Background: The neural extracellular matrix protein RPTPζ/phosphacan is abnormally glycosylated in models of congenital muscular dystrophies (CMDs).
Results: RPTPζ/phosphacan is invested with unique and cell-specific O-mannosyl carbohydrate structures.
Conclusion: RPTPζ/phosphacan is a major substrate for O-mannosyl glycosylation, which is a pathway critical in CMDs.
Significance: Abnormal glycosylation of RPTPζ/phosphacan is neural cell-specific and may play a role in CMDs.
Keywords: Brain, Extracellular Matrix, Glycosylation, Muscular Dystrophy, Proteoglycan, Cat-315, O-Glycan, O-Mannose, POMGnT1, RPTPzeta/Phosphacan
Abstract
Protein O-mannosylation is a glycan modification that is required for normal nervous system development and function. Mutations in genes involved in protein O-mannosyl glycosylation give rise to a group of neurodevelopmental disorders known as congenital muscular dystrophies (CMDs) with associated CNS abnormalities. Our previous work demonstrated that receptor protein-tyrosine phosphatase ζ (RPTPζ)/phosphacan is hypoglycosylated in a mouse model of one of these CMDs, known as muscle-eye-brain disease, a disorder that is caused by loss of an enzyme (protein O-mannose β-1,2-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 1) that modifies O-mannosyl glycans. In addition, monoclonal antibodies Cat-315 and 3F8 were demonstrated to detect O-mannosyl glycan modifications on RPTPζ/phosphacan. Here, we show that O-mannosyl glycan epitopes recognized by these antibodies define biochemically distinct glycoforms of RPTPζ/phosphacan and that these glycoforms differentially decorate the surface of distinct populations of neural cells. To provide a further structural basis for immunochemically based glycoform differences, we characterized the O-linked glycan heterogeneity of RPTPζ/phosphacan in the early postnatal mouse brain by multidimensional mass spectrometry. Structural characterization of the O-linked glycans released from purified RPTPζ/phosphacan demonstrated that this protein is a significant substrate for protein O-mannosylation and led to the identification of several novel O-mannose-linked glycan structures, including sulfo-N-acetyllactosamine containing modifications. Taken together, our results suggest that specific glycan modifications may tailor the function of this protein to the unique needs of specific cells. Furthermore, their absence in CMDs suggests that hypoglycosylation of RPTPζ/phosphacan may have different functional consequences in neurons and glia.
Introduction
Protein glycosylation is an essential post-translational modification of cell surface and secreted proteins in organisms ranging from archaea to mammals. For the most part, glycans are added to proteins at Asn residues (N-linked) or at Ser/Thr residues (O-linked), although other linkages have been described (for a review, see Ref. 1). Among the O-linked class of glycoprotein glycans in vertebrates, the monosaccharide composition defines the biosynthetic pathways responsible for their production: mucin-type, O-Fuc, O-Glc, O-GlcNAc, glycosaminoglycans, and O-Man. Although originally thought to only occur in fungi, it is now appreciated that protein O-mannosylation is evolutionarily conserved, occurring in insects, fish, and mammals, among other species (for a review, see Ref. 2). Pioneering biochemical studies documented that O-mannose-initiated glycans comprise nearly one-third of the total O-glycans in the brain (3–6). Despite its conservation across species and high abundance in the brain, only a few proteins have been identified as carriers of this unique glycan modification, and their function remains poorly understood.
Proper O-mannosyl glycosylation is required for normal central nervous system (CNS) development. Mutations in genes involved in O-mannosylation give rise to congenital muscular dystrophies (CMDs)2 with associated CNS abnormalities (7–10). Previous studies have clearly shown that abnormal glycosylation of α-dystroglycan (α-DG), perhaps the most well characterized O-mannosylated protein, accounts for many of the neurological phenotypes associated with these disorders (11, 12). Recent studies have identified additional novel protein substrates for O-mannosyl glycosylation (13–17), raising the possibility that abnormal glycosylation of these proteins may also contribute to neurological abnormalities.
Muscle-eye-brain disease is a type of CMD caused by mutations in the POMGNT1 gene, encoding protein O-mannose β-1,2-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 1 (POMGnT1) (18, 19). POMGnT1 catalyzes the addition of β-1,2-GlcNAc onto the mannose residue linked to a protein Ser/Thr residue. The addition of this GlcNAc is required for all subsequent modifications of branched and terminal non-reducing end glycan structures (19, 20). Our previous work demonstrated that receptor protein-tyrosine phosphatase ζ (RPTPζ)/phosphacan is hypoglycosylated in a mouse model of muscle-eye-brain disease lacking POMGnT1 activity (14), indicating that RPTPζ/phosphacan is modified with O-mannose-linked glycans and may contribute to the neurological abnormalities in CMDs.
RPTPζ/phosphacan is encoded by the PTPRZ1 gene, and the full-length protein is a trans-membrane receptor protein-tyrosine phosphatase (RPTPζ) (21). Alternative splicing gives rise to a long-secreted isoform, phosphacan, which is a well characterized secreted chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan (CSPG) of the neural extracellular matrix (21–23). Two additional isoforms, a short receptor form and a short secreted variant (PSI), primarily associate with the cell membrane (24, 25). RPTPζ/phosphacan is predominately expressed in the CNS (26, 27), where it contributes to a diverse array of biological processes required for normal development and brain function (28–37). In contrast, the precise functions of the O-mannosylated forms of RPTPζ/phosphacan have been difficult to determine using animal models that lack O-mannosylation because the concomitant aberrant glycosylation of α-DG drives dominant neurological phenotypes. Additionally, our previous biochemical and immunochemical characterization of RPTPζ/phosphacan glycosylation indicated that the protein is decorated with an array of distinct O-mannosyl-dependent epitopes that we hypothesize may individually and uniquely affect function (14).
Here we demonstrate that distinct O-mannosyl glycoforms of RPTPζ/phosphacan are expressed in a cell-specific manner, in that glial cells express different glycoforms than neurons. Further analysis by immunoprecipitation demonstrates that the cell-specific glycoforms are biochemically distinct variants of RPTPζ/phosphacan. Finally to comprehensively define the O-mannosyl glycome of RPTPζ/phosphacan, we performed in depth glycan structural analysis. Our results show that this protein is modified by a heterogeneous array of O-mannosyl glycan structures, including sulfated forms. Our data demonstrate the cell specificity of O-mannosyl glycosylation in the brain and provide a new perspective on historical studies that characterized the function and ligands of RPTPζ/phosphacan.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Animals
Protocols for animal usage were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Upstate Medical University. Wild type pregnant CD1 mice were purchased from Charles River Laboratory (Wilmington, MA). POMGnT1 knock-out mice (strain: B6; 129S5-POMGnT1tm1lex/Mmucd) were purchased from MMRRC at the University of California (Davis, CA).
Antibodies
Cat-315 has been previously published and characterized (38, 39). The 3F8 antibody developed by Dr. Margolis was obtained from the Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank (developed under the auspices of the NICHD, National Institutes of Health, and maintained by the University of Iowa) (21, 23). The rabbit polyclonal anti-RPTPζ/phosphacan core antibody was made against amino acids 25–47 in the N-terminal domain, peptide sequence YYRQQRKLVEEIGWSYTGALNQKC, and affinity-purified and tested for its specificity (YenZym Antibodies, LLC, South San Francisco, CA). Polyclonal anti-neurocan was purchased from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN). Polyclonal anti-brevican and monoclonal anti-HNK-1 were purchased from BD Biosciences. Mouse monoclonal anti-phosphacan 5210 (clone 122.2) and rabbit polyclonal anti-NG2 were purchased from Chemicon, EMD Millipore (Billerica, MA). Mouse monoclonal anti-βIII-tubulin (TuJ1) was purchased from Covance (Princeton, NJ).
Primary Cortical Cultures
Mixed primary cortical cultures were prepared essentially as described previously (40). Briefly, the cortices from embryonic day 16 CD-1 wild type or POMGnT1 embryos were removed and digested in 0.25% trypsin-EDTA. Cells were plated in Neurobasal Medium containing 3% B27, 1× Glutamax, and 1× penicillin/streptomycin (Life Technologies, Inc.) on glass coverslips coated with 50 μg/ml poly-d-lysine (Sigma-Aldrich). For arabinofuranosyl cytidine (AraC) treatment, 5 μm AraC (Sigma-Aldrich) was added at 1 day in vitro (DIV) and removed with a full medium change at 3 DIV. All cells received either a half or full medium change at 3 DIV.
Immunohistochemistry and Microscopy
Cells were rinsed in 1× Dulbecco's phosphate-buffered saline and fixed by submersion into −20 °C methanol for 2 min. Cells were then washed with 1× Dulbecco's phosphate-buffered saline and treated with 0.6 units/ml bovine testicular hyaluronidase (BTH) (Sigma-Aldrich) diluted in PBS for 4 h at 37 °C to enhance 3F8 immunoreactivity. Cells were blocked in 5% nonfat dry milk diluted in 1× PBST with 0.5% Triton X-100 for 45 min at room temperature. Primary antibodies were diluted in 5% nonfat dry milk in 1× PBST and incubated overnight at 4 °C. Alexa-Fluor-conjugated secondary antibodies (Life Technologies) were used, and nuclei were visualized with Hoechst stain. Coverslips were mounted on glass slides with the ProLong anti-fade kit (Life Technologies) and imaged on an epifluorescent Zeiss Imager.A2 with Nikon Elements software package. Final images were formatted and compiled into figures using Photoshop CS5.5.
Histology
For staining with the Cat-315 antibody, postnatal day 0 (P0) mice were transcardially perfused with PBS followed by 4% phosphate-buffered paraformaldehyde. Whole brains were postfixed for 1 h in 4% phosphate-buffered paraformaldehyde and cryoprotected by sinking in 30% phosphate-buffered sucrose. 14-μm coronal sections were cut using a cryostat and mounted and stained directly on glass slides. Tissue sections were blocked and stained in screening medium (DMEM, 5% FBS, 0.2% sodium azide, 1.0% Triton X-100). Mouse monoclonal anti-βIII-tubulin (TuJ1) was used as a neuronal marker. Sequential staining was performed with TuJ1, followed by Cat-315 and Ig subclass-specific secondary antibodies.
For staining with the 3F8 antibody, P0 mouse brains were removed, embedded in O.C.T, and flash-frozen in isopentane on dry ice. Coronal sections were prepared as above. Tissue sections were fixed for 10 min in 4% phosphate-buffered paraformaldehyde and then blocked and stained in 5% nonfat dry milk in 1× PBST with 1.0% Triton X-100. Rabbit polyclonal anti-NG2 was used to stain oligodendrocytes. In all cases, nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst and imaged as described above.
Preparation of Homogenates, Soluble Fraction
Tissue homogenates with respective soluble and particulate fractions were prepared as described previously (41). For O-linked glycan analysis, whole brains from P4 wild type CD1 mice were homogenized in 3 volumes of 25 mm Tris-HCl (pH 7.4) containing 0.32 m sucrose and a protease inhibitor mixture (EDTA-free Complete, Roche Applied Science). For biochemical studies, whole brains from wild type or POMGnT1 knock-out P4 mice were similarly homogenized in 10 volumes. The soluble fraction was isolated by centrifugation at 950 × g for 10 min at 4 °C, and the resulting postnuclear supernatant was centrifuged again at 20,000 × g for 30 min. The postmembrane supernatant was centrifuged at 100,000 × g for 60 min to obtain final soluble and particular fractions.
Immunoprecipitation
Soluble fraction from wild type P4 mouse brain was diluted to 2.0 mg/ml in 40 mm sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.5, 25 mm NaCl, protease inhibitor tablet, mini, EDTA-free (Roche Applied Science). Deglycosylation was performed by incubating samples for 2 h at 37 °C with 150 units/ml BTH (which also removes CS-GAG chains) (Sigma-Aldrich).
