Abstract
Background
Preventable mortality is a good indicator of possible problems to be investigated in the primary prevention chain, making it also a useful tool with which to evaluate health policies particularly public health policies. This study describes inequalities in preventable avoidable mortality in relation to socioeconomic status in small urban areas of thirty three Spanish cities, and analyses their evolution over the course of the periods 1996–2001 and 2002–2007.
Methods
We analysed census tracts and all deaths occurring in the population residing in these cities from 1996 to 2007 were taken into account. The causes included in the study were lung cancer, cirrhosis, AIDS/HIV, motor vehicle traffic accidents injuries, suicide and homicide. The census tracts were classified into three groups, according their socioeconomic level. To analyse inequalities in mortality risks between the highest and lowest socioeconomic levels and over different periods, for each city and separating by sex, Poisson regression were used.
Results
Preventable avoidable mortality made a significant contribution to general mortality (around 7.5%, higher among men), having decreased over time in men (12.7 in 1996–2001 and 10.9 in 2002–2007), though not so clearly among women (3.3% in 1996–2001 and 2.9% in 2002–2007). It has been observed in men that the risks of death are higher in areas of greater deprivation, and that these excesses have not modified over time. The result in women is different and differences in mortality risks by socioeconomic level could not be established in many cities.
Conclusions
Preventable mortality decreased between the 1996–2001 and 2002–2007 periods, more markedly in men than in women. There were socioeconomic inequalities in mortality in most cities analysed, associating a higher risk of death with higher levels of deprivation. Inequalities have remained over the two periods analysed. This study makes it possible to identify those areas where excess preventable mortality was associated with more deprived zones. It is in these deprived zones where actions to reduce and monitor health inequalities should be put into place. Primary healthcare may play an important role in this process.
Keywords: Preventable avoidable mortality, Causes of death, Inequalities in health, Small area analysis
Background
The use of avoidable mortality as a measure of the performance of healthcare services was first introduced by Rutstein [1], who presented the first theoretical study on this issue, where he proposed a list of unnecessary diseases and disabilities or unnecessary untimely deaths, based on the assertion that if health services had acted correctly, they would have been prevented or delayed. The definition and concept of avoidable mortality, as well the list of conditions considered sentinel health events, have changed over time [2-9] in line with developments in medicine and technology.
Avoidable mortality can be disaggregated into two groups [10], according to the type of healthcare intervention: 1) Preventable mortality – having to do with primary prevention, lifestyle, intervention programmes, etc. and 2) Amenable mortality – having to do with secondary prevention and directly with healthcare interventions, in the form of counselling, diagnosis or treatment.
The WHO World Health Report 2000 [11] defines health systems inclusively, as systems whose primary aim is to promote, restore and maintain health. From this point of view, preventable mortality must be considered a good indicator of possible problems to be investigated in the primary prevention chain, both in health promotion and protection and in health education [5], making it also a useful tool with which to evaluate health policies, particularly public health policies [12].
Studies conducted in several European countries have linked population socioeconomic indicators with avoidable mortality [13-17] and, in particular with preventable mortality, as a whole or in relation to specific conditions included under the definition showing higher mortality rates in the least favoured groups [18-27]. These inequalities are themselves a risk factor for population health and need to be studied in order to identify the most vulnerable groups and regions, to put in place specific interventions [28].
In recent decades, improvements in living conditions and the increasing inclusiveness of healthcare systems have reduced premature and, accordingly, avoidable mortality, both amenable and preventable. Several studies have analysed trends in mortality from avoidable causes over time in specific regions or groups [5,7,29-32] and found a decrease, although other studies described increases in avoidable mortality [33].
Some studies have associated this trend with socioeconomic inequalities, pointing to maintained and even increased socioeconomic inequalities in avoidable mortality in recent years [13,19,34-38]. Some have analysed avoidable mortality in small areas [39-41] or combined their analysis with a study of the relationship to inequality [13,15,22,27], associating the most deprived areas with higher mortality rates.
While improvements in indicators such as preventable and amenable mortality continue to be analysed to evaluate the quality, access and equity of healthcare systems [9,42-44], it is also necessary to continue to identify the zones associated with a higher risk of these causes of mortality in the urban areas of large cities, where so much of the population is concentrated, in order to take specific public health actions aimed at decreasing mortality and reducing inequalities. Studies in small areas of cities are important as neighbourhood is recognised as a health determinant independently of individual determinants [45]. In Spain no study has been conducted to date on overall preventable mortality in small areas of large cities, so the aim of this study was to describe trends in preventable mortality and analyse its relationship to socioeconomic inequalities in small areas of 33 large cities between 1996–2001 and 2002–2007.
Methods
This study was performed within the framework of the MEDEA project (Socioeconomic and environmental inequalities in mortality in small areas of Spanish cities: http://www.proyectomedea.org) as an ecological study on preventable mortality trends in small areas of 33 Spanish cities (Figure 1) in the 1996–2001 and 2002–2007 periods. The population of these cities accounted for 30.1% of the Spanish population in 2001, according to figures from the Spanish National Statistics Institute (NSI). The units analysed were Census Tract (CT) and all deaths occurring in the population residing in these cities from 1996 to 2007 were taken into account.
Figure 1.
Location of the cities analyzed.
The mortality figures for each CT were obtained from the death records of the corresponding autonomous community. Deaths were assigned to census sector according to their postal address. The percentage of deaths which could not be assigned to a CT due to problems in locating the residence varied from 0.02% in Pamplona to 5.0% in Cartagena-La Unión. Population figures for each CT, sex and age group (five year intervals) were obtained from the NSI. For each CT the indicators necessary for socioeconomic classification were obtained from the 2001 Population and Housing Census.
The causes of avoidable mortality included in the study were considered preventable in the MEDEA project (Table 1) and are lung cancer, cirrhosis, Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome and Human Immunodeficiency Virus infection (AIDS and HIV), considered together, motor vehicle traffic accidents injuries, suicide and homicide. These causes are based on those proposed by Nolte and McKee [5], adding AIDS and HIV, suicide and homicide, because of their particular importance as preventable causes, as held by many recent articles [6,22,26,27,29,36,46,47]. Deaths occurring between 1996 and 1998 were coded using the International Classification of Diseases, 9th edition (ICD-9); ICD-10 was used for deaths occurring between 1999 and 2007. For the first two causes, only deaths occurring before the age of 75 years were taken into account, following Nolte and McKee [5]. For the rest of causes, all deaths occurring were taken into account.
Table 1.
Frequencies and percentages with regard to the overall mortality by sex, age, period and cause of death(*) in all the 33 cities studied
| Period | Sex | Age | Lung cancer | Cirrhosis | AIDS, HIV | Motor vehicle injuries | Suicide | Homicide | All preventable | All causes | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |||
| 1996-2001 | Men | 0-44 | 744 | 2.9 | 866 | 3.4 | 4370 | 17.1 | 3209 | 12.5 | 1524 | 6.0 | 308 | 1.2 | 11021 | 43.1 | 25595 | 100 |
