Abstract
AIM: To summarize the clinical impact of a formal training for the effectiveness and safety of endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastrointestinal cancer.
METHODS: We searched databases including PubMed, EMBASE and the Cochrane Library and Science citation Index updated to August 2014 to include eligible articles. In the Meta-analysis, the main outcome measurements were en bloc resection rate, local recurrence rate (R0) and the incidence of procedure-related complications (perforation, bleeding).
RESULTS: En bloc resection was high for both, dissecting stomach tumors with an overall percentage of 93.2% (95%CI: 90.5-95.8) and dissecting colorectal tumors with an overall percentage of 89.4% (95%CI: 85.1-93.7). Although the number of studies reporting R0 resection (the dissected specimen was revealed free of tumor in both vertical and lateral margins) was small, the overall estimates for R0 resection were 81.4% (95%CI: 72-90.8) for stomach and 85.9% (95%CI: 77.5-95.5) for colorectal tumors, respectively. The analysis showed that the percentage of immediate perforation and bleeding were very low; 4.96 (95%CI: 3.6-6.3) and 1.4% (95%CI: 0.8-1.9) for colorectal tumors and 3.1% (95%CI: 2.0-4.1) and 4.8% (95%CI: 2.8-6.7) for stomach tumors, respectively.
CONCLUSION: In order to obtain the same rate of success of the analyzed studies it is a necessity to create training centers in the western countries during the “several years” of gastroenterology residence first only to teach EGC diagnose and second only to train endoscopic submucosal dissection.
Keywords: Endoscopic submucosal dissection, Training
Core tip: Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) has gained widespread use in Asia because of a well-documented higher en bloc and curative resection rates for early neoplastic gastrointestinal lesions. Unfortunately, ESD has not been yet widespread in the West due to remain the very flat learning curve and lack of training resources. In Asia, ESD skills are acquired in the time-honored mentor/apprentice model over a period of few years. Although, there is a great heterogeneity in the medical literature reports about training and learning curve of ESD. In this meta analysis we had analyzed the results from these training centers reports. Because technical maturation often requires measurable standard to achieve.
INTRODUCTION
There are few training centers around the world in which an endoscopy fellow can be trained in the ESD technique. There is probably only a formal ESD training program in Asian countries (Japan, South Korea and China). As ESD is a highly technical and demanding minimal invasive procedure, endoscopists require training before performing the procedure. The operator must possess a good understanding of all aspects of ESD: full knowledge of early GI lesions, the endoscopes, EUS, ESD knives, electro surgical unit parameters, injection agents, sedation, complications and other aspects.
In Asian countries like Japan, South Korea and China, gastrointestinal intraepithelial neoplasm is more prevalent than in Western countries. Accordingly, most medical institutions in Japan provide training (in a stepwise manner): initially, endoscopists participate as an assistant, starting with ESD in the gastric antrum or the rectum with a supervisor, then in the proximal stomach, the colon or the esophagus. In contrast, in Western countries, cases of early gastrointestinal lesions are less diagnosed, resulting in a slow introduction of the ESD technique. Efforts are currently underway to change this situation. Possible solutions to improve training and experience are the use of animal models and the establishment of training centers. Further, deficiencies in training and experience can now be more rapidly overcome as a result of new technologies. As described above, new advances have led to devices that are easy to handle, making it simpler for beginners to perform ESD. Devices with scissors and forceps, like the Clutch Cutter or other covered devices, are easier to use, leading to fewer complications (e.g., perforation), although the procedure time is longer than those with non-covered devices. The other new approach in ESD, the use of mesna (2-mercaptoethanesulfonate sodium), may also make submucosal dissection safer and faster.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Data sources and searches
We searched databases including PubMed, EMBASE and the Cochrane Library and Science citation Index updated to August 2014 to identify related articles in English language that review Endoscopic submucosal dissection training[1-121]. All bibliographies were indentified in the reference lists and were analyzed separately by two experts in ESD during the selection process. The initial searching Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) used were “Endoscopic submucosal dissection”, afterwards “Endoscopic submucosal dissection training” and finally the articles that does not analyze the operation time, en bloc resection rate, local recurrence rate and the incidence of procedure-related complications were excluded (Figure 1A).
Figure 1.
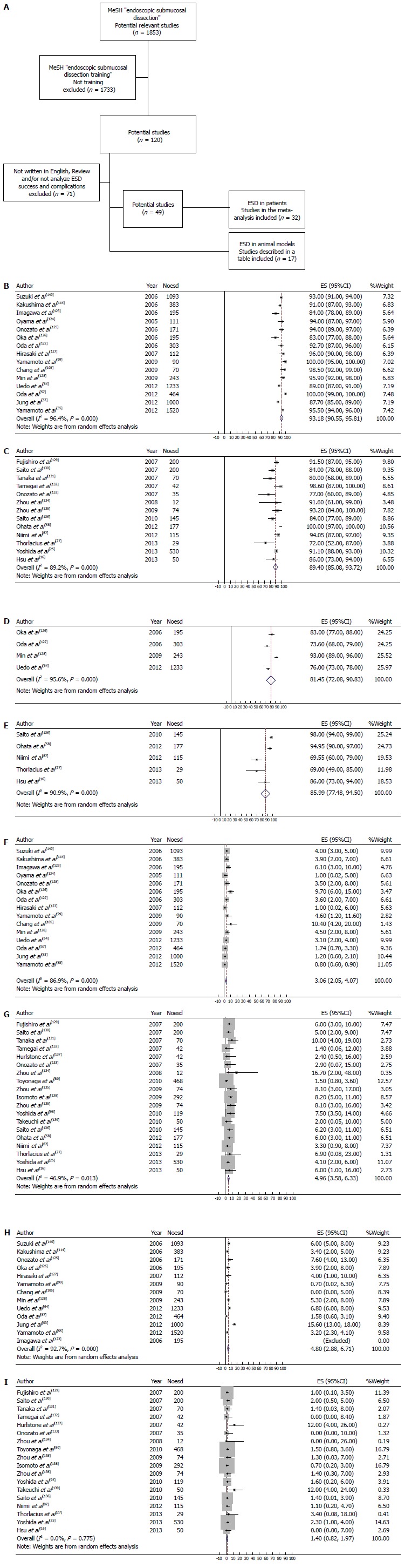
Flow diagram of trial selection and en-bloc resection percentage %. A: Flow diagram of trial selection; B: Stomach ESD: En-bloc resection percentage %; C: Colorectal ESD: En-bloc resection percentage %; D: Stomach ESD: Local recurrence (R0) rate %; E: Colorectal ESD: Local recurrence (R0) rate %; F: Stomach ESD: Perforation rate %; G: Colorectal ESD: Perforation rate %; H: Stomach ESD: Bleeding rate %; I: Colorectal ESD: Bleeding rate %. MeSH: Medical Subject Heading; ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection.