Ten volumes of Cat-315 hybridoma medium was incubated with goat anti-mouse IgM-agarose beads (Sigma-Aldrich) at 4 °C overnight. Similarly, 3F8 was diluted 1:30 in PBS and incubated with protein A/G beads (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Dallas, TX) at 4 °C overnight. For immunoprecipitation, samples were diluted to 1 mg/ml in 25 mm Tris, pH 8.0, with protease inhibitor tablet, mini, EDTA-free (Roche Applied Science), and 500 μg was used in each reaction. Protein samples and antibody/bead mixture were incubated overnight, rotating at 4 °C. Beads were washed three times in 25 mm Tris, pH 8.0, followed by two washes in PBS and boiled under reducing conditions in 2× sample buffer. Starting material and immunoprecipitated material were electrophoresed on 5% SDS-polyacrylamide gels and processed for blotting as described below. To directly compare immunoprecipitated samples, we controlled for the amount of RPTPζ/phosphacan electrophoresed by loading amounts of immunoprecipitated material that yielded similar levels of immunoreactivity for an antibody against the protein core of RPTPζ/phosphacan (generated as described above). Membranes were then stripped and reprobed with antibodies against O-mannosyl carbohydrate epitopes on RPTPζ/phosphacan.
SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
Prior to electrophoresis, protein concentrations were determined by a BCA assay. Samples were treated with BTH to remove CS-GAG chains prior to SDS-PAGE. Samples were diluted in 1× BTH buffer (40 mm sodium phosphate buffer with 25 mm NaCl, pH 7.4) and incubated with 1 mg/ml BTH for 2 h at 37 °C. Samples were then reduced and denatured.
SDS-polyacrylamide gels (5, 7, or 4–12%) were used (gradient gels only were purchased from Bio-Rad). Stains-all staining for the visualization of acidic proteins was completed on SDS-polyacrylamide gels according to a published protocol (42). For Western blotting, SDS-polyacrylamide gels were transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. Western blots were completed as described previously (41). Blots were incubated with primary antibodies and detected with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies followed by Supersignal West Pico or Femto chemiluminescent substrate (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL) and Kodak Biomax MR film (Sigma-Aldrich). In some cases, blots were stripped with Re-Blot Plus Strong reagent (Chemicon) and reprobed.
Anion Exchange Chromatography
Anion exchange chromatography was performed to enrich for RPTPζ/phosphacan in the soluble fraction. Previous work has suggested that phosphacan is one of the more abundant soluble CSPGs in the early postnatal mouse brain.
To purify RPTPζ/phosphacan for O-glycan analysis, ∼100 wild type mouse brains were collected at P4. The soluble fraction was isolated using non-dissociative conditions as described above and pooled. To further enrich for phosphacan, we performed anion exchange chromatography. The total P4 soluble fraction was diluted 1:1 in 25 mm Tris-HCl (pH 7.4) containing 0.5 m NaCl and filtered. Anion exchange chromatography was performed using a 1-ml HiTrap Q HP column and peristaltic PI pump connected to an Amersham Biosciences Pharmacia RediFrac fraction collector (GE Healthcare). Prior to and following sample binding, the column was equilibrated and washed in 25 mm Tris-HCl (pH 7.4) containing 0.5 m NaCl. Elution was done in a continuous gradient from 0.5 to 1.0 m NaCl over 10 column volumes ending with a final 2 m NaCl bump. 125-μl fractions were collected at a rate of 250 μl/min. Most protein eluted at ∼0.58 m NaCl, whereas RPTPζ/phosphacan eluted as a single peak between ∼0.95 and 1.0 m NaCl. Fractions of eluate containing phosphacan were identified by dot blot analysis and then pooled into a single sample and dialyzed into 40 mm Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) containing 40 mm sodium acetate using 7,000 molecular weight cut-off Slide-A-Lyzer dialysis cassettes (Pierce) overnight at 4 °C. The dialyzed sample was then concentrated in 100,000 molecular weight cut-off concentrators (AmiconUltra, EMD Millipore) by centrifugation.
Analysis of O-Linked Glycans
Dialyzed samples were dried, and O-glycans were released using reductive β-elimination as described previously (20, 43). Briefly, dried samples were resuspended in 1 m NaBH4 in 50 mm NaOH and incubated at 45 °C for 18 h. The reaction mixture was neutralized with 10% acetic acid and desalted using an AG-50W-X8 column. Released oligosaccharides were dried, and borate was removed by adding 10% acetic acid in methanol and drying. Released oligosaccharides were permethylated according to Anumula and Taylor (44). After permethylation, organic-aqueous partition was employed to separate sulfated and non-sulfated glycans into aqueous and organic (dichloromethane) phases, respectively (45). The partitioned, permethylated glycans were dried and dissolved in 1 mm NaOH in 50% methanol and directly infused into an Orbitrap (Fourier transform) or a linear ion trap mass spectrometer equipped with a nanospray ionization source (LTQ-Orbitrap, Thermo Fisher Scientific). For fragmentation by collision-induced dissociation in MS/MS and multidimensional MS (MSn) modes, 35–40% collision energy was applied. The total ion mapping functionality of the Xcalibur instrument control software was invoked to monitor MS/MS fragmentation of all precursor ions by acquiring automated MS/MS spectra in collection windows 2.8 mass/charge units in width as described previously (43).
RESULTS
Cat-315 and 3F8 O-Mannosyl Epitopes on RPTPζ/Phosphacan Decorate Different Cell Populations
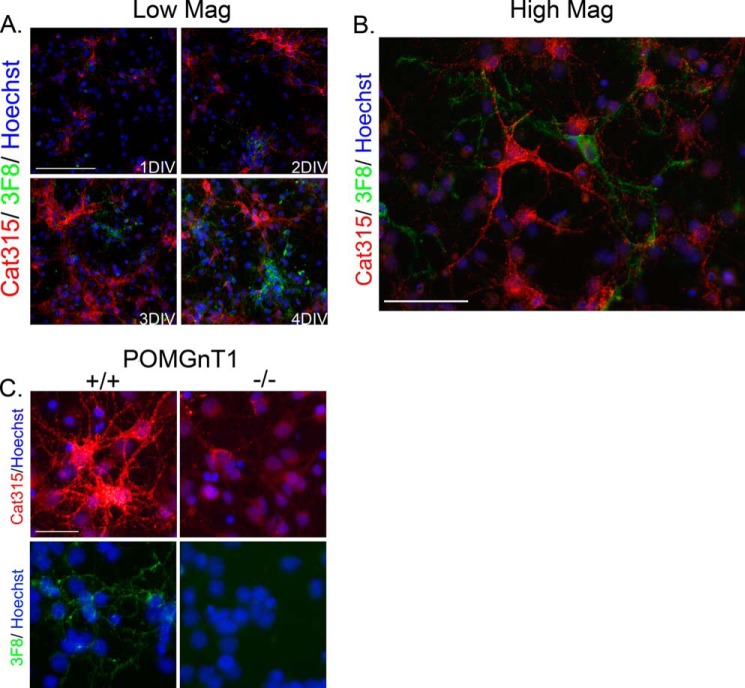
Our previous work indicates that carbohydrate antibodies specific for RPTPζ/phosphacan, including Cat-315, 6B4, and 3F8, detect epitopes that are O-mannose-linked (14). However, it remained unclear whether these antibodies define cell-specific modifications of RPTPζ/phosphacan because some studies have considered antibody binding to neurons and some to glia, but a careful comparative analysis has not been presented (39, 46). Therefore, we prepared cortical cell cultures containing both neurons and glia from the brains of embryonic mice and stained these cells with our O-mannosyl-directed antibodies. We found that over the first several days in culture, Cat-315 and 3F8 immunoreactivity increased on non-overlapping populations of cells (Fig. 1, A and B). To confirm that immunostaining obtained with these antibodies was indeed on O-mannosylated carbohydrate epitopes, we also performed Cat-315 and 3F8 staining in mixed cortical cultures from wild type and POMGnT1 knock-out mice. In agreement with our previous reports, the immunoreactivity of both Cat-315 and 3F8 was largely eliminated from POMGnT1 knock-out cultures, with the exception of subtle residual staining that remained for Cat-315 (Fig. 1C).
FIGURE 1.
Cat-315- and 3F8-reactive forms of RPTPζ/phosphacan decorate different neural cell populations. Primary mixed neural cell cultures were generated from the cortex of embryonic day 16 animals and stained for antibodies against O-mannosyl-linked carbohydrate epitopes on RPTPζ/phosphacan. A, cultures were fixed at 1–4 DIV and double-stained for Cat-315 (red) and 3F8 (green) and imaged at low magnification. The immunoreactivity of both Cat-315 and 3F8 increased from 1 to 4 DIV and labeled mutually exclusive cell populations. Scale bar, 100 μm. B, high magnification image showing the characteristic punctate staining pattern of Cat-315- and 3F8-reactive RPTPζ/phosphacan on the cell soma and processes of mutually exclusive cell types at 4 DIV. Scale bar, 50 μm. C, cultures were prepared from littermate wild type (+/+) and POMGnT1 knock-out (−/−) embryos at embryonic day 16, fixed at 4 DIV, and stained separately for Cat-315 (red) and 3F8 (green). Consistent with our previous findings, cells decorated with Cat-315 and 3F8 immunoreactivity were present in +/+ cultures but were largely eliminated in cultures prepared from POMGnT1 −/− embryos. Scale bar, 50 μm. In all cases, cells are counterstained with Hoechst nuclear stain (blue).
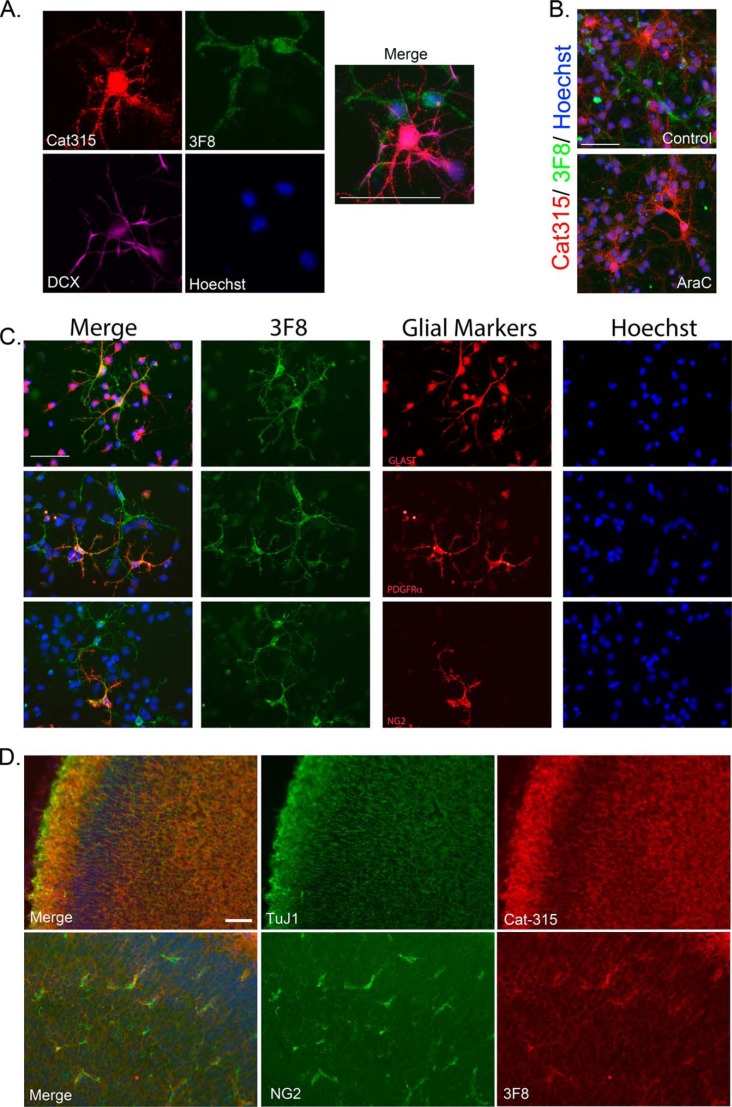
Although previous studies have characterized the immunoreactivity of neurons for the Cat-315 and 6B4 epitopes, the fate of cells reactive for 3F8 remains incompletely characterized. Therefore, we performed triple labeling with Cat-315, 3F8, and the early neuronal cell marker, doublecortin (DCX). In agreement with previous studies (39), we observed that Cat-315-reactive punctate staining decorated a subpopulation of DCX-positive neurons. In contrast, 3F8 immunoreactive cells were not DCX-positive (Fig. 2A). To determine whether 3F8 reactivity was on a population of neurons not labeled by DCX, we treated cultures with AraC, which preferentially eliminates actively dividing cells and spares postmitotic neurons. We found that AraC treatment had no effect on Cat-315 reactivity but eliminated 3F8 reactivity (Fig. 2B), suggesting that the cells reactive for 3F8 were probably actively dividing and potentially glial in nature. Therefore, we performed immunocytochemistry with 3F8 and markers of glial cell subclasses. We observed that 3F8-reactive cells were reactive for the immature astrocyte marker, GLAST. Additionally, we found that subpopulations of 3F8-reactive cells were also reactive for PDGFRα and NG2, markers of oligodendrocyte precursors (Fig. 2C).
