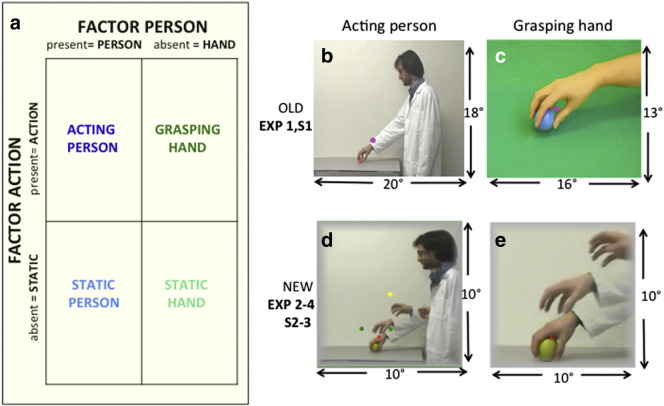
Fig. 1.
Factorial design (a) and the two types of action video in old (b, c) and new (d, e) action videos: acting person (b, d) and grasping hand (c, e). Static frames of the four videos are shown: frames near the middle of the video in a, c, and multiple frames showing the pre-shaping of the hand in d, e. Sizes were 18 × 20° in b, 13 × 16° in c, and 10 × 10° in d, e. The colored dots in d indicate the positions of the fixation point (red in the actual experiments) relative to the target object: red dot: Experiment 2: (monkey); right green dot: Experiments 1 & S1, both green dots: Experiments 3–4 and part of Experiment S3, yellow dot: Experiment S2. In a the factorial design shown is for the new stimuli; for the old stimuli several control conditions were used: 3 in Experiment 1 and 2 in Experiment S1 (Table 1). For calculation of the interaction the different controls were averaged, so that in practice the design remained 2 × 2.