Study selection
The inclusion and exclusion criteria are shown in Table 1.
Table 1.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
| Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria |
| ESD in patients | Case report |
| Report ESD success en bloc resection rate, local recurrence rate | Comment |
| (R0) and the incidence of procedure-related complications | Review |
| (perforation, bleeding) | Letters to editor |
| Written in English | Insufficient data |
| Guidelines |
ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection.
Data extraction and quality assessment
Data were extracted with a predefined MeSH criteria by one investigator and confirmed by the others according to a data extraction form. The following data were collected: year of publication, first author, country, number of participants, site of the lesions and lesions in each group, tumor size and endpoints (en bloc resection rate, local recurrence rate, and complications). The definitions of the endpoints were: (1) site of resection; (2) en bloc -removal in one piece without fragmentation; (3) local recurrencte rate - during the follow-up an histological diagnosis of tumor at the resected site; (4) operation time - from marking to complete resection; and (5) rate of complications - related bleeding or perforation incidence.
Statistical analysis
Meta-analysis: The statistical review of the study was performed by a biomedical statician of the Infectology department from the National Institute of Medical Sciences and Nutrition S.Z. (Mexico). The DerSimonian/Laird random effects model was used due to expected heterogeneity among studies. Statistical heterogeneity was assessed using the Higgins I2 test. For the Higgins test, I2 < 25% indicates low heterogeneity, 25%-50% moderate and > 50% severe heterogeneity. Preplanned analyses included analyses limited to studies including resection of stomach tumors and colorectal tumors using endoscopic submucosal dissection. Data quality assurance and data analysis were conducted using StataTM 12.0 (Statistics/Data analysis Special Edition; Statacorp, College Station, Texas, United States). All statistical test in the analysis were two-sided and were conducted with α = 0.05 (95%CI).
RESULTS
Study selection
A total of 1853 were retrieved with the MeSH “endoscopic submucosal dissection” to estimate the potential studies for the meta-analysis. Afterwards, we refine the search including the word training with the MeSH “endoscopic submucosal dissection training” and 1733 were excluded. In the remaining 120 potential studies 71 were excluded because of the exclusion criteria in Table 1[1-12,14-16,18-28,30-33,35-40,42-50,52-62,64-82,95-114].
From the 49 remaining studies 32 were included in the meta-analysis. All of these 32 studies were in human patients respective case/control studies, not randomized controlled trials.
En bloc resection rate (Figures 1B and C)
The present analysis shows that the percentage of en bloc resection was high for both, dissecting stomach tumors with an overall percentage of 93.2% (95%CI: 90.5-95.8) and dissecting colorectal tumors with an overall percentage of 89.4% (95%CI: 85.1-93.7).
Local recurrence rate (Figures 1D and E)
Although the number of studies reporting R0 resection (the dissected specimen was revealed free of tumor in both vertical and lateral margins) was small, the overall estimates for R0 resection were 81.4% (95%CI: 72-90.8) and 85.9% (95%CI: 77.5-95.5) for stomach and colorectal tumors, respectively.
Procedure-related complications
Data for procedure-related complications were reported in all of the studies included in the meta-analysis. The analysis showed that the percentage of immediate perforation and bleeding were very low.
Perforation rate (Figures 1F and G)
The perforation rate was 3.1% (95%CI: 2.0-4.1) for stomach tumors and 4.96 (95%CI: 3.6-6.3) for colorectal tumors. In most studies, late perforation and bleeding was not reported and thus not included in the current analysis.
Bleeding rate (Figures 1H and I)
The bleeding rate was 4.8% (95%CI: 2.8-6.7) for stomach tumors and 1.4% (95%CI: 0.8-1.9) for colorectal tumors.
Finally, the last 17 studies were in animal models and even though they were not included in the meta-analysis, we resume them in a table that contains: author, year, type of animal model, number of patients, organ and main conclusion (Table 2)[13,17,29,34,41,51,63,83,94,96,115-121].
Table 2.
Endoscopic submucosal dissection studies in animal models
| Ref. | Year | Model | n | Organ | Main conclusion |
| González et al[17] | 2013 | Porcine | 30 | Stomach | A sequential ESD training program of a unique endoscopist contributed to learning ESD for its subsequent application in humans, yielding good results in efficacy and safety |
| Takizawa et al[13] | 2013 | Porcine | 30 | Colon | Large mucosal target sites in the rectum and distal colon could be safely removed en bloc by means of a hybrid technique, SEMR, with blunt submucosal balloon dissection |
| Moss et al[115] | 2012 | Porcine | 10 | Colon | HK-ESD with SG submucosal injection is superior to CSI-EMR for en bloc excision of 50 mm diameter lesions. The technique is rapidly learn |
| Gostout et al[41] | 2012 | Porcine | 16 | Rectum and colon | Large mucosal target sites in the rectum and distal colon can be safely removed en bloc by means of a hybrid technique, ie, submucosal endoscopy with mucosal resection, combining elements of ESD with our SEMF method |
| Kumano et al[117] | 2012 | Porcine | 24 | Esophagus | PCH permits more reliable ESD of the esophagus without complications than do SH and HS |
| Balogh et al[51] | 2012 | Porcine | 15 | Esophagus | Training in live pig models could help endoscopists to overcome the learning curve and minimize the risk of complications before starting the procedure in humans Reduction in the resection time and low risk of complications, especially bleeding, could be achieved by the application of a flush knife |
| Tanaka et al[63] | 2012 | Porcine ex vivo | 10 | stomach | Ex vivo training model was helpful to endoscopists with experience in gastric ESD in acquiring the basic skills for performing esophageal ESD |
| Parra-Blanco et al[29] | 2011 | Porcine | 18 | Stomach | A Clip-band traction technique is feasible, safe, effective, and relatively inexpensive gastric ESD |
| Von Renteln et al[118] | 2011 | Porcine | 12 | Stomach | Submucosal mesna injection did not affect ESD procedure times but was associated with a trend toward a lower incidence of intraprocedural bleeding |
| Tanimoto et al[94] | 2011 | Canine | 10 | Esophagus | ECE-ESD training is feasible in canine models for postgraduate endoscopy fellows |
| Hon et al[96] | 2010 | Porcine | 10 | Colon | Technical proficiency improved by repetition. This setup may be a promising training model for endoscopists working in areas with a low incidence of early gastric cancer |
| Von Renteln et al[119] | 2010 | Porcine | 12 | Stomach | The flexible Maryland dissector was demonstrated to be efficient, safe, and feasible for facilitating gastric ESD |
| Parra-Blanco et al[34] | 2010 | Porcine | 30 | Esophagus stomach | Training in animal models could help endoscopists overcome the learning curve before starting ESD in humans |
| Moss et al[116] | 2010 | Porcine | 10 | Colon | CSI-EMR with submucosal injection of succinylated gelatin is safe and superior to conventional EMR.With experience, total procedure duration is comparable |
| Von Delius et al[120] | 2008 | Porcine | 10 | Stomach | PMT-ESD is feasible and safe. With the use of PA-ES, mucosal pieces of various sizes can be resected en bloc in gastric locations that are difficult to access by flexible endoscopy alone |
| Yamasaki et al[121] | 2006 | Porcine | 2 | Stomach | ESD by submucosal injection of viscous SCMC solution appeared to be an easy, safe, and technically efficient method for dissection of gastric lesions |
| Neuhaus et al[83] | 2006 | Porcine | 17 | Stomach | The R-scope (double channel endoscope) facilitated ESD of large gastric areas. Procedure is technically demanding and time-consuming, with a high risk of perforation may be related to an insufficient volume of solution being injected submucosally |
HK: Hybrid knife; ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection; CSI-EMR: Circumferential submucosal incision endoscopic mucosal resection; SEMF: Mucosal safety valve flap; HS: Hypertonic saline solution; PCH: Photocrosslinkable chitosan hydrogel; SFC: Submucosal fluid cushion; SH: Sodium hyaluronate; ECE: En bloc circumferential esophageal; PA-ES: Percutaneously assisted endoscopic surgery; PMT-ESD: PEG-minitrocar ESD; SCMC: Sodium carboxymethylcellulose.