| 45-64 | 8690 | 15.0 | 3232 | 5.6 | 798 | 1.4 | 1138 | 2.0 | 817 | 1.4 | 107 | 0.2 | 14782 | 25.5 | 58052 | 100 | ||
| >64 | 10427 | 4.4 | 2497 | 1.1 | 144 | 0.1 | 979 | 0.4 | 955 | 0.4 | 41 | 0.0 | 15043 | 6.3 | 237720 | 100 | ||
| Total | 19861 | 6.2 | 6595 | 2.1 | 5312 | 1.7 | 5326 | 1.7 | 3296 | 1.0 | 456 | 0.1 | 40846 | 12.7 | 321367 | 100 | ||
| Women | 0-44 | 274 | 2.5 | 209 | 1.9 | 1140 | 10.2 | 908 | 8.1 | 479 | 4.3 | 98 | 0.9 | 3108 | 27.9 | 11157 | 100 | |
| 45-64 | 1095 | 4.3 | 949 | 3.7 | 127 | 0.5 | 436 | 1.7 | 387 | 1.5 | 42 | 0.2 | 3036 | 11.9 | 25524 | 100 | ||
| >64 | 997 | 0.4 | 1458 | 0.6 | 30 | 0.0 | 693 | 0.3 | 493 | 0.2 | 44 | 0.0 | 3715 | 1.4 | 263798 | 100 | ||
| Total | 2366 | 0.8 | 2616 | 0.9 | 1297 | 0.4 | 2037 | 0.7 | 1359 | 0.5 | 184 | 0.1 | 9859 | 3.3 | 300479 | 100 | ||
| 2002-2007 | Men | 0-44 | 656 | 3.1 | 702 | 3.3 | 1908 | 9.0 | 2486 | 11.7 | 1563 | 7.4 | 393 | 1.9 | 7708 | 36.4 | 21172 | 100 |
| 45-64 | 9323 | 16.2 | 2988 | 5.2 | 876 | 1.5 | 900 | 1.6 | 984 | 1.7 | 148 | 0.3 | 15219 | 26.4 | 57622 | 100 | ||
| >64 | 9739 | 3.8 | 1962 | 0.8 | 136 | 0.1 | 810 | 0.3 | 1046 | 0.4 | 50 | 0.0 | 13743 | 5.4 | 256376 | 100 | ||
| Total | 19718 | 5.9 | 5652 | 1.7 | 2920 | 0.9 | 4196 | 1.3 | 3593 | 1.1 | 591 | 0.2 | 36670 | 10.9 | 335170 | 100 | ||
| Women | 0-44 | 316 | 3.2 | 195 | 2.0 | 561 | 5.7 | 582 | 5.9 | 535 | 5.4 | 133 | 1.3 | 2322 | 23.5 | 9896 | 100 | |
| 45-64 | 1958 | 7.5 | 803 | 3.1 | 122 | 0.5 | 276 | 1.1 | 525 | 2.0 | 62 | 0.2 | 3746 | 14.4 | 26095 | 100 | ||
| ≥64 | 1230 | 0.4 | 966 | 0.3 | 24 | 0.0 | 547 | 0.2 | 492 | 0.2 | 55 | 0.0 | 3314 | 1.1 | 291098 | 100 | ||
| Total | 3504 | 1.1 | 1964 | 0.6 | 707 | 0.2 | 1405 | 0.4 | 1552 | 0.5 | 250 | 0.1 | 9382 | 2.9 | 327089 | 100 | ||
| 1996-2007 | Men | 0-44 | 1400 | 3.0 | 1568 | 3.4 | 6278 | 13.4 | 5695 | 12.2 | 3087 | 6.6 | 701 | 1.5 | 18729 | 40.0 | 46767 | 100 |
| 45-64 | 18013 | 15.6 | 6220 | 5.4 | 1674 | 1.4 | 2038 | 1.8 | 1801 | 1.6 | 255 | 0.2 | 30001 | 25.9 | 115674 | 100 | ||
| >64 | 20166 | 4.1 | 4459 | 0.9 | 280 | 0.1 | 1789 | 0.4 | 2001 | 0.4 | 91 | 0.0 | 28786 | 5.8 | 494096 | 100 | ||
| Total | 39579 | 6.0 | 12247 | 1.9 | 8232 | 1.3 | 9522 | 1.5 | 6889 | 1.0 | 1047 | 0.2 | 77516 | 11.8 | 656537 | 100 | ||
| Women | 0-44 | 590 | 2.8 | 404 | 1.9 | 1701 | 8.1 | 1490 | 7.1 | 1014 | 4.8 | 231 | 1.1 | 5430 | 25.8 | 21053 | 100 | |
| 45-64 | 3053 | 5.9 | 1752 | 3.4 | 249 | 0.5 | 712 | 1.4 | 912 | 1.8 | 104 | 0.2 | 6782 | 13.1 | 51619 | 100 | ||
| >64 | 2227 | 0.4 | 2424 | 0.4 | 54 | 0.0 | 1240 | 0.2 | 985 | 0.2 | 99 | 0.0 | 7029 | 1.3 | 554896 | 100 | ||
| Total | 5870 | 0.9 | 4580 | 0.7 | 2004 | 0.3 | 3442 | 0.5 | 2911 | 0.5 | 434 | 0.1 | 19241 | 3.1 | 627568 | 100 | ||
Spain, 1996-2007.
(*)ICD codes and age: Lung cancer (ICD-9: 162; ICD-10: C33,C34; Age: 0–74), Cirrhosis (ICD-9: 571, 573.0; ICD-10: K70, K72.1, K73, K74, K76.1.9, Age: 0–74), AIDS and HIV (ICD-9: 279.1.5.6.8, 042, 795.8; ICD-10: B20-B24, R75; Age: all), Motor vehicle injuries (ICD-9: E810-E825; ICD-10: V02-V04, V09.0.2, V12-V14, V19.0.1.2.4.5.6, V20-V79, V80.3.4.5, V81.0.1, V82.0.1, V83-V86, V87-V88.0.1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8, V89.0.2; Age: all), Suicide (ICD-9: E950-E959; ICD-10: X60-X84; Age: all), Homicide (ICD-9: E960-E969; ICD-10: X85-Y09; Age: all).
To establish the socioeconomic status of each CT in each city the following indicators were used: Unemployment: percentage of people aged over 16 years out of work (unemployed people and first time job seekers), out of the total active population.
Education: percentage of people aged over 16 years who, according to the Spanish National Statistics Register figures, cannot read or write, can read and write but went to school for less than five years or for more than five years but without terminating primary studies, out of the total population aged 16 years and over.
Education in young people: percentage of persons aged between 16 and 29 years with low educational levels, out of the total population aged between 16 and 29 years.
Manual workers: percentage of persons aged 16 years employed in manual labour (services, agriculture, farming, fishing, crafts, specialised manufacture industry workers, construction, mining, installers and non-specialised workers) out of the total number of persons in employment aged 16 years or over.
Temporary workers: percentage of people aged 16 years or over employed in temporary jobs (part-time self-employed workers, temporary workers) out of the total of persons in employment aged 16 years or over.
These indicators had previously been used on the MEDEA project [48] and were used to build socioeconomic status (SES) variables in each city. Three levels were established: SES1 (the most privileged socioeconomic group), which includes all CTs in the city with values below the 25th percentile for all five indicators; SES3 (the least privileged socioeconomic group), which represents all CTs with values above the 75th percentile for all indicators; all other CTs were included in SES2 (intermediate socioeconomic level). This variable had previously been used to classify CTs by socioeconomic level and proved to be a good tool [22].
Frequencies and percentages (of total preventable deaths and death from all causes) were calculated for all causes studied and all preventable causes in each city. To study the trend in risk of death over time, the dates were classified into two time periods: 1996–2001 (P1) and 2002–2007 (P2) (In the cases of La Coruña, Ferrol, Lugo, Ourense, Pontevedra, Santiago and Vigo mortality figures were available from 1998 onwards, so for these cities the first period goes from 1998 to 2001). The age standardised mortality rates (ASR) and their 95% confidence intervals were calculated for all preventable cases, adjusted using the direct method and taking as standard the Spanish population in 2001 (centre of the period) by sex and age group, obtained from the NSI, for each city, in each period and by sex.
To analyse inequalities in mortality risks between the highest and lowest socioeconomic levels and over different periods, for each city and separating by sex, Poisson regression models with variable responses to the rate of death logarithm were adapted, using variables explaining SES (reference level:SES1), period (reference level: P1) and age, into three groups: younger than 45 years (reference level), 45 to 64 and older than 64 years. The age limit of 65 years was chosen as it is the cut-off age normally used in studies to define ‘old age’ [49]. Subjects aged under 65 were classified into two groups, depending on the lesser or greater prematurity of death. This model made it possible to estimate the Relative Risk (RR) of death and the corresponding 95% confidence intervals for each level of explicative SES variables, period and age group compared to the chosen reference level. We analysed possible interactions between SES and period, SES and age group and between age group and period. The existence of significant interaction between SES and period demonstrates the change between RR periods across socioeconomic levels. In order to control for overdispersion, which takes place when a certain distribution for the data is assumed and the variability of these data is higher than the one expected from the model assumed, quasi-likelihood models have been used. This kind of models enable a lack of precise likelihood for the answers and enable modelling on the basis of the linear predictor and the form assumed to represent the variance based on the average [50]. In the case of Poisson models, the variance function is supposed to differ only by a scale factor ϕ from the variance function in the corresponding likelihood model, i.e. Variance = ϕ Mean. In this way, the estimations of the parameters are equal. Nevertheless, the standard errors obtained by quasi-likelihood are the maximum likelihood estimators multiplied by ϕ ½. In order to control overdispersion in Poisson models, the parameter ϕ has been estimated. It has been tested whether it is statistically different from the unit. The estimator of ϕ takes the form D/df, where D is the deviance of the Poisson model adjusted, and df the degrees of freedom. If it is different from the unit, a quasi-Poisson model is adjusted, which is the appropriate model when there is overdispersion. This comparison and the estimation of all the models have been conducted by means of the R statistics package 2.12.2.
Results
The populations and number of census tracts (CTs) in the cities analysed (Table 2) varied, according to 2001 figures, from a minimum of 75864 inhabitants and 57 sectors in Pontevedra to a maximum of 2874732 inhabitants and 2358 sectors in Madrid, with an mean population of 373283 inhabitants per city, with a mean of 297 sectors per city and a mean sector size of 1257 inhabitants.
Table 2.