FIGURE 2.
3F8 reactive forms of RPTPζ/phosphacan decorate glial subclasses. Primary mixed neural cell cultures were generated from the cortex of embryonic day 16 animals and stained for antibodies against O-mannosyl-linked carbohydrate epitopes on RPTPζ/phosphacan. A, cultures were fixed at 4 DIV and triple-stained for Cat-315 (red), 3F8 (green), and DCX (violet). Whereas Cat-315 immunoreactivity was confirmed to be localized to DCX-positive neurons, 3F8-immunoreactive cells were not DCX-positive. B, cultures were treated with 5 μm AraC from 1 to 3 DIV to remove actively dividing cells and fixed at 4 DIV. Cultures were then double-stained for Cat-315 (red) and 3F8 (green). In untreated control cultures, populations of cells reactive for Cat-315 and 3F8 were present. Following AraC treatment, cultures retained Cat-315 immunoreactivity but lost 3F8 immunoreactivity. C, cultures were fixed at 4 DIV and double-stained for 3F8 and markers of glial cell subclasses, including glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 (GLAST), platelet-derived growth factor receptor α (PDGFRα), and NG2 chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan (NG2). Cells decorated with 3F8 immunoreactivity were reactive for glial cell class markers GLAST, PDGFRα, and NG2. D, tissue sections from P0 brains stained with the neuronal marker TuJ1 and Cat-315 demonstrate that Cat-315-reactive phosphacan is associated with neuronal cells and processes. In contrast, sections stained with NG2 and 3F8 demonstrate that 3F8-reactive phosphacan is enriched around a subset of glial cells. Together, these data reveal the cell-specific expression of different phosphacan glycoforms. In all cases, cells are counterstained with Hoechst nuclear stain (blue). Scale bar, 50 μm.
We next conducted immunohistological studies to confirm that neuronal and glial subclasses were also preferentially decorated with either the Cat-315 or 3F8 epitope, respectively, in brain sections. We found that the distribution of Cat-315 immunoreactivity overlapped with βIII-tubulin (TuJ1) staining in the cortex. In contrast, 3F8 immunoreactivity was preferentially enriched surrounding a small subpopulation of cells, which were positive for the oligodendrocyte marker, NG2 (Fig. 2D). Taken together, the antibody probes indicate that Cat-315- and 3F8-reactive glycoforms of RPTPζ/phosphacan preferentially decorate subclasses of neurons and glia, respectively, in primary neuronal cultures and in brain tissue.
Antibodies against O-Mannosyl Epitopes on RPTPζ/Phosphacan Recognize Distinct Structural Topologies
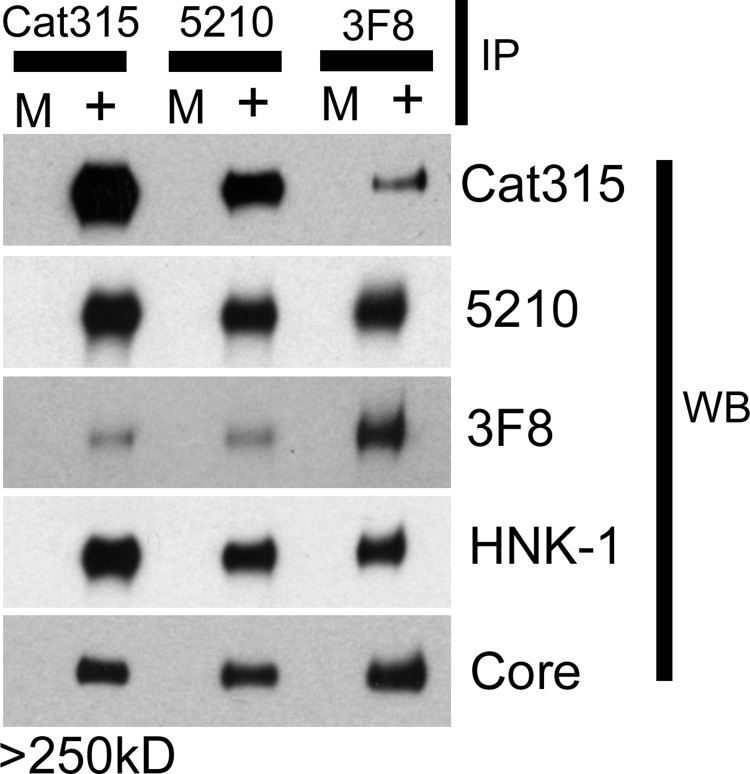
The specific expression of Cat-315 and 3F8 by non-overlapping cell populations led us to hypothesize that these antibodies may be detecting biochemically distinct glycoforms of RPTPζ/phosphacan in the brain. To investigate this possibility, we immunoprecipitated RPTPζ/phosphacan from the soluble fraction of early postnatal mouse brain using either the Cat-315, 3F8, or 5210 antibody and then cross-probed Western blots with each antibody. In all cases, a single band of apparent molecular mass greater than 250 kDa was detected with antibodies against RPTPζ/phosphacan. We did not observe differences in the molecular mass of this band across samples immunoprecipitated using different antibodies (Fig. 3).
FIGURE 3.
O-Mannosyl carbohydrate epitopes detected by Cat-315, 3F8, and 5210 on RPTPζ/phosphacan are biochemically exclusive and detect different O-mannosylated glycoforms of RPTPζ/phosphacan. Cat-315-, 3F8-, and 5210-immunoreactive glycoforms of RPTPζ/phosphacan were immunoprecipitated (IP) from the soluble fraction of early postnatal mouse brain. The total amount of RPTPζ/phosphacan electrophoresed was normalized using an antibody directed against the peptide core by Western blot analysis (WB). The reactivity of IP samples for opposing antibodies against O-mannosyl-linked carbohydrate epitopes on RPTPζ/phosphacan was investigated. Cat-315 IP material was preferentially reactive for the Cat-315 and 5210 antibodies and not for 3F8. 3F8 IP material was preferentially reactive for the 3F8 and 5210 antibodies and not for Cat-315. 5210 IP material was preferentially reactive for Cat-315 and 5210 and not for the 3F8 antibody. All IP samples were similarly reactive for the 5210 antibody and an antibody against the HNK-1 epitope. In all cases, the only bands that were detected resolved above 250 kDa and corresponded to RPTPζ/phosphacan. M, mock sample with beads only; +, with antibody included in reaction.
Studies from our laboratory and others have suggested that Cat-315 detects a terminal HNK-1 epitope that is O-mannose-linked to phosphacan in the early developing brain. Our previous study suggested that 3F8 also detects an O-mannose-linked epitope on phosphacan, whose structure remains undetermined. We found that RPTPζ/phosphacan immunoprecipitated with Cat-315 was poorly reactive for 3F8 and preferentially reactive for the Cat-315 antibody. Conversely, RPTPζ/phosphacan immunoprecipitated with 3F8 was poorly reactive for Cat-315 and preferentially reactive for the 3F8 antibody (Fig. 3). These results suggest that Cat-315 and 3F8 detect largely distinct glycoforms of O-mannosylated RPTPζ/phosphacan.
Our previous study suggested that the 5210 antibody detects both N- and O-mannose-linked epitopes on RPTPζ/phosphacan. We found that material immunoprecipitated with Cat-315 or 3F8 was similarly reactive for 5210 (Fig. 3). However, material immunoprecipitated with 5210 was only poorly reactive for 3F8 and preferentially reactive for 5210 and Cat-315 (Fig. 3). These results indicate that only a small percentage of 5210-reactive glycoforms of RPTPζ/phosphacan are modified with the 3F8-reactive epitope, whereas a greater percentage of 3F8-reactive glycoforms are modified with the 5210 epitope.
We have reported a high degree of similarity in the reactivity of 5210 and anti-HNK-1 antibodies (14). Both antibodies detect O-mannose and N-linked glycans on RPTPζ/phosphacan in addition to primarily N-linked glycans on several other lower molecular mass proteins. We investigated whether proteins immunoprecipitated with Cat-315, 5210, and 3F8 were also recognized by anti-HNK-1 antibody. We found similar levels of HNK-1 immunoreactivity across all immunoprecipitated samples (Fig. 3). Together, these results suggest that 3F8 and Cat-315 define mutually exclusive O-mannosylated glycoforms of RPTPζ/phosphacan, although both glycoforms possess epitopes reactive for 5210 and anti-HNK-1 antibodies.
RPTPζ/Phosphacan Enrichment from the Soluble Fraction of Early Postnatal Mouse Brains
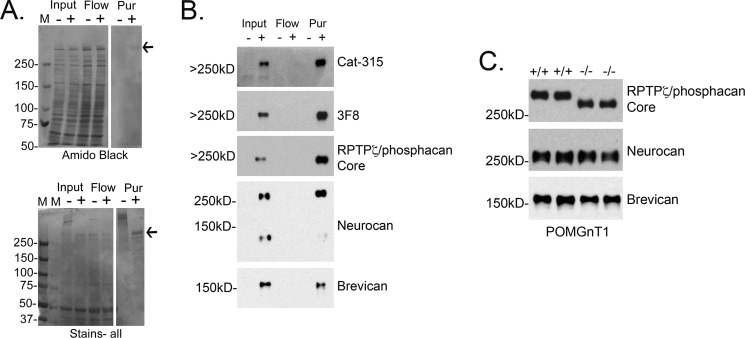
To define the diversity of O-linked glycan structures, including O-mannosyl glycans, on phosphacan, we enriched brain extracts for phosphacan using anion exchange chromatography. To assess the chromatographic enrichment for phosphacan, we took advantage of glycosylation with CS-GAG chains. Without removal of CS-GAG chains, the molecular mass of phosphacan is highly heterogeneous, running as a high molecular mass smear by SDS-PAGE. However, enzymatic removal of CS-GAG chains (by BTH treatment) collapses this smear into a single band of apparent molecular mass ≥250 kDa. Amido Black does not stain the undigested protein well due to its high density of negative charge and did not clearly detect phosphacan. However, after treatment with BTH to remove CS-GAG chains, a single high molecular mass band corresponding to phosphacan appeared at 250 kDa following Amido Black staining (Fig. 4A). To more clearly visualize the shift of phosphacan from a smear to a single band, we employed Stains-all, which detects acidic proteins with greater sensitivity. Again, we found that a high molecular mass smear was present in the purified sample and that this smear collapsed into one major band of apparent molecular mass ≥250 kDa following BTH treatment (Fig. 4A). An additional minor band of lower apparent molecular mass was also detected by Stains-all. By Western blot analysis, we confirmed that the predominant high molecular mass band was phosphacan and that it carried O-mannosyl glycans based on its reactivity with both Cat-315 and 3F8. We also assessed the presence of other CSPGs, known to be expressed during this developmental time window, in our phosphacan-enriched material and were able to detect neurocan and brevican as additional, minor components (Fig. 4B). Of these two components, only neurocan exhibited an enrichment by anion exchange chromatography, albeit to a lesser extent than the enrichment of phosphacan.