DISCUSSION
To our knowledge, this systematic review and meta-analysis is the first to analyze the impact of a formal training in ESD for early gastrointestinal cancer. Probably there are ESD formal training centers only in the Asian countries (Japan, China and South Korea). For the above reason almost 100% of the analyzed studies were from Asia. All the studies included in our analysis were done in a formal ESD training setting although most of them does not include the number of trainees and/or a comparison between preceptees vs experts and thus not included in the current analysis. The present study shows that the percentage of en bloc resection was high for both, dissecting stomach and colorectal tumors. Even with a small number of studies reporting R0 resection (the dissected specimen was revealed free of tumor in both vertical and lateral margins), the overall estimates for R0 resection were 81.4% (95%CI: 72-90.8) and 85.9% (95%CI: 77.5-95.5) for stomach and colorectal tumors respectively. The analysis also showed that the percentage of immediate perforation and bleeding were very low. ESD was developed in Japan in the year 1999 to preserve intact gastrointestinal function and for en bloc resection of lesions larger than 2 cm. ESD also has made it possible to resects early gastrointestinal tumors even with large submucosal fibrosis or ulcerative scars in an en bloc fashion and it has gradually gained acceptance as a standard treatment for these tumors. The ESD era began with pioneers trained in Japan on South Korea (2003-now) and in China (2006-now) rapidly gaining expertise and acceptance. Hotta et al[77] reported that 80 procedures must be carried out to acquire skill at ESD. In order to acquire this skill all the procedures even in animal models must be carried out under supervision of ESD experts and with availability of all the equipment and high trained team. Because this is not just a fact of endoscopic skills but of knowledge, technology and team work. This procedure should never be trained in an experimental (“not supervised by an ESD expert”) fashion with animal models just focusing on the dissection technique without firstly make a good analysis of the borders and deepness of the early gastrointestinal cancer (EGC) lesion invasion under an expert supervision. Probably the lack of research, diagnose and case series of early gastrointestinal cancer lesions in the Western countries are due to a lack of formal training centers firstly with certified EGC experts and afterwards ESD experts. In order to obtain the same rate of success of the analyzed studies it is a necessity to create training centers in the western countries during the “several years” of gastroenterology residence first only to teach EGC diagnose and second only to train ESD. In the same manner that the medical techniques should never anticipate the clinic, nor the endoscopic skills, nor the technology or both could substitute tutorial training by an expert.
Although, there is a great heterogeneity in the medical literature reports about training and learning curve of ESD. In this meta analysis we had analyzed the results only from the formal training centers reports. The results presented in the literature that can be included in our meta analysis to clarify the training efficacy concerning the procedure length, completeness and complications such as En bloc resection rate, Local recurrence rate, Procedure-related complications, Perforation and Bleeding rate were included. But unfortunately, we can only assume that the procedure was done in a formal training center, such as the one in which some of the authors had been trained. Even when there are very detailed description of the learning curve specially in the Japanese and European reports there is a great heterogeneity of the numeric information presented and thus cannot be included in a meta analysis. There is not uniform information if the procedure was done by a trainee with/without supervision. Also, the analyzed issues in each report has great heterogeneity (animal model, human, periods of time, etc.) and the results are presented for example in ranges but not in mean ± SD. Because technical maturation often requires measurable standard to achieve. As this procedure become more standardized in the Western countries we can also be able to make more precise comparisons between training centers and learning curve. There are no shortcuts and probably we have to find out the way to establish training centers with the same training scheme as the Asian countries if we are expecting to have similar rates of success, but as always time will say.
COMMENTS
Background
Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) was originally developed to preserve intact gastrointestinal function after en bloc resection of early GI cancer lesions larger than 2 cm.
Research frontiers
This systematic review and meta-analysis is the first to analyze the impact of a formal training in ESD for early gastrointestinal cancer.
Innovations and breakthroughs
Authors designed the meta-analysis to systematically evaluate the ESD formal training impact in the early gastrointestinal cancer regarding en bloc resection rate, local recurrence rate and procedure-related complications rate.
Applications
The conclusions of this meta-analysis can help the endoscopists to select the right tool to treat early gastrointestinal cancer lesions.
Terminology
ESD is a newly developed technique in which submucosal dissection is carried out using an electrocautery knife to acquire a single-piece specimen, it is developed for en bloc removal of large (> 2 cm) GI tract lesions.
Peer-review
This paper is intereting and valuable because technical maturation often requires measurable standard to achieve.
Footnotes
Conflict-of-interest: All authors declare non conflict-of-interest.
Data sharing: No additional data are available.