Characteristics of the studied cities: population, number of census tracts (CTs) and percentage of sections in worse socioeconomic status (SES3)
| City (Population 2001) | CTs | % CTs. in SES3 | Sex(*) | Lung cancer | Cirrhosis | AIDS-VIH | Motor vehicle accidents | Suicide | Homicide | TOTAL preventable | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | ||||
| ALICANTE | 215 | 9.3 | M | 921 | 48.4 | 301 | 15.8 | 199 | 10.5 | 259 | 13.6 | 191 | 10.0 | 32 | 1.7 | 1903 | 100 |
| (283243) | W | 144 | 28.9 | 131 | 26.3 | 53 | 10.6 | 81 | 16.3 | 77 | 15.5 | 12 | 2.4 | 498 | 100 | ||
| ALMERIA | 118 | 10.2 | M | 443 | 42.2 | 152 | 14.5 | 107 | 10.2 | 209 | 19.9 | 103 | 9.8 | 36 | 3.4 | 1050 | 100 |
| (176709) | W | 38 | 18.4 | 51 | 24.8 | 19 | 9.2 | 54 | 26.2 | 36 | 17.5 | 8 | 3.9 | 206 | 100 | ||
| AVILES | 72 | 8.3 | M | 352 | 54.0 | 109 | 16.7 | 40 | 6.1 | 77 | 11.8 | 66 | 10.1 | 8 | 1.2 | 652 | 100 |
| (83553) | W | 42 | 30.9 | 27 | 19.9 | 8 | 5.9 | 33 | 24.3 | 23 | 16.9 | 3 | 2.2 | 136 | 100 | ||
| BARCELONA | 1491 | 8.7 | M | 5761 | 56.5 | 1563 | 15.3 | 985 | 9.7 | 869 | 8.5 | 920 | 9.0 | 90 | 0.9 | 10188 | 100 |
| (1505336) | W | 900 | 31.4 | 813 | 28.3 | 262 | 9.1 | 383 | 13.3 | 450 | 15.7 | 62 | 2.2 | 2870 | 100 | ||
| BILBAO | 288 | 8.0 | M | 1356 | 50.8 | 458 | 17.2 | 310 | 11.6 | 268 | 10.0 | 255 | 9.6 | 23 | 0.9 | 2670 | 100 |
| (349972) | W | 244 | 31.5 | 181 | 23.4 | 110 | 14.2 | 107 | 13.8 | 117 | 15.1 | 16 | 2.1 | 775 | 100 | ||
| CADIZ | 111 | 11.7 | M | 522 | 49.5 | 237 | 22.5 | 133 | 12.6 | 94 | 8.9 | 66 | 6.3 | 3 | 0.3 | 1055 | 100 |
| (133242) | W | 46 | 17.7 | 122 | 46.9 | 29 | 11.2 | 25 | 9.6 | 34 | 13.1 | 4 | 1.5 | 260 | 100 | ||
| CARTAGENA-LU | 146 | 8.2 | M | 667 | 44.7 | 221 | 14.8 | 123 | 8.2 | 291 | 19.5 | 161 | 10.8 | 30 | 2.0 | 1493 | 100 |
| (212952) | W | 70 | 22.9 | 73 | 23.9 | 36 | 11.8 | 70 | 22.9 | 48 | 15.7 | 9 | 2.9 | 306 | 100 | ||
| CASTELLON | 95 | 5.3 | M | 481 | 48.0 | 118 | 11.8 | 94 | 9.4 | 194 | 19.4 | 107 | 10.7 | 8 | 0.8 | 1002 | 100 |
| (146563) | W | 59 | 27.1 | 39 | 17.9 | 14 | 6.4 | 54 | 24.8 | 46 | 21.1 | 6 | 2.8 | 218 | 100 | ||
| CORDOBA | 224 | 10.7 | M | 885 | 46.0 | 336 | 17.5 | 291 | 15.1 | 222 | 11.5 | 174 | 9.0 | 17 | 0.9 | 1925 | 100 |
| (319692) | W | 79 | 21.6 | 81 | 22.2 | 60 | 16.4 | 81 | 22.2 | 52 | 14.2 | 12 | 3.3 | 365 | 100 | ||
| CORUNA | 181 | 4.4 | M | 733 | 58.5 | 121 | 9.7 | 99 | 7.9 | 141 | 11.3 | 149 | 11.9 | 10 | 0.8 | 1253 | 100 |
| (239434) | W | 96 | 28.5 | 62 | 18.4 | 25 | 7.4 | 77 | 22.8 | 72 | 21.4 | 5 | 1.5 | 337 | 100 | ||
| FERROL | 69 | 7.2 | M | 274 | 55.6 | 82 | 16.6 | 36 | 7.3 | 48 | 9.7 | 49 | 9.9 | 4 | 0.8 | 493 | 100 |
| (80347) | W | 43 | 31.9 | 30 | 22.2 | 16 | 11.9 | 23 | 17.0 | 21 | 15.6 | 2 | 1.5 | 135 | 100 | ||
| GIJON | 191 | 5.2 | M | 1063 | 50.5 | 379 | 18.0 | 161 | 7.6 | 227 | 10.8 | 250 | 11.9 | 26 | 1.2 | 2106 | 100 |
| (269270) | W | 150 | 28.5 | 113 | 21.5 | 50 | 9.5 | 104 | 19.8 | 101 | 19.2 | 8 | 1.5 | 526 | 100 | ||
| GRANADA | 181 | 12.7 | M | 589 | 39.6 | 324 | 21.8 | 192 | 12.9 | 206 | 13.9 | 152 | 10.2 | 23 | 1.5 | 1486 | 100 |
| (237720) | W | 88 | 22.6 | 114 | 29.2 | 28 | 7.2 | 67 | 17.2 | 78 | 20.0 | 15 | 3.8 | 390 | 100 | ||
| HUELVA | 101 | 10.9 | M | 475 | 47.5 | 150 | 15.0 | 178 | 17.8 | 128 | 12.8 | 61 | 6.1 | 8 | 0.8 | 1000 | 100 |
| (144369) | W | 44 | 21.9 | 49 | 24.4 | 36 | 17.9 | 34 | 16.9 | 32 | 15.9 | 6 | 3.0 | 201 | 100 | ||
| JAEN | 76 | 11.8 | M | 250 | 37.8 | 200 | 30.3 | 40 | 6.1 | 73 | 11.0 | 88 | 13.3 | 10 | 1.5 | 661 | 100 |
| (115917) | W | 23 | 16.1 | 60 | 42.0 | 8 | 5.6 | 21 | 14.7 | 29 | 20.3 | 2 | 1.4 | 143 | 100 | ||
| LAS PALMAS | 263 | 9.1 | M | 981 | 47.5 | 415 | 20.1 | 178 | 8.6 | 237 | 11.5 | 224 | 10.8 | 31 | 1.5 | 2066 | 100 |
| (364775) | W | 178 | 36.8 | 93 | 19.2 | 42 | 8.7 | 74 | 15.3 | 86 | 17.8 | 11 | 2.3 | 484 | 100 | ||
| LOGRONO | 91 | 4.4 | M | 333 | 42.7 | 85 | 10.9 | 76 | 9.7 | 166 | 21.3 | 116 | 14.9 | 4 | 0.5 | 780 | 100 |
| (131143) | W | 39 | 20.2 | 27 | 14.0 | 14 | 7.3 | 68 | 35.2 | 40 | 20.7 | 5 | 2.6 | 193 | 100 | ||
| LUGO | 69 | 2.9 | M | 216 | 51.2 | 44 | 10.4 | 24 | 5.7 | 81 | 19.2 | 51 | 12.1 | 6 | 1.4 | 422 | 100 |
| (88901) | W | 29 | 20.7 | 24 | 17.1 | 5 | 3.6 | 49 | 35.0 | 28 | 20.0 | 5 | 3.6 | 140 | 100 | ||
| MADRID | 2358 | 7.5 | M | 9213 | 54.5 | 2504 | 14.8 | 2276 | 13.5 | 1643 | 9.7 | 969 | 5.7 | 312 | 1.8 | 16917 | 100 |
| (2874732) | W | 1593 | 37.5 | 960 | 22.6 | 498 | 11.7 | 733 | 17.2 | 362 | 8.5 | 104 | 2.4 | 4250 | 100 | ||
| MALAGA | 422 | 9.2 | M | 1708 | 46.0 | 653 | 17.6 | 448 | 12.1 | 479 | 12.9 | 359 | 9.7 | 67 | 1.8 | 3714 | 100 |
| (546601) | W | 202 | 24.9 | 238 | 29.3 | 85 | 10.5 | 107 | 13.2 | 168 | 20.7 | 11 | 1.4 | 811 | 100 | ||
| MURCIA | 295 | 3.7 | M | 960 | 44.4 | 384 | 17.7 | 118 | 5.5 | 461 | 21.3 | 207 | 9.6 | 34 | 1.6 | 2164 | 100 |
| (398815) | W | 103 | 26.1 | 85 | 21.5 | 24 | 6.1 | 97 | 24.6 | 71 | 18.0 | 15 | 3.8 | 395 | 100 | ||
| OURENSE | 79 | 3.8 | M | 275 | 51.8 | 53 | 10.0 | 40 | 7.5 | 97 | 18.3 | 61 | 11.5 | 5 | 0.9 | 531 | 100 |
| (109051) | W | 51 | 35.4 | 19 | 13.2 | 7 | 4.9 | 27 | 18.8 | 33 | 22.9 | 7 | 4.9 | 144 | 100 | ||
| OVIEDO | 173 | 8.7 | M | 720 | 51.4 | 235 | 16.8 | 106 | 7.6 | 160 | 11.4 | 163 | 11.6 | 16 | 1.1 | 1400 | 100 |
| (201005) | W | 118 | 33.7 | 54 | 15.4 | 23 | 6.6 | 77 | 22.0 | 71 | 20.3 | 7 | 2.0 | 350 | 100 | ||
| PAMPLONA | 122 | 4.1 | M | 562 | 52.7 | 97 | 9.1 | 79 | 7.4 | 173 | 16.2 | 146 | 13.7 | 9 | 0.8 | 1066 | 100 |
| (173272) | W | 105 | 35.4 | 33 | 11.1 | 30 | 10.1 | 72 | 24.2 | 53 | 17.8 | 4 | 1.3 | 297 | 100 | ||
| PONTEVEDRA | 57 | 5.3 | M | 191 | 50.7 | 36 | 9.5 | 38 | 10.1 | 73 | 19.4 | 38 | 10.1 | 1 | 0.3 | 377 | 100 |