FIGURE 4.
Enrichment of O-mannosylated RPTPζ/phosphacan from early postnatal mouse brains. The soluble fraction from ∼100 early postnatal mouse brains was isolated and subjected to anion exchange chromatography to enrich for RPTPζ/phosphacan. A and B, input, flow-through (Flow), and fractions of eluate identified to contain RPTPζ/phosphacan were combined (Pur), dialyzed, and treated with either a control buffer (−) or BTH to remove CS-GAG chains (+). A, samples were then electrophoresed on a 4–12% SDS-polyacrylamide gradient gel. Gels were transferred to nitrocellulose or stained directly using Amido Black stain as a general protein stain or Stains-all to detect heavily charged proteins. The majority of nonspecific protein was identified in input and flow-through samples. In the Pur sample, a single Amido Black-reactive band that resolved above 250 kDa appeared only following BTH treatment (arrow). Staining with Stains-all revealed a high molecular mass smear that resolved well above 250 kDa; following BTH treatment, this smear collapsed into two single bands. The most intensely stained band resolved above 250 kDa (arrow), and a second less reactive band appeared just below this band and resolved around 250 kDa. M, molecular mass marker. B, Western blot analysis of the samples from A revealed that the most intense and highest molecular mass band in Pur was reactive for a core peptide antibody against RPTPζ/phosphacan, which appeared in both input and Pur samples only after treatment with BTH. The same band reactive for the RPTPζ/phosphacan core antibody was also reactive for Cat-315 and 3F8 antibodies, which detect O-mannose-linked epitopes and are specific to RPTPζ/phosphacan. The second less reactive band that resolved around 250 kDa was reactive for a peptide antibody against neurocan. Whereas bands corresponding to lower molecular mass CSPGs were not detected by Amido or Stains-all staining, a band that was weakly immunoreactive for an antibody against brevican was present in both the input and Pur samples. Increases in the intensity of bands reactive for RPTPζ/phosphacan and neurocan in the Pur relative to input were observed, suggesting that our protocol efficiently enriched for these CSPGs, whereas a similar enhancement of brevican reactivity was not observed. C, the soluble fraction from early postnatal wild type (+/+) or POMGnT1 (−/−) whole brains was prepared and treated with BTH to remove CS-GAG chains and then electrophoresed on 5% SDS-polyacrylamide gels. A single band reactive for core peptide antibody against RPTPζ/phosphacan resolved above 250 kDa and was shifted to a lower molecular mass in POMGnT1 −/− samples. The intensity of reactive bands in both +/+ and −/− samples was similar. These findings are consistent with our previous study; however, these samples are from a different POMGnT1 mouse strain and demonstrate the specificity of our newly generated peptide antibody against RPTPζ/phosphacan. To determine whether other CSPGs also in our Pur sample were heavily decorated with O-mannose-linked glycans similar to RPTPζ/phosphacan, we performed Western blot analysis with core peptide antibodies against neurocan and brevican. No detectable shift in molecular mass was detected for neurocan- or brevican-reactive bands in samples from POMGnT1 −/− brains.
To examine whether the other CSPGs present at lower abundance than phosphacan were also modified with O-mannosyl-linked glycans, we performed Western blot analysis on soluble fractions from early postnatal wild type and POMGnT1 knock-out brains. As expected, a single band reactive for an antibody against the core protein of phosphacan was detected at an apparent molecular mass of ≥250 kDa in wild type samples (Fig. 4C). In POMGnT1 knock-out samples, the phosphacan band was detected at a lower apparent molecular mass, consistent with the absence of extended O-mannosyl glycans. A similar shift in the apparent molecular mass was not detected for proteins recognized by antibodies against either neurocan or brevican, comparing wild type with POMGnT1 knock-out samples (Fig. 4C). Together with the glycomic characterization of the enriched material (see below), these results suggest that phosphacan was the predominant carrier of O-mannose-linked glycans in the preparation.
Glycomic Analysis of Phosphacan Preparations Reveals a Novel Diversity of O-Mannose-initiated Structures
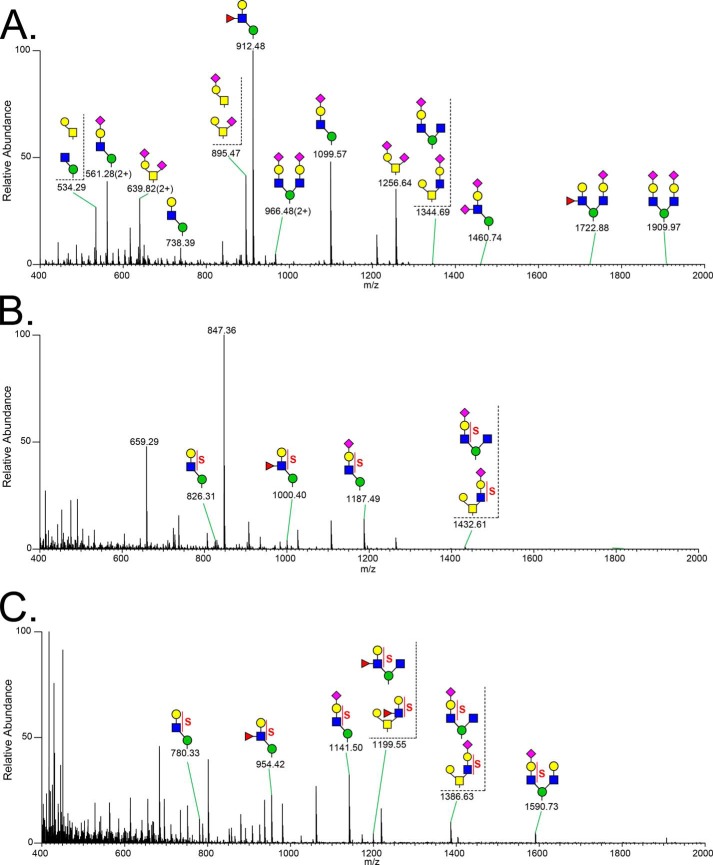
Having confirmed that our sample was highly enriched for O-mannosylated phosphacan, we characterized the O-linked glycan structures released by reductive β-elimination. Released glycans were permethylated to enhance the depth of structural information obtained by nanospray ionization-MS and by MSn. Full MS profiles of non-sulfated O-glycans (Fig. 5A) and sulfated O-glycans (Fig. 5, B and C) over the range of m/z <2000 demonstrate the enhanced abundance of O-mannosyl structures in comparison with O-GalNAc (mucin-type) structures. At least 37 O-mannose-linked and 18 O-GalNAc-linked structures were detected (Table 1). Based on signal intensity in the full MS profile of the glycans recovered in the organic phase following permethylation (non-sulfated structures), the most abundant O-glycans are O-mannosyl structures, Fuc1Gal1GlcNAc1Man-itol (m/z 912.5 [M + Na]+) and NeuAc1Gal1GlcNAc1Man-itol (m/z 1099.6 [M + Na]+). This glycoprotein glycan profile is the first example in which O-mannose-linked structures have been shown to quantitatively predominate over O-GalNAc mucin-type structures. Among O-GalNAc-initiated glycans, mono- and disialylated Core 1 structures (NeuAc2Gal1GalNAc-itol (m/z 1256.6 [M + Na]+) and NeuAc1Gal1GalNAc-itol (m/z 895.5 [M + Na]+)) are the most abundant mucin-type structures. However, even when added together, the abundance of these two mucin-type glycans is only comparable with that of the most abundant O-mannosyl glycan, Fuc1Gal1GlcNAc1Man-itol.
FIGURE 5.
Full MS spectra of permethylated O-glycans released from RPTPζ/phosphacan enriched from early postnatal mouse brains. O-Glycans were released from RPTPζ/phosphacan-enriched samples by reductive β-elimination. Following permethylation, O-glycans were subjected to aqueous-organic partition to separate sulfated glycans from non-sulfated glycans. Full MS spectra are presented for the organic phase in positive ion mode (non-sulfated glycans) (A), aqueous phase in positive ion mode (sulfated glycans) (B), and aqueous phase in negative ion mode (sulfated glycans) (C).
TABLE 1.
Permethylated O-linked glycans from the enriched RPTPζ identified by ion-trap tandem MS analysis
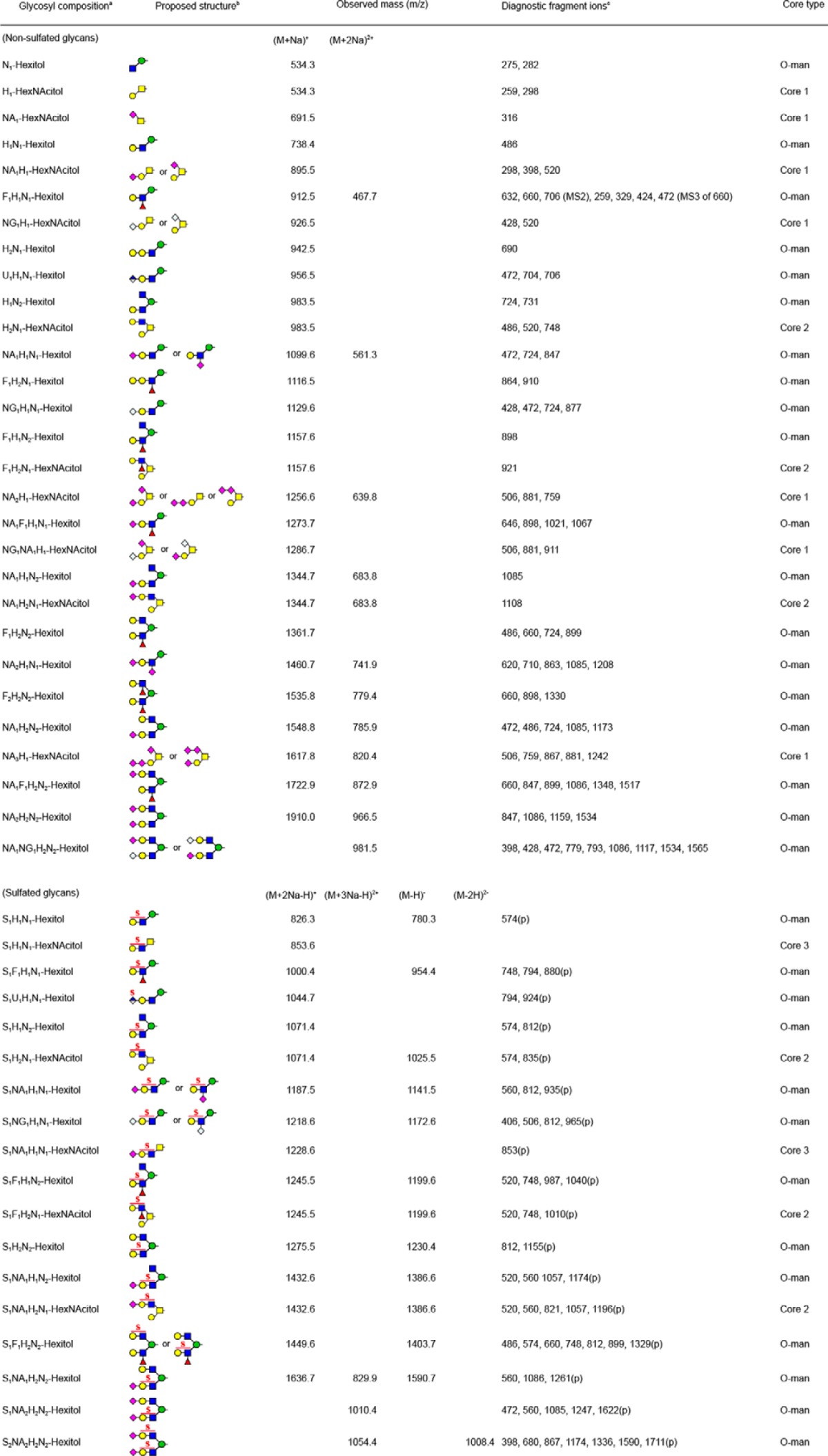
a Following abbreviations are used, Hexose, H; N-acetylhexosamine, N; Fucose, F; Uronic acid, U; N-acetylneuraminic acid, NA; N-glycosylneuraminic acid, NG; Sulfate group, S.