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article which was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Peer-review started: September 9, 2014
First decision: October 28, 2014
Article in press: February 9, 2015
P- Reviewer: Kita H, Suzuki N S- Editor: Ji FF L- Editor: A E- Editor: Zhang DN
References
- 1.Spychalski M, Dziki A. Safe and efficient colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection in European settings: Is successful implementation of the procedure possible? Dig Endosc. 2015;27:368–373. doi: 10.1111/den.12353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Yoshida N, Fernandopulle N, Inada Y, Naito Y, Itoh Y. Training methods and models for colonoscopic insertion, endoscopic mucosal resection, and endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dig Dis Sci. 2014;59:2081–2090. doi: 10.1007/s10620-014-3308-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sato-Uemura R, Christiano-Sakai M, Duarte-Jordão R, Guimarães-Horneaux de Moura E, Velázquez-Aviña J, Sobrino-Cossío S, Sakai P. [Endolifter, a new tool for safe and rapid submucosal endoscopic dissection] Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2014;79:161–165. doi: 10.1016/j.rgmx.2014.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ponsky JL, Marks JM, Orenstein SB. Retrograde myotomy: a variation in per oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) technique. Surg Endosc. 2014;28:3257–3259. doi: 10.1007/s00464-014-3568-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Draganov PV, Chang M, Coman RM, Wagh MS, An Q, Gotoda T. Role of observation of live cases done by Japanese experts in the acquisition of ESD skills by a western endoscopist. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:4675–4680. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Aslan F, Akpinar Z, Seren AR, Alper E, Cekic C, Ekinci N, Vatansever S, Unsal B. Are endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection risky for patients with cirrhosis? Endoscopy. 2014;46 Suppl 1 UCTN:E149–E150. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1364946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Herreros de Tejada A. ESD training: A challenging path to excellence. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2014;6:112–120. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v6.i4.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Suk KT, Ham YL, Baik GH, Sung HT, Sohn KM, Kim DY, Hong SH. Efficacy of partial endoscopic submucosal dissection with polypectomy of gastric neoplasm during a learning period. Hepatogastroenterology. 2013;60:2107–2112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Berr F, Wagner A, Kiesslich T, Friesenbichler P, Neureiter D. Untutored learning curve to establish endoscopic submucosal dissection on competence level. Digestion. 2014;89:184–193. doi: 10.1159/000357805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sato K, Ito S, Kitagawa T, Saida Y, Maetani I. Education and imaging. Gastrointestinal: endoscopic management for a delayed perforation after endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;29:417. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fukami N. ESD around the world: United States. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2014;24:313–320. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2013.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gotoda T, Ho KY, Soetikno R, Kaltenbach T, Draganov P. Gastric ESD: current status and future directions of devices and training. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2014;24:213–233. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2013.11.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Takizawa K, Knipschield MA, Gostout CJ. Submucosal endoscopy with mucosal resection (SEMR): a new hybrid technique of endoscopic submucosal balloon dissection in the porcine rectosigmoid colon. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:4457–4462. doi: 10.1007/s00464-013-3085-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yoo CH, Park MI, Park SJ, Moon W, Kim HH, Song JY, Kim do H. Observer variability in gastric neoplasm assessment using the vessel plus surface classification for magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging. Clin Endosc. 2014;47:74–78. doi: 10.5946/ce.2014.47.1.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Vila JJ, Kutz M, Fernández-Esparrach G, López-Rosés L, Rodríguez S, Sánchez-Yague A. Endoscopic submucosal dissection in Spain: outcomes and development possibilities. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2013;105:544–552. doi: 10.4321/s1130-01082013000900006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hsu WH, Sun MS, Lo HW, Tsai CY, Tsai YJ. Clinical practice of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early colorectal neoplasms by a colonoscopist with limited gastric experience. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2013;2013:262171. doi: 10.1155/2013/262171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.González N, Parra-Blanco A, Villa-Gómez M, Gamba A, Taullard A, Silveira A, Sanguinetti A, Olano C, Cohen H. Gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection: from animal model to patient. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19:8326–8334. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i45.8326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yu L, Xu W, Shen W, Cao L, Liu Y, Li Z, Ding J. Poly(lactic acid-co-glycolic acid)-poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactic acid-co-glycolic acid) thermogel as a novel submucosal cushion for endoscopic submucosal dissection. Acta Biomater. 2014;10:1251–1258. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2013.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Iacucci M, Eustace G, Uraoka T, Saito Y, Fort Gasia M, Love J, Yahagi N. Endoscopic submucosal dissection in the colorectum: Feasibility in the Canadian setting. Can J Gastroenterol. 2013;27:689–693. doi: 10.1155/2013/536190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Draganov PV, Coman RM, Gotoda T. Training for complex endoscopic procedures: how to incorporate endoscopic submucosal dissection skills in the West? Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;8:119–121. doi: 10.1586/17474124.2014.864552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gómez V, Wallace MB. Advances in diagnostic and therapeutic colonoscopy. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2014;30:63–68. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kim JY, Kim WG, Jeon TY, Kim GH, Jeong EH, Kim DH, Park do Y, Lauwers GY. Lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer: evaluation of a novel method for measuring submucosal invasion and development of a nodal predicting index. Hum Pathol. 2013;44:2829–2836. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2013.07.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Martinek J, Stefanova M, Suchanek S, Zavada F, Svobodova B, Strosova A, Zavoral M. Training of different endoscopic skills on ex-vivo animal model. Simul Healthc. 2014;9:112–119. doi: 10.1097/SIH.0b013e31829be99e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Pham DV, Shah A, Borao FJ, Gorcey S. Endoscopic submucosal dissection training with ex vivo human gastric remnants. Surg Endosc. 2014;28:222–226. doi: 10.1007/s00464-013-3164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Yoshida N, Yagi N, Inada Y, Kugai M, Yanagisawa A, Naito Y. Prevention and management of complications of and training for colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2013;2013:287173. doi: 10.1155/2013/287173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Coman RM, Gotoda T, Draganov PV. Training in endoscopic submucosal dissection. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;5:369–378. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v5.i8.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Thorlacius H, Uedo N, Toth E. Implementation of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early colorectal neoplasms in Sweden. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2013;2013:758202. doi: 10.1155/2013/758202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wang HY, Shih SC, Hung CY, Shieh TY, Chen YB, Chen MJ. Use of artificial tissue to practice endoscopic submucosal dissection. Endoscopy. 2013;45 Suppl 2 UCTN:E175–E176. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1326497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Parra-Blanco A, González N, González R, Ortiz-Fernández-Sordo J, Ordieres C. Animal models for endoscopic training: do we really need them? Endoscopy. 2013;45:478–484. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1344153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Xiong X, Barkun AN, Waschke K, Martel M. Current status of core and advanced adult gastrointestinal endoscopy training in Canada: Survey of existing accredited programs. Can J Gastroenterol. 2013;27:267–272. doi: 10.1155/2013/186284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ono S, Kato M, Nakagawa M, Imai A, Yamamoto K, Shimizu Y. Outcomes and predictive factors of “not self-completion” in gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection for novice operators. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:3577–3583. doi: 10.1007/s00464-013-2929-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Uraoka T, Parra-Blanco A, Yahagi N. Colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection: is it suitable in western countries? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28:406–414. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bok GH, Cho JY. ESD Hands-on Course Using Ex Vivo and In Vivo Models in South Korea. Clin Endosc. 2012;45:358–361. doi: 10.5946/ce.2012.45.4.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Parra-Blanco A, Gonzalez N, Arnau MR. Ex vivo and in vivo models for endoscopic submucosal dissection training. Clin Endosc. 2012;45:350–357. doi: 10.5946/ce.2012.45.4.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kwon CI. Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD) Training and Performing ESD with Accurate and Safe Techniques. Clin Endosc. 2012;45:347–349. doi: 10.5946/ce.2012.45.4.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ahn JY, Choi KD, Lee JH, Choi JY, Kim MY, Choi KS, Kim do H, Song HJ, Lee GH, Jung HY, et al. Is transnasal endoscope-assisted endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric neoplasm useful in training beginners? A prospective randomized trial. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:1158–1165. doi: 10.1007/s00464-012-2567-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Iacopini F, Bella A, Costamagna G, Gotoda T, Saito Y, Elisei W, Grossi C, Rigato P, Scozzarro A. Stepwise training in rectal and colonic endoscopic submucosal dissection with differentiated learning curves. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;76:1188–1196. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2012.08.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Chang DK. Current status of colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection in Korea. Clin Endosc. 2012;45:288–289. doi: 10.5946/ce.2012.45.3.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chen MJ, Liu CY, Chen CJ, Shih SC, Wang HY. Simulating target lesion for endoscopic submucosal dissection training in a live pig model. Endoscopy. 2012;44 Suppl 2 UCTN:E300–E301. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1309986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kato M, Nishida T, Yamamoto K, Hayashi S, Kitamura S, Yabuta T, Yoshio T, Nakamura T, Komori M, Kawai N, et al. Scheduled endoscopic surveillance controls secondary cancer after curative endoscopic resection for early gastric cancer: a multicentre retrospective cohort study by Osaka University ESD study group. Gut. 2013;62:1425–1432. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Gostout CJ, Knipschield MA. Submucosal endoscopy with mucosal resection: a hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection in the porcine rectum and distal colon. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;76:829–834. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2012.05.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Uraoka T, Saito Y, Yahagi N. What are the latest developments in colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection? World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;4:296–300. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v4.i7.296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Vormbrock K, Mönkemüller K. Difficult colon polypectomy. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;4:269–280. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v4.i7.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kato M, Gromski M, Jung Y, Chuttani R, Matthes K. The learning curve for endoscopic submucosal dissection in an established experimental setting. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:154–161. doi: 10.1007/s00464-012-2402-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Yoshida N, Yagi N, Inada Y, Kugai M, Kamada K, Katada K, Uchiyama K, Ishikawa T, Takagi T, Handa O, et al. Possibility of ex vivo animal training model for colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2013;28:49–56. doi: 10.1007/s00384-012-1531-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Lee SP, Lee HL, Hahm JS, Choi HS, Joe I, Shimizu S. International live endoscopic multichannel demonstration using superfast broadband internet connections. Clin Endosc. 2012;45:73–77. doi: 10.5946/ce.2012.45.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Goda K, Fujishiro M, Hirasawa K, Kakushima N, Morita Y, Oda I, Takeuchi M, Yamamoto Y, Uedo N. How to teach and learn endoscopic submucosal dissection for upper gastrointestinal neoplasm in Japan. Dig Endosc. 2012;24 Suppl 1:136–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2012.01274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kakushima N, Hirasawa K, Morita Y, Takeuchi M, Yamamoto Y, Oda I, Goda K, Uedo N, Fujishiro M. Terminology for training of endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dig Endosc. 2012;24 Suppl 1:133–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2012.01257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Uedo N, Jung HY, Fujishiro M, Lee IL, Zhou PH, Chiu PW, Chang D, Goda K. Current situation of endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial neoplasms in the upper digestive tract in East Asian countries: a questionnaire survey. Dig Endosc. 2012;24 Suppl 1:124–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2012.01281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Fujishiro M, Jung HY, Goda K, Hirasawa K, Kakushima N, Lee IL, Morita Y, Oda I, Takeuchi M, Yamamoto Y, et al. Desirable training and roles of Japanese endoscopists towards the further penetration of endoscopic submucosal dissection in Asia. Dig Endosc. 2012;24 Suppl 1:121–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2012.01254.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Balogh G, Dubravcsik Z, Szepes A, Madácsy L. [Endoscopic submucosal dissection in our practice -- new possibilities in the endoscopic treatment of neoplastic changes in the alimentary canal] Orv Hetil. 2012;153:824–833. doi: 10.1556/OH.2012.29382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Cai MY, Zhou PH, Yao LQ. Current status of endoscopic resection in China. Dig Endosc. 2012;24 Suppl 1:166–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2012.01268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Jung HY. Endoscopic resection for early gastric cancer: current status in Korea. Dig Endosc. 2012;24 Suppl 1:159–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2012.01275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Niimi K, Fujishiro M, Goto O, Kodashima S, Koike K. Safety and efficacy of colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection by the trainee endoscopists. Dig Endosc. 2012;24 Suppl 1:154–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2012.01251.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Yamamoto Y, Fujisaki J, Ishiyama A, Hirasawa T, Igarashi M. Current status of training for endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric epithelial neoplasm at Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research, a famous Japanese hospital. Dig Endosc. 2012;24 Suppl 1:148–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2012.01278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Hirasawa K, Kokawa A, Kou R, Oka H, Maeda S, Tanaka K. Determining early gastric cancer lesions appropriate for endoscopic submucosal dissection trainees: a proposal related to curability. Dig Endosc. 2012;24 Suppl 1:143–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2012.01258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Oda I, Odagaki T, Suzuki H, Nonaka S, Yoshinaga S. Learning curve for endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer based on trainee experience. Dig Endosc. 2012;24 Suppl 1:129–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2012.01265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ohata K, Ito T, Chiba H, Tsuji Y, Matsuhashi N. Effective training system in colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dig Endosc. 2012;24 Suppl 1:84–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2012.01272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Uraoka T, Parra-Blanco A, Yahagi N. Colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection in Japan and Western countries. Dig Endosc. 