Abstract
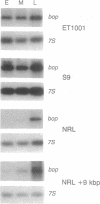
Oxygen and light affect the expression of the bacterioopsin gene (bop), which encodes a light-driven proton pump in the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. This response is thought to be mediated by a set of genes located adjacent to the bop gene. DNA fragments containing either the bop gene or the entire bop gene cluster reversed the phenotype of purple membrane-deficient strains with mutations in the bop gene. Purple membrane synthesis was constitutive in one of these strains transformed with the bop gene alone. The same strain transformed with the bop gene cluster was inducible by low oxygen tension. Moreover, another strain that constitutively expresses purple membrane remained constitutive when transformed with the bop gene alone but the phenotype of the strain changed to inducible when transformed with the bop gene cluster. Additional experiments have confirmed that one of the genes of the bop gene cluster, the bat gene, encodes a trans-acting factor that is necessary and sufficient to confer inducibility of purple membrane synthesis by low oxygen tension.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betlach M. C., Shand R. F., Leong D. M. Regulation of the bacterio-opsin gene of a halophilic archaebacterium. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):134–140. doi: 10.1139/m89-020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betlach M., Friedman J., Boyer H. W., Pfeifer F. Characterization of a halobacterial gene affecting bacterio-opsin gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7949–7959. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betlach M., Pfeifer F., Friedman J., Boyer H. W. Bacterio-opsin mutants of Halobacterium halobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1416–1420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco G., Drummond M., Woodley P., Kennedy C. Sequence and molecular analysis of the nifL gene of Azotobacter vinelandii. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Aug;9(4):869–879. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01745.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaseio U., Pfeifer F. Transformation of Halobacterium halobium: development of vectors and investigation of gas vesicle synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6772–6776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline S. W., Doolittle W. F. Efficient transfection of the archaebacterium Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1341–1344. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1341-1344.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline S. W., Schalkwyk L. C., Doolittle W. F. Transformation of the archaebacterium Halobacterium volcanii with genomic DNA. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4987–4991. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4987-4991.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassarma S., Rajbhandary U. L., Khorana H. G. Bacterio-opsin mRNA in wild-type and bacterio-opsin-deficient Halobacterium halobium strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):125–129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Daveran M. L., Batut J., Dedieu A., Domergue O., Ghai J., Hertig C., Boistard P., Kahn D. Cascade regulation of nif gene expression in Rhizobium meliloti. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):671–683. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M. H., Wootton J. C. Sequence of nifL from Klebsiella pneumoniae: mode of action and relationship to two families of regulatory proteins. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Jul;1(1):37–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00524.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrando E., Schweiger U., Oesterhelt D. Homologous bacterio-opsin-encoding gene expression via site-specific vector integration. Gene. 1993 Mar 15;125(1):41–47. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90743-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilles-Gonzalez M. A., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. A haemoprotein with kinase activity encoded by the oxygen sensor of Rhizobium meliloti. Nature. 1991 Mar 14;350(6314):170–172. doi: 10.1038/350170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Baldwin J. M., Ceska T. A., Zemlin F., Beckmann E., Downing K. H. Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):899–929. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. Functional inactivation of genes by dominant negative mutations. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):219–222. doi: 10.1038/329219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamekura M., Oesterhelt D., Wallace R., Anderson P., Kushner D. J. Lysis of halobacteria in bacto-peptone by bile acids. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Apr;54(4):990–995. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.4.990-995.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs M. P., Hauss T., Heyn M. P., RajBhandary U. L., Khorana H. G. Expression of the bacterioopsin gene in Halobacterium halobium using a multicopy plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):859–863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs M. P., Mollaaghababa R., Khorana H. G. Gene replacement in Halobacterium halobium and expression of bacteriorhodopsin mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1987–1991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn I., Stephenson F. H., Boyer H. W., Greene P. J. Positive-selection vectors utilizing lethality of the EcoRI endonuclease. Gene. 1986;42(3):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90229-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam W. L., Doolittle W. F. Shuttle vectors for the archaebacterium Halobacterium volcanii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5478–5482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong D., Boyer H., Betlach M. Transcription of genes involved in bacterio-opsin gene expression in mutants of a halophilic archaebacterium. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4910–4915. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4910-4915.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong D., Pfeifer F., Boyer H., Betlach M. Characterization of a second gene involved in bacterio-opsin gene expression in a halophilic archaebacterium. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4903–4909. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4903-4909.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monson E. K., Weinstein M., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. The FixL protein of Rhizobium meliloti can be separated into a heme-binding oxygen-sensing domain and a functional C-terminal kinase domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4280–4284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moritz A., Lankat-Buttgereit B., Gross H. J., Goebel W. Common structural features of the genes for two stable RNAs from Halobacterium halobium. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 11;13(1):31–43. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni B. F., Chang M., Duschl A., Lanyi J., Needleman R. An efficient system for the synthesis of bacteriorhodopsin in Halobacterium halobium. Gene. 1990 May 31;90(1):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90456-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Functions of a new photoreceptor membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2853–2857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer F., Weidinger G., Goebel W. Genetic variability in Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):375–381. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.375-381.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shand R. F., Betlach M. C. Expression of the bop gene cluster of Halobacterium halobium is induced by low oxygen tension and by light. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4692–4699. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4692-4699.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shand R. F., Betlach M. C. bop gene cluster expression in bacteriorhodopsin-overproducing mutants of Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1994 Mar;176(6):1655–1660. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.6.1655-1660.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and related pigments of halobacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:587–616. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and the purple membrane of halobacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 14;505(3-4):215–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumper M., Herrmann G. Biogenesis of purple membrane: regulation of bacterio-opsin synthesis. FEBS Lett. 1976 Oct 15;69(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80673-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toeckenius W., Kunau W. H. Further characterization of particulate fractions from lysed cell envelopes of Halobacterium halobium and isolation of gas vacuole membranes. J Cell Biol. 1968 Aug;38(2):337–357. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. F., DasSarma S. Transcriptional induction of purple membrane and gas vesicle synthesis in the archaebacterium Halobacterium halobium is blocked by a DNA gyrase inhibitor. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):4118–4121. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.4118-4121.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]