| (75864) | W | 25 | 24.8 | 22 | 21.8 | 14 | 13.9 | 23 | 22.8 | 17 | 16.8 | 0 | 0.0 | 101 | 100 | ||
| SAN SEBASTIAN | 140 | 5.7 | M | 573 | 50.8 | 186 | 16.5 | 88 | 7.8 | 159 | 14.1 | 111 | 9.8 | 11 | 1.0 | 1128 | 100 |
| (178377) | W | 130 | 37.8 | 58 | 16.9 | 25 | 7.3 | 60 | 17.4 | 66 | 19.2 | 5 | 1.5 | 344 | 100 | ||
| S. C. TENERIFE | 157 | 6.4 | M | 606 | 49.4 | 227 | 18.5 | 130 | 10.6 | 129 | 10.5 | 124 | 10.1 | 11 | 0.9 | 1227 | 100 |
| (214153) | W | 115 | 42.8 | 58 | 21.6 | 26 | 9.7 | 35 | 13.0 | 30 | 11.2 | 5 | 1.9 | 269 | 100 | ||
| SANTIAGO | 73 | 4.1 | M | 242 | 54.6 | 48 | 10.8 | 23 | 5.2 | 86 | 19.4 | 42 | 9.5 | 2 | 0.5 | 443 | 100 |
| (93381) | W | 42 | 36.2 | 15 | 12.9 | 6 | 5.2 | 42 | 36.2 | 10 | 8.6 | 1 | 0.9 | 116 | 100 | ||
| SEVILLA | 510 | 12.7 | M | 2205 | 49.2 | 800 | 17.9 | 481 | 10.7 | 530 | 11.8 | 408 | 9.1 | 55 | 1.2 | 4479 | 100 |
| (704305) | W | 256 | 28.6 | 230 | 25.7 | 89 | 9.9 | 151 | 16.9 | 154 | 17.2 | 15 | 1.7 | 895 | 100 | ||
| VALENCIA | 533 | 8.5 | M | 2623 | 49.5 | 847 | 16.0 | 629 | 11.9 | 663 | 12.5 | 456 | 8.6 | 80 | 1.5 | 5298 | 100 |
| (746612) | W | 345 | 23.8 | 429 | 29.6 | 206 | 14.2 | 191 | 13.2 | 246 | 17.0 | 34 | 2.3 | 1451 | 100 | ||
| VIGO | 236 | 4.7 | M | 751 | 52.0 | 182 | 12.6 | 126 | 8.7 | 217 | 15.0 | 143 | 9.9 | 26 | 1.8 | 1445 | 100 |
| (287282) | W | 133 | 34.3 | 72 | 18.6 | 37 | 9.5 | 81 | 20.9 | 56 | 14.4 | 9 | 2.3 | 388 | 100 | ||
| VITORIA | 168 | 4.2 | M | 559 | 44.2 | 184 | 14.6 | 98 | 7.8 | 245 | 19.4 | 166 | 13.1 | 12 | 0.9 | 1264 | 100 |
| 216852) | W | 81 | 24.9 | 60 | 18.5 | 36 | 11.1 | 91 | 28.0 | 51 | 15.7 | 6 | 1.8 | 325 | 100 | ||
| ZARAGOZA | 462 | 5.4 | M | 2089 | 54.1 | 516 | 13.4 | 286 | 7.4 | 617 | 16.0 | 313 | 8.1 | 37 | 1.0 | 3858 | 100 |
| (614905) | W | 259 | 28.1 | 157 | 17.0 | 83 | 9.0 | 250 | 27.1 | 153 | 16.6 | 20 | 2.2 | 922 | 100 | ||
(*) M: Men, W:Women.
Frequency and percentage of deaths (relative to the total preventable deaths) for each preventable cause, sex and city. Spain, 1996–2007.
The total number of preventable deaths for all cities in the period analysed was 96757. Of these, 77516 were men and 19241 were women, accounting for 11.8% and 3.1% of all deaths, respectively (Table 1). By periods and for all cities, there was a reduction in the number of preventable deaths in men, from 40846 in the 1996–2001 period to 36670 in the 2002–2007 period. This drop was attributable mainly to AIDS and HIV, road traffic accidents, cirrhosis and, to a lesser degree, lung cancer, while the number of suicides and homicides rose. There was also a reduction, albeit a smaller one, in the number of preventable deaths among women, from 9859 in the first period to 9382 in the second, with fewer deaths from AIDS, HIV, cirrhosis and road traffic accidents, with higher numbers of deaths from lung cancer, suicide and homicide.
Table 2 shows the frequencies and percentages of deaths (compared to total preventable deaths) per city, sex and specific cause. The most frequent cause for men, in all cities, was lung cancer, with a percentage out of total deaths from all causes varying from 37.8% in Jaén to 58.5% in Coruña. In the case of women, in 20 of the 33 cities analysed (60.6%) the most frequent cause of death was lung cancer, in 7 cities (21.2%) it was cirrhosis, and in 6 (18.2%) it was road traffic accidents.
Table 3 shows the age standardized rates (ASRs) for all preventable deaths studied for each city, sex and period. In the case of men, there is an average decrease of 15.7%, with a decrease of all the rates adjusted in every city. Women showed a mean reduction of 11.3%, although some cities such as Avilés, Lugo, Pamplona and Pontevedra showed slight increases in the second period.
Table 3.
Age standardized mortality rates (95%CI) for the 33 cities studied, by sex and period
| CITY | SEX | 1996-2001 | 2002-2007 | 1996-2007 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALICANTE | Men | 134.1 (125.9-142.3) | 99.3 (92.7-105.9) | 115.5 (110.3-120.7) |
| Women | 29.1 (25.4-32.7) | 26.1 (22.8-29.3) | 27.5 (25.1-29.9) | |
| ALMERIA | Men | 130.2 (119.1-141.3) | 111.1 (101.3-120.8) | 120.1 (112.8-127.5) |
| Women | 21.9 (17.6-26.2) | 19.9 (16.0-23.8) | 20.9 (18.0-23.8) | |
| AVILES | Men | 131.3 (117.3-145.3) | 114.4 (101.5-127.3) | 122.5 (113.0-131.9) |
| Women | 22.8 (17.0-28.5) | 25.3 (19.5-31.0) | 24.2 (20.1-28.3) | |
| BARCELONA | Men | 119.2 (116.1-122.4) | 93.9 (91.2-96.6) | 105.9 (103.9-108.0) |
| Women | 28.7 (27.2-30.1) | 24.3 (23.0-25.6) | 26.4 (25.4-27.4) | |
| BILBAO | Men | 132.9 (126.0-139.7) | 108.1 (101.9-114.2) | 120.7 (116.1-125.3) |
| Women | 33.7 (30.4-37.0) | 30.4 (27.3-33.6) | 32.1 (29.8-34.4) | |
| CÁDIZ | Men | 152.6 (140.0-165.3) | 121.9 (111.0-132.9) | 137.1 (128.7-145.4) |
| Women | 35.5 (29.8-41.3) | 25.5 (20.7-30.3) | 30.5 (26.7-34.2) | |
| CARTAGENA | Men | 145.9 (135.3-156.4) | 127.4 (118.2-136.6) | 135.6 (128.7-142.5) |
| Women | 29.6 (25.1-34.2) | 23.6 (19.7-27.5) | 26.6 (23.6-29.6) | |
| CASTELLÓN | Men | 135.2 (123.6-146.8) | 106.3 (96.7-115.9) | 118.7 (111.3-126.1) |
| Women | 28.4 (23.2-33.5) | 21.5 (17.3-25.7) | 24.7 (21.4-28.0) | |
| CORDOBA | Men | 132.6 (124.5-140.8) | 103.0 (96.3-109.8) | 117.0 (111.7-122.2) |
| Women | 21.7 (18.6-24.8) | 18.1 (15.4-20.8) | 19.7 (17.7-21.7) | |
| CORUÑA | Men | 111.7 (102.1-121.4) | 96.5 (89.4-103.5) | 102.3 (96.6-107.9) |
| Women | 26.1 (21.8-30.4) | 22.4 (19.2-25.5) | 23.9 (21.4-26.5) | |
| FERROL | Men | 123.7 (106.6-140.9) | 116.1 (102.7-129.6) | 119.8 (109.2-130.4) |
| Women | 29.7 (21.6-37.7) | 28.0 (21.8-34.2) | 28.8 (23.9-33.7) | |
| GIJÓN | Men | 132.9 (125.1-140.8) | 109.9 (103.0-116.8) | 121.2 (116.0-126.4) |