2012;24 Suppl 1:80–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2012.01279.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Matsui N, Akahoshi K, Nakamura K, Ihara E, Kita H. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for removal of superficial gastrointestinal neoplasms: A technical review. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;4:123–136. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v4.i4.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Lee CT, Chang CY, Tai CM, Wang WL, Tseng CH, Hwang JC, Lin JT. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early esophageal neoplasia: a single center experience in South Taiwan. J Formos Med Assoc. 2012;111:132–139. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2010.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Nicolás-Pérez D. [Endoscopic submucosal dissection: only for expert endoscopists?] Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;35:344–367. doi: 10.1016/j.gastrohep.2011.12.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Tanaka S, Morita Y, Fujita T, Wakahara C, Ikeda A, Toyonaga T, Azuma T. Ex vivo pig training model for esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for endoscopists with experience in gastric ESD. Surg Endosc. 2012;26:1579–1586. doi: 10.1007/s00464-011-2074-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Uedo N, Takeuchi Y, Ishihara R. Endoscopic management of early gastric cancer: endoscopic mucosal resection or endoscopic submucosal dissection: data from a Japanese high-volume center and literature review. Ann Gastroenterol. 2012;25:281–290. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Tsuji Y, Ohata K, Sekiguchi M, Ito T, Chiba H, Gunji T, Yamamichi N, Fujishiro M, Matsuhashi N, Koike K. An effective training system for endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastric neoplasm. Endoscopy. 2011;43:1033–1038. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1291383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Inoue H, Ikeda H, Hosoya T, Yoshida A, Onimaru M, Suzuki M, Kudo SE. Endoscopic mucosal resection, endoscopic submucosal dissection, and beyond: full-layer resection for gastric cancer with nonexposure technique (CLEAN-NET) Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2012;21:129–140. doi: 10.1016/j.soc.2011.09.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Deprez PH. Endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of upper gastrointestinal tumors. Endoscopy. 2011;43:966–970. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1291427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Tanimoto MA, Torres-Villalobos G, Fujita R, Santillan-Doherty P, Albores-Saavedra J, Chable-Montero F, Martin-Del-Campo LA, Vasquez L, Bravo-Reyna C, Villanueva O, et al. Learning curve in a Western training center of the circumferential en bloc esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection in an in vivo animal model. Diagn Ther Endosc. 2011;2011:847831. doi: 10.1155/2011/847831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Berr F, Ponchon T, Neureiter D, Kiesslich T, Haringsma J, Kaehler GF, Schmoll F, Messmann H, Yahagi N, Oyama T. Experimental endoscopic submucosal dissection training in a porcine model: learning experience of skilled Western endoscopists. Dig Endosc. 2011;23:281–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2011.01129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Sakamoto T, Saito Y, Fukunaga S, Nakajima T, Matsuda T. Learning curve associated with colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection for endoscopists experienced in gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dis Colon Rectum. 2011;54:1307–1312. doi: 10.1097/DCR.0b013e3182282ab0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Lai LH, Chan FK. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for colonic lesions: why and how should we do it? J Dig Dis. 2011;12:229–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-2980.2011.00516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Wang TE, Wang HY, Lin CC, Chen TY, Chang CW, Chen CJ, Chen MJ. Simulating a target lesion for endoscopic submucosal dissection training in an ex vivo pig model. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;74:398–402. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2011.04.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Kim EY, Jeon SW, Kim GH. Chicken soup for teaching and learning ESD. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:2618–2622. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i21.2618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Kim YJ, Park DK. Management of complications following endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric cancer. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;3:67–70. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v3.i4.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Othman MO, Wallace MB. Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) in 2011, a Western perspective. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2011;35:288–294. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2011.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Fukami N, Ryu CB, Said S, Weber Z, Chen YK. Prospective, randomized study of conventional versus HybridKnife endoscopic submucosal dissection methods for the esophagus: an animal study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73:1246–1253. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2010.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Hotta K, Oyama T, Shinohara T, Miyata Y, Takahashi A, Kitamura Y, Tomori A. Learning curve for endoscopic submucosal dissection of large colorectal tumors. Dig Endosc. 2010;22:302–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2010.01005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Figueroa-Barojas P, Sobrino-Cossío S, Hernández-Guerrero A, Ramírez-Solís ME, Alonso-Lárraga JO, Rodríguez-Brambila V, Álvaro-Villegas J. [Endoscopic inanimate biological simulators for training in endoscopic mucosal dissection] Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2010;75:380–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Sashiyama H, Fu KI, Hoshino T, Tsujinaka Y. Education and imaging: Gastrointestinal: gastric anisakiasis presenting as a submucosal tumour diagnosed by endoscopic submucosal dissection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25:1806. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Toyonaga T, Man-i M, Chinzei R, Takada N, Iwata Y, Morita Y, Sanuki T, Yoshida M, Fujita T, Kutsumi H, et al. Endoscopic treatment for early stage colorectal tumors: the comparison between EMR with small incision, simplified ESD, and ESD using the standard flush knife and the ball tipped flush knife. Acta Chir Iugosl. 2010;57:41–46. doi: 10.2298/aci1003041t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Kuroki Y, Hoteya S, Mitani T, Yamashita S, Kikuchi D, Fujimoto A, Matsui A, Nakamura M, Nishida N, Iizuka T, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for residual/locally recurrent lesions after endoscopic therapy for colorectal tumors. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25:1747–1753. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06331.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Lee JH, Jung HY. Usefulness of endoscopic ultrasonography in endoscopic submucosal dissection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25:1715–1716. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Neuhaus H. Endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection in the West--too many concerns and caveats? Endoscopy. 2010;42:859–861. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1255724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Wang AY, Emura F, Oda I, Cox DG, Kim HS, Yeaton P. Endoscopic submucosal dissection with electrosurgical knives in a patient on aspirin therapy (with video) Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72:1066–1071. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2010.06.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Tomita T, Arai E, Kohno T, Kondo T, Kim Y, Oshima T, Hori K, Watari J, Matsumoto T, Miwa H. Outcomes of treatment of argon plasma coagulation therapy in elderly or high-risk patients with early gastric cancer: a comparison of outcomes among experienced and nonexperienced endoscopists. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2011;45:e54–e59. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181ef3612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Rieder E, Swanstrom LL. Advances in cancer surgery: natural orifice surgery (NOTES) for oncological diseases. Surg Oncol. 