Abstract
We conducted a case-control study in a Chinese population, and investigated the role of STAT3 rs4796793 and STAT5b rs6503691 polymorphisms in the risk and clinical outcome of breast cancer. STAT5b rs6503691 polymorphisms and STAT3 rs4796793 polymorphisms were genotyped by TaqMan SNP Genotyping Assays on the ABI 7500 fast real-time PCR platform. Unconditional logistic regression analyses showed that subjects carrying the GG genotype of STAT3 rs4796793 had a significantly increased risk of breast cancer, with an adjusted OR (95% CI) of 0.35 (0.12-0.95). In the Cox proportional hazards model, we observed that individuals carrying CG+GG genotype of STAT3 rs4796793 was associated with reduced risk of death from breast cancer when compared with CC genotype (HR = 0.43, 95% CI = 0.20-0.93). Our study found that STAT3 rs4796793 polymorphism plays an important role in influence the development and overall survival of breast cancer patients.
Keywords: STAT3, STAT5b, polymorphism, breast cancer
Introduction
Currently, breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women worldwide, and the incidence is still increasing in China [1,2]. Multiple environmental and hereditary factors play an important role in the pathogenesis of breast cancer. Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) proteins are a member family of cytoplasmic transcription factors, which play an important role in the signal transduction through cytokines, hormones and growth factors [3].
Recent studies established that STAT3 and STAT5 play important roles in the development of a wide variety of human malignancies, including breast cancer [3-5]. STAT3 and STAT5 are two important factors, and they have a role in mediating multiple oncogenic signaling pathways and regulating tumor cell survival, such as EGFR and JAK/STAT signaling pathways [6]. Recent genetic studies have shown that genetic variations in the STAT3 and STAT5 genes contribute to susceptibility, development, and therapeutic outcome of many human malignancies [7-11].
It is estimated that there were more than 100 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the STAT3 and STAT5 genes. However, few studies have investigated the association of STATs genotypes with the susceptibility and survival of malignancies [7-11], and few studies investigated the association between STAT3 rs4796793 and STAT5b rs6503691 polymorphisms and risk of breast cancer in Chinese population.
In the present study, we conducted a case-control study in a Chinese population, and investigated the role of STAT3 rs4796793 and STAT5b rs6503691 polymorphisms in the risk and clinical outcome of breast cancer.
Materials and methods
Patients and clinical characteristics
A total of 182 patients with breast cancer were consecutively recruited from the Tumor Hospital of Harbin Medical University. All the 182 patients had newly diagnosed, histopathologically confirmed, and untreated breast cancer. A total of 182 control subjects were randomly selected from individuals who came to seek a routine health examination in the outpatients department during the same period in the Tumor Hospital of Harbin Medical University. All the control subjects were found to be free of cancers. One control was matched with one case by sex and age at enrollment (within ± 5 years). The study was approved by the Tumor Hospital of Harbin Medical University, and all subjects gave their informed consent prior to inclusion in the study.
Clinical data were collected from the pre-designed questionnaires and medical records, including age at diagnosis, sex, menopausal status, tumor size, clinical stage, lymph mode metastasis, ER status and PR status. Tumor type and disease stage were evaluated according to the World Health Organization criteria and the TNM classification system, respectively. Cancer stage was divided into two groups, including early stage (stages I and II) and late stage (stages III and IV).
A clinical oncologist retrospectively collected clinical and pathological data and chemotherapeutic responses from medical records. Of the 182 patients, 146 patients received anthracycline-based chemotherapy for at least 4~6 cycles. 12 patients received paclitaxel-based chemotherapy consisting of T or TC (docetaxel or paclitaxel and/or capecitabine) regimen. 10 patients received both anthracycline and paclitaxel-based chemotherapy (n=109). The remaining 14 patients received other chemotherapies such as CP/GP regimens (cyclophosphamide and platinum/gemcitabine and cisplatin) and NP (navelbine and platinum) regimens or without chemotherapies such as surgery and/or radiation therapy.