| Women | 29.8 (26.1-33.4) | 27.0 (23.6-30.3) | 28.3 (25.8-30.7) | |
| GRANADA | Men | 128.5 (119.6-137.4) | 103.4 (95.6-111.2) | 115.3 (109.4-121.2) |
| Women | 25.1 (21.5-28.7) | 25.4 (21.9-29.0) | 25.2 (22.7-27.7) | |
| HUELVA | Men | 150.9 (137.7-164.1) | 125.5 (114.2-136.8) | 136.7 (128.2-145.3) |
| Women | 25.2 (20.2-30.3) | 23.3 (18.7-27.8) | 24.3 (20.9-27.7) | |
| JAÉN | Men | 126.3 (112.5-140.2) | 112.6 (100.5-124.8) | 118.6 (109.5-127.6) |
| Women | 23.6 (17.9-29.3) | 22.5 (17.4-27.6) | 23.1 (19.3-26.9) | |
| LAS PALMAS | Men | 121.4 (114.2-128.6) | 89.9 (84.1-95.8) | 104.9 (100.3-109.5) |
| Women | 25.3 (22.1-28.5) | 21.3 (18.5-24.0) | 23.1 (21.0-25.2) | |
| LOGROÑO | Men | 114.5 (103.4-125.5) | 93.4 (83.8-103.0) | 103.3 (96.0-110.5) |
| Women | 26.9 (21.7-32.1) | 20.3 (16.1-24.6) | 23.6 (20.2-26.9) | |
| LUGO | Men | 103.9 (88.4-119.5) | 92.5 (81.0-104.0) | 96.6 (87.4-105.9) |
| Women | 27.2 (19.8-34.6) | 28.8 (22.7-34.8) | 28.1 (23.4-32.8) | |
| MADRID | Men | 107.8 (105.6-110.0) | 85.2 (83.2-87.1) | 95.8 (94.3-97.2) |
| Women | 22.4 (21.5-23.4) | 19.6 (18.7-20.4) | 20.9 (20.2-21.5) | |
| MÁLAGA | Men | 144.4 (137.9-151.0) | 122.4 (116.7-128.1) | 132.5 (128.2-136.8) |
| Women | 27.2 (24.6-29.9) | 24.2 (21.8-26.6) | 25.7 (23.9-27.4) | |
| MURCIA | Men | 119.6 (112.4-126.8) | 104.6 (98.3-110.9) | 111.2 (106.5-115.9) |
| Women | 20.6 (17.7-23.4) | 17.3 (14.9-19.8) | 18.8 (16.9-20.6) | |
| OURENSE | Men | 110.5 (95.9-125.1) | 93.9 (83.3-104.4) | 100.1 (91.5-108.7) |
| Women | 23.8 (17.4-30.1) | 23.6 (18.7-28.6) | 23.7 (19.8-27.6) | |
| OVIEDO | Men | 124.8 (115.7-133.9) | 107.6 (99.4-115.8) | 115.9 (109.8-122.0) |
| Women | 27.6 (23.6-31.6) | 22.3 (18.8-25.7) | 24.8 (22.2-27.4) | |
| PAMPLONA | Men | 111.9 (102.4-121.3) | 95.1 (86.8-103.3) | 103.0 (96.8-109.2) |
| Women | 25.0 (20.8-29.3) | 27.4 (23.1-31.7) | 26.1 (23.1-29.1) | |
| PONTEVEDRA | Men | 120.3 (101.5-139.0) | 100.7 (87.3-114.2) | 108.0 (97.0-118.9) |
| Women | 23.9 (16.0-31.7) | 26.3 (19.9-32.8) | 25.2 (20.3-30.2) | |
| SAN SEBASTIÁN | Men | 114.2 (104.9-123.4) | 96.4 (88.2-104.6) | 105.5 (99.3-111.7) |
| Women | 31.2 (26.7-35.7) | 24.1 (20.3-27.9) | 27.7 (24.8-30.7) | |
| SANTA CRUZ de TENERIFE | Men | 113.3 (104.2-122.3) | 101.0 (92.9-109.0) | 106.9 (100.9-112.9) |
| Women | 21.0 (17.3-24.6) | 20.5 (17.1-24.0) | 20.8 (18.3-23.3) | |
| SANTIAGO | Men | 101.4 (86.3-116.5) | 99.9 (87.9-111.9) | 100.7 (91.3-110.1) |
| Women | 29.1 (21.5-36.8) | 19.4 (14.5-24.3) | 23.2 (19.0-27.5) | |
| SEVILLA | Men | 133.1 (127.7-138.6) | 109.7 (105.0-114.4) | 120.9 (117.4-124.5) |
| Women | 21.8 (19.8-23.8) | 20.2 (18.3-22.1) | 21.0 (19.6-22.4) | |
| VALENCIA | Men | 135.0 (130.1-140.0) | 107.3 (103.0-111.5) | 120.4 (117.1-123.6) |
| Women | 33.5 (31.1-35.8) | 25.6 (23.6-27.6) | 29.4 (27.9-31.0) | |
| VIGO | Men | 107.1 (98.2-115.9) | 102.3 (95.5-109.1) | 104.4 (99.0-109.8) |
| Women | 25.8 (21.7-30.0) | 24.9 (21.7-28.1) | 25.2 (22.7-27.7) | |
| VITORIA | Men | 105.2 (97.1-113.3) | 87.3 (80.3-94.3) | 95.8 (90.5-101.1) |
| Women | 30.8 (26.4-35.2) | 18.6 (15.3-21.8) | 24.4 (21.7-27.1) | |
| ZARAGOZA | Men | 110.8 (105.9-115.6) | 95.8 (91.3-100.2) | 103.1 (99.9-106.4) |
| Women | 23.2 (21.1-25.3) | 22.6 (20.5-24.6) | 22.9 (21.4-24.4) |
Spain, 1996-2007.
Figures 2 and 3 show the RRs of death between the least privileged and most privileged levels (SES3 and SES1, respectively) of the SES variables estimated using Poisson regression. These relative risks show the excess risk of death at the lowest level (SES3) compared to the highest level (SES1). The estimated RRs are presented by age groups, as significant interaction between age group and SES was detected in several cases. Nevertheless, no significant interaction was detected between the period under analysis and SES, there being accordingly no evidence that RRs among SES levels vary between periods in any city, in men or in women.
Figure 2.
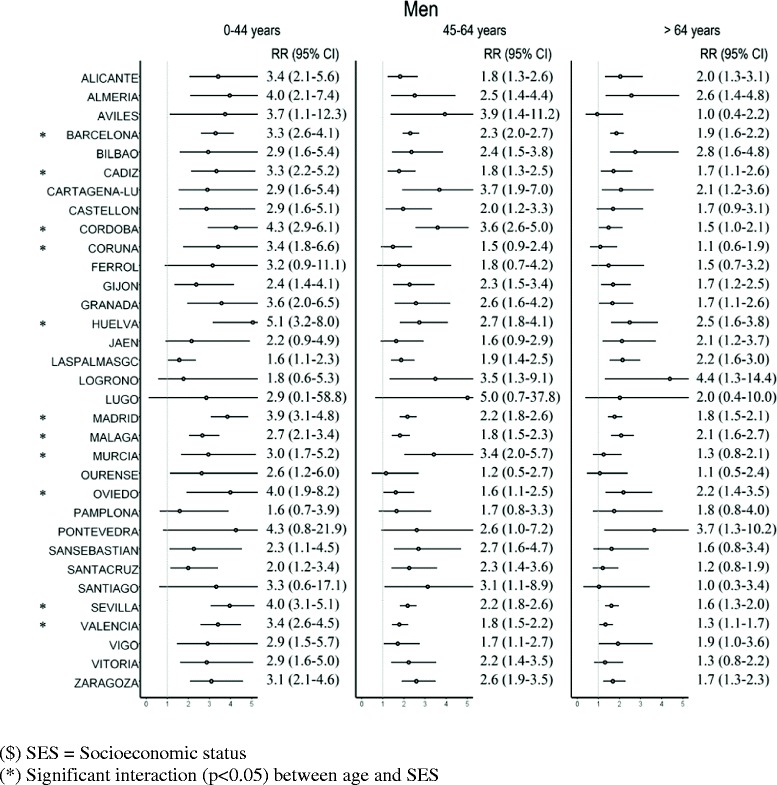
Relative Risk (RR) of death and 95% confidence interval (95% CI) in SES3 vs. SES1 $ for men in each city, by age group.
Figure 3.

Relative Risk (RR) of death and 95% confidence interval (95% CI) in SES3 vs. SES1 $ for women in each city, by age group.
In men (Figure 2) the RR of death in SES3 compared to SES1 was higher than 1 in all cities and at all ages, significantly so (p < 0.05) in 26 cities in the 0–44 age group, in 27 cities in the 45–64 age group, and in 21 cities in the group aged over 64 years. Significant interaction was detected between age group and SES in 11 of the 33 cities analysed, while in the rest the SES effect was constant over the three age groups. In general, the interaction detected translates into higher RRs among SES levels for the youngest groups. This is the case, for example, of Madrid, with RRs of 3.9 in the 0–44 age group, 2.2 in the 45–64 age group, 2.2 in the 45–64 age group and 1.8 in the group aged 65 or over.
In the case of women (Figure 3), the estimated RR were higher than 1 in 27 cities in the 0–44 age group (significantly so in 9 cities), in 26 cities in the 45–64 age group (significant in 3 cities) and in 20 cities in the group aged 64 years and older (significant in 5 cities). There was significant interaction between SES and age group in 5 of the 33 cities studied; in the rest the SES effect was constant over the three age groups. The interaction effect detected in these cities was due, as in men, to significant excesses in risk among younger women.
Table 4 shows the median and mean calculated using the relative risks of the 33 cities when SES3 and SES1 are compared. It shows that, on average, the RRs for the SES variable decreased with age, being highest in the 0–44 years age group.
