Abstract
Cyclin A is a cell cycle regulatory protein that functions in mitotic and S-phase control in mammalian somatic cells. Its deregulated expression may have a role in cellular transformation. We have cloned and sequenced the human cyclin A gene and cDNAs representing its mRNAs and have characterized its promoter. Using synchronized cultures of NIH 3T3 cells stably transfected with cyclin A promoter/luciferase constructs, we show that the promoter is repressed during the G1 phase of the cell cycle and is activated at S-phase entry. Cell cycle regulation of the cyclin A gene promoter is mediated by sequences extending from -79 to +100 relative to the predominant transcription start site. It does not require the presence of a functional retinoblastoma protein.
Full text
PDF


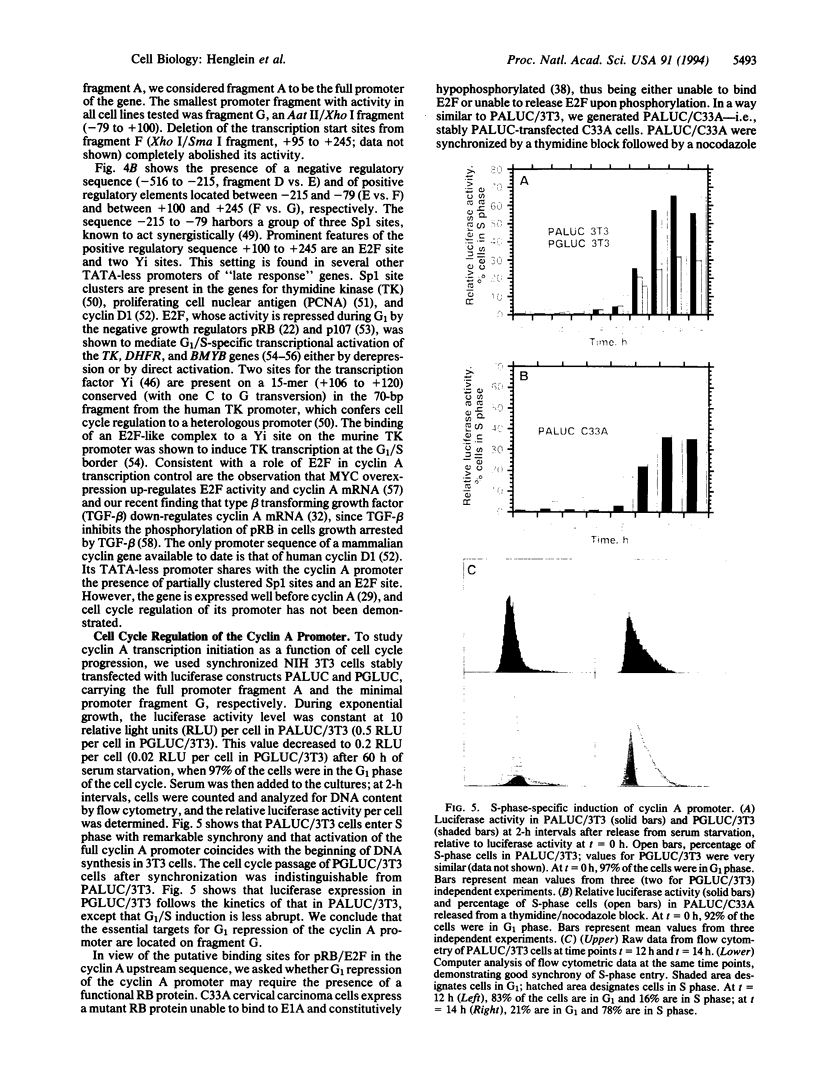

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson G. M., Freytag S. O. Synergistic activation of a human promoter in vivo by transcription factor Sp1. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1935–1943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi S., Raychaudhuri P., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus E1A proteins can dissociate heteromeric complexes involving the E2F transcription factor: a novel mechanism for E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):659–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90112-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldin V., Lukas J., Marcote M. J., Pagano M., Draetta G. Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for cell cycle progression in G1. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):812–821. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandara L. R., La Thangue N. B. Adenovirus E1a prevents the retinoblastoma gene product from complexing with a cellular transcription factor. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):494–497. doi: 10.1038/351494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlat I., Fesquet D., Bréchot C., Henglein B., Dupuy d'Angeac A., Vié A., Blanchard J. M. Loss of the G1-S control of cyclin A expression during tumoral progression of Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Feb;4(2):105–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burggraf S., Larsen N., Woese C. R., Stetter K. O. An intron within the 16S ribosomal RNA gene of the archaeon Pyrobaculum aerophilum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2547–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso M. C., Leonhardt H., Nadal-Ginard B. Reversal of terminal differentiation and control of DNA replication: cyclin A and Cdk2 specifically localize at subnuclear sites of DNA replication. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):979–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90721-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chellappan S. P., Hiebert S., Mudryj M., Horowitz J. M., Nevins J. R. The E2F transcription factor is a cellular target for the RB protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90557-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Urso G., Marraccino R. L., Marshak D. R., Roberts J. M. Cell cycle control of DNA replication by a homologue from human cells of the p34cdc2 protein kinase. Science. 1990 Nov 9;250(4982):786–791. doi: 10.1126/science.2173140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devoto S. H., Mudryj M., Pines J., Hunter T., Nevins J. R. A cyclin A-protein kinase complex possesses sequence-specific DNA binding activity: p33cdk2 is a component of the E2F-cyclin A complex. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dou Q. P., Fridovich-Keil J. L., Pardee A. B. Inducible proteins binding to the murine thymidine kinase promoter in late G1/S phase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1157–1161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dou Q. P., Markell P. J., Pardee A. B. Thymidine kinase transcription is regulated at G1/S phase by a complex that contains retinoblastoma-like protein and a cdc2 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3256–3260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta A., Stillman B. cdc2 family kinases phosphorylate a human cell DNA replication factor, RPA, and activate DNA replication. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2189–2199. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05278.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eick D. Elongation and maturation of c-myc RNA is inhibited by differentiation inducing agents in HL60 cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1199–1205. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Richman R., Hall F. L., Williams R. T., Lodgson N., Harper J. W. CDK2 encodes a 33-kDa cyclin A-associated protein kinase and is expressed before CDC2 in the cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2907–2911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Rosenthal E. T., Youngblom J., Distel D., Hunt T. Cyclin: a protein specified by maternal mRNA in sea urchin eggs that is destroyed at each cleavage division. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):389–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90420-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Faha B., Harlow E., Livingston D. M. Interaction of p107 with cyclin A independent of complex formation with viral oncoproteins. Science. 1992 Jan 3;255(5040):85–87. doi: 10.1126/science.1532457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano A., Whyte P., Harlow E., Franza B. R., Jr, Beach D., Draetta G. A 60 kd cdc2-associated polypeptide complexes with the E1A proteins in adenovirus-infected cells. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):981–990. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90949-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard F., Strausfeld U., Fernandez A., Lamb N. J. Cyclin A is required for the onset of DNA replication in mammalian fibroblasts. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1169–1179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90293-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotzer M., Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):132–138. doi: 10.1038/349132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe P. H., Draetta G., Leof E. B. Transforming growth factor beta 1 inhibition of p34cdc2 phosphorylation and histone H1 kinase activity is associated with G1/S-phase growth arrest. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1185–1194. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Bruskin A., Jarosz D., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Identification of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1708–1711. doi: 10.1126/science.2047879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Livingston D. M., Massagué J. Growth inhibition by TGF-beta linked to suppression of retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):175–185. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90251-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E. W., Watson R. J. An E2F-binding site mediates cell-cycle regulated repression of mouse B-myb transcription. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2705–2713. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05932.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Hai T. Y., SivaRaman L., Thimmappaya B., Hurst H. C., Jones N. C., Green M. R. A cellular protein, activating transcription factor, activates transcription of multiple E1A-inducible adenovirus early promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8355–8359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner C. F., O'Farrell P. H. Expression and function of Drosophila cyclin A during embryonic cell cycle progression. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):957–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90629-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner C. F., O'Farrell P. H. The roles of Drosophila cyclins A and B in mitotic control. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):535–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90535-m. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luca F. C., Shibuya E. K., Dohrmann C. E., Ruderman J. V. Both cyclin A delta 60 and B delta 97 are stable and arrest cells in M-phase, but only cyclin B delta 97 turns on cyclin destruction. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4311–4320. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05009.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucibello F. C., Sewing A., Brüsselbach S., Bürger C., Müller R. Deregulation of cyclins D1 and E and suppression of cdk2 and cdk4 in senescent human fibroblasts. J Cell Sci. 1993 May;105(Pt 1):123–133. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. L., Slansky J. E., McMahon S. L., Knuth M. W., Farnham P. J. The HIP1 binding site is required for growth regulation of the dihydrofolate reductase gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1054–1063. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. F., Mathews M. B. Analysis of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen promoter and its response to adenovirus early region 1. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16116–16125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motokura T., Arnold A. PRAD1/cyclin D1 proto-oncogene: genomic organization, 5' DNA sequence, and sequence of a tumor-specific rearrangement breakpoint. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1993 Jun;7(2):89–95. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870070205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., Hiebert S. W., Nevins J. R. A role for the adenovirus inducible E2F transcription factor in a proliferation dependent signal transduction pathway. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2179–2184. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Pepperkok R., Verde F., Ansorge W., Draetta G. Cyclin A is required at two points in the human cell cycle. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):961–971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05135.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J. Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases: take your partners. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jun;18(6):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90185-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cyclin A is adenovirus E1A-associated protein p60 and behaves differently from cyclin B. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):760–763. doi: 10.1038/346760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal N. Identification of regulatory elements of cloned genes with functional assays. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:704–720. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Münger K., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. The state of the p53 and retinoblastoma genes in human cervical carcinoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5523–5527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewing A., Bürger C., Brüsselbach S., Schalk C., Lucibello F. C., Müller R. Human cyclin D1 encodes a labile nuclear protein whose synthesis is directly induced by growth factors and suppressed by cyclic AMP. J Cell Sci. 1993 Feb;104(Pt 2):545–555. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.2.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. Mammalian G1 cyclins. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1059–1065. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90636-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirodkar S., Ewen M., DeCaprio J. A., Morgan J., Livingston D. M., Chittenden T. The transcription factor E2F interacts with the retinoblastoma product and a p107-cyclin A complex in a cell cycle-regulated manner. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90214-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobczak-Thepot J., Harper F., Florentin Y., Zindy F., Brechot C., Puvion E. Localization of cyclin A at the sites of cellular DNA replication. Exp Cell Res. 1993 May;206(1):43–48. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson K. I., Farrell K. M., Ruderman J. V. The clam embryo protein cyclin A induces entry into M phase and the resumption of meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):861–870. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90801-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L. H., Harlow E., Meyerson M. Isolation of the human cdk2 gene that encodes the cyclin A- and adenovirus E1A-associated p33 kinase. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):174–177. doi: 10.1038/353174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Maller J. L. Role for cyclin A in the dependence of mitosis on completion of DNA replication. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):314–317. doi: 10.1038/354314a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Chenivesse X., Henglein B., Bréchot C. Hepatitis B virus integration in a cyclin A gene in a hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1990 Feb 8;343(6258):555–557. doi: 10.1038/343555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Zindy F., Chenivesse X., Lamas E., Henglein B., Bréchot C. Modification of cyclin A expression by hepatitis B virus DNA integration in a hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 1992 Aug;7(8):1653–1656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L., van den Heuvel S., Helin K., Fattaey A., Ewen M., Livingston D., Dyson N., Harlow E. Inhibition of cell proliferation by p107, a relative of the retinoblastoma protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1111–1125. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zindy F., Lamas E., Chenivesse X., Sobczak J., Wang J., Fesquet D., Henglein B., Bréchot C. Cyclin A is required in S phase in normal epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 14;182(3):1144–1154. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91851-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]