DNA extraction and genotyping analysis
Each patient was asked to provide a 5-ml peripheral venous blood sample after participating into our study. Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood lymphocytes using TIANamp Blood DNA kit (Tiangen Biotech Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. STAT5b rs6503691 polymorphisms and STAT3 rs4796793 polymorphisms were genotyped by TaqMan SNP Genotyping Assays on the ABI 7500 fast real-time PCR platform (Applied Biosystems, ABI Technologies, USA). PCR was conducted in a mixture containing 2 μL DNA, 12.5 μL Taqman Master Mix, 1.25 μL Applied Biosystems SNP assay, and 9.25 μL DNase-free H2O. The PCR conditions were as follows: an initial denaturation at 95°C for 5 min, 35 cycles of amplification with denaturation at 95°C for 30 sec, annealing at 56°C for 30 sec, and extension at 72°C for 30 sec, followed by a final extension step of 7 min at 72°C. For quality control, approximately 10% of the patients were randomly selected to repeatedly the genotyping procedure with different researchers. The reproducibility was 100%.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables were shown by mean ± SD, and categorical variables were shown by n of subjects (%). The association between STAT5b rs6503691 and STAT3 rs4796793 polymorphisms and risk of breast cancer were described as odds ratio (ORs) and 95% confidence interval (CI) using conditional logistic regression analysis. The prognostic value of STAT5b rs6503691 and STAT3 rs4796793 polymorphisms for the OS was estimated by multivariate analysis using the Cox proportional hazards models, describing as the hazard ratio (HR) and 95% CI. Overall survival (OS) was calculated as the time between the first day of treatment and death or last known follow-up. Survival probabilities were estimated by using the Kaplan-Meier method. Two-tailed P values < 0.05 with were considered statistical difference. All statistical analyses were conducted using the STATA version 9.0 statistical software.
Results
The demographic and clinical characteristics of all the breast cancer cases and controls were shown in Table 1. There were age-related differences were observed between the groups (P > 0.05). The mean age of breast cancer patients and controls were 51.3 ± 11.3 and 50.5 ± 10.7 years, respectively. Of the 182 breast cancer patients, 119 (65.38%) had tumor size ≥ 2.0 cm, 130 (71.43%) had clinical stage of I-II, 100 (54.95%) had positive lymph node metastasis, 114 (62.64%) had positive ER status, and 101 (55.49%) had positive PR status.
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of 182 breast cancer patients and 182 control subjects
| Characteristics | Cases | % | Controls | % | χ2 test | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age, years | 51.3 ± 11.3 | 50.5 ± 10.7 | ||||
| < 50 | 85 | 46.70 | 88 | 48.35 | ||
| ≥ 50 | 97 | 53.30 | 94 | 51.65 | 0.10 | 0.75 |
| Menopausal status | ||||||
| Pre-menopausal | 93 | 51.10 | 99 | 54.40 | ||
| Post-menopausal | 89 | 48.90 | 83 | 45.60 | 0.40 | 0.53 |
| Tumor size | ||||||
| < 2.0 cm | 62 | 34.07 | ||||
| ≥ 2.0 cm | 119 | 65.38 | ||||
| Clinical stage | ||||||
| I-II | 130 | 71.43 | ||||
| III-IV | 52 | 28.57 | ||||
| Lymph node metastasis | ||||||
| Negative | 82 | 45.05 | ||||
| Positive | 100 | 54.95 | ||||
| Estrogen receptor (ER) status | ||||||
| Negative | 68 | 37.36 | ||||
| Positive | 114 | 62.64 | ||||
| Progesterone receptor (PR) status | ||||||
| Negative | 81 | 44.51 | ||||
| Positive | 101 | 55.49 | ||||
The genotype distributions of STAT3 rs4796793 and STAT5b rs6503691 were found to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium in the control group (Table 2). Unconditional logistic regression analyses showed that subjects carrying the GG genotype of STAT3 rs4796793 had a significantly increased risk of breast cancer, with an adjusted OR (95% CI) of 0.35 (0.12-0.95). However, we did not found significant association between STAT5b rs6503691 polymorphism and risk of breast cancer.
Table 2.
Distribution of STAT3 rs4796793 and STAT5b rs6503691 polymorphisms and association of risk of breast cancer
| Genotypes | Cases | % | Controls | % | Adjusted OR (95% CI)1 | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STAT3 rs4796793 | ||||||
| CC | 98 | 53.85 | 84 | 46.15 | 1.0 (Ref.) | |
| CG | 77 | 42.31 | 81 | 44.51 | 0.81 (0.52-1.28) | 0.35 |
| GG | 7 | 3.85 | 17 | 9.34 | 0.35 (0.12-0.95) | 0.02 |
| GC+GG | 84 | 46.15 | 98 | 53.85 | 0.73 (0.48-1.13) | 0.14 |
| STAT5b rs6503691 | ||||||
| CC | 104 | 57.14 | 97 | 53.30 | 1.0 (Ref.) | |
| CT | 66 | 36.26 | 70 | 38.46 | 0.88 (0.56-1.39) | 0.56 |
| TT | 12 | 6.59 | 16 | 8.79 | 0.70 (0.29-1.67) | 0.38 |
| CT+TT | 78 | 42.86 | 86 | 47.25 | 0.85 (0.55-1.31) | 0.43 |
Adjusted for age and menopausal status.