Table 4.
Median, 10% truncated mean and standard deviation for the Relative Risk when comparing SES3 vs. SES 1 $ in the studied cities, by age group, period and sex
| Age group | Period | Men | Women | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | n(*) | Mean | SD | Median | n(*) | Mean | SD | ||
| 0-44 years | 1996-2001 | 3.3 | 27 | 3.3 | 1.1 | 2.1 | 28 | 2.2 | 1.6 |
| 2002-2007 | 3.0 | 27 | 3.0 | 0.7 | 1.9 | 28 | 2.4 | 1.5 | |
| 45-64 years | 1996-2001 | 2.1 | 27 | 2.2 | 0.6 | 1.3 | 28 | 1.6 | 1.2 |
| 2002-2007 | 2.3 | 28 | 2.4 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 28 | 1.3 | 0.5 | |
| >64 years | 1996-2001 | 1.8 | 27 | 1.9 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 27 | 1.4 | 0.8 |
| 2002-2007 | 1.7 | 29 | 1.7 | 0.5 | 1.2 | 27 | 1.5 | 0.9 | |
($) SES = Socioeconomic status.
(*) Number of cities.
Discussion
This is the first time that preventable avoidable mortality has been analyzed in such a high number of Spanish cities. Using data from thirty-three major Spanish cities, basic socioeconomic indicators of the educational and working environment have been used in this study to examine socioeconomic inequalities in preventable avoidable mortality and thus to detect urban areas to investigate possible problems in the chain of primary prevention, both in the promotion and protection of health and in health education, or over which should address specific health policies. The existence of preventable mortality inequalities should be an indicator of differences in health policy outcomes between different socioeconomic groups. The results of this study show that preventable avoidable mortality made a significant contribution to general mortality (around 7.5%, higher among men), having clearly decreased over time in men (12.7 in 1996–2001 and 10.9 in 2002–2007), though not so clearly among women (3.3% in 1996–2001 and 2.9% in 2002–2007). In the thirty-three cities studied, it has been observed in men, with great consistency, that the risks of death are higher in areas of greater deprivation, and that these excesses have not modified over time. The result in women was different and differences in mortality risks by socioeconomic level could not be established in many cities.
Preventable deaths as a percentage of general mortality dropped between the first and second periods. Men contributed more heavily to the reduction, which was a consequence of the drop in mortality from AIDS and HIV, road traffic injuries, cirrhosis and other liver diseases and, to a lesser degree, lung cancer. For men there was a drop in ASRs in all cities. The effect was different in women, who experienced an increase in the percentage of avoidable deaths between the first and second period, due to lung cancer, suicide and homicide. Consequently, there was greater variability in mortality risk trends, and ASRs increased between the first and second periods in several cities.
The general downward tendency coincides with other studies on avoidable mortality [29,30]. Grabauskas et al. described a growing tendency in avoidable mortality in Lithuania [33]. By causes, in Spain, Dalmau-Bueno et al. found a decrease in deaths due cirrhosis between 1992 and 2004 in Barcelona, in both men and women [23]. Other studies have described a reduction in AIDS and HIV mortality, particularly as a consequence of Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART), among them Borrell et al. in Barcelona [19] and Regidor et al. in the Madrid region [24]. With regard to lung cancer, the general tendency in European countries points towards a reduction among men (particularly young men) and an increase among women [51]. In Spain, the results are similar, rising among women and falling among men [32].
The socioeconomic inequalities found in this study for all deaths from preventable causes confirm the others. Thus, Gotsens et al. found socioeconomic inequalities in 15 European cities for death from injuries (road traffic injuries, suicide, homicide, other external causes) between 2000 and 2008 [26]. Socioeconomic inequalities were also found in AIDS and HIV mortality in cities such as Barcelona [20], in mortality from cirrhosis in Zaragoza [25] or inequalities in educational level in mortality from AIDS, cirrhosis and accident and suicide injuries in the Madrid region [18], and for the lung cancer, cirrhosis, motor traffic accident injuries and AIDS in Castellón, Valencia and Alicante [22].
In this study we found no changes in time in the effects of socioeconomic inequalities on mortality, as the effects of the interaction between SES and period were not significant in any city. Thus we may interpret that the inequalities remained constant in both periods. Considering the 33 cities studied, in the case of men the median RR between SES3 and SES1 did not differ between the two periods for any age group, varying from 1.7 and 1.8, in the group aged over 65 years, in the first and second periods, respectively, and 3.3 (period 1) and 3.0 (period 2) in the group aged under 45 years. These findings consistently show the existence of generalised socioeconomic inequalities for all preventable causes analysed for men. In the case of women, the median for the three RRs is roughly 1 for the group aged over 65 years and, in the group aged under 45, 2.1 for the first period and 1.9 for the second one. Although the results are not significant in many cities and age groups, the estimated RRs are mainly higher than 1, indicating inequality between SES levels, though not quite so pronounced as in men. The lack of statistical significance may be due to the lower number of deaths among women in comparison with men. The results obtained in the group aged over 65 years are in the same range as those presented by Huisman et al. [49], who reviewed socioeconomic inequalities in mortality in old age in the World Health Organization Europe Region and found that RR are rarely higher than 2.0.
Some studies in other countries point either to an increase in socioeconomic inequalities in preventable causes [36,52] or to their decrease [13]. In the case of the causes analysed here, results in trends in inequality vary. In a study conducted in Barcelona using figures from the 1992–2003 period, Borrell et al. [21] found that inequalities in mortality by educational level did not change substantially over time. There are studies which point to an increase in socioeconomic inequalities due to cirrhosis [34,53] or towards their remaining the same or increasing in certain age groups [23]. In the case of AIDS and HIV several studies show that socioeconomic inequalities have been maintained over time [19,20]. In the case of suicide, studies conducted in other countries have found that socioeconomic inequalities either remained steady [52,54] or increased over time [55]. In a study conducted on men in 26 Spanish cities, Gotsens et al. [27] found that socioeconomic inequalities in mortality from injuries (including drug overdose, road traffic injuries and suicide) did not change between the 1996–2001 and 2002–2007 periods. The results of this study are similar to those observed in a study conducted in Valencia, Castellón and Alicante analysing trends in socioeconomic inequalities in mortality from preventable causes (lung cancer, cirrhosis, traffic accidents injuries and AIDS) and which found RRs similar to those of this study, presenting a similar differential effect between men and women (higher RRs in men).
We believe special attention should be paid to age group inequalities, as this study shows that it is the under 45 years group where the greatest inequality occurs. In all cities where significant interaction was detected between SES and age (14 cities for men and 5 for women), it was in the under 45 years age group where the highest RR was estimated. This result offers clear guidelines for interventions aimed at reducing inequalities.
In a study conducted on 11 Spanish cities [56], varying patterns in relation between size of city and magnitude of socioeconomic inequalities in mortality were found, particularly a certain link to lung cancer and cirrhosis in men. Looking at the population characteristics of the cities analysed we can see that the geographical distribution of cities according to the percentage of CTs at the most deprived level (SES3) shows a certain grouping. Thus, the percentage for Lugo, Murcia, Ourense, Pamplona, Santiago, Vitoria, Logroño, Coruña, Vigo, Gijón, Castellón, Pontevedra, Zaragoza, San Sebastián, Santa Cruz de Tenerife and Ferrol is below the median, while the other cities – Madrid, Bilbao, Cartagena-La Unión, Avilés, Valencia, Oviedo, Barcelona, Las Palmas, Málaga, Alicante, Almería, Córdoba, Huelva, Cádiz, Jaén, Granada and Sevilla, are above it. We could say that the first group are clearly in the northern part of Spain (except Murcia and Castellón), while the rest are in the southern and Mediterranean parts (except Avilés, Oviedo and Bilbao). This result leads to the conclusion that higher proportions of deprived populations, according to the calculated indicator, lived in cities in the southern and Mediterranean regions of Spain. However, when we inspected the relationship between population size and percentage of CTs in level SES3 with socioeconomic inequalities (RRs of SES3 vs. SES1), low or moderate Spearman correlations were obtained (below 0.30 and non-significant), showing a weak relationship between inequalities and city size and percentage of deprived CTs.
This study has its limitations. First of all, we have to take into account that it is an ecological study, with the constraints inherent to this type of study. Thus, it does not allow the proof of a causal association. The association found between SES and mortality using CTs may not be applicable at an individual level (i.e. ecological fallacy) and the ecological associations found may reflect both the effect of individual socioeconomic level and the contextual effect of the area. Regarding the causes analysed, other lists could have been used. The causes were chosen on the basis of comparability with other studies and it should be taken into account that exposure to risk factors for some of the causes analysed may have occurred in places other than the place of residence, such as in the work place, as the persons most exposed may live in very deprived neighbourhoods. Nevertheless, an analysis using small areas makes it possible to chase down and identify populations at risk, although some of the exposure may occur outside of them. Another constraint may arise from the use of different mortality classifications throughout the study period. In 1999, there was a switchover from ICD-9 to ICD-10. Two studies conducted in Spain concluded that the introduction of ICD-10 caused no important changes to the causes analysed here [57,58]. The classification of CTs into SES was performed using accumulated data from the 2001 census and remained the same throughout the study period, which was relatively short. Regarding SES classifications used in this study, we should mention that the relative risks estimated between the most favoured and least favoured categories show, for each city, the relative risk between the worst and the best population group in all indicators used. Thus, the interpretation of these relative risks differs from that obtained using other classifications based on percentiles or the continuous value of socioeconomic indicators composed from originals, and reports the level of extreme inequalities between categories which could be identified as maximum and minimum deprivation. This classification makes it possible to identify the most deprived areas, which require greater surveillance and attention, and the consistency of the results obtained using this classification is worth noting. Another aspect to be taken into account is that the term mortality, avoidable or not, takes only deaths, but not other health outcomes, into consideration. This gives an limited view of overall health outcomes, such as suicides, by not providing information about suicide attempts instead of deaths, or that it is not the best indicator of the efficacy of preventive measures, such as the reduction in accident injuries or improvements in quality of life as outcomes other than death.
