalling on the risk for coronary heart disease.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Writing assistance was provided by Santo D'Angelo, PhD, MS.
Footnotes
Contributors: IBM was involved in the design of the study, conducting the research, analysis and interpretation of the data, drafting of the manuscript, and approval of the final draft to be published. LT was involved in the design of the study, data collection, analysis and interpretation of the data, drafting of the manuscript and approval of the final draft to be published. JTG was involved in conducting the research, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript and approval of the final draft to be published. JMB and JSL were involved in the design of the study, analysis and interpretation of the data, drafting of the manuscript and approval of the final draft to be published. JES and NS were involved in the design of the study, drafting of the manuscript, and approval of the final draft to be published. ADB was involved in conducting the research, drafting of the manuscript and approval of the final draft to be published. CEC was involved in conducting the research, review and revision of the manuscript, and approval of the final draft to be published. THC was involved in the design of the study, conducting the research, drafting of the manuscript and approval of the final draft to be published. CD was involved in the design of the study, conducting the research, analysis and interpretation of the data, review and revision of the manuscript, and approval of the final draft to be published. NS was also involved in analysis and interpretation of the data.
Funding: This study was funded by Roche. F. Hoffmann-La Roche was responsible for the study design together with several authors, principally IBM, JSL and NS. The other authors contributed to data interpretation and were responsible for the writing and review of the manuscript. The lead author had the final responsibility for the decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Competing interests: IBM: research grants and honoraria from Roche, Pfizer, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Abbott. LT: employee of Roche Products Ltd. JTG: consultant to Roche. JES: consultant to Quidel and Alexion Pharmaceuticals, served on advisory board for Bristol-Myers Squibb, research grants to Hospital for Special Surgery from F. Hoffmann-La Roche and the National Institutes of Health. ADB: research grant from Roche. CEC: research grant to institution for study participation. JSL: employee of Roche. NS: consultant to and on speaker's bureau for Roche.
Patient consent: Obtained.
Ethics approval: The trial was approved by an independent Ethics Committee or Institutional Review Board, and all patients gave written informed consent for participation in the trial. This two-arm, randomised, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, phase III study was conducted in the USA, Canada and the UK (figure 1) at 34 sites (the MEASURE study).
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Open Access: This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 3.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/
References
- 1.Peters MJ, Symmons DP, McCarey D, et al. EULAR evidence-based recommendations for cardiovascular risk management in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other forms of inflammatory arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:325–31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gonzalez-Gay MA, Gonzalez-Juanatey C, Lopez-Diaz MJ, et al. HLA-DRB1 and persistent chronic inflammation contribute to cardiovascular events and cardiovascular mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2007;57:125–32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.McKellar GE, McCarey DW, Sattar N, et al. Role for TNF in atherosclerosis? Lessons from autoimmune disease. Nat Rev Cardiol 2009;6:410–17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sattar N, McCarey DW, Capell H, et al. Explaining how ‘high-grade’ systemic inflammation accelerates vascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis. Circulation 2003;108:2957–63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hurt-Camejo E, Paredes S, Masana L, et al. Elevated levels of small, low-density lipoprotein with high affinity for arterial matrix components in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: possible contribution of phospholipase A2 to this atherogenic profile. Arthritis Rheum 2001;44:2761–67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chung CP, Oeser A, Raggi P, et al. Lipoprotein subclasses determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and coronary atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 2010;37:1633–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Choy E, Sattar N. Interpreting lipid levels in the context of high-grade inflammatory states with a focus on rheumatoid arthritis: a challenge to conventional cardiovascular risk actions. Ann Rheum Dis 2009;68:460–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Packard CJ. Small dense low-density lipoprotein and its role as an independent predictor of cardiovascular disease. Curr Opin Lipidol 2006;17:412–17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Khovidhunkit W, Kim MS, Memon RA, et al. Effects of infection and inflammation on lipid and lipoprotein metabolism: mechanisms and consequences to the host. J Lipid Res 