In the Cox proportional hazards model, after adjusting for potential confounding factors, we observed that individuals carrying CG+GG genotype of STAT3 rs4796793 was associated with reduced risk of death from breast cancer when compared with CC genotype (HR = 0.43, 95% CI = 0.20-0.93) (Table 3). However, we observed no association between STAT5b rs6503691 polymorphism and OS in breast cancer patients.
Table 3.
Cox regression analysis of the association between STAT3 rs4796793 and STAT5b rs6503691 polymorphisms and OS of breast cancer
| Genotypes | Event | % | Alive | % | Adjusted HR (95% CI)1 | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STAT3 rs4796793 | ||||||
| CC | 31 | 68.89 | 67 | 48.91 | 1.0 (Ref.) | - |
| CG | 12 | 26.67 | 65 | 47.45 | 0.40 (0.17-0.89) | 0.01 |
| GG | 2 | 4.44 | 5 | 3.65 | 0.86 (0.08-5.65) | 0.87 |
| GC+GG | 14 | 31.11 | 70 | 51.09 | 0.43 (0.20-0.93) | 0.02 |
| STAT5b rs6503691 | ||||||
| CC | 26 | 57.78 | 78 | 52.56 | 1.0 (Ref.) | - |
| CT | 15 | 33.50 | 51 | 35.56 | 0.88 (0.39-1.93) | 0.74 |
| TT | 4 | 8.72 | 8 | 11.88 | 1.5 (0.30-6.15) | 0.53 |
| CT+TT | 19 | 42.22 | 59 | 47.44 | 0.97 (0.46-2.01) | 0.92 |
Ajusted for age, tumor size, clinical stage, lymph mode metastasis and ER and PR status.
By Kaplan-Meier method, we found that individuals carrying CG+GG genotype of STAT3 rs4796793 had a longer OS of breast cancer when compared with CC genotype (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
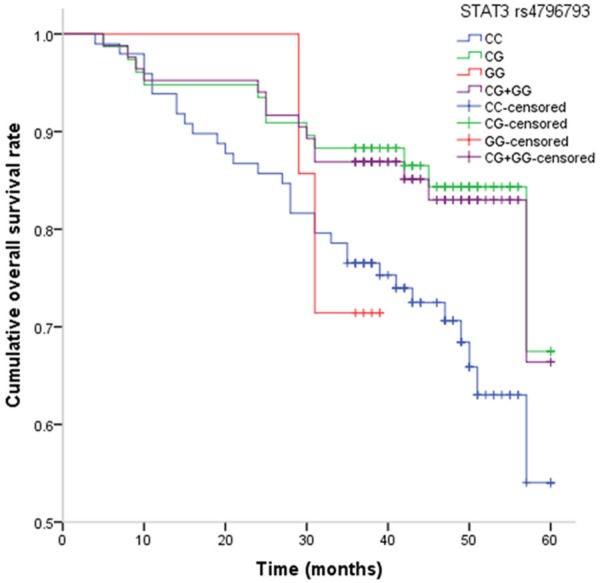
Kaplan-Meier analysis of STAT3 rs4796793 polymorphism on the overall survival of breast cancer patients.
Discussion
STATs are ligand-induced transcriptional factors that are activated in response to a wide range of cytokines, growth factors, and hormones [12,13]. STAT3 and STAT5 are constitutively activated in various cancers including breast cancer, and are associated with progression, metastasis, and poor prognosis of breast cancer [14-20]. However, few studies investigated the role of STAT3 rs4796793 and STAT5b rs6503691 polymorphisms in the development of breast cancer. In our study, we conducted a case-control study to investigate the role of the two gene polymorphisms on the risk and prognosis of breast cancer. We found that GG genotype of STAT3 rs4796793 was associated with decreased risk of breast cancer, and individuals carrying CG+GG genotype of STAT3 rs4796793 had a longer OS of breast cancer. Our findings suggest that STAT3 rs4796793 can be a predictive factor for the development and prognosis in breast cancer patients.
