Abstract
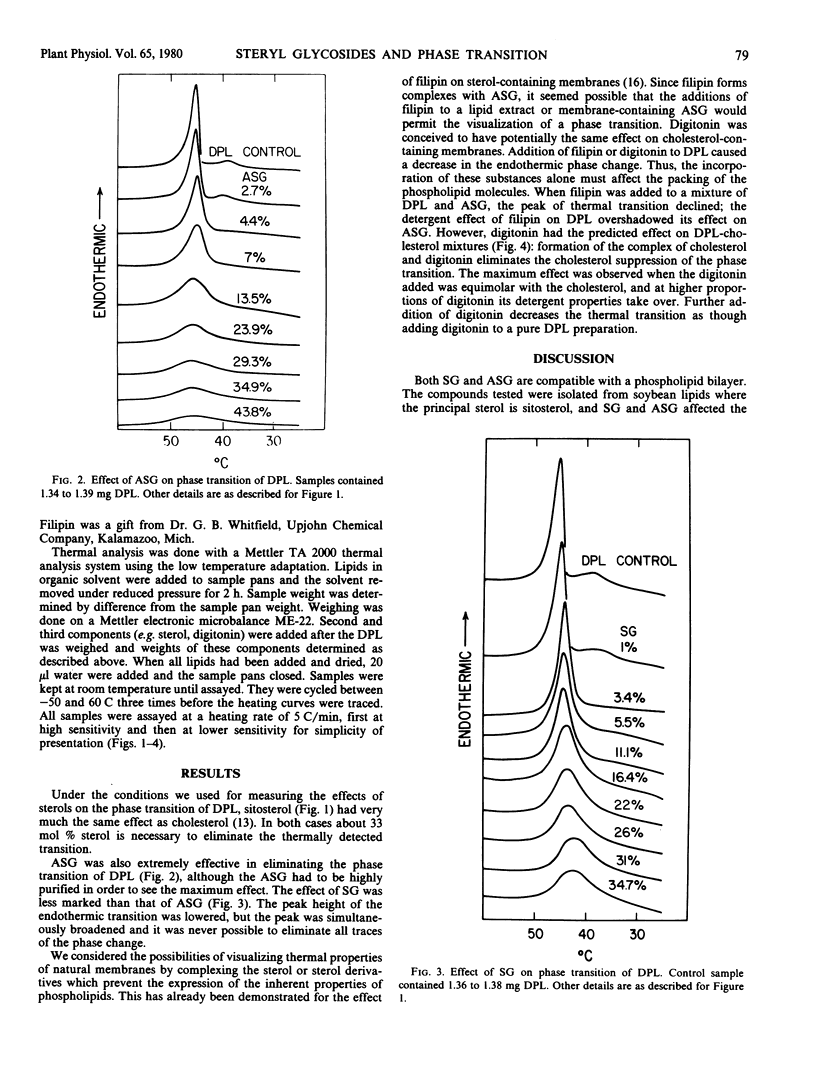
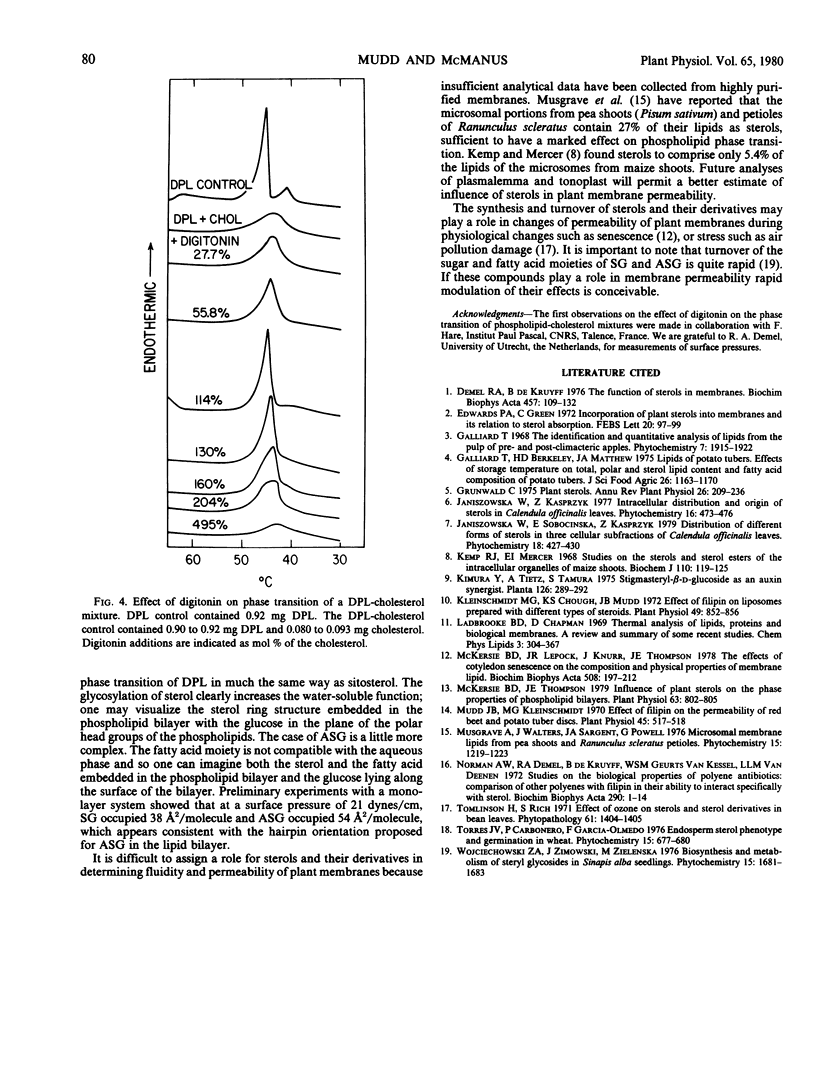
The phase transition of dipalmitoyl lecithin, measured by thermal analysis, was eliminated by the plant sterol, sitosterol, and by the derivatives steryl glucoside and acylated steryl glucoside, which were isolated from soybean lipids.