2011;20:211–218. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2010.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Niimi K, Fujishiro M, Kodashima S, Goto O, Ono S, Hirano K, Minatsuki C, Yamamichi N, Koike K. Long-term outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal epithelial neoplasms. Endoscopy. 2010;42:723–729. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1255675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Yen HH, Chen CJ. Education and Imaging. Gastrointestinal: endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric inflammatory fibroid polyp. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25:1465. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Ho KY, Phee SJ, Shabbir A, Low SC, Huynh VA, Kencana AP, Yang K, Lomanto D, So BY, Wong YY, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastric lesions by using a Master and Slave Transluminal Endoscopic Robot (MASTER) Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72:593–599. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2010.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Deprez PH, Bergman JJ, Meisner S, Ponchon T, Repici A, Dinis-Ribeiro M, Haringsma J. Current practice with endoscopic submucosal dissection in Europe: position statement from a panel of experts. Endoscopy. 2010;42:853–858. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1255563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Tanimoto MA. [Submucosal endoscopic dissection] Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2010;75:177–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Parra-Blanco A, Arnau MR, Nicolás-Pérez D, Gimeno-García AZ, González N, Díaz-Acosta JA, Jiménez A, Quintero E. Endoscopic submucosal dissection training with pig models in a Western country. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:2895–2900. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i23.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Yamashita T, Zeniya A, Otani S. Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) using the needle knife: its superiority to ESD using the insulation-tipped diathermic knife in physicians intending to master ESD. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2010;20:180–185. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0b013e3181e0d5db. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Tanimoto MA, Torres-Villalobos G, Fujita R, Santillan-Doherty P, Albores-Saavedra J, Gutierrez G, Martin-del-Campo LA, Bravo-Reyna C, Villanueva O, Villalobos JJ, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection in dogs in a World Gastroenterology Organisation training center. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:1759–1764. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i14.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Yoshida N, Yagi N, Naito Y, Yoshikawa T. Safe procedure in endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal tumors focused on preventing complications. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:1688–1695. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i14.1688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Hon SS, Ng SS, Lee JF, Li JC, Lo AW. In vitro porcine training model for colonic endoscopic submucosal dissection: an inexpensive and safe way to acquire a complex endoscopic technique. Surg Endosc. 2010;24:2439–2443. doi: 10.1007/s00464-010-0982-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Teoh AY, Chiu PW, Wong SK, Sung JJ, Lau JY, Ng EK. Difficulties and outcomes in starting endoscopic submucosal dissection. Surg Endosc. 2010;24:1049–1054. doi: 10.1007/s00464-009-0724-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Hyatt BJ, Paull PE, Wassef W. Gastric oncology: an update. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2009;25:570–578. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0b013e328331b5c9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Yamamoto S, Uedo N, Ishihara R, Kajimoto N, Ogiyama H, Fukushima Y, Yamamoto S, Takeuchi Y, Higashino K, Iishi H, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer performed by supervised residents: assessment of feasibility and learning curve. Endoscopy. 2009;41:923–928. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1215129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Vázquez-Sequeiros E, de Miquel DB, Olcina JR, Martín JA, García M, Lucas DJ, Garrido E, González C, Blanco AP, Arnau MR, et al. Training model for teaching endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastric tumors. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2009;101:546–552. doi: 10.4321/s1130-01082009000800005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Kobayashi N, Saito Y, Uraoka T, Matsuda T, Suzuki H, Fujii T. Treatment strategy for laterally spreading tumors in Japan: before and after the introduction of endoscopic submucosal dissection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24:1387–1392. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.05893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Neuhaus H. Endoscopic submucosal dissection in the upper gastrointestinal tract: present and future view of Europe. Dig Endosc. 2009;21 Suppl 1:S4–S6. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2009.00864.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Ivanov D, Toyonaga T. The first case of endoscopic submucosal dissection of cecal adenoma in Serbia. Med Pregl. 2009;62:27–30. doi: 10.2298/mpns0902027i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Fan JK, Tong DK, Law S, Law WL. Transvaginal cholecystectomy with endoscopic submucosal dissection instruments and single-channel endoscope: a survival study in porcine model. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2009;19:29–33. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0b013e3181902ba7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Chang CC, Lee IL, Chen PJ, Wang HP, Hou MC, Lee CT, Chen YY, Cho YP, Lin JT. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric epithelial tumors: a multicenter study in Taiwan. J Formos Med Assoc. 2009;108:38–44. doi: 10.1016/S0929-6646(09)60030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Verna EC, Larghi A. Endoscopic submucosal dissection: learning from the Japanese experience. Dig Liver Dis. 2009;41:210–211. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2008.12.091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Goto O, Fujishiro M, Kodashima S, Ono S, Omata M. Is it possible to predict the procedural time of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24:379–383. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05675.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Lee SY, Kawai T. Transnasal route: new approach to endoscopy. Gut Liver. 2008;2:155–165. doi: 10.5009/gnl.2008.2.3.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Sánchez-Salas RE, Palmer-Román KJ, Dávila Barrios H, Sánchez-Ismayel A, Miquilarena R. [Laparoscopic vesical autoaugmentation: an animal model in rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus)] Actas Urol Esp. 2008;32:722–726. doi: 10.1016/s0210-4806(08)73921-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Kakushima N, Fujishiro M. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastrointestinal neoplasms. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:2962–2967. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Kobayashi N, Ishikawa T, Hirabayashi K, Fu KI, Hirahara Y, Yamabe Y, Igarashi S, Sekiguchi R. Education and imaging. Gastrointestinal: intramucosal gastric cancer treated by endoscopic submucosal dissection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;23:500. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Yamamoto H. Technology insight: endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastrointestinal neoplasms. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;4:511–520. doi: 10.1038/ncpgasthep0906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Larghi A, Waxman I. State of the art on endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2007;17:441–469, v. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2007.05.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Kakushima N, Fujishiro M, Kodashima S, Muraki Y, Tateishi A, Omata M. A learning curve for endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastric epithelial neoplasms. Endoscopy. 2006;38:991–995. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-944808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Moss A, Bourke MJ, Metz AJ, McLeod D, Tran K, Godfrey C, McKay G, Chandra AP, Pasupathy A. Beyond the snare: technically accessible large en bloc colonic resection in the West: an animal study. Dig Endosc. 2012;24:21–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2011.01154.