In the present study, we found that genetic variation of STAT3 rs4796793 was associated with development and overall survival of breast cancer. Several previous studies reported the STAT3 rs4796793 polymorphism and cancer risk [21-23]. Xie et al. conducted a case-control study in a Chinese population, and found that STAT3 rs4796793 polymorphism significantly increased HCC risk after adjusting for covariates including HBV mutations in the preS region [21]. Jiang et al. conducted a case-control study to investigate the association between STAT3 rs4796793 polymorphism and NSCLC risk, and found that STAT3 rs4796793 polymorphism decreased the risk of NSCLC, and was associated with tumor stage of NSCLC [22]. Moreover, Ito et al. conducted a case-control study in a Japanese population, and suggested that STAT3 polymorphism was a useful diagnostic marker to predict the response to IFN-alpha therapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma [23]. For the association between STAT3 rs4796793 and breast cancer risk, only one previous study reported the association between them [24]. However, STAT3 rs4796793 did not influence the risk of breast cancer [24].
We further analyzed the association between STAT3 rs4796793 and overall survival of breast cancer patients, and we found that CG+GG genotype of STAT3 rs4796793 had a longer OS of breast cancer. STAT3 rs4796793 polymorphisms may be used as a potential marker for identification of the malignant and invasive TNBC and BRCA1-associated breast cancer. STAT3 rs4796793 polymorphism is more frequently occurred in BRCA1-positive breast cancer, which suggests that STAT3 rs4796793 polymorphism may play a role in the development of BRCA1–related breast cancer patients [12,14-20]. Two previous studies reported the association between STAT3 rs4796793 polymorphism and response to chemotherapy in cancers [23,25]. Eto et al. conducted a prospective study in a Japanese population, and found that STAT3 polymorphism can be a predictive marker for treatment with IFN-α for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma [25]. Ito et al. also suggested that STAT3 rs4796793 is a useful diagnostic marker to predict the response to IFN-alpha therapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma [23]. Further studies with large sample size are greatly needed to confirm the association between STAT3 rs4796793 and prognosis of breast cancer.
Several limitations should be considered in our study. First, cases and controls were selected from one hospital, which may not be representative of other populations. Selection bias may exist in this study. Second, the number of cases analyzed in the present study was relatively small, which may reduce the statistical power to detect the association between STAT3 and STAT5 polymorphisms and development and prognosis of breast cancer. Therefore, further studies with more subjects are needed to confirm the results in our study.
In conclusion, our study found that STAT3 rs4796793 polymorphism plays an important role in influence the development and overall survival of breast cancer patients. Further multicenter studies involving various populations are required to confirm our results.
Disclosure of conflict of interest
None.
References
- 1.Fan L, Strasser-Weippl K, Li JJ, St Louis J, Finkelstein DM, Yu KD, Chen WQ, Shao ZM, Goss PE. Breast cancer in China. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:e279–289. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70567-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jemal A, Center MM, DeSantis C, Ward EM. Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends. Cancer epidemiology, biomarkers & prevention: a publication of the American Association for Cancer Research, cosponsored by the American Society of Preventive. Oncology. 2014;19:1893–1907. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-10-0437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wei W, Liu W, Cassol CA, Zheng W, Asa SL, Ezzat S. The breast cancer susceptibility gene product fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 serves as a scaffold for regulation of NF-κB signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 2012;32:4662–73. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00935-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 4.Diaz N, Minton S, Cox C, Bowman T, Gritsko T, Garcia R, Eweis I, Wloch M, Livingston S, Seijo E, Cantor A, Lee JH, Beam CA, Sullivan D, Jove R, Muro-Cacho CA. Activation of stat3 in primary tumors from high-risk breast cancer patients is associated with elevated levels of activated SRC and survivin expression. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:20–8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cerliani JP, Guillardoy T, Giulianelli S, Vaque JP, Gutkind JS, Vanzulli SI, Martins R, Zeitlin E, Lamb CA, Lanari C. Interaction between FGFR-2, STAT5, and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2011;71:3720–31. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Quintás-Cardama A, Verstovsek S. Molecular pathways: Jak/STAT pathway: mutations, inhibitors, and resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:1933–1940. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yuan K, Liu H, Huang L, Ren X, Liu J, Dong X, Tian W, Jia Y. rs744166 polymorphism of the STAT3 gene is associated with risk of gastric cancer in a Chinese population. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:527918. doi: 10.1155/2014/527918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Domańska D, Antczak A, Pastuszak-Lewandoska D, Górski P, Kordiak J, Czarnecka K, Migdalska-Sęk M, Nawrot E, Kiszałkiewcz J, Brzeziańska E. STAT3 rs3816769 polymorphism correlates with gene expression level and may predispose to nonsmall cell lung cancer: a preliminary study. