Abstract
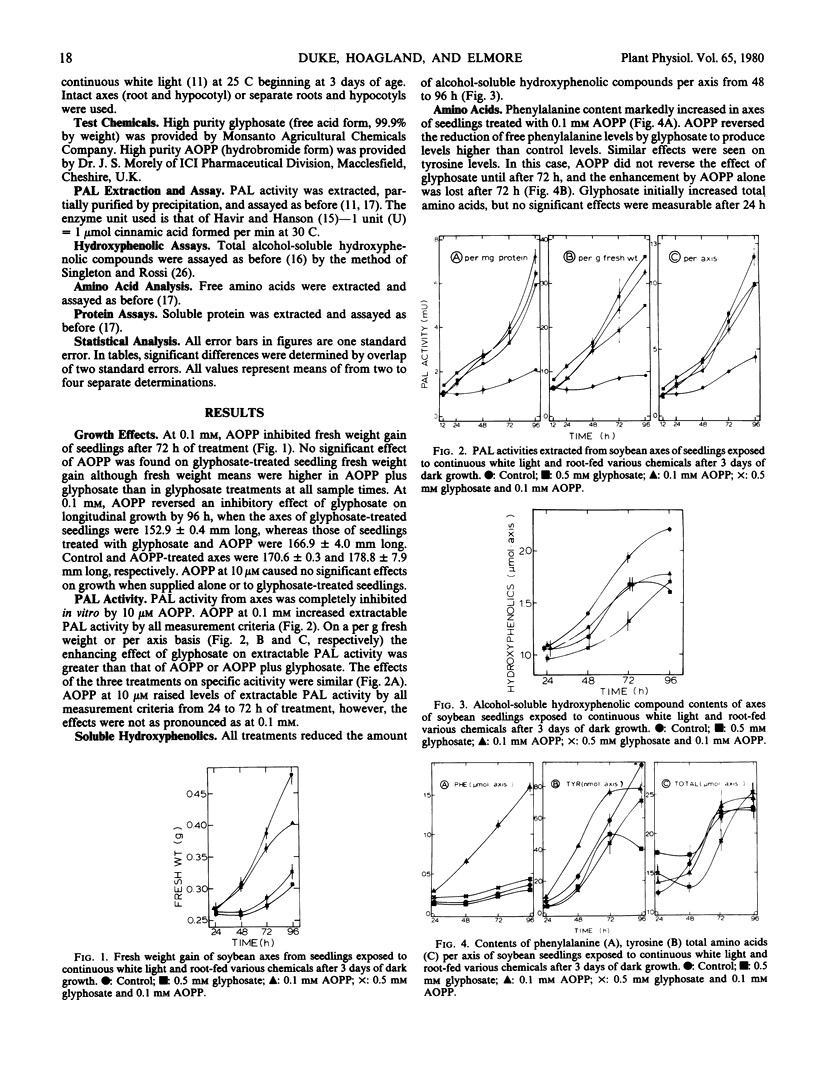
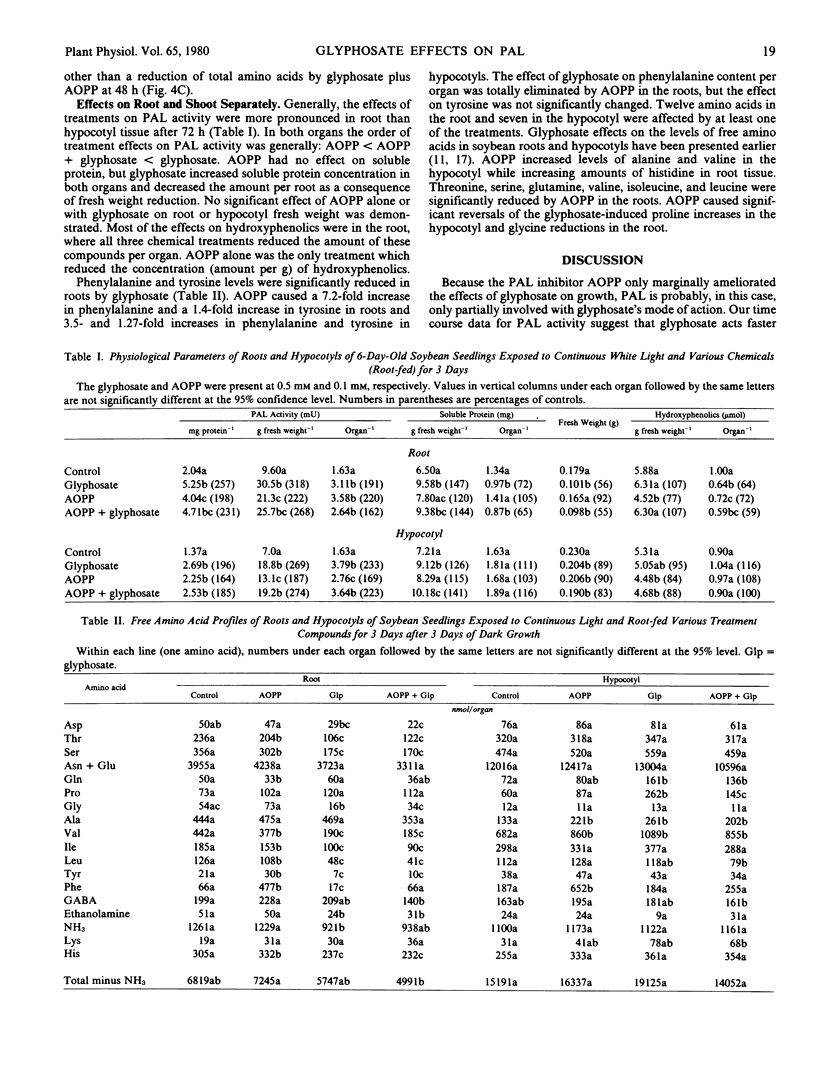
The phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) inhibitor l-α-aminooxy-β-phenylpropionic acid (AOPP) was root-fed to light-exposed soybean seedlings alone or with glyphosate [N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine] to test further the hypothesis that PAL activity is involved in the mode of action of glyphosate. Extractable PAL activity was increased by 0.01 and 0.1 millimolar AOPP. AOPP reduced total soluble hydroxyphenolic compound levels and increased phenylalanine and tyrosine levels, indicating that in vivo PAL activity was inhibited by AOPP. The increase in extractable PAL caused by AOPP may be a result of decreased feedback inhibition of PAL synthesis by cinnamic acid and/or its derivatives. AOPP alone had no effect on growth (fresh weight and elongation) at either concentration, but at 0.1 millimolar it slightly alleviated growth (fresh weight) inhibition caused by 0.5 millimolar glyphosate after 4 days. Reduction of the free pool of phenylalanine by glyphosate was reversed by AOPP. These results indicate that glyphosate exerts some of its effects through reduction of aromatic amino acid pools through increases in PAL activity and that not all growth effects of glyphosate are due to reductions of aromatic amino acids.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amrhein N., Gerhardt J. Superinduction of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in gherkin hypocotyls caused by the inhibitor, L-alpha-aminooxy-beta-phenylpropionic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 3;583(4):434–442. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90060-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelsma G. On the Mechanism of the Changes in Phenylalanine Ammonia-lyase Activity Induced by Ultraviolet and Blue Light in Gherkin Hypocotyls. Plant Physiol. 1974 Nov;54(5):702–705. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.5.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haderlie L. C., Widholm J. M., Slife F. W. Effect of glyphosate on carrot and tobacco cells. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jul;60(1):40–43. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C., Attridge T., Smith H. Regulation of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase synthesis by cinnamic acid. Its implication for the light mediated regulation of the enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 14;385(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olorunsogo O. O., Bababunmi E. A., Bassir O. Uncoupling of corn shoot mitochondria by N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jan 15;97(2):279–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