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Moss A, Bourke MJ, Tran K, Godfrey C, McKay G, Chandra AP, Sharma S. Lesion isolation by circumferential submucosal incision prior to endoscopic mucosal resection (CSI-EMR) substantially improves en bloc resection rates for 40-mm colonic lesions. Endoscopy. 2010;42:400–404. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1243990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Kumano I, Ishihara M, Nakamura S, Kishimoto S, Fujita M, Hattori H, Horio T, Tanaka Y, Hase K, Maehara T. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for pig esophagus by using photocrosslinkable chitosan hydrogel as submucosal fluid cushion. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;75:841–848. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2011.10.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.von Renteln D, Dulai PS, Pohl H, Vassiliou MC, Rösch T, Rothstein RI. Endoscopic submucosal dissection with a flexible Maryland dissector: randomized comparison of mesna and saline solution for submucosal injection (with videos) Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;74:906–911. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2011.05.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.von Renteln D, Pohl H, Vassiliou MC, Walton MM, Rothstein RI. Endoscopic submucosal dissection by using a flexible Maryland dissector: a randomized, controlled, porcine study (with videos) Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;71:1056–1062. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2010.01.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.von Delius S, Karagianni A, von Weyhern CH, Feussner H, Schuster T, Schmid RM, Frimberger E. Percutaneously assisted endoscopic surgery using a new PEG-minitrocar for advanced endoscopic submucosal dissection (with videos) Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;68:365–369. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2008.02.093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Yamasaki M, Kume K, Yoshikawa I, Otsuki M. A novel method of endoscopic submucosal dissection with blunt abrasion by submucosal injection of sodium carboxymethylcellulose: an animal preliminary study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;64:958–965. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2006.07.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Oda I, Saito D, Tada M, Iishi H, Tanabe S, Oyama T, Doi T, Otani Y, Fujisaki J, Ajioka Y, et al. A multicenter retrospective study of endoscopic resection for early gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2006;9:262–270. doi: 10.1007/s10120-006-0389-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Imagawa A, Okada H, Kawahara Y, Takenaka R, Kato J, Kawamoto H, Fujiki S, Takata R, Yoshino T, Shiratori Y. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer: results and degrees of technical difficulty as well as success. Endoscopy. 2006;38:987–990. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-944716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Oyama T, Tomori A, Hotta K, Morita S, Kominato K, Tanaka M, Miyata Y. Endoscopic submucosal dissection of early esophageal cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;3:S67–S70. doi: 10.1016/s1542-3565(05)00291-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Onozato Y, Ishihara H, Iizuka H, Sohara N, Kakizaki S, Okamura S, Mori M. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancers and large flat adenomas. Endoscopy. 2006;38:980–986. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-944809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Oka S, Tanaka S, Kaneko I, Mouri R, Hirata M, Kawamura T, Yoshihara M, Chayama K. Advantage of endoscopic submucosal dissection compared with EMR for early gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;64:877–883. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2006.03.932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Hirasaki S, Kanzaki H, Matsubara M, Fujita K, Ikeda F, Taniguchi H, Yumoto E, Suzuki S. Treatment of over 20 mm gastric cancer by endoscopic submucosal dissection using an insulation-tipped diathermic knife. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:3981–3984. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i29.3981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Min BH, Lee JH, Kim JJ, Shim SG, Chang DK, Kim YH, Rhee PL, Kim KM, Park CK, Rhee JC. Clinical outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for treating early gastric cancer: comparison with endoscopic mucosal resection after circumferential precutting (EMR-P) Dig Liver Dis. 2009;41:201–209. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2008.05.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Kakushima N, Kodashima S, Muraki Y, Ono S, Yamamichi N, Tateishi A, Oka M, Ogura K, et al. Outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal epithelial neoplasms in 200 consecutive cases. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;5:678–683; quiz 645. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2007.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Saito Y, Uraoka T, Matsuda T, Emura F, Ikehara H, Mashimo Y, Kikuchi T, Fu KI, Sano Y, Saito D. Endoscopic treatment of large superficial colorectal tumors: a case series of 200 endoscopic submucosal dissections (with video) Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;66:966–973. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2007.02.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Tanaka S, Oka S, Kaneko I, Hirata M, Mouri R, Kanao H, Yoshida S, Chayama K. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal neoplasia: possibility of standardization. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;66:100–107. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2007.02.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Tamegai Y, Saito Y, Masaki N, Hinohara C, Oshima T, Kogure E, Liu Y, Uemura N, Saito K. Endoscopic submucosal dissection: a safe technique for colorectal tumors. Endoscopy. 2007;39:418–422. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-966427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Onozato Y, Kakizaki S, Ishihara H, Iizuka H, Sohara N, Okamura S, Mori M, Itoh H. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for rectal tumors. Endoscopy. 2007;39:423–427. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-966237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Zhou PH, Yao LQ, Chen WF. [Endoscopic therapy of adenomatous polyps and early-stage carcinomas of the colon and rectum] Zhonghua Wai Ke Zazhi. 2008;46:1386–1389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Zhou PH, Yao LQ, Qin XY. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal epithelial neoplasm. Surg Endosc. 2009;23:1546–1551. doi: 10.1007/s00464-009-0395-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Saito Y, Uraoka T, Yamaguchi Y, Hotta K, Sakamoto N, Ikematsu H, Fukuzawa M, Kobayashi N, Nasu J, Michida T, et al. A prospective, multicenter study of 1111 colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissections (with video) Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72:1217–1225. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2010.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Hurlstone DP, Atkinson R, Sanders DS, Thomson M, Cross SS, Brown S. Achieving R0 resection in the colorectum using endoscopic submucosal dissection. Br J Surg. 2007;94:1536–1542. doi: 10.1002/bjs.5720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Isomoto H, Nishiyama H, Yamaguchi N, Fukuda E, Ishii H, Ikeda K, Ohnita K, Nakao K, Kohno S, Shikuwa S. Clinicopathological factors associated with clinical outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal epithelial neoplasms. Endoscopy. 2009;41:679–683. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1214979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Takeuchi Y, Uedo N, Ishihara R, Iishi H, Kizu T, Inoue T, Chatani R, Hanaoka N, Taniguchi T, Kawada N, et al. Efficacy of an endo-knife with a water-jet function (Flushknife) for endoscopic submucosal dissection of superficial colorectal neoplasms. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105:314–322. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2009.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Suzuki H, Oda I, Sekiguchi M, Abe S, Nonaka S, Yoshinaga S. Process of technical stabilization of gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection at the National Cancer Center in Japan. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2014;25:619–623. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2014.14077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