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2013;123:672–9. doi: 10.20452/pamw.2009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chen Y, Lan Q, Zheng T, Zhao N, Holford TR, Lerro C, Dai M, Huang H, Liang J, Ma S, Leaderer B, Boyle P, Chanock S, Rothman N, Zhang Y. Polymorphisms in JAK/STAT signaling pathway genes and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk Res. 2013;37:1120–4. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2013.05.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kwon EM, Holt SK, Fu R, Kolb S, Williams G, Stanford JL, Ostrander EA. Androgen metabolism and JAK/STAT pathway genes and prostate cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol. 2012;36:347–53. doi: 10.1016/j.canep.2012.04.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Slattery ML, Lundgreen A, Kadlubar SA, Bondurant KL, Wolff RK. JAK/STAT/SOCS-signaling pathway and colon and rectal cancer. Mol Carcinog. 2013;52:155–66. doi: 10.1002/mc.21841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Clevenger CV. Roles and Regulation of Stat Family Transcription Factors in Human Breast Cancer. Am J Pathol. 2004;165:1449–1460. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63403-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bromberg J. Signal transducers and activators of transcription as regulators of growth, apoptosis and breast development. Breast Cancer Res. 2000;2:86–90. doi: 10.1186/bcr38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Walker SR, Nelson EA, Zou L, Chaudhury M, Signoretti S, Richardson A, Frank DA. Reciprocal Effects of STAT5 and STAT3 in Breast Cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2009;7:966–976. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Groner B, Hennighausen L. Linear and cooperative signaling: roles for Stat proteins in the regulation of cell survival and apoptosis in the mammary epithelium. Breast Cancer Res. 2000;2:149–153. doi: 10.1186/bcr47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Turkson J, Jove R. STAT proteins: novel molecular targets for cancer drug discovery. Oncogene. 2000;19:6613–6626. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tweardy D, Chang JC. Stat5: from breast development to cancer prognosis, prediction, and progression. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011;29:2443–2444. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.34.2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wei W, Tweardy DJ, Zhang M, Zhang X, Landua J, Petrovic I, Bu W, Roarty K, Hilsenbeck SG, Rosen JM, Lewis MT. STAT3 signaling is activated preferentially in tumor-initiating cells in claudin-low models of human breast cancer. Stem Cells. 2014;32:2571–82. doi: 10.1002/stem.1752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Siveen KS, Sikka S, Surana R, Dai X, Zhang J, Kumar AP, Tan BK, Sethi G, Bishayee A. Targeting the STAT3 signaling pathway in cancer: Role of synthetic and natural inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1845:136–154. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2013.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chen Y, Wang J, Wang X, Liu X, Li H, Lv Q, Zhu J, Wei B, Tang Y. STAT3, a Poor Survival Predicator, Is Associated with Lymph Node Metastasis from Breast Cancer. J Breast Cancer. 2013;16:40–49. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2013.16.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Xie J, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Han Y, Yin J, Pu R, Shen Q, Lu W, Du Y, Zhao J, Han X, Zhang H, Cao G. Interaction of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 polymorphisms with hepatitis B virus mutations in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2013;57:2369–77. doi: 10.1002/hep.26303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jiang B, Zhu ZZ, Liu F, Yang LJ, Zhang WY, Yuan HH, Wang JG, Hu XH, Huang G. STAT3 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to non-small cell lung cancer. Genet Mol Res. 2011;10:1856–65. doi: 10.4238/vol10-3gmr1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ito N, Eto M, Nakamura E, Takahashi A, Tsukamoto T, Toma H, Nakazawa H, Hirao Y, Uemura H, Kagawa S, Kanayama H, Nose Y, Kinukawa N, Nakamura T, Jinnai N, Seki T, Takamatsu M, Masui Y, Naito S, Ogawa O. STAT3 polymorphism predicts interferon-alfa response in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007;25:2785–91. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.09.8897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Vaclavicek A, Bermejo JL, Schmutzler RK, Sutter C, Wappenschmidt B, Meindl A, Kiechle M, Arnold N, Weber BH, Niederacher D, Burwinkel B, Bartram CR, Hemminki K, Försti A. Polymorphisms in the Janus kinase 2 (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) genes: putative association of the STAT gene region with familial breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2007;14:267–77. doi: 10.1677/ERC-06-0077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Eto M, Kamba T, Miyake H, Fujisawa M, Kamai T, Uemura H, Tsukamoto T, Azuma H, Matsubara A, Nishimura K, Nakamura T, Ogawa O, Naito S Japan Immunotherapy SNPs-Study Group for Kidney Cancer. STAT3 polymorphism can predict the response to interferon-α therapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2013;63:745–52. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.09.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