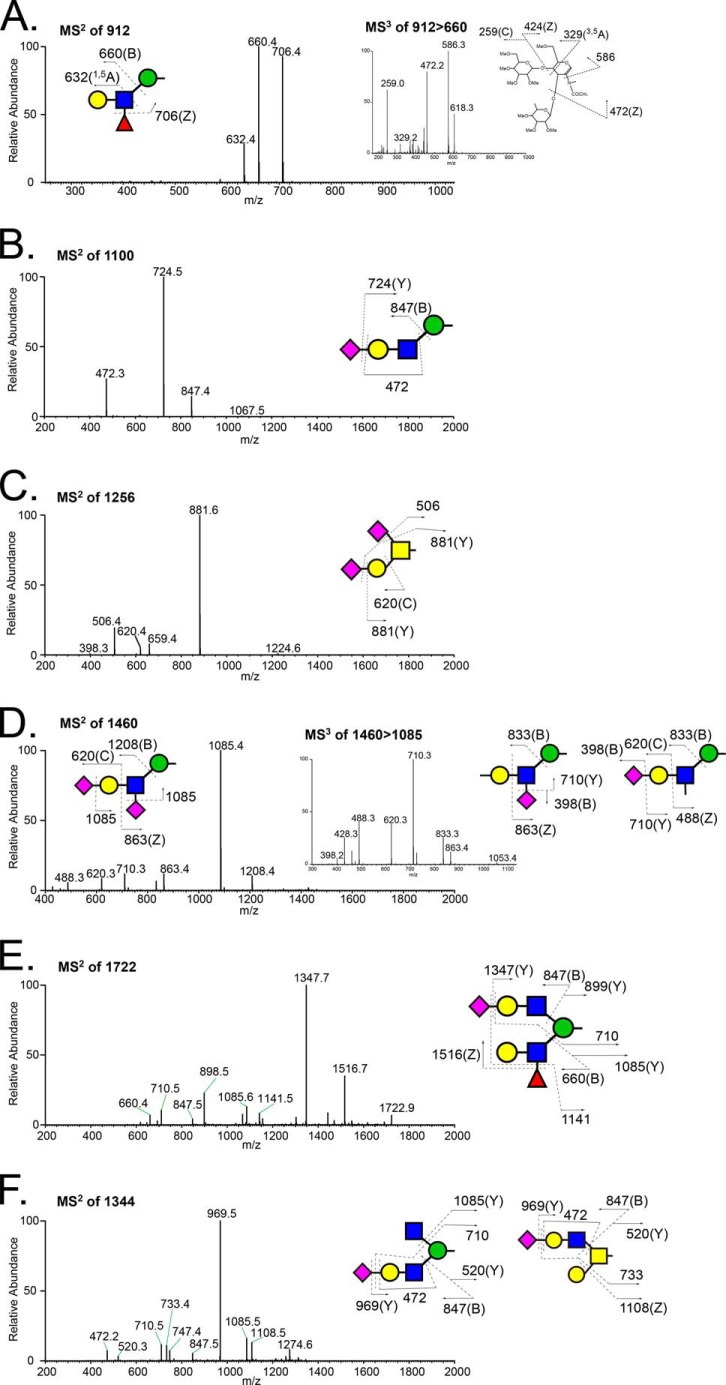
The glycan structures reported in Table 1 were assigned based, at a minimum, on MS/MS fragmentation, and a selected set were further validated by MSn fragmentation to more completely investigate structural diversity (Fig. 6). The most abundant O-mannosyl and mucin-type glycans gave robust fragmentation at MS2 (Fig. 6, A–C). For the major O-mannosyl glycan (Fuc1Gal1GlcNAc1Man-itol, m/z 912.5), MS3 localized the Fuc substitution to the 3-position of the subterminal HexNAc, consistent with a Lewisx epitope (Fig. 6A). Other O-mannose-linked structures with novel structural features were also detected, including a terminally sialylated O-mannosyl tetrasaccharide containing a sialylated internal GlcNAc (NeuAc-Gal-[NeuAc-]GlcNAc-Man-itol, m/z 1460.7 [M + Na]+; Fig. 6D) and a complex O-mannose-linked glycan carrying a sialyl-LacNAc trisaccharide on one arm and a Lewis epitope on the other (Fig. 6E). Fragmentation also demonstrated the existence of isobaric mixtures of glycans containing both O-mannosyl and mucin-type glycans. For instance, the molecular ion at m/z 1344.7 [M + Na]+ contained a mixture of two different structures, including a branched terminally sialylated O-GalNAc trisaccharide and a branched terminally sialylated O-mannose trisaccharide (Fig. 6F). In this case, the nearly equivalent intensity of the diagnostic fragments at m/z 1085.5 and m/z 1108.5 indicates an approximately equal mixture of these two relatively minor glycans. Another isobaric pair composed of O-mannosyl and mucin-type glycans was detected at m/z 983.5 (Table 1).
FIGURE 6.
MSn fragmentation spectra of O-linked glycans released from RPTPζ/phosphacan prepared from early postnatal mouse brains. A, MS2 spectrum of the most abundant molecular ion (m/z 912) detected in full MS scans of the permethylated O-glycans partitioned into the organic phase (positive ion mode). Fragment ions in MS2 define a fucosylated O-mannosyl trisaccharide: m/z 660, 706, and 632 are B ion of cleavage of a glycosidic linkage between GlcNAc and mannitol, removal of Fuc (Z ion), and 1,5A cross-ring cleavage of GlcNAc, respectively. Inset, MS3 spectrum of m/z 660 in MS2 of m/z 912, in which the diagnostic fragment ions (m/z 259, 329, 424) indicate that fucosylated O-mannosyl trisaccharide contains a Lewisx structure, Gal(β1–4)[Fuc(α1–3)]GlcNAc. B, MS2 spectrum of the second most abundant O-mannosyl glycan, the sialylated tetrasaccharide detected at m/z 1100. The most prominent fragment ion represents loss of sialic acid. C, MS2 spectrum of the most abundant mucin-type, O-GalNAc-linked glycan, the disialylated Core 1 disaccharide carrying a sialic acid on both the terminal Gal residue and the GalNAc residue linked to the protein backbone. The most prominent fragment ion results from loss of both sialic acids. D, MS2 spectrum of a precursor ion at m/z 1460; inset, MS3 spectrum of a fragment ion at m/z 1085, loss of sialic acid. Each fragment corresponds to disassembly of a Gal- and GlcNAc-disialylated O-mannosyl trisaccharide (NeuAc-Gal-(NeuAc)GlcNAc-Man-itol). E, MS2 spectrum of precursor ion m/z 1722. The proposed structure is a complex branched sialylated fucosylated O-mannosyl glycan (NeuAc-Gal-GlcNAc-(Gal-(Fuc-)GlcNAc)-Man-itol). F, MS2 spectrum of a precursor ion at m/z 1344. Diagnostic fragment ions indicate a mixture of two different O-linked glycan structures: m/z 710 and 1085 for a branched O-mannosyl structure (NeuAc-Gal-GlcNAc-(GlcNAc-)Man-itol) and m/z 733 and 1108 for a sialylated Core 3 structure (NeuAc-Gal-GlcNAc-[Gal-]GalNAc-itol).
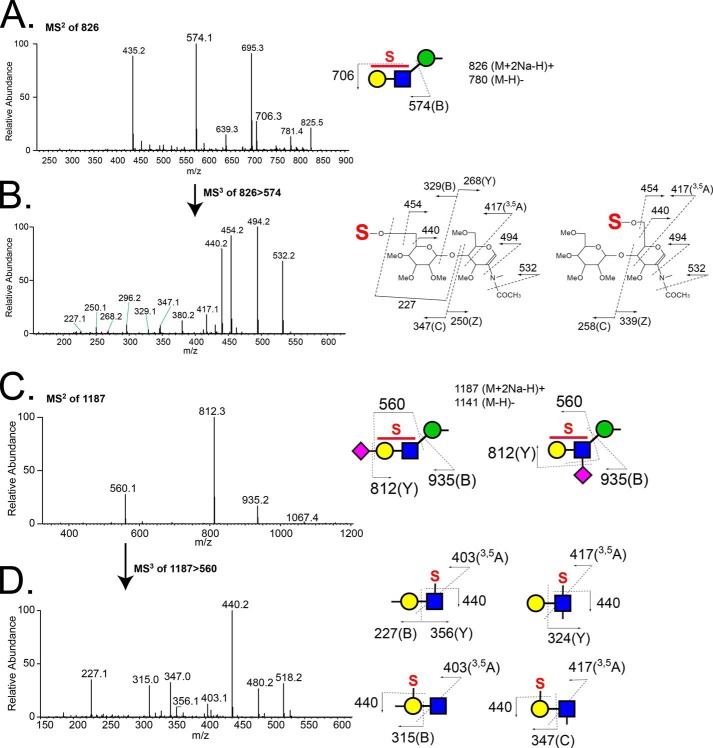
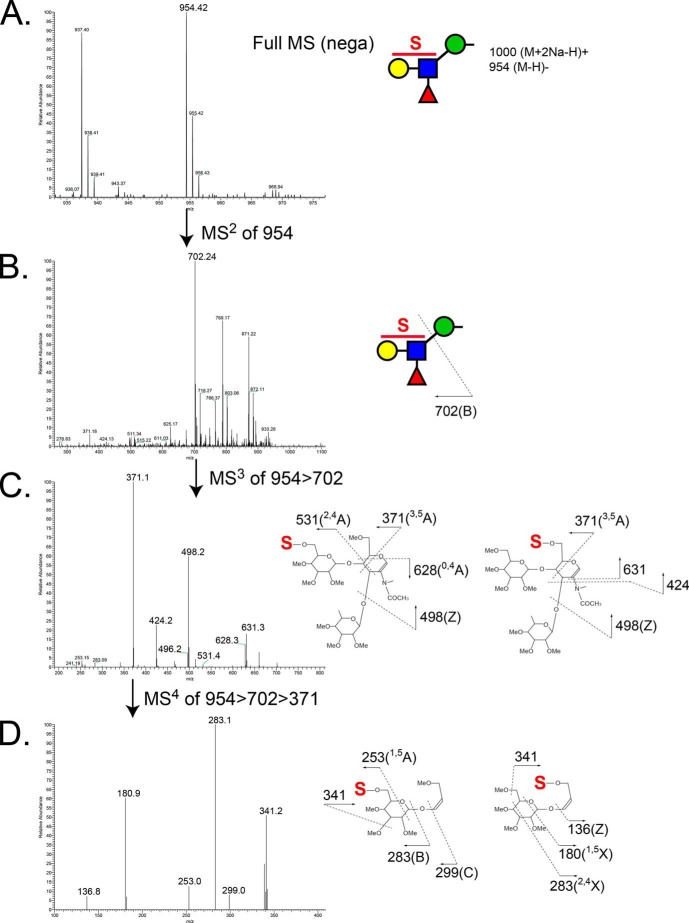
Structural characterization of glycans that partitioned into the aqueous phase following permethylation revealed the presence of sulfation on O-GalNAc-initiated glycans and on a broad range of O-mannose-linked glycans. The most abundant sulfated O-mannosyl glycan was detected as a sulfated, sialylated tetrasaccharide (S1NeuAc1Gal1GlcNAc1Man-itol, m/z 1187.5 [M + 2Na − H]+). The asialo trisaccharide core of this structure (S1Gal1GlcNAc1Man-itol, m/z 826.3 [M + 2Na − H]+) and a sulfated, fucosylated O-mannosyl tetrasaccharide (m/z 954 [M − H]−) were detected as the next most abundant sulfated O-mannosyl glycans (Fig. 5B). For all three sulfoglycans, MSn fragmentation supported the assignment of sulfation on either the Gal or the GlcNAc residue (Fig. 7). In the case of the sulfated, sialylated O-mannosyl tetrasaccharide (S1NeuAc1Gal1GlcNAc1Man-itol, m/z 1187.5 [M + 2Na − H]+), sulfation and sialylation were detected on both the Gal and GlcNAc residues; MS3 of m/z 560 yielded a fragment ion at m/z 347 indicating Gal sulfate and an internally sialylated GlcNAc, whereas the fragment ion at m/z 315 demonstrates the existence of sialyl Gal sulfate (Fig. 7, C and D). Likewise, in the case of the sulfated, fucosylated O-mannosyl tetrasaccharide, m/z 954, sulfate was also detected on both the Gal and GlcNAc residues (Fig. 8).