2004;45:1169–96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Clarke R, Peden JF, Hopewell JC, et al. Genetic variants associated with Lp(a) lipoprotein level and coronary disease. N Engl J Med 2009;361:2518–28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wannamethee SG, Whincup PH, Shaper AG, et al. Circulating inflammatory and hemostatic biomarkers are associated with risk of myocardial infarction and coronary death, but not angina pectoris, in older men. J Thromb Haemost 2009;7:1605–11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kishimoto T. IL-6: from its discovery to clinical applications. Int Immunol 2010;22:347–52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sattar N, Murray HM, Welsh P, et al. Are markers of inflammation more strongly associated with risk for fatal than for nonfatal vascular events?. PLoS Med 2009;6:e1000099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Danesh J, Kaptoge S, Mann AG, et al. Long-term interleukin-6 levels and subsequent risk of coronary heart disease: two new prospective studies and a systematic review. PLoS Med 2008;5:e78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Libby P, Ridker PM, Hansson GK. Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature 2011;473:317–25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Interleukin 6 Receptor Mendelian Randomisation Analysis (IL6R MR) Consortium Hingorani AD, Casas JP. The interleukin-6 receptor as a target for prevention of coronary heart disease: a Mendelian randomisation analysis. Lancet 2012;379:1214–24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.IL6R Genetics Consortium Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration Sarwar N, Butterworth AS, et al. Interleukin-6 receptor pathways in coronary heart disease: a collaborative meta-analysis of 82 studies. Lancet 2012;379:1205–13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mäki-Petäjä KM, Hall FC, Booth AD, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis is associated with increased aortic pulse-wave velocity, which is reduced by anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy. Circulation 2006;114:1185–92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Laurent S, Cockcroft J, Van Bortel L, et al. Expert consensus document on arterial stiffness: methodological issues and clinical applications. Eur Heart J 2006;27:2588–605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Patel AM, Moreland LW. Interleukin-6 inhibition for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a review of tocilizumab therapy. Drug Design Dev Ther 2010;4:263–78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kume K, Amano K, Yamada S, et al. Tocilizumab monotherapy reduces arterial stiffness as effectively as etanercept or adalimumab monotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis: an open-label randomized controlled trial. J Rheumatol 2011;38:2169–71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.van Eijk IC, de Vries MK, Levels JH, et al. Improvement of lipid profile is accompanied by atheroprotective alterations in high-density lipoprotein composition upon tumor necrosis factor blockade: a prospective cohort study in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 2009;60:1324–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kontush A, Chantepie S, Chapman MJ. Small, dense HDL particles exert potent protection of atherogenic LDL against oxidative stress. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2003;23:1881–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hashizume M, Yoshida H, Koike N, et al. Overproduced interleukin 6 decreases blood lipid levels via upregulation of very-low-density lipoprotein receptor. Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:741–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gierens H, Nauck M, Roth M, et al. Interleukin-6 stimulates LDL receptor gene expression via activation of sterol-responsive and Sp1 binding elements. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2000;20:1777–83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hashizume M, Mihara M. Atherogenic effects of TNF-α and IL-6 via up-regulation of scavenger receptors. Cytokine 2012;58:424–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Carpentier YA, Scruel O. Changes in the concentration and composition of plasma lipoproteins during the acute phase response. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2002;5:153–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cushman M, Lemaitre RN, Kuller LH, et al. Fibrinolytic activation markers predict myocardial infarction in the elderly: the Cardiovascular Health Study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1999;19:493–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Danesh J, Whincup P, Walker M, et al. Fibrin D-dimer and coronary heart disease: prospective study and meta-analysis. Circulation 2001;103:2323–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration Erqou S, Kaptoge S, et al. Lipoprotein(a) concentration and the risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and nonvascular mortality. JAMA 2009;302:412–23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sattar N, Crompton P, Cherry L, et al. Effects of tumor necrosis factor blockade on cardiovascular risk factors in psoriatic arthritis: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arthritis Rheum 2007;56:831–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.