When digitonin was added to dipalmitoyl lecithin-sterol mixtures, in amounts equimolar to sterol, the phase transition of the phospholipid was revealed presumably because of the formation of a sterol complex. When digitonin in molar excess of sterol was added, the endothermic peak disappeared again.
Full text
PDF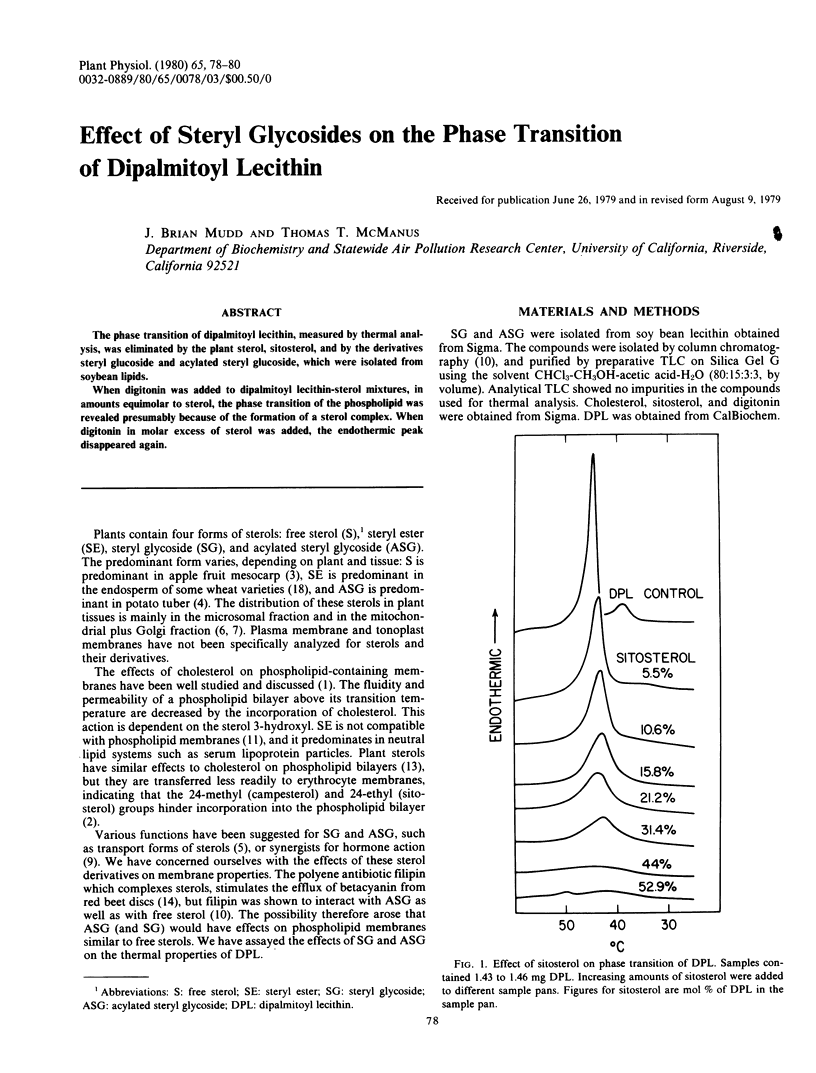
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Demel R. A., De Kruyff B. The function of sterols in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 26;457(2):109–132. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards P. A., Green C. Incorporation of plant sterols into membranes and its relation to sterol absorption. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jan 15;20(1):97–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp R. J., Mercer E. I. Studies on the sterols and sterol esters of the intracellular organelles of maize shoots. Biochem J. 1968 Nov;110(1):119–125. doi: 10.1042/bj1100119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt M. G., Chough K. S. Effect of filipin on liposomes prepared with different types of steroids. Plant Physiol. 1972 May;49(5):852–856. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.5.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladbrooke B. D., Chapman D. Thermal analysis of lipids, proteins and biological membranes. A review and summary of some recent studies. Chem Phys Lipids. 1969 Dec;3(4):304–356. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(69)90040-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKersie B. D., Lepock J. R., Kruuv J., Thompson J. E. The effects of cotyledon senescence on the composition and physical properties of membrane lipid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 4;508(2):197–212. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90325-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKersie B. D., Thompson J. E. Influence of plant sterols on the phase properties of phospholipid bilayers. Plant Physiol. 1979 May;63(5):802–805. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.5.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd J. B., Kleinschmidt M. G. Effect of filipin on the permeability of red beet and potato tuber discs. Plant Physiol. 1970 Apr;45(4):517–518. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.4.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman A. W., Demel R. A., de Kruyff B., Geurts van Kessel W. S., van Deenen L. L. Studies on the biological properties of polyene antibiotics: comparison of other polyenes with filipin in their ability to interact specifically with sterol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 1;290(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