FIGURE 7.
Fragmentation spectra of the major sulfated, non-fucosylated O-mannose-linked glycans released from RPTPζ/phosphacan prepared from early postnatal mouse brains. A, MS2 spectrum of a precursor ion at m/z 826 (S1Hex1HexNAc1Hex-itol [M + 2Na − H]+) detected in the full MS of the aqueous phase in the positive ion mode. Fragment ions at m/z 574 and 706 correspond to a B ion of a sulfated Hex-HexNAc structure and loss of a sulfate group (−120 Da), respectively. B, MS3 spectrum of a fragment ion at m/z 574. Fragment ions indicate that the precursor ion is a mixture of Hex-sulfated and HexNAc-sulfated structures. Fragmentation patterns of 6′-sulfated (left) and 6-sulfated (right) LacNAc structures are depicted. C, MS2 spectrum of the precursor ion at m/z 1187 (S1NA1Hex1HexNAc1Hex-itol [M + 2Na − H]+) from the aqueous phase, detected in positive ion mode. D, subsequent MS3 of a fragment ion at m/z 560 reveals a mixture of Hex-sulfated/sialylated and HexNAc-sulfated/sialylated trisaccharides, as shown by structural diagrams.
FIGURE 8.
MS spectra of the major sulfated, fucosylated O-mannose-linked glycan released from RPTPζ/phosphacan prepared from early postnatal mouse brains. A, enlarged view of full MS spectrum showing sulfated fucosylated O-mannosyl tetrasaccharide, m/z 954, from aqueous phase in the negative ion mode. B, MS2 spectrum of the precursor ion at m/z 954 in negative ion mode. The fragment ion at m/z 702 corresponds to B ion from the cleavage between GlcNAc and Man (sulfated fucosyl-LacNAc moiety). C, MS3 spectrum of the fragment ion at m/z 702 in negative ion mode. Ion peaks were assigned as the fragments of the indicated sulfated fucosyl-LacNAc structures. The most prevalent fragment ion at m/z 371 corresponds to cross-ring cleavage (3,5A) of a GlcNAc residue. D, further fragmentation of the ion at m/z 371 in MS3 produced fragment ions at m/z 253, 283, 299, and 341, which indicate sulfation of the Gal residue, and fragment ions at m/z 136, 180, 283, and 341, which indicate sulfation of the GlcNAc residue.
Previous characterization of the epitope recognized by Cat-315 antibody identified sulfated HNK-1 epitope as a likely candidate, composed of a sulfated terminal glucuronic acid that is O-mannose-linked to RPTPζ/phosphacan (14, 38). Consistent with this assignment, we detected glycans having both non-sulfated and sulfated terminal glucuronic acid on O-mannose-linked glycans (Fig. 9). Together, these data suggest that phosphacan is heavily decorated with a variety of O-mannosyl glycan structures, including novel sulfo-LacNAc modifications and terminal O-mannose-linked HNK-1 glycans.
FIGURE 9.
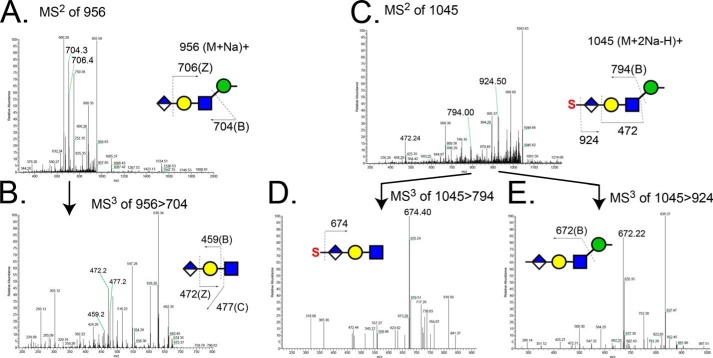
Detection of O-mannose-linked HNK-1 glycans released from RPTPζ/phosphacan prepared from early postnatal mouse brains. A, MS2 spectrum of the precursor ion of an O-mannosyl HNK-1 epitope (non-sulfated form, m/z 956 [M + Na]+) detected in the organic phase in positive ion mode. Fragment ions at m/z 704 and 706 correspond to B ion resulting from cleavage between GlcNAc and Man and Z ion from the cleavage between GlcA and Gal, respectively. B, MS3 spectrum of m/z 704 in A includes peaks for B ion (m/z 459) and C ion (m/z 477) resulting from cleavage between Gal and GlcNAc and Z ion (m/z 472) resulting from the cleavage between GlcA and Gal. C, MS2 spectrum of the precursor ion of an O-mannosyl HNK-1 epitope (sulfated form, m/z 1045 [M + 2Na − H]+) detected in the aqueous phase in positive ion mode. Fragment ions at m/z 794 and 924 correspond to B ions resulting from cleavage between GlcNAc and Man and the loss of sulfate group, respectively. D, MS3 spectrum of the molecular ion at m/z 794 in C. The sulfation position is defined by the fragment ion at m/z 674 (loss of sulfate group, −120 Da) to be exclusively on the hexuronic acid. E, MS3 spectrum of the fragment ion at m/z 924 in C. A fragment ion at m/z 672 corresponds to the B ion resulting from cleavage between Glc and Man.
DISCUSSION
RPTPζ/phosphacan is required for normal nervous system development and function (32, 33, 35). Whether O-mannosylation of this protein contributes to its function has been more difficult to determine, due to the predominating role of another highly mannosylated glycoprotein (α-DG) in CMDs. Nonetheless, the enriched expression of RPTPζ/phosphacan in the CNS and its abundant decoration with O-mannosyl glycans suggest that it may contribute to neurological pathology in these disorders. This study provides a detailed analysis of O-mannosyl antibody epitopes on RPTPζ/phosphacan, a comprehensive characterization of the O-mannose-linked glycan structures that decorate this protein, and a clear demonstration of its cell-specific glycosylation. These elements comprise critical steps toward understanding the precise function of RPTPζ/phosphacan glycosylation.
Previous studies have convincingly demonstrated that Cat-315 and 3F8 are specific to RPTPζ/phosphacan in the early developing brain (21, 38). Our results suggest that O-mannosyl glycoforms of RPTPζ/phosphacan detected by the Cat-315 and 3F8 antibodies predominately detect non-overlapping populations of neural cells. Whereas Cat-315-immunoreactive RPTPζ/phosphacan primarily decorates neurons in the brain (39), 3F8-immunoreactive RPTPζ/phosphacan primarily stains the surface of glial cells, including astrocyte and oligodendrocyte precursors. It is interesting to speculate that in the normal brain, the specific elaboration of O-mannosyl structures may serve to tailor ligand interactions in a cell type-specific manner to modify the function of RPTPζ/phosphacan.
The distribution of Cat-315, 3F8, and 5210 epitopes across the entire population of RPTPζ/phosphacan protein molecules has been largely unknown. Our data demonstrate that the O-mannosylated glycoforms of RPTPζ/phosphacan detected by Cat-315 and 3F8 are largely separable. Furthermore, RPTPζ/phosphacan recognized by antibody 5210 was preferentially detected by Cat-315 over 3F8. All three glycoform populations were similarly reactive for the HNK-1 epitope. These results highlight the specificity with which proteins can acquire differential glycosylation patterns and indicate that glycoform heterogeneity is not random. Given the discrete nature of the glycoforms detected by antibodies against RPTPζ/phosphacan, it is essential that efforts to identify endogenous ligands for RPTPζ/phosphacan consider the potential biases associated with antibody-based enrichment strategies (22, 23, 47).
The presence of reducing end mannitol in preparations of brain CSPGs was described nearly 3 decades ago (4, 6, 48). Our previous work further showed that RPTPζ/phosphacan is hypoglycosylated in the brains of POMGnT1 knock-out animals and shifted to a lower molecular mass, suggesting that RPTPζ/phosphacan is a significant substrate for O-mannosyl glycosylation (14). However, the full structural diversity of these glycans has been only partially characterized. We have now expanded the breadth of the characterized O-linked glycan structures on RPTPζ/phosphacan using a highly enriched preparation.
A recent study by Pacharra and colleagues (49) reported the presence of O-mannose-linked glycans on CSPGs belonging to the lectican family, especially neurocan, brevican, and versican. We show that our RPTPζ/phosphacan preparation was significantly depleted of brevican and somewhat enriched in neurocan, albeit to a lesser extent than the enrichment for RPTPζ/phosphacan. In calf brain lysates, Pacharra and colleagues (49) reported almost 10-fold greater abundance of mucin-type O-GalNAc-linked glycans in comparison with O-mannosyl glycans in samples enriched for neurocan, brevican, or versican. Likewise, a neurocan-enriched fraction that they prepared from mouse brain was more than 2-fold enriched for the mucin-type mono- and disialyl-Core 1 glycans in comparison with O-mannosyl glycans. This enrichment in mucin-type glycans is in stark contrast to the more than 2-fold enrichment of O-mannosyl glycans that we detected in our RPTPζ/phosphacan preparations, indicating a significantly higher relative abundance of O-mannosyl glycans on RPTPζ/phosphacan in comparison with neurocan/brevican/versican. Although it is possible that differences in developmental timing or interspecies glycosylation may impact RPTPζ/phosphacan glycan profiles, the relative enrichment of O-mannosyl glycans, coupled with our inability to detect a molecular mass shift for neurocan or brevican in POMGnT1 knock-out brains, indicates that the glycan profile reported here faithfully represents the diversity of O-mannosyl glycans linked to RPTPζ/phosphacan.
The O-mannose-linked glycans that we detected on RPTPζ/phosphacan include a variety of elongated and branched structures. POMGnT1 activity is required for extension of O-mannosyl glycans and for β1,6-branching of O-mannosyl glycans by GnTVb/GnT1X (20, 50, 51). The O-mannosyl glycans detected on our enriched RPTPζ/phosphacan preparation were also reported to be absent in POMGnT1 knock-out brains (20), strongly suggesting that RPTPζ/phosphacan is a major contributor to O-mannosyl glycan diversity in the mouse brain. The major O-mannosyl glycan detected in our enriched RPTPζ/phosphacan preparation was a fucosylated tetrasaccharide (Lewisx epitope) (m/z = 912.5; Fig. 5), in agreement with previous reports of O-mannosyl glycan diversity in wild-type mice (20). Interestingly, this fucosylated O-mannose glycan is also the major O-mannosyl glycan detected in mice lacking α-DG, further indicating that RPTPζ/phosphacan is a major brain substrate for O-mannosylation (20). Consistent with these observations, Oka and colleagues (52) have recently reported that RPTPζ/phosphacan is the primary carrier of the Lewisx glycan in the developing brain. Our current data detail the precise glycan structure of the Lewisx epitope on RPTPζ/phosphacan as well as its relative abundance within the whole glycan profile and its multiple forms (sulfated, sialylated, and unextended), which should assist further efforts to decipher the function of this modification.