The mortality analysed in this study may be reduced by means of well-designed health interventions and policies aimed at preventing disease and disability. Several measures established by Spanish governments since the beginning of this century, for example in road safety, established as a priority in 2004, or campaigns aimed at reducing tobacco use, which made it possible to introduce the smoking ban, may be effective in reducing mortality, but transferring the effects of these measures to the reduction of socioeconomic inequalities in mortality requires investments in public health activities to promote health and prevent disease. These activities include efforts in monitoring the state of health of the community, investigating the areas at most risk, educating the population regarding health risks and prevention strategies, intensifying health promotion initiatives, and reinforcing and adapting laws and regulations. In this line, primary healthcare may play an important role in contributing to reducing health inequalities. Hernández et al. [59] proposes recommendations made by the Spanish Commission for the Reduction of Health Inequalities, for putting actions of this type into effect.
The period studied here falls within a period of economic boom in the country, ending in 2007, when the current world economic crisis, which having serious effects in Spain, commenced. Accordingly, this work aims to serve as a point of reference for future studies which evaluate trends in inequalities in preventable mortality in later periods.
Conclusions
This study shows that preventable mortality analysed decreased between the 1996–2001 and 2002–2007 periods, more markedly in men than in women, and that there were socioeconomic inequalities in mortality in most cities analysed, particularly among the youngest population, associating a higher risk of death with higher levels of deprivation. Moreover, inequalities emained over the two periods analysed. This type of study makes it possible to identify those areas where excess preventable mortality is associated with more deprived zones. It is in these deprived zones where actions to reduce and monitor health inequalities should be put into place. Primary healthcare may play an important role in this process.
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the FIS-FEDER projects PI080330, PI081713, PI081978, PI0463/2010, PI081017, PI081785, PI081058, PI080142, and the FUNDACIÓN CAJAMURCIA project FFIS/CM10/27.
We would like to thank Marc Nolasco Miñana for his help and assistance with the final translation of the text.
Abbreviations
- CT
Census tract
- NSI
National statistics institute
- AIDS and HIV
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome and human immunodeficiency virus infection
- ICD-9
International classification of diseases, 9th version
- ICD-10
International classification of diseases, 10th version
- SES
Socioeconomic status
- SES1
Most privileged socioeconomic status
- SES2
Intermediate socioeconomic status
- SES3
Least privileged socioeconomic status
- P1
Time period 1996–2001
- P2
Time period 2002–2007
- ASR
Age standardized rate
- RR
Relative risk
- IHD
Ischaemic heart disease
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contribution
The study was conceived and designed collectively by all the authors. AN and JAQ coordinated and conducted the analysis and wrote the first version of the manuscript. All the authors contributed equally to the analysis of the data, interpretation, and discussion of results. All the authors have read and approved the final version.
Contributor Information
Andreu Nolasco, Email: nolasco@ua.es.
Joaquin Moncho, Email: joaquin.moncho@ua.es.
Jose Antonio Quesada, Email: ja.quesada@ua.es.
Inmaculada Melchor, Email: melchor_inm@gva.es.
Pamela Pereyra-Zamora, Email: pamela.pereyra@ua.es.
Nayara Tamayo-Fonseca, Email: nayara.tamayo@ua.es.
Miguel Angel Martínez-Beneito, Email: martinez_mig@gva.es.
Oscar Zurriaga, Email: zurriaga_osc@gva.es.
Mónica Ballesta, Email: monica.ballesta@carm.es.
Antonio Daponte, Email: antonio.daponte.easp@juntadeandalucia.es.
Ana Gandarillas, Email: ana.gandarillas@salud.madrid.org.
Mª Felicitas Domínguez-Berjón, Email: felicitas.dominguez@salud.madrid.org.
Marc Marí-Dell’Olmo, Email: mmari@aspb.cat.
Mercè Gotsens, Email: mgotsens@aspb.cat.
Natividad Izco, Email: nizcog@larioja.org.
Mª Concepción Moreno, Email: mmorenoi@cfnavarra.es.
Marc Sáez, Email: marc.saez@udg.edu.
Carmen Martos, Email: martos_car@gva.es.
Pablo Sánchez-Villegas, Email: pablo.sanchez.easp@juntadeandalucia.es.
Carme Borrell, Email: cborrell@aspb.cat.
References
- 1.Rutstein DD, Berenberg W, Chalmers TC, Child CG, III, Fishman AP, Perrin EB. Measuring the quality of medical care. A clinical method. N Engl J Med. 1976;294:582–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197603112941104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Charlton JR, Hartley RM, Silver R, Holland WW. Geographical variation in mortality from conditions amenable to medical intervention in England and Wales. Lancet. 1983;1:691–6. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(83)91981-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Holland WW. European community atlas of avoidable death - report No 3. Brussels: Oxford University Press; 1988. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mackenbach JP, Kunst AE, Looman CW, Habbema JD, van der Maas PJ. Regional differences in mortality from conditions amenable to medical intervention in The Netherlands: a comparison of four time periods. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1988;42:325–32. doi: 10.1136/jech.42.4.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nolte E, McKee M. Does Health Care save lives? Avoidable mortality revisited. London: The Nuffield Trust; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gispert R, Bares MA, Puigdefabregas A. Avoidable mortality: a consensus list of causes to update the indicator in Spain. Gac Sanit. 2006;20:184–93. doi: 10.1157/13088849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nolte E, McKee CM. Measuring the health of nations: updating an earlier analysis. Health Aff (Millwood ) 2008;27:58–71. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.27.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tobias M, Yeh LC. How much does health care contribute to health inequality in New Zealand? Aust N Z J Public Health. 2007;31:207–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-6405.2007.00049.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hoffmann R, Plug I, Khoshaba B, McKee M, Mackenbach JP. Amenable mortality revisited: the AMIEHS study. Gac Sanit. 2013;27:199–206. doi: 10.1016/j.gaceta.2012.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Holland WW. European community atlas of avoidable death - report No 6. Brussels: Oxford University Press; 1991. [Google Scholar]
- 11.World Health Organization . The world health report 2000 - health systems: improving performance. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Stevens G, Mathers C. Avoidable mortality–a tool for policy evaluation in developing countries? Eur J Public Health. 2010;20:241–2. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/ckq051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.James PD, Wilkins R, Detsky AS, Tugwell P, Manuel DG. Avoidable mortality by neighbourhood income in Canada: 25 years after the establishment of universal health insurance. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2007;61:287–96. doi: 10.1136/jech.2006.047092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mackenbach JP, Stirbu I, Roskam AJ, Schaap MM, Menvielle G, Leinsalu M, et al. Socioeconomic inequalities in health in 22 European countries. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2468–81. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa0707519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cano-Serral G, Azlor E, Rodriguez-Sanz M, Pasarin MI, Martinez JM, Puigpinos R, et al. Socioeconomic inequalities in mortality in Barcelona: a study based on census tracts (MEDEA Project) Health Place. 2009;15:186–92. doi: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2008.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Stirbu I, Kunst AE, Bopp M, Leinsalu M, Regidor E, Esnaola S, et al. Educational inequalities in avoidable mortality in Europe. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2010;64:913–20. doi: 10.1136/jech.2008.081737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Baburin A, Aareleid T, Padrik P, Valvere V, Innos K. Time trends in population-based breast cancer survival in Estonia: analysis by age and stage. Acta Oncol. 2014;53:226–34. doi: 10.3109/0284186X.2013.806992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Regidor E, de la Fuente L, Calle ME, Navarro P, Dominguez V. Unusually strong association between education and mortality in young adults in a community with a high rate of injection-drug users. Eur J Public Health. 2003;13:334–9. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/13.4.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Borrell C, Rodriguez-Sanz M, Pasarin MI, Brugal MT, Garcia-de-Olalla P, Mari-Dell’olmo M, et al. AIDS mortality before and after the introduction of highly active antiretroviral therapy: does it vary with socioeconomic group in a country with a National Health System? Eur J Public Health. 2006;16:601–8. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/ckl062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mari-Dell’olmo M, Rodriguez-Sanz M, Garcia-Olalla P, Pasarin MI, Brugal MT, Cayla JA, et al. Individual and community-level effects in the socioeconomic inequalities of AIDS-related mortality in an urban area of southern Europe. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2007;61:232–40. doi: 10.1136/jech.2006.048017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Borrell C, Azlor E, Rodriguez-Sanz M, Puigpinos R, Cano-Serral G, Pasarin MI, et al. Trends in socioeconomic mortality inequalities in a southern European urban setting at the turn of the 21st century. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2008;62:258–66. doi: 10.1136/jech.2006.057166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nolasco A, Melchor I, Pina JA, Pereyra-Zamora P, Moncho J, Tamayo N, et al. Preventable avoidable mortality: evolution of socioeconomic inequalities in urban areas in Spain, 1996–2003. Health Place. 2009;15:702–11. doi: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2008.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Dalmau-Bueno A, Garcia-Altes A, Mari-Dell’olmo M, Perez K, Espelt A, Kunst AE, et al. Trends in socioeconomic inequalities in cirrhosis mortality in an urban area of Southern Europe: a multilevel approach. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2010;64:720–7. doi: 10.1136/jech.2008.086538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Regidor E, Sanchez E, de la Fuente L, Santos JM, Martinez D. A proposal of measures for monitoring social disparities in health using AIDS and liver disease mortality before and after HAART. Eur J Public Health. 2011;21:116–21. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/ckp229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Aguilar I, Feja C, Compés ML, Rabanaque MJ, Esteban M, Alcalá T, et al. Men inequalities and liver cirrhosis mortality (Zaragoza, Spain, 1996–2003) Gac Sanit. 2011;25(2):139–45. doi: 10.1016/j.gaceta.2010.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gotsens M, Mari-Dell’olmo M, Perez K, Palencia L, Martinez-Beneito MA, Rodriguez-Sanz M, et al. Socioeconomic inequalities in injury mortality in small areas of 15 European cities. Health Place. 2013;24:165–72. doi: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2013.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gotsens M, Mari-Dell’olmo M, Perez K, Palencia L, Borrell C. Trends in socio-economic inequalities in injury mortality among men in small areas of 26 Spanish cities, 1996–2007. Accid Anal Prev. 2013;51:120–8. doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2012.10.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Rodriguez-Sanz M, Carrillo P, Borrell C. Desigualdades sociales en la salud, los estilos de vida y la utilización de servicios sanitarios en las CC.AA., 1993–2003. Observatorio de la Mujer, Secretaria General de Sanidad, Ministerio de Sanidad y Consumo; 2006.
- 29.Barés MA, Gispert R, Puig X, Puigfàbregas A, Treserras R. Geographical distribution and time trends of suicide mortality in Catalonia and Spain (1986–2002) Gac Sanit. 2005;19:315. [Google Scholar]
- 30.James PD, Manuel DG, Mao Y. Avoidable mortality across Canada from 1975 to 1999. BMC Public Health. 2006;6:137. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-6-137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gispert R, Serra I, Bares MA, Puig X, Puigdefabregas A, Freitas A. The impact of avoidable mortality on life expectancy at birth in Spain: changes between three periods, from 1987 to 2001. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2008;62:783–9. doi: 10.1136/jech.2007.066027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Cayuela A, Rodríguez-Domínguez S, López-Campos JL, Virgil E, Otero R. Lung cancer mortality trends in Spain between 1980 and 2005. Arch Bronconeumol. 2008;44:70–4. doi: 10.1157/13115745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Grabauskas V, Gaizauskiene A, Sauliune S, Miseikyte R. Trends in avoidable mortality in Lithuania during 2001–2008 and their impact on life expectancy. Medicina (Kaunas ) 2011;47:504–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Leyland AH, Dundas R, McLoone P, Boddy FA. Cause-specific inequalities in mortality in Scotland: two decades of change. A population-based study. BMC Public Health. 2007;7:172. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-7-172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Weisz D, Gusmano MK, Rodwin VG, Neuberg LG. Population health and the health system: a comparative analysis of avoidable mortality in three nations and their world cities. Eur J Public Health. 2008;18:166–72. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/ckm084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Korda RJ, Butler JR, Clements MS, Kunitz SJ. Differential impacts of health care in Australia: trend analysis of socioeconomic inequalities in avoidable mortality. Int J Epidemiol. 2007;36:157–65. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyl282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lumme S, Sund R, Leyland AH, Keskimaki I. Socioeconomic equity in amenable mortality in Finland 1992–2008. Soc Sci Med. 2012;75:905–13. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2012.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mackenbach JP, Kulhanova I, Menvielle G, Bopp M, Borrell C, Costa G, et al. Trends in inequalities in premature mortality: a study of 3.2 million deaths in 13 European countries. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2014;69(3):207–17. doi: 10.1136/jech-2014-204319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Vergara M, Benach J, Martinez JM, Buxó M, Yasui Y. Avoidable and nonavoidable mortality: geographical distribution in small areas in Spain (1990–2001) Gac Sanit. 2007;23:16–22. doi: 10.1016/j.gaceta.2007.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sundmacher L, Kimmerle J, Latzitis N, Busse R. Amenable mortality in Germany: spatial distribution and regional concentrations. Gesundheitswesen. 2011;73:229–37. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1254154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hoffmann R, Borsboom G, Saez M, Mari DM, Burstrom B, Corman D, et al. Social differences in avoidable mortality between small areas of 15 European cities: an ecological study. Int J Health Geogr. 2014;13:8. doi: 10.1186/1476-072X-13-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tang KK, Petrie D, Rao DS. Measuring health inequalities between genders and age groups with realization of potential life years (RePLY) Bull World Health Organ. 2007;85:681–7. doi: 10.2471/BLT.06.037382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Mackenbach JP, Hoffmann R, Khoshaba B, Plug I, Rey G, Westerling R, et al. Using ‘amenable mortality’ as indicator of healthcare effectiveness in international comparisons: results of a validation study. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2013;67:139–46. doi: 10.1136/jech-2012-201471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Quercioli C, Messina G, Basu S, McKee M, Nante N, Stuckler D. The effect of healthcare delivery privatisation on avoidable mortality: longitudinal cross-regional results from Italy, 1993–2003. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2013;67:132–8. doi: 10.1136/jech-2011-200640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Diez Roux AV. Investigating neighborhood and area effects on health. Am J Public Health. 2001;91:1783–9. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.91.11.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Melchor I, Nolasco A, Garcia-Senchermes C, Pereyra-Zamora P, Pina JA, Moncho J, et al. Avoidable mortality. Changes in the new century? Gac Sanit. 2008;22:200–9. doi: 10.1157/13123965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Varnik A, Sisask M, Varnik P, Wu J, Kolves K, Arensman E, et al. Drug suicide: a sex-equal cause of death in 16 European countries. BMC Public Health. 2011;11:61. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-11-61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Dominguez-Berjon MF, Borrell C, Cano-Serral G, Esnaola S, Nolasco A, Pasarin MI, et al. Constructing a deprivation index based on census data in large Spanish cities (the MEDEA project) Gac Sanit. 2008;22:179–87. doi: 10.1157/13123961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Huisman M, Read S, Towriss CA, Deeg DJ, Grundy E. Socioeconomic Inequalities in Mortality Rates in Old Age in the World Health Organization Europe Region. Epidemiol Rev. 2013;85(1):84–97. doi: 10.1093/epirev/mxs010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Martínez MA, Morales J. Generalized linear models. Elche (Alicante): Universidad Miguel Hernandez; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Didkowska J, Manczuk M, McNeill A, Powles J, Zatonski W. Lung cancer mortality at ages 35–54 in the European Union: ecological study of evolving tobacco epidemics. BMJ. 2005;331:189–91. doi: 10.1136/bmj.331.7510.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Windenberger F, Rican S, Jougla E, Rey G. Spatiotemporal association between deprivation and mortality: trends in France during the nineties. Eur J Public Health. 2012;22:347–53. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/ckr029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Najman JM, Williams GM, Room R. Increasing socioeconomic inequalities in male cirrhosis of the liver mortality: Australia 1981–2002. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2007;26:273–8. doi: 10.1080/09595230701247699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Burrows S, Auger N, Roy M, Alix C. Socio-economic inequalities in suicide attempts and suicide mortality in Québec, Canada, 1990–2005. Public Health. 2010;124:425. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2010.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kim MH, Jung-Choi K, Jun HJ, Kawachi I. Socioeconomic inequalities in suicidal ideation, parasuicides, and completed suicides in South Korea. Soc Sci Med. 2010;70:1254–61. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2010.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Martinez-Beneito MA, Zurriaga O, Botella-Rocamora P, Mari-Dell’olmo M, Nolasco A, Moncho J, et al. Do socioeconomic inequalities in mortality vary between different Spanish cities? a pooled cross-sectional analysis. BMC Public Health. 2013;13:480. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Cano-Serral G, Perez G, Borrell C. Comparability between ICD-9 and ICD-10 for the leading causes of death in Spain. Rev Epidemiol Sante Publique. 2006;54:355–65. doi: 10.1016/S0398-7620(06)76730-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Cirera Suárez L, Rodriguez Barranco M, Madrigal de Torez E, Carrillo Prieto J, Hasiak Santo A, Augusto Beker R, et al. Correspondences from 10th to 9th Revision of the International Classification of diseases in the causes of death lists of the National Institute of Statistics and the Regional Health Authority of Murcia in Spain. Rev Esp Salud Publica. 2006;80:157–75. doi: 10.1590/S1135-57272006000200005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Hernández-Aguado I, Santaolaya CM, Campos EP. Social inequalities in health and primary care. SESPAS Report 2012. Gac Sanit. 2012;26 Suppl 1:6–13. doi: 10.1016/j.gaceta.2011.09.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