Recent work has shown that a phosphorylated O-mannosyl trisaccharide (GalNAc-β3-GlcNAc-β4-(phosphate 6)-Man-itol) is required for α-DG to bind laminin. This glycan structure is synthesized by the cooperative efforts of the atypical protein kinase SGK196, which phosphorylates mannose at the 6-position, and protein O-mannose β-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 2 (POMGNT2/AGO61/GTDC2), which catalyzes the addition of a β1,4-linked GlcNAc. This GlcNAc residue is then extended with a terminal β3GalNAc, catalyzed by β-1,3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 2 (53). The presence of this phosphorylated O-mannose trisaccharide is required for the addition of laminin-binding glycans catalyzed by LARGE, consisting of a repeating xylose and glucuronic acid oligosaccharide (53–58). Our previous study demonstrated that the molecular mass and reactivity of O-mannose-linked glycan epitopes on RPTPζ/phosphacan were unchanged in mouse models of LARGE myodystrophy mutant mice (14). Accordingly, we did not detect a phosphorylated mannose modification or GalNAc-GlcNAc-Man-itol disaccharides that would be consistent with a β1,4-linked branch structure. This result suggests that RPTPζ/phosphacan is not a substrate for SGK196, AGO61, β-1,3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 2, or LARGE and therefore does not have Core M3 modifications and laminin-binding glycans. The findings from this study support that RPTPζ/phosphacan is decorated with β1,2-elongated and β1,6-branched structures, having both Core M1 and Core M2 structures, and is an apparent substrate for POMGnT1 and GnTVb, which agrees with previously published work (14, 59, 60).
Although the laminin-binding function of Core M3 modifications on α-DG is well characterized, the function of the Core M1 and M2 modifications is less understood. Recently, it was demonstrated that GnTVb/GnTIX knock-out mice, which lack β1,6-branched structures and have reduced Cat-315-immunoreactive RPTPζ/phosphacan, had no obvious neurological phenotypic abnormalities (60, 61). However, a study by Kanekiyo et al. (61) demonstrated that GnTVb/GnTIX knock-out mice had impaired astrocyte activation and an enhanced ability to remyelinate axons in a cuprizone-induced demyelinating model. Therefore, a possible function of branched O-mannose-linked glycan structures may be in mediating responses following neural insult and injury. Other data suggest that branched O-mannose-linked glycans also have a role in regulating the phosphatase activity of RPTPζ. Abbott et al. (57) showed that forced expression of GnTVb/GnT1X enhanced the branching of O-mannosyl glycans on RPTPζ and induced galectin-1-mediated receptor dimerization, which subsequently inhibited the phosphatase activity of RPTPζ and increased the phosphorylation of β-catenin.
Our past work suggested that RPTPζ/phosphacan was elaborated with rare O-mannose-linked HNK-1 glycans (14). Recent work detailed the structures of glycans carrying the HNK-1 epitope on RPTPζ/phosphacan and showed that this protein is the main carrier of unique O-mannose-linked terminal HNK-1 glycans (62). HNK-1 glycans have a role in learning and memory (63, 64), and RPTPζ/phosphacan knock-out mice have been shown to exhibit parallel deficits (35), suggesting that O-mannosyl glycans may be responsible for these changes.
In our O-glycan analysis, we identified several novel O-mannose-linked glycan structures. Of particular interest were the numerous O-mannosyl structures bearing sulfo-LacNAc modifications. The existence of sulfated O-mannosyl glycans on brain CSPGs was first suggested in elegant compositional and fast atom bombardment MS studies performed over 25 years ago (48). Our results further define the diversity of the glycan core structures found on RPTPζ/phosphacan that carry sulfate. For instance, all of the sulfo-LacNAc disaccharides that we detected existed as isomeric mixtures of glycan topologies that encompass sulfated Gal or sulfated GlcNAc residues, with and without sialic acid. The identified set of proteins bearing O-mannosyl glycans is growing rapidly and now includes the lecticans (49), cadherins (15, 17), Neurofascin186 (16), and CD29 (13) in addition to RPTPζ/phosphacan and α-DG. However, it is currently unclear whether all of these O-mannosylated proteins carry the same array of glycan structures, particularly sulfated O-mannosylated glycans. The technologies that we have used to characterize glycan sulfation on our RPTPζ/phosphacan preparation will now need to be applied to enriched preparations of other O-mannosylated proteins in order to more fully appreciate the protein specificity of O-mannosyl glycan diversity.
In summary, our results demonstrate that O-mannosyl-linked carbohydrate epitopes on RPTPζ/phosphacan, detected by Cat-315 and 3F8 antibodies, differentially decorate neuronal and glial subclasses, respectively. We also demonstrate that Cat-315- and 3F8-reactive RPTPζ/phosphacan pools are biochemically distinct. Our analysis of the structural diversity of O-mannose-linked glycans on RPTPζ/phosphacan, including sulfated structures, indicates that RPTPζ/phosphacan is a significant substrate for O-mannosyl glycosylation and suggests that these glycan modifications tailor protein function in a cell type-specific manner.
Acknowledgment
We thank Wendi Burnette for technical assistance.
This work was supported, in whole or in part, by National Institutes of Health (NIH), NINDS, Grant NS069660 (to R. T. M.). Support and access to instrumentation was also provided through NIH, NCRR, Grant P41RR018502 and NIH, NIGMS, Grant P41GM103490.
- CMD
- congenital muscular dystrophy
- α-DG
- α-dystroglycan
- POMGnT1
- protein O-mannose β-1,2-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 1
- RPTPζ
- receptor protein-tyrosine phosphatase ζ
- CSPG
- chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan
- AraC
- arabinofuranosyl cytidine
- DIV
- day(s) in vitro
- BTH
- bovine testicular hyaluronidase
- DCX
- doublecortin
- CS-GAG
- chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycan
- MSn
- multidimensional MS
- Hex
- hexose
- Man
- mannose
- Fuc
- fucose
- HexNAc
- N-acetylhexosamine
- NeuAc
- N-acetylneuraminic acid
- Pn
- postnatal day n
- Pur
- fractions of eluate identified to contain RPTPζ/phosphacan
- IP
- immunoprecipitated.
REFERENCES
- 1. Moremen K. W., Tiemeyer M., Nairn A. V. (2012) Vertebrate protein glycosylation: diversity, synthesis and function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 13, 448–462 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Lommel M., Strahl S. (2009) Protein O-mannosylation: conserved from bacteria to humans. Glycobiology 19, 816–828 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Chai W., Yuen C. T., Kogelberg H., Carruthers R. A., Margolis R. U., Feizi T., Lawson A. M. (1999) High prevalence of 2-mono- and 2,6-di-substituted manol-terminating sequences among O-glycans released from brain glycopeptides by reductive alkaline hydrolysis. Eur. J. Biochem. 263, 879–888 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Finne J., Krusius T., Margolis R. K., Margolis R. U. (1979) Novel mannitol-containing oligosaccharides obtained by mild alkaline borohydride treatment of a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan from brain. J. Biol. Chem. 254, 10295–10300 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Kogelberg H., Chai W., Feizi T., Lawson A. M. (2001) NMR studies of mannitol-terminating oligosaccharides derived by reductive alkaline hydrolysis from brain glycoproteins. Carbohydr. Res. 331, 393–401 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Krusius T., Finne J., Margolis R. K., Margolis R. U. (1986) Identification of an O-glycosidic mannose-linked sialylated tetrasaccharide and keratan sulfate oligosaccharides in the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan of brain. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 8237–8242 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Beltrán-Valero de Bernabe D., Currier S., Steinbrecher A., Celli J., van Beusekom E., van der Zwaag B., Kayserili H., Merlini L., Chitayat D., Dobyns W. B., Cormand B., Lehesjoki A. E., Cruces J., Voit T., Walsh C. A., van Bokhoven H., Brunner H. G. (2002) Mutations in the O-mannosyltransferase gene POMT1 give rise to the severe neuronal migration disorder Walker-Warburg syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71, 1033–1043 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Brockington M., Blake D. J., Prandini P., Brown S. C., Torelli S., Benson M. A., Ponting C. P., Estournet B., Romero N. B., Mercuri E., Voit T., Sewry C. A., Guicheney P., Muntoni F. (2001) Mutations in the fukutin-related protein gene (FKRP) cause a form of congenital muscular dystrophy with secondary laminin α2 deficiency and abnormal glycosylation of α-dystroglycan. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 69, 1198–1209 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Brockington M., Yuva Y., Prandini P., Brown S. C., Torelli S., Benson M. A., Herrmann R., Anderson L. V., Bashir R., Burgunder J. M., Fallet S., Romero N., Fardeau M., Straub V., Storey G., Pollitt C., Richard I., Sewry C. A., Bushby K., Voit T., Blake D. J., Muntoni F. (2001) Mutations in the fukutin-related protein gene (FKRP) identify limb girdle muscular dystrophy 2I as a milder allelic variant of congenital muscular dystrophy MDC1C. Hum. Mol. Genet. 10, 2851–2859 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Schessl J., Zou Y., Bönnemann C. G. (2006) Congenital muscular dystrophies and the extracellular matrix. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 13, 80–89 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Moore S. A., Saito F., Chen J., Michele D. E., Henry M. D., Messing A., Cohn R. D., Ross-Barta S. E., Westra S., Williamson R. A., Hoshi T., Campbell K. P. (2002) Deletion of brain dystroglycan recapitulates aspects of congenital muscular dystrophy. Nature 418, 422–425 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Satz J. S., Ostendorf A. P., Hou S., Turner A., Kusano H., Lee J. C., Turk R., Nguyen H., Ross-Barta S. E., Westra S., Hoshi T., Moore S. A., Campbell K. P. (2010) Distinct functions of glial and neuronal dystroglycan in the developing and adult mouse brain. J. Neurosci. 30, 14560–14572 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Bleckmann C., Geyer H., Lieberoth A., Splittstoesser F., Liu Y., Feizi T., Schachner M., Kleene R., Reinhold V., Geyer R. (2009) O-Glycosylation pattern of CD24 from mouse brain. Biol. Chem. 390, 627–645 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Dwyer C. A., Baker E., Hu H., Matthews R. T. (2012) RPTPζ/phosphacan is abnormally glycosylated in a model of muscle-eye-brain disease lacking functional POMGnT1. Neuroscience 220, 47–61 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Lommel M., Winterhalter P. R., Willer T., Dahlhoff M., Schneider M. R., Bartels M. F., Renner-Müller I., Ruppert T., Wolf E., Strahl S. (2013) Protein O-mannosylation is crucial for E-cadherin-mediated cell adhesion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 21024–21029 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Pacharra S., Hanisch F. G., Breloy I. (2012) Neurofascin 186 is O-mannosylated within and outside of the mucin domain. J. Proteome Res. 11, 3955–3964 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Winterhalter P. R., Lommel M., Ruppert T., Strahl S. (2013) O-Glycosylation of the non-canonical T-cadherin from rabbit skeletal muscle by single mannose residues. FEBS Lett. 587, 3715–3721 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Liu J., Ball S. L., Yang Y., Mei P., Zhang L., Shi H., Kaminski H. J., Lemmon V. P., Hu H. (2006) A genetic model for muscle-eye-brain disease in mice lacking protein O-mannose 1,2-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (POMGnT1). Mech. Dev. 123, 228–240 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Yoshida A., Kobayashi K., Manya H., Taniguchi K., Kano H., Mizuno M., Inazu T., Mitsuhashi H., Takahashi S., Takeuchi M., Herrmann R., Straub V., Talim B., Voit T., Topaloglu H., Toda T., Endo T. (2001) Muscular dystrophy and neuronal migration disorder caused by mutations in a glycosyltransferase, POMGnT1. Dev. Cell 1, 717–724 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Stalnaker S. H., Aoki K., Lim J. M., Porterfield M., Liu M., Satz J. S., Buskirk S., Xiong Y., Zhang P., Campbell K. P., Hu H., Live D., Tiemeyer M., Wells L. (2011) Glycomic analyses of mouse models of congenital muscular dystrophy. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 21180–21190 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Maurel P., Rauch U., Flad M., Margolis R. K., Margolis R. U. (1994) Phosphacan, a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan of brain that interacts with neurons and neural cell-adhesion molecules, is an extracellular variant of a receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91, 2512–2516 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Barnea G., Grumet M., Milev P., Silvennoinen O., Levy J. B., Sap J., Schlessinger J. (1994) Receptor tyrosine phosphatase β is expressed in the form of proteoglycan and binds to the extracellular matrix protein tenascin. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 14349–14352 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Rauch U., Gao P., Janetzko A., Flaccus A., Hilgenberg L., Tekotte H., Margolis R. K., Margolis R. U. (1991) Isolation and characterization of developmentally regulated chondroitin sulfate and chondroitin/keratan sulfate proteoglycans of brain identified with monoclonal antibodies. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 14785–14801 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Garwood J., Heck N., Reichardt F., Faissner A. (2003) Phosphacan short isoform, a novel non-proteoglycan variant of phosphacan/receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase-β, interacts with neuronal receptors and promotes neurite outgrowth. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 24164–24173 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Maurel P., Meyer-Puttlitz B., Flad M., Margolis R. U., Margolis R. K. (1995) Nucleotide sequence and molecular variants of rat receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase-ζ/β. DNA Sequence 5, 323–328 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Maeda N., Hamanaka H., Oohira A., Noda M. (1995) Purification, characterization and developmental expression of a brain-specific chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan, 6B4 proteoglycan/phosphacan. Neuroscience 67, 23–35 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Shitara K., Yamada H., Watanabe K., Shimonaka M., Yamaguchi Y. (1994) Brain-specific receptor-type protein-tyrosine phosphatase RPTP β is a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 20189–20193 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Canoll P. D., Petanceska S., Schlessinger J., Musacchio J. M. (1996) Three forms of RPTP-β are differentially expressed during gliogenesis in the developing rat brain and during glial cell differentiation in culture. J. Neurosci. Res. 44, 199–215 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Harroch S., Furtado G. C., Brueck W., Rosenbluth J., Lafaille J., Chao M., Buxbaum J. D., Schlessinger J. (2002) A critical role for the protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type Z in functional recovery from demyelinating lesions. Nat. Genet. 32, 411–414 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Hayashi N., Miyata S., Yamada M., Kamei K., Oohira A. (2005) Neuronal expression of the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans receptor-type protein-tyrosine phosphatase β and phosphacan. Neuroscience 131, 331–348 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Ida M., Shuo T., Hirano K., Tokita Y., Nakanishi K., Matsui F., Aono S., Fujita H., Fujiwara Y., Kaji T., Oohira A. (2006) Identification and functions of chondroitin sulfate in the milieu of neural stem cells. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 5982–5991 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Lamprianou S., Chatzopoulou E., Thomas J. L., Bouyain S., Harroch S. (2011) A complex between contactin-1 and the protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPRZ controls the development of oligodendrocyte precursor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 17498–17503 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. McClain C. R., Sim F. J., Goldman S. A. (2012) Pleiotrophin suppression of receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase-β/ζ maintains the self-renewal competence of fetal human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells. J. Neurosci. 32, 15066–15075 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Meng K., Rodriguez-Peña A., Dimitrov T., Chen W., Yamin M., Noda M., Deuel T. F. (2000) Pleiotrophin signals increased tyrosine phosphorylation of β-catenin through inactivation of the intrinsic catalytic activity of the receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase β/ζ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97, 2603–2608 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Niisato K., Fujikawa A., Komai S., Shintani T., Watanabe E., Sakaguchi G., Katsuura G., Manabe T., Noda M. (2005) Age-dependent enhancement of hippocampal long-term potentiation and impairment of spatial learning through the Rho-associated kinase pathway in protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type Z-deficient mice. J. Neurosci. 25, 1081–1088 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Ranjan M., Hudson L. D. (1996) Regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation and protein tyrosine phosphatases during oligodendrocyte differentiation. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 7, 404–418 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Soh B. S., Song C. M., Vallier L., Li P., Choong C., Yeo B. H., Lim E. H., Pedersen R. A., Yang H. H., Rao M., Lim B. (2007) Pleiotrophin enhances clonal growth and long-term expansion of human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 25, 3029–3037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Dino M. R., Harroch S., Hockfield S., Matthews R. T. (2006) Monoclonal antibody Cat-315 detects a glycoform of receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase β/phosphacan early in CNS development that localizes to extrasynaptic sites prior to synapse formation. Neuroscience 142, 1055–1069 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Lander C., Zhang H., Hockfield S. (1998) Neurons produce a neuronal cell surface-associated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan. J. Neurosci. 18, 174–183 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Giamanco K. A., Morawski M., Matthews R. T. (2010) Perineuronal net formation and structure in aggrecan knockout mice. Neuroscience 170, 1314–1327 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Viapiano M. S., Matthews R. T., Hockfield S. (2003) A novel membrane-associated glycovariant of BEHAB/brevican is up-regulated during rat brain development and in a rat model of invasive glioma. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 33239–33247 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Goldberg H. A., Warner K. J. (1997) The staining of acidic proteins on polyacrylamide gels: enhanced sensitivity and stability of “Stains-all” staining in combination with silver nitrate. Anal. Biochem. 251, 227–233 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Aoki K., Porterfield M., Lee S. S., Dong B., Nguyen K., McGlamry K. H., Tiemeyer M. (2008) The diversity of O-linked glycans expressed during Drosophila melanogaster development reflects stage- and tissue-specific requirements for cell signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 30385–30400 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Anumula K. R., Taylor P. B. (1992) A comprehensive procedure for preparation of partially methylated alditol acetates from glycoprotein carbohydrates. Anal. Biochem. 203, 101–108 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Kumagai T., Katoh T., Nix D. B., Tiemeyer M., Aoki K. (2013) In-gel β-elimination and aqueous-organic partition for improved O- and sulfoglycomics. Anal. Chem. 85, 8692–8699 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Faissner A., Heck N., Dobbertin A., Garwood J. (2006) DSD-1-proteoglycan/phosphacan and receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase-β isoforms during development and regeneration of neural tissues. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 557, 25–53 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Milev P., Friedlander D. R., Sakurai T., Karthikeyan L., Flad M., Margolis R. K., Grumet M., Margolis R. U. (1994) Interactions of the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan phosphacan, the extracellular domain of a receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase, with neurons, glia, and neural cell adhesion molecules. J. Cell Biol. 127, 1703–1715 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Krusius T., Reinhold V. N., Margolis R. K., Margolis R. U. (1987) Structural studies on sialylated and sulphated O-glycosidic mannose-linked oligosaccharides in the chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan of brain. Biochem. J. 245, 229–234 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Pacharra S., Hanisch F. G., Mühlenhoff M., Faissner A., Rauch U., Breloy I. (2013) The lecticans of mammalian brain perineural net are O-mannosylated. J. Proteome Res. 12, 1764–1771 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Alvarez-Manilla G., Troupe K., Fleming M., Martinez-Uribe E., Pierce M. (2010) Comparison of the substrate specificities and catalytic properties of the sister N-acetylglucosaminyltransferases, GnT-V and GnT-Vb (IX). Glycobiology 20, 166–174 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Inamori K., Endo T., Gu J., Matsuo I., Ito Y., Fujii S., Iwasaki H., Narimatsu H., Miyoshi E., Honke K., Taniguchi N. (2004) N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase IX acts on the GlcNAc β1,2-Man α1-Ser/Thr moiety, forming a 2,6-branched structure in brain O-mannosyl glycan. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 2337–2340 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Yaji S., Manya H., Nakagawa N., Takematsu H., Endo T., Kannagi R., Yoshihara T., Asano M., Oka S. (2015) Major glycan structure underlying expression of the Lewis X epitope in the developing brain is O-mannose-linked glycans on phosphacan/RPTPβ. Glycobiology 25, 376–385 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Yoshida-Moriguchi T., Willer T., Anderson M. E., Venzke D., Whyte T., Muntoni F., Lee H., Nelson S. F., Yu L., Campbell K. P. (2013) SGK196 is a glycosylation-specific O-mannose kinase required for dystroglycan function. Science 341, 896–899 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Inamori K., Hara Y., Willer T., Anderson M. E., Zhu Z., Yoshida-Moriguchi T., Campbell K. P. (2013) Xylosyl- and glucuronyltransferase functions of LARGE in α-dystroglycan modification are conserved in LARGE2. Glycobiology 23, 295–302 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Yagi H., Nakagawa N., Saito T., Kiyonari H., Abe T., Toda T., Wu S. W., Khoo K. H., Oka S., Kato K. (2013) AGO61-dependent GlcNAc modification primes the formation of functional glycans on α-dystroglycan. Sci. Rep. 3, 3288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Yoshida-Moriguchi T., Yu L., Stalnaker S. H., Davis S., Kunz S., Madson M., Oldstone M. B., Schachter H., Wells L., Campbell K. P. (2010) O-Mannosyl phosphorylation of α-dystroglycan is required for laminin binding. Science 327, 88–92 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Praissman J. L., Live D. H., Wang S., Ramiah A., Chinoy Z. S., Boons G. J., Moremen K. W., Wells L. (2014) B4GAT1 is the priming enzyme for the LARGE-dependent functional glycosylation of α-dystroglycan. eLife 10.7554/eLife.03943 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Willer T., Inamori K., Venzke D., Harvey C., Morgensen G., Hara Y., Beltran Valero de Bernabe D., Yu L., Wright K. M., Campbell K. P. (2014) The glucuronyltransferase B4GAT1 is required for initiation of LARGE-mediated α-dystroglycan functional glycosylation. eLife 10.7554/eLife.03941 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Abbott K. L., Matthews R. T., Pierce M. (2008) Receptor tyrosine phosphatase β (RPTPβ) activity and signaling are attenuated by glycosylation and subsequent cell surface galectin-1 binding. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 33026–33035 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Lee J. K., Matthews R. T., Lim J. M., Swanier K., Wells L., Pierce J. M. (2012) Developmental expression of the neuron-specific N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase Vb (GnT-Vb/IX) and identification of its in vivo glycan products in comparison with those of its paralog, GnT-V. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 28526–28536 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Kanekiyo K., Inamori K., Kitazume S., Sato K., Maeda J., Higuchi M., Kizuka Y., Korekane H., Matsuo I., Honke K., Taniguchi N. (2013) Loss of branched O-mannosyl glycans in astrocytes accelerates remyelination. J. Neurosci. 33, 10037–10047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Morise J., Kizuka Y., Yabuno K., Tonoyama Y., Hashii N., Kawasaki N., Manya H., Miyagoe-Suzuki Y., Takeda S., Endo T., Maeda N., Takematsu H., Oka S. (2014) Structural and biochemical characterization of O-mannose-linked human natural killer-1 glycan expressed on phosphacan in developing mouse brains. Glycobiology 24, 314–324 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Yamamoto S., Oka S., Inoue M., Shimuta M., Manabe T., Takahashi H., Miyamoto M., Asano M., Sakagami J., Sudo K., Iwakura Y., Ono K., Kawasaki T. (2002) Mice deficient in nervous system-specific carbohydrate epitope HNK-1 exhibit impaired synaptic plasticity and spatial learning. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 27227–27231 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Yoshihara T., Sugihara K., Kizuka Y., Oka S., Asano M. (2009) Learning/memory impairment and reduced expression of the HNK-1 carbohydrate in β4-galactosyltransferase-II-deficient mice. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 12550